INTERMEDIATE PHASE–SOCIAL SCIENCES
GRADE 6
TERM 3
WORKBOOK
–
GEOGRAPHY
An image showing the difference between weather and climate
LEARNER’S GUIDE
Page 1 of 41
Week #
Table of content
Week 1
Revise from Term 2
•
Page #
Introduction to the topic on climate and vegetation around
the world
•
Link the revision to term 3 Grade 5- difference between
weather and climate
Week 2
Climate around the world
•
Difference between climate and weather – hot, mild and
cold
•
Climates of the world including January to July temperature
maps
Week 3
Climate around the world
•
Week 4
Wet and dry areas of the world including rainfall maps
Tropical rain forests
•
Climate, temperatures and rainfall patterns- monthly
averages
Week 5
Week 6
Week 7
Week 8
Tropical rain forests
•
Natural vegetation and wildlife a rain forest
•
Deforestation – reasons, consequences with a case study
Hot deserts
•
Location on earth
•
Climate and rainfall patterns- monthly averages
Hot deserts
•
Natural vegetation and wildlife in a deserts
•
How people live in a desert – examples of lifestyles
Coniferous forests
•
Location on Earth
•
Climate and rainfall patterns- monthly averages
Page 2 of 41
Week #
1.1
Week # 2
2.1
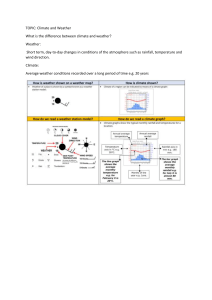
Difference between weather and climate
The world has a variety of climates. Very hot conditions can be found close to the equator and
very cold conditions at the North and South pole. Certain regions in the world get heavy rain
every day and others hardly ever get rain and are very dry. The weather changes every day,
but we can experience the same kind of weather from month to month and season to season.
In South Africa, we have summer from November to February and winter from May to August.
Both weather and climate describe the state of the atmosphere and include things such as
temperature, precipitation (rain, hail, and snow), air pressure, wind, and cloud cover.
Weather describes these conditions over a short period of time, such as a day or even a few
specific hours. The weather describes a small area, such as a town or a specific area of a
province.
Climate describes the same conditions, but over a longer period, such as a few weeks,
months, or even a year. The climate describes conditions over a bigger area such as a
province, a country, or even the whole world.
Temperate means that the climate of a region is not extremely cold or hot.
Words we use when describing the weather and climate:
hot
cold
cool
warm
degree
celcius (°c)
wet
dry
acid
millimetres (mm)
icy
shine
blow
strong
weak
Page 3 of 41
Hot, mild, and cold climates of the world
The average temperatures during different seasons tell us if a region has a hot climate, a
mild climate, or a cold climate.
The climate of an area depends on three factors:
• Latitude
How far north and south the area lies off the equator?
If the area is located very close to or on the equator, it will be hot all year round, because the
rays of the sunshine directly onto the equator for 365 days of the year. It will however also
have rain daily. The further away the area is situated north and south of the equator the colder
it will be. These areas will experience some weak sunlight but mostly experience snow and
ice.
•
Altitude - How high the area is above sea level.
The temperature drops by about 6,5°C for every 1000m above sea level.
•
Location regarding the ocean.
How far away the area is from the ocean?
Ocean currents influence the climate. An area that is situated near a warm ocean current
will have warmer weather. An example of an area like this is Durban. If an area is
situated near a cold ocean current, it will experience colder weather. An example of an
area like this is Cape Town.
Winds also blow the hot or cold oceans, towards the land, which increases or reduces
the land temperatures. Wind also blows north and south from the Polar regions, bringing
cold air onto the land.
There are eight major climatic zones on the earth.
Mountain
Polar
Cold temperate
Wet temperate
Dry temperate
Desert and semi Sub-Tropical
Tropics
desert
Interesting Facts
The coldest areas on earth are Greenland and the Antarctic as they have high latitude and
a
high elevation.
The highest temperature recorded on earth was at Tripolitania in Libya in 1922 at 58,8°C.
The highest annual average temperature recorded was 34,4°C at Dallol in Ethiopia.
The lowest temperature ever recorded on earth was at Vostok, Russia in 1983 at -88,8°C.
The lowest annual average temperature recorded was -50,55°C at the Amundsen-Scott
station in Antarctica.
Page 4 of 41
January and July are the two months all over the world that fall in the middle of summer and
winter. The northern and southern hemisphere divides the world with the equator being in
the middle.
January temperatures
In January, it is summer in the southern hemisphere and winter in the northern hemisphere.
The highest average temperatures are over 30°C. The northern part of Australia and the
middle of Southern Africa have temperatures over 30°C. These regions have a hot summer.
