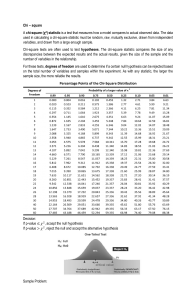
Chi – square A chi-square (χ2) statistic is a test that measures how a model compares to actual observed data. The data used in calculating a chi-square statistic must be random, raw, mutually exclusive, drawn from independent variables, and drawn from a large enough sample. Chi-square tests are often used to test hypotheses. The chi-square statistic compares the size of any discrepancies between the expected results and the actual results, given the size of the sample and the number of variables in the relationship. For these tests, degrees of freedom are used to determine if a certain null hypothesis can be rejected based on the total number of variables and samples within the experiment. As with any statistic, the larger the sample size, the more reliable the results. Decision: If p-value ≤ 𝜒 2 , accept the null hypothesis If p-value > 𝜒 2 , reject the null and accept the alternative hypothesis Sample Problem: 100 learners are asked to their choice of learning modality: online, modular, blended learning, face – to – face. The responses of the learners are indicated in the table below. Category Observed Expected (O-E) (O-E)2 (𝟎 − 𝑬)𝟐 𝑬 Online Modular Blended F2F 25 25 25 – 25 = 0 0 0/25 = 0 5 25 5 – 25 = -20 400 400/25 = 16 20 25 20 – 25 = -5 25 25/25 = 1 50 25 50 – 25 = 25 625 625/25 = 25 100 100 42 Ho (null hypothesis): The modality of learning has equal distribution Ha (alternative hypothesis): The modality of learning has unequal distribution 𝜒 2 = 42 (chi -square) ∝ = 0.05 (critical value) df = 4 – 1 = 3 (degree of freedom) number of categories subtracted by 1 p-value = 7.81 Conclusion: Reject the null hypothesis and accept the alternative hypothesis. The modality of learning has unequal distribution Activities: a. The enrollment of Kinder to Grade 3 learners are given below. Every year, they expect 2% increase in their enrollment. Will there be a significant relationship between the enrollment this school year compared to the previous? Category Observed Expected Kinder Grade 1 Grade 2 Grade 3 Total 512 624 671 641 N= 523 644 695 612 N= Ho: Ha: 𝜒2 = df = Conclusion: (O-E) (O-E)2 (𝟎 − 𝑬)𝟐 𝑬 𝜒2 = ∝= p-value = b. In the Licensure Examination for Professional Teachers (LET), the applicants think that in a 100 – item test quesitons, there is an equal distribution of answers per letter. Category Observed Expected A B C D E Total 18 15 24 17 26 N= 20 20 20 20 20 N= Ho: Ha: 𝜒2 = df = Conclusion: (O-E) (O-E)2 (𝟎 − 𝑬)𝟐 𝑬 𝜒2 = ∝= p-value =