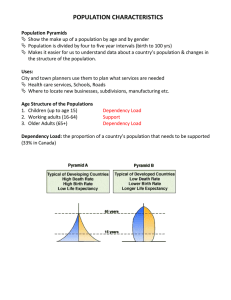
population growth and structure ( s develop, growth of population declines. a death rate decreases, birth rates fall at greater rate reason: better healthcare, education, sanitation, housing and nutrition-- live longer; decline in infant mortality, increased cost of bringing up children, increase in women participation in labour-- decline in birth rate. ) c ountries with high income & development-natural rate of decrease in population/ rise in population ( attract net immigration) causes of changes in population l ow development--high rates of growth. reason: need to have children to support parents in old age, lack of availability of methods of birth control, low costs of raising children, lack of education of women, high infant mortality rate because will not expect all of them to survive. igher birth rate with low development--low h average age of population--high dependency ratios-- small proportion of working population has to produce enough goods to sustain a large number of young people igh development -- decreasing birth rate h and death rate-- ageing population-dependency ratio high since old people rely on them. when living longer--costs of health and pensions rise--to reduce the cost-government increase retirement age. optimum population hapter 51. C Characteristics of countries at different levels of development ptimum population when output per head o is the greatest l ow income per head-- high proportion in rural areas; rapid rates of rual-urban migration-- put pressure on infrastructure, housing and schools in urban areas. level of urbanisation igh income country--majority in urban h areas--little growth in urban population; some people move out of urban area as advances in tech allow more people to work from home. s ome countries income unevenly distributed-- income-generating assets, like land, are owned by a few people-- great extremes of wealth and poverty (Latin America) income distribution Gini coefficient numerical measure of extent of inequality igh income per head--most labour in h tertiary sector; low income have a high dependence on primary sector--- high dependency on agricultural output makes the economy vulnerable to nature (drought-famine) employment in different sectors hen develops, contribution of primary w sector declines--secondary becomes major source--tertiary Economic structure pattern of trade l ow development and income--primary products most export revenue--vulnerable in trading relations-- dmeand and supply change significantly.