The lowest average temperatures are under -20°C. The northern part of North America and
the northern part of Asia have temperatures under -20°C. These regions have a very cold
winter.
July temperature
In July, it is winter in the southern hemisphere and summer in the northern hemisphere.
Activity 1: Temperatures in January and July
Page 5 of 41
2.1.1
2.1.1. What is the highest temperature shown on the map? Over 30⁰C
2.1.2. Name a region of the world that has this temperature in July.
___________________
2.1.3. What is the lowest temperature shown on the map?
______________________
2.1.4. Name a region in the southern hemisphere that has this temperature in
July._____________________________
2.1.5. Identify a region in the northern hemisphere that has this temperature in
July. _______________________________________________________
2.1.6. Name a part of the world that has:
___________________________________________________________
a) A very hot summer in July. __________________________
b) A warm summer in July. ___________________________
c) A mild winter in July. _____________________________
d) A cool summer in July. ___________________________
2.1.7. Which continent, not shown on this map, has very low temperatures in
July?
_____________________________
Wet and dry areas of the world
Rainfall is different all over the world. The amount of rain that falls in a region is
seasonal.
Winter can be cold and wet, or cold and dry.
Summer can be hot and wet, or warm and dry.
The annual rainfall is usually measured by the amount of rain that falls in one
year on average. Rainfall is measured in millimeters (mm).
Reasons for different amounts of rainfall in different regions:
Distance from the equator
Places along the equator are usually hot and get a lot of rain.
Distance from the ocean
Page 6 of 41
Places inland and far from the ocean are usually drier than places along the
coast. The air along the coast is very moist and it rains often.
2.2
Activity 2: World Rainfall
Study the map of the world’s average rainfall and answer the questions that follow.
2.2.1.Around which line of latitude is the world’s wettest region?
________________________________
2.2.2. How much rain does this region receive in one year?
_________________________________
2.2.3. How much rain does the world’s driest region receive in a year?
_________________________________
2.2.4. Look at the very cold regions of the world on the temperature maps. Are
the coldest parts of the world dry or wet?
______________________________________________________________
Study the graph that indicates the average temperature and precipitation
of Barrow in Alaska.
Page 7 of 41
2.2.5. What would the two coldest months of the year be in Barrow?
______________________________________________________________
2.2.6. What would the warmest month of the year be in Barrow?
______________________________________________________________
2.2.7. What do you think the main type of precipitation in this area?
______________________________________________________________
2.2.8. Why do you think the temperatures are so low during the year in this
area?
____________________________________________________________
Activity 3: Drawing graphs
Use the following information to draw a double graph (a bar graph and a line graph).
Make sure your graph has all the necessary information.
Line graph: Represent rainfall - measured in 10mm
Bar graph: Represent temperature - measured at 5°C
Climate for Boksburg
Temperature
Rainfall
January
30°C
20mm
February
35°C
45mm
March
30°C
50mm
April
25°C
60mm
May
20°C
65mm
June
20°C
70mm
July
15°C
80mm
August
18°C
75mm
September
25°C
70mm
October
25°C
65mm
November
28°C
50mm
December
35°C
20mm
Important rules and steps:
Page 8 of 41
-
Write the main heading.
Write the information at the bottom of the graph (months)
Write the information on the sides of the graph (°C and mm). Always start with zero.
Write the heading for your different axis.
Start with your line graph. Start on the line furthest to the left.
Complete your bar graph.
Remember to indicate with a key which graph indicates which information.
Activity 4 – A: Drawing a graph
Use the following information to draw a double graph (a bar graph and a line graph).
Make sure your graph has all the necessary information.
Bar graph: Represent rainfall - measured in 15mm
Line graph: Represent temperature - measured at 5°C
Climate for Cape Town
Temperature
Rainfall
January
32°C
10mm
February
30°C
12mm
March
28°C
29mm
April
25°C
86mm
May
22°C
120mm
June
20°C
185mm
July
16°C
162mm
August
17°C
100mm
September
21°C
86mm
October
26°C
50mm
November
28°C
30mm
December
35°C
22mm
Activity 4 – B: Doing calculations
Use the information regarding Cape Town’s climate to do the following calculations.
Write out all your calculations.
2.3.1. Calculate the average temperature during each season.
a) summer _________
b) autumn _________ c) winter _______ d) spring _____
2.3.2. Calculate the average rainfall during each season.
a) summer _________
b) autumn __________ c) winter ________ d) spring _____
2.3.3. Calculate the average annual temperature. ____________________
2.3.4. Calculate the average annual rainfall. ________________________
Remember
Temperature: All the necessary numbers.
Divide by the amounts of numbers you added up.
Example: Average temperature for summer.
