For each statement, name the law:
a)
In any chemical reaction involving gases, the volumes of the reactants
are always in small whole-number ratios.
b)
In any chemical reaction, there is no detectable difference between the
total mass of the reactants and the total mass of the products.
C)
The total pressure of a mixture of gases is equal to the sum of the partial
pressures of the component gases.
d)
A specific compound has the same composition anywhere in the
universe.
At constant pressure, the volume of a fixed mass of gas is proportional to
the temperature of the gas.‘
2)
Give an example for each of the following:
A covalent molecule
a)
1)
An acidic oxide
m)
A diatomic gas in the
same period as iron
b)
Homogenous mixture
C)
Heterogeneous mixture
d)
Alloy
0)
An alkaline earth metal
e)
A gas that is not
diatomic
p)
A salt containing sulphur
q)
A basic oxide
r)
An oxyacid
s)
A salt of an oxyacid
t)
A hydrocarbon
u)
A precipitate at low
concentration.
A noble gas
g)
h)
A transition metal
An alkali metal
A halogen
“k”
"x.
j)
k)
A polar covalent
molecule
An ionic molecule
3)
4)
Give four properties generally common to metals
a)
b)
c)
d)
Give four ways to recognise a chemical reaction
a)
b)
c)
(1)
[4]
5)'
Please circle which of the following statements form a part of Dalton’s atomic
theory? (marks may be deducted for incorrect answers)
a)
b)
c)
6)
a)
b)
c)
d)
7)
All substances are made up of tiny indivisible particles called atoms.
The atoms of each element are alike in that they have the same number
of protons.
Atoms cannot be created of destroyed during a chemical reaction.
What are the main differences between Rutherford’s model and
Thompson’s plum pudding model?
What are the main differences between Rutherford’s model and Bohr’s
model?
What was wrong with Rutherford’s model?
What experiment did Rutherford carry out to determine the presence of a
nucleus.
Please complete the equation beneath and provide two balanced molecular
equations that would represent such a reaction.
Acid
+
Base
—>
+
+
—>
+
+
—>
+
Please complete the table for the following neutral atoms:
8)
Atomic
Number
A to
m
Mass #
# of
protons
in the
most
common
isotope
#
of
# of
.
neutrons m
the most
common
isoto p e
.
electrpns m
the most
common
Ground
state
confl g 11
.
ratlon
isoto p e
2.8.18.
As
5
P
15
C
4
9)
Isotope
symbol
Draw Lewis dot representations for the following:
a)
N2
b)
C02
0)
CO
d)
803
6)
NaCl
f)
Ban
g)
AlF3
h)
NH3
j)
Can
i)
NaCl
10)
"Please place in order
Property
Electronegativity
Atomic radius
Reactivity
Electronegativity
Ionization energy
Atomic radius
Element/