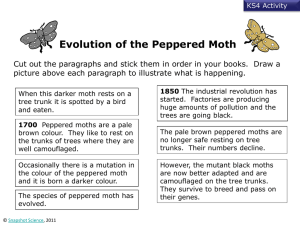
4.4 NATURAL SELECTION How did this happen?! 1. Why do we use selective breeding? 2. How did selective breeding make the cows so big? Today’s aim ■ To outline a theory on natural selection ■ To be able to explain the difference between natural selection and selective breeding ■ To look at Charles Darwin’s discoveries How did giraffes get their long neck? DISCLAIMER: this is just a theory. We are not sure. How did giraffes get their long neck? How did giraffes get their long neck? How did giraffes get their long neck? How did giraffes get their long neck? This is called natural selection Differences Natural selection Selective breeding ■ Species adapting in response to natural changes ■ Species changing due to human control Draw a flow chart ■ Draw pictures to complete the flow chart ■ It will compare selective breeding and natural selection ■ Use page 53 in your coursebook to help you Recap/warm up Sometimes the DNA doesn’t copy perfectly and the new bacteria is a tiny bit different Discuss in pairs Lichens ■ Lichens are weird ■ They aren’t plants, but they can photosynthesise ■ They don’t have roots to absorb water and nutrients ■ Can grow on almost any surface ■ Can even live INSIDE solid rock ■ Up to 6% of the EARTH’S SURFACE is covered in lichen ■ Some of the OLDEST LIVING THINGS in the world Lichens They’re really good at absorbing things in the air. What do you think they can tell us? Timeline 1849 Almost all peppered moths were pale Timeline 184 9 Almost all peppered moths were pale 190 0 Near cities, almost all peppered moths were dark. Why? Timeline 184 9 Almost all peppered moths were pale Industrial revolution reduced air quality. Lichens died. 190 0 Near cities, almost all peppered moths were dark. Why? Timeline 184 9 Almost all peppered moths were pale Industrial revolution reduced air quality. Lichens died. Pale peppered moths lost their camouflage 190 0 Near cities, almost all peppered moths were dark. Why? Timeline 184 9 Almost all peppered moths were pale Industrial revolution reduced air quality. Lichens died. Birds could see the pale moths easily. They ate them. Pale peppered moths lost their camouflage. 190 0 Near cities, almost all peppered moths were dark. Why? Timeline 184 9 Almost all peppered moths were pale. Industrial revolution reduced air quality. Lichens died. Birds could see the pale moths easily. They ate them. Pale peppered moths lost their camouflage. Dark moths were left to reproduce. 190 0 Near cities, almost all peppered moths were dark. Warm up ■ Look carefully at the camel. ■ Write down 5 features that make it a camel, such as its hump. ■ Write down why you think these features would help it to survive in the desert. Who was Charles darwin? Write down what you can remember about the theory of evolution. Galapagos islands ■ Use your map of the Galapagos islands, information and pictures of the birds that live there. ■ You have to figure out which bird lives where and why. Adaptations of animals ■ You and your partner will be given a picture of an animal. ■ Think about it’s adaptations. ■ Write down how you think these features help the animal survive. Swap pictures and notes with the next group along ■ Work together to mark the other group’s work. ■ Think of at least one reason why their work is good. ■ Think of at least one way you think their work could be made better. ■ Swap back and read through your feedback. Evolution happens through natural selection: Members of the same species have genes that are slightly different. Individuals with genes most suited to the environment are more likely to survive and reproduce. These genes are passed to the offspring in the next generation. Animals can become extinct when they are not well adapted to their environment. Today’s aim ■ To outline a theory on natural selection ■ To be able to explain the difference between natural selection and selective breeding ■ To look at Charles Darwin’s discoveries Summary ■ Natural selection occurs when the individuals in a species most suited to the environment survive and reproduce Summary ■ Individuals in a species that survive can reproduce. They pass on their genes and the species changes to be more like them