Page 9 of 41
Nov 28°C + Dec 31°C + Jan 34°C + Feb 27°C
= 120°C
= 120°C ÷ 4 (Because we added up 4 different numbers)
= 30°C average
Rainfall: Add up all the necessary numbers.
Example: Average rainfall for summer.
Nov 15mm + Dec 55mm + Jan 65mm + Feb 42mm
= 177mm average
Week Topic: What is the difference between weather and climate
#2 b
Various options are provided as possible answers to the following questions.
Choose the correct answer and circle only the correct letter, e.g.,
D
d at a
2.1.1. The day-to-day condition of the atmosphere of a given place and
1x1(1)
given time. It describes the current atmospheric conditions of an area.
A. Climate
B. Weather
C. Trend
D. Season
2.1.2.The amount of water vapour in the air
1x1(1)
A. Warmth
B. Precipitation
C. Humidity
D. air pressure
2.1.3. Rain, snow sleet, or hail that falls from the clouds in the sky.
A. Humidity
B. Liquid
C. Precipitation
D. Weather
2.1.4. The average or general weather conditions of a region year after year/
recorded over a long period.
Page 10 of 41
Map showing average conditions of a region
A. Weather
B. Season
C. Cold
D. Climate
2.1.5. Which best describes climate?
A. Summers are usually hot and dry
B. It rained last week
C. Yesterday it was cold and windy
D. Dangerous events caused by
weather (floods, tornadoes, hurricanes, etc.)
2.2.
Use the following words to complete the sentence below
Weather, world, location
Taken fromhttps://keydifferences.com
Different areas of the ______________ have different climate based on their
physical _______________. Their climate is based on the average
_____________ they have over a long period.
Consolidation Activity
1x9(9)
Various options are provided as possible answers. Select from the sentences
below to show that you understand the difference between weather and climate.
Also, note that both atmospheric conditions use the same weather elements to
describe the conditions of various regions places. Make a list of those weather
elements included in the words/sentences provided below. Use the table below
to write your answers
Condition of a particular area describing day by day condition, rainfall, covers
a large area such as province, country or world’s region, temperature, cloud
cover, condition of an area which can either describe a season or years e.g.,
atmospheric condition over 30 years, atmospheric condition over a longer
period, wind direction, atmospheric condition which reports on covers township
or town, atmospheric condition over a short period of time.
2.3.
WEATHER
ELEMENTS OF WEATHER
CLIMATE
Page 11 of 41
L2
2.4.
Hot, mild, and cold climatic regions of the world.
Use the map below to identify the different climatic regions
A
B
C
D
Image link Map showing the location of climatic regions from various continents
Read the world map above and answer the following questions.
2.5.
Name the climatic regions shown with the letters above and what are the
conditions in those areas.
A.___________________________________________________________
B. __________________________________________________________
C. __________________________________________________________
D.__________________________________________________________
The diagram below shows the key factors that influence temperatures in various regions of
the world depending on where a region is located. Use the hamburger method of paragraph
writing to guide you to structure your paragraph. In a short paragraph of approximately 5
sentences discuss how different regions have different temperatures
Page 12 of 41
Diagram showing factors influencing climatic regions
Diagram which can assist you as guide to structure your paragraph writing.
______________________________________________________________
1x5(5)
______________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________
Assessment criteria
0
1
2
The learner is accommodating most facts according to
the instructions given
The learner uses mostly relates to a great extent to the
topic.
Used proper punctuation and spelling
TOTAL
/5
Refer to Source A: world maps below showing average temperature in January and in July.
Source A: World Map showing – Average Temperature in January
Page 13 of 41
2.6.
2.6.1. What is the highest temperature recorded in January?
1x1(1)
_______________
2.6.2. Name the region that has this temperature. What could be the reason
1x1(1)
why temperatures are higher in these regions?
______________________________________________________
2.6.3. List three regions that experience the lowest temperatures in January.
1x3(3)
Also, mention the hemisphere where these regions are located.
______________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________
2.7.
Refer to source B: world maps below showing average temperature in July
Source B: World Map: Average Temperature
in July
2.7.1 When you are in the Northern part of Africa which temperatures would
1x1(1)
you experience in July? _________________________
2.7.2. At the tip of South America residents of that region would be
1x1(1)
experiencing what type of summer in July. ___________________
2.7.3. In South Africa what type of temperatures do we experience July?
1x1(1)
___________________________________
Page 14 of 41
2.8.
Use source A and source B to extract your answer to the following question. South Africa
experiences different temperatures in January and in July. Mention seasons that we
experience during these months and at least give one example of how such temperatures
affect human activities around the country
2.8.1. January-
1x1(1)
__________________________________________________________
2.8.2. July –
___________________________________________________________
1x1(1)
Week #
3.1 a
WET AND DRY AREAS OF THE WORLD
Rainfall is different all over the world. Annual rainfall is dependent on the
climatic conditions of different locations. Wet areas usually get above 1000
mm of rain and dry areas usually get less than 250 mm of rainfall a year.
Choose the correct answers between brackets by underlining them.
3.1.1 (Wet/ dry) areas of the world are found far away from the sea.
1x1(1)
3.1.2. Places along the equator usually have average rainfall (above/below)
1x1(1)
L1
of 1000 mm.
3.1.3. A desert climate exists in areas where rainfall is very (high/low) making
1x1(1)
it a (wet/dry) area.
3.2.
3.2.1.Explain what an average annual rainfall map is.
1x2(2)
L2
1x2(2)
L2
______________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________
___
3.3.
Differentiate between wet areas and dry areas of the world.
3.3.1. Wet Areas
______________________________________________________________
Page 15 of 41
______________________________________________________________
__
3.3.2. Dry Areas
1x2(2)
______________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________
__
3.4.
Study the map below to answer the questions that follow.
3.4.1. Indicates the least amount of rainfall that appears on the map.
1x1(1)
___________________________
3.4.2. Name the two driest continents on the map.
1x2(2)
________________________________
________________________________
3.4.3. Identify the colour that indicates the wettest area in the world.
1X1(1)
__________________________
3.4.4. State the name of any country that received rainfall all year round.
1X1(1)
_____________________________.
3.1.B
Topic: Climate and Vegetation Around the World
Page 16 of 41
L2
Study the map below of extremely wet and dry areas of the world and answer the questions
that follows:
Moderate rainfall
http://www.seafriends.org.nz/enviro/soil/rocktbl2.htm
3.1.1. State whether South Africa is in the dry, moderate, or wet region based
1X1(1)
L1
on the map above
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------3.1.2 Select the region from the choices given below that is extremely wet
1X1(1)
{the south pole, north pole, midlatitude, and the equator}.
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------3.1.3. Support your answer to question 3.1.2 above with three reasons.
1X2(2)
L2
Write a paragraph of approximately FIVE facts, comparing wet and dry regions 1X5(5)
L3
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
of the world
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Page 17 of 41
Assessment guideline for a paragraph
Level 1
● Uses evidence in an elementary manner e.g., shows
little or no understanding. Uses evidence partially to Marks: 0-1
report on the topic or cannot report on the topic
Level 2
Level 3
Week
● Evidence is mostly relevant and relates to a great
extent to the topic. Uses evidence in a very basic Marks: 2-3
manner.
● Uses relevant evidence e.g. demonstrates a
Marks: 4-5
thorough understanding.
● Uses evidence very effectively in an organized
paragraph that shows an understanding of the topic
TOPIC: Tropical rainforest: The location of tropical rainforests on Earth.
#4
Activity 4
4.1.a
Study the source below which shows tropical rainforests and answer the questions that
follow.
4.1.1.List the latitudinal lines where tropical rainforests are in the world.
1x1(1)
L1
1x2(1)
L2
______________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________
4.1.2. Use an atlas to locate countries that have tropical rainforests on
different continents
______________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________
Page 18 of 41
4.2.3. What do you think will be the effect on the temperature of a region if the
rays of the sun are more concentrated?
______________________________________________________________
1x2(2)
L2
1x2(2)
L2
______________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________
4.2.
Activity 4. 2
The climate of tropical rainforests
4.2.1.What do you think the effect of high temperatures will have on the
humidity in tropical rainforests?
______________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________
4.2.2. What do you think the effect of a combination of high temperatures and
1x2(2)
high humidity on the amount of rainfall received in equatorial regions will be?
______________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________
4.2.3. Give examples of biodiversity in the tropical rainforest?
1x2(2)
______________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________
Page 19 of 41
L1
Activity 4.3
Climate of a tropical rainforest
Study the climatic graph below and answer the questions
4.3.1. Which month received the highest amount of rainfall?
______________________________________________________________
1x2(2)
L2
______________________________________________________________
4.3.2. Which month received the least amount of rainfall
1x2(2)
______________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________
4.4.
Study the climatic graph of the tropical rainforest below and answer the questions.
Months
J
F
M
A
M
J
J
A
S
O
N
D
Rainfall
(mm)
270
260
290
280
220
120
70
60
70
120
270
270
Temp c
27
27
25
27
26
27
28
26
26
24
26
25
4.4.1. Calculate the average rainfall for the year. Show your working
(Enrichment activity)
1x2(2)
L2
1x2(2)
L2
_____________________________________________________________
4.5
Activity 4.5
Page 20 of 41
Natural vegetation and wildlife in tropical rainforests.
4.5.1.Describe the plants and animals found in tropical rainforests.
______________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________
Week
Topic: tropical rain forests
#4
4.1.c
4.1.1.Write a paragraph and discuss what tropical rain forests are.
1x5(5)
______________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________
4.2.
Study the rainfall and temperature graphs for Singapore
Page 21 of 41
4.2.2. What are the temperatures for Singapore from Jan to May?
1x1(1)
L2
_________________________________________________
4.2.3. Which months does it rain the most in Singapore?
1x3(3)
______________________
______________________
______________________
4.2.4. In which month does Singapore receive less rainfall?
1x1(1)
__________________
Does this mean that Singapore is a wet or dry region and say Why?
1x2(2)
____________________________________________________________
Week # 5
4.1
TROPICAL forests are forests that grows in an area that is Hot and Wet for
most of the year. A Tropical rainforest is also known as a Jungle.
LOCATION: Most of rainforests occur along the Equator. The tropical rainforests are mostly
between 10 degrees North and 10 degrees South of the Equator. The tropical rainforests
stretch across the Equator as far as the Tropic of Cancer in the North and the tropic of
Capricorn in the South.
VEGETATION: Rainfall and temperature affect the kinds of plants that grow in an area. The
hot and wet climate of rainforest allows a variety of vegetation to grow. There are plants that
grow low on the ground, tall trees and plants that climb and grow on other plants. Vegetation
in rainforests is divided into four layers, namely: Emergent layer, Canopy layer, Understorey
layer and the Forest floor.
WILDLIFE: Tropical rainforest have a greater number and a variety of animals than any other
area on earth. There are Mountain Gorillas, Butterflies, Frogs, Jaguars, Monkeys, Okapi’s,
Tapirs, Chimpanzees and many other animals.
DEFORESTATION: Deforestation is a process of cutting down and clearing away of forests
without planting new ones. Large parts of rainforests are cut down or burnt because of the
following reasons:
*Building Materials, Space for roads, Farming, Settlement, Dams, mining, Pastures, and
sports fields.
Consequences of Deforestation: Soil erosion; Imbalance of gasses in the air; Flooding;
Global warming; loss of plants and animal species, soil erosion and flooding.
Page 22 of 41
5.1.1.Name Two (2) continents where we find Tropical rainforests.
1x2(2)
L1
1x2(2)
L2
1x4(4)
L1
1x1(2)
L1
1X2(2)
L1
1X2(2)
L2
____________________________
____________________________
5.1.2.Where are tropical rainforests located on Earth?
____________________________
__________________________
5.1.3.Name the four layers of the vegetation found in rainforests?
__________________________
____________________________
__________________________
____________________________
5.1.4. Name two continents where there are no Tropical rainforests?
__________________________
Study the Bar graph below and answer questions below the graph.
Average Rainfall
350
300
RAINFALL IN MM
5.2.
____________________________
250
200
150
100
50
0
5.2.1.Name 2 months where this area receive more than 200mm of rainfall
__________________________________
_________________________________
5.2.2. In which month does this place receive the least rainfall?
___________________________________
Page 23 of 41
5.2.3. How much rain in mm does this area receive during the month of July?
1X2(2)
________________________________
5.2.4. In which month does this area receive the highest rainfall?
1X2(2)
L2
1X3(3)
L2
_________________________________
5.3.
5.3.1.Give three consequences of Deforestation.
______________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________
5.3.2.Give five reasons for Deforestation.
1X5(5)
______________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________
5.3.3. Name two animals that are found in Tropical rainforests.
1X2(2)
______________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________
Week
Topic: Natural vegetation and wildlife in a rainforest
#5
New words:
Vegetation – the plant’s bushes and trees that grow in an area.
Wildlife – animals, and plants growing in natural conditions.
Tropical rainforest – a forest that grows in an area that is hot and wet for
most of the year.
Humid – when the air in the area feels hot and wet.
Logging – cutting down trees for wood.
Timber – wood that we use for building and making things.
Deforestation – the disappearance of natural forests due to cutting down
trees.
Global warming – a gradual increase in the overall temperature of the earth’s
atmosphere.
If there are many different plants and animals, then the area has a high
biodiversity.
Page 24 of 41
L1
5.1.b.
Multiple choice. Choose and fill in the correct answer in the sentences below:
Source A
Adapted from Teachers pay teachers
5.1.1.Tropical rainforests are found along the low-lying areas of the
1x1(1)
____________.
A. arctic circle
B. equator
C. Antarctic circle
D. south pole
5.1.2.____________ is the amount of water vapour in the air.
1x1(1)
A. humidity
B. oxygen
C. clouds
D. wind
5.1.3.Tropical rainforests have a very __________ annual rainfall.
1x1(1)
A. low
B. moderate
C. high
D. none of the above
5.1.4.The tropical forests have a very ___________temperature of about 28˚C
1x1(1)
all year around.
A. cold
B. warm
C. warm and cold
D. None of the above
Page 25 of 41
L1
5.1.5.If there are many different plants and animals, then the area has a high
1x1(1)
L1
_____.
A. trees
B. birds
C. reptiles
D. biodiversity
5.1.6.The ______________ is the world’s largest rainforest.
1X1(1)
A. Amazon
B. Congo basin
C. New guinea
D.Daintree
5.1.7.Tropical rainforests supply the earth with a lot of _____________.
1X1(1)
A. carbon dioxide
B. carbon monoxide
C. oxygen
D. Sulphur
5.2.
The picture below shows the vegetation of the rainforest that grows in four layers. Name the
layers 1 – 4. Write your answers in the spaces provided below.
Level 1
Level 2
Level 3
Level 4
Istockphoto.com
Page 26 of 41
5.3.
5.2.1.Layer 1: ____________________________________________
1X1(1)
5.2.2.Layer 2: ____________________________________________
1X1(1)
5.2.3. Layer 3: ____________________________________________
1X1(1)
5.2.4. Layer 4: ____________________________________________
1X1(1)
L1
Refer to a source below and answer the questions that follow:
Source B
Case study
Deforestation in Ivory Coast
Ivory Coast used to be covered in tropical rainforests. In only 25 years 12 million
hectares of forest shrunk to 4 million hectares. Now there are hardly any trees left.
Forestry companies cut down more and more trees but did not replace them. Farmers
cleared land for crops like coffee and cocoa.
Losing their forest affected the economy, the climate and soil of the Ivory Coast:
• The fall in timber sales caused the country to get less money from exports.
• In the timber industry 30 000 workers have lost their jobs.
• As the forest was cleared, the rainwater either dried up in the hot sun or ran off
the land instead of seeping in the soil.
• There was no longer a carpet of leaves rotting to form compost, so the soil
became infertile.
• The drier savannah vegetation took over from the forest
Source: Oxford Successful Learners’ book
5.3.1.Define the word “Deforestation”
1x1(1)
L1
1x2(2)
L2
________________________________
5.3.2. Why are people cutting down trees? Give two reasons.
_________________________________________________________
_________________________________________________________
5.3.3. Write done two negative effects of cutting down trees.
__________________________________________________________
1x2(2)
___________________________________________________________
What caused the soil to become infertile?
1x2(2)
______________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________
Week
#6
Page 27 of 41
Week
Topic: Hot deserts: Natural vegetation and wildlife in a desert
#7
7.1.
7.1.1. Define the following term:
A. Desert
____________________________________
1x1(1)
7.1.2. Name the two types of deserts and give an example of each.
a. __________________________
1x2(2)
L1
b. __________________________
7.1.3. Give two examples of desert animals.
1x3(3)
a. ______________________________
b. ______________________________
c. _________________________________
7.2.
Describe how animals survive the hot desert temperatures.
1x4(4)
L2
______________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________
7.3.
Compare the adaptation of an Old Man Cactus and an Aloe in the desert, refer to the two
pictures in Source C.
Old Man Cactus
Aloe
Retrieved: https://thumbs.dreamstime.com
7.3.1. Aloe_____________________________________________________
1x3(3)
_________________________________________________________
Page 28 of 41
L2
_________________________________________________________
_________________________________________________________
7.3.2. Old Man Cactus:
1x3(3)
_________________________________________________________
_________________________________________________________
_________________________________________________________
_________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________.
7.4.
Study the picture of a Camel in Source D and analyse its adaptation in the desert.
SOURCE D: A Camel
https://st.depositphotos.com
7.4.1.
1x3(3)
L2
__________________________________________________________.
__________________________________________________________.
__________________________________________________________.
7.5.
7.5.1. Deserts are too hot and dry for many plants to survive. In a paragraph
explain how desert plants have adapted to survive in the desert and give
examples of specific plants to illustrate how they have adapted to the climate
they live in.
__________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________
Page 29 of 41
__________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________
Rubric:
Level 1
Level 2
Level 3
Use evidence and own knowledge in an elementary way i.e.,
show little or no understanding on the survival of plants in the
desert and the examples of specific plants.
MARKS: 0-1
Use evidence partially to report on topic or cannot report on
the topic.
Evidence is mostly relevant and is largely related to the subject.
Demonstrate an understanding on the survival of plants in the
MARKS: 2-3
desert and the examples of specific plants.
Use evidence in a simple way.
Demonstrate thorough understanding on the survival of
plants in the desert and the examples of specific plants.
MARKS: 4-5
Evidence relates well to the topic.
Use evidence very effectively in an organized paragraph
that shows an understanding of the topic.
Week
# 7 b.
Study the following source to answer the questions that follows.
Page 30 of 41
7.1.1. Name two hot deserts that are found in the continent of Africa.
1x2(2)
L2
(a) ________________________________________
(b) ________________________________________
7.1.2. Sechura and Atacama deserts are found in which continent?
1X1(1)
___________________________________________
7.1.3. According to the source which is the biggest hot desert in the world?
1X1(1)
___________________________________________
7.2.
State whether the following statements are True or False
7.2.1. Mojave and Sonoran deserts are found in the eastern side of North
1X1(1)
America ____________________
7.2.2. The Arabian desert is found in the Middle East.____________________
1X1(1)
7.2.3. Deserts are wet areas that receive more than 250mm of rainfall per year
1X1(1)
_____________________
7.2.4. There is no rain experienced at the desert. ____________________
1X1(1)
All types of animals and plants can survive at the desert.
1X1(1)
___________________
7.3.
7.2.5. The plants that grow in a desert do not need a lot of water.
____________________
The desert plants cannot store water for themselves.
____________________
CLIMATE: Temperature and rainfall
1X1(1)
1X1(1)
Study the following source to answer the question that follows
Match the sentence to the month or months you think it refers to.
Page 31 of 41
L2
7.3.1. The two coldest months in the year.
1X2(2)
L2
______________________________________________________________
7.4.
7.3.2. It hasn’t rained in over four months.
1X1(1)
______________________________________________________________
7.3.3. Two months where it is very hot and rainy.
1X2(2)
______________________________________________________________
7.3.4. The two months where it was cold and raining.
1X2(2)
______________________________________________________________
Study the following diagram about plants that grow in the desert to answer the questions that
follow
Choose and underline the correct answer from the list given in brackets.
7.4.1.Desert plants have waxy or leathery leaves that (increase moisture
loss, reduce moisture loss)
7.4.2.The large roots of the desert plants will collect the (underground water,
moisture on the surface)
7.4.3. Name the animal that is used to carry goods at the desert
________________________________________
Explain the following words
7.5.
7.5.1. Lifestyle
1X2(2)
____________________________________________________________
Page 32 of 41
_____________________________________________________________
7.5.2.The dromedary camel
1X2(2)
______________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________
7.5.3. Nomads
1X2(2)
______________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________
7.5.4. Oasis
______________________________________________________________
1X2(2)
______________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________
7.6.
Complete the diagrams by filling in ways in which each of the following has adapted to the
desert environment.
PLANTS
ANIMALS
Page 33 of 41
L2
HUMAN
7.7.
Write a paragraph about how people live in a desert. The following rubric will be used to mark
the paragraph. (5)
__________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________
Level 1
Week
Uses evidence in an elementary manner e.g. shows
little or no understanding. Uses evidence partially to
report on a topic or cannot report on a topic.
Level 2
Evidence is mostly relevant and relates to a great
extent to the topic. Uses evidence in a very basic
manner.
Level 3
Uses relevant evidence e.g., demonstrates a
thorough understanding
Uses evidence very effectively in an organized
paragraph that shows an understanding of the topic.
Topic: CONIFEROUS FORESTS: LOCATION ON EARTH
Marks: 0 - 1
Marks: 2 - 3
Marks: 4 - 5
#8
8.1.
Look at the source below and fill in the missing blanks based on the topic
Coniferous Forests: Location on Earth.
Choose from the words given below to complete the passage:
Siberia, Scandanavia, latitude north, southern hemisphere, 15 %, canada, northern
hemisphere, alaska, North America, AlbertaCanada, Northern Hemisphere, Alberta
,15%, latitude nortlah, Alaska, North America, Southern Hemisphere,
ScandinaviCanada, Northern Hemisphere, Alberta ,15%, latitude north, Alaska,
Coniferous forests cover about a. _______________ of the Earth’s land surface. Coniferous
North America, Southern Hemisphere, Scandinavia
, Northern
Hemisphere,
Alberta ,15%, latitude north, Alaska
Canada,
Northern
Forests
are in the
b. ________________________________.
It NorI,
is because
there
are no large
Hemisphere, Alberta ,15%, latitude north, Alaska, North America, Southern
Hemisphere,
Scandinavia
areas
of Coniferous
Forests in inavia
the c. _____________________________. Coniferous forests
Page 34 of 41
are located far north of d. ________________________, Europe, and Asia between 50°
e.__________________________ and the Arctic Circle. You will find the most extensive
coniferous forest spans northern Russia and f. ________________________. Other significant
coniferous
forests
include
h.____________________
North
and,
America;
i.
g.
_________________________,
_____________________)
and
j.
_______________________ (Finland, Norway, and Sweden).
8.2.
Source: Grade 6 Social Sciences Platinum Textbook and Oxford Successful
8.2.1. Describe the climate where coniferous forests grow.
1x2(2)
L2
______________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________
8.2.2. Write a paragraph explaining how animals in coniferous forests adapt to 1x5(5)
the extreme cold and thick snow. Your work will be marked with the use of the
rubric attached below:
__________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________
Page 35 of 41
__________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________
Level 1
Level 2
Level 3
8.3.
Uses evidence in an elementary manner e.g. shows little or no
understanding. Uses evidence partially to report on a topic or
cannot report on another n topic.
Evidence is mostly relevant and relates to a great extent to the
topic. Uses evidence in a very basic manner.
MARKS: 01
MARKS: 23
Uses relevant evidence e.g., demonstrates a thorough Marks 4 - 5
understanding Uses evidence very effectively in an organized
paragraph that shows an understanding of the topic
8.3.1. Explain five ways that coniferous trees have adapted to suit the cold and 1x5(5)
dry winters in the northern hemisphere.
a)_______________________________________________________
L2
b)_______________________________________________________
c)_______________________________________________________
d)_______________________________________________________
e)_______________________________________________________
Week
Revision and consolidation of work covered
#9
Topics: Climate around the world
9.1.1. Define the following terms.
1x1(1)
Weather
______________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________
9.1.2. Climate
1x1(1)
______________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________
9.2.
(weather and climate)
9.2.1. Name any three elements of weather.
1x3(3)
______________________________________________________________
9.3.
(hot, mild, and cold climates)
9.3.1. Which areas of the world have a hot type of climate?
1x1(1)
Choose and underline from the answers provided
A. around the Equator
Page 36 of 41
L2
B. around the North Pole
C. around the South Pole
9.3.2. Which of the following areas have a mild type of climate?
1x1(1)
L1
A. The North Pole
B. The South Pole
C. places near the sea
9.3.3. Which places have a cold climate?
1x1(1)
A. areas near the equator
B. Areas near the sea
C. Areas around the North and South Poles
9.4.
(Weather map of South Africa)
Source: weatherblog.co.za
Use the map above to answer the questions that follow.
9.4.1.What is the title of the map shown above?
1x1(1)
______________________________________________________________
9.4.2. What units are used to show temperatures on a weather map?
1x1(1)
______________________________________________________________
9.4.3. When were the temperatures recorded?
1x1(1)
______________________________________________________________
9.4.4. Name the season in which these temperatures were recorded.
1x1(1)
Page 37 of 41
L2
______________________________________________________________
9.5.
(The tropical rainforests)
Source: twinkl.com
Use the diagram of the tropical rainforest to answer the questions that follow.
9.5.2. Name three living things that can be found on the forest floor.
1x3(3)
_____________________________________________________________
9.5.3. Name any two animals that can live in the canopy and the emergent
1x2(2)
layers of the rainforest.
_____________________________________________________________
9.5.4. Why do trees grow in layers in the tropical rainforest?
1x1(1)
_____________________________________________________________
9.5.5 Identify one adaptation of rainforest plants.
1x1(1)
_____________________________________________________________
9.6.
(Paragraph writing)
Write a paragraph about the importance of the rainforest. Include information about global
warming, habitats, provision of oxygen, removal of carbon dioxide from the air, source
of food)
__________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________
Page 38 of 41
__________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________
Level 1
Omissions in coverage
Question inadequately addressed or not at all
Level 2
The question has been answered to a certain extent
Content adequately covered and relevant
Level 3
The question has been fully answered
Content selection relevant to the line of argument
0-1
marks
2-3
marks
4-5
marks
A planned and structured paragraph
9.7.
Source: blogspot.com
Page 39 of 41
Which of the following are true or false regarding hot deserts? Underline
the correct answer
9.7.1.The largest hot desert is the Sahara Desert. (True/False)
9.7.2. Most hot deserts are located on the western side of continents.
(True/False)
9.7.3.The Namib desert is found in South Africa. (True/False)
9.7.4. Write three sentences on how a camel adapts to hot desert
conditions.
Week
Topics: Coniferous forests
#9
Location of coniferous forests in the world
Source: Benders.E. Hyde
Answer the questions that follow
9.1.1. In what type of climate do coniferous forests grow?
1x1(1)
__________________________________________________________
9.1.2. Coniferous forests are found in the _____________________
hemisphere.
9.1.3. What type of precipitation is received in the areas where coniferous
forests grow?
___________________________________________________________
Page 40 of 41
9.1.4. Name two continents in which we find coniferous forests.
1x2(2)
__________________________________________________________
Page 41 of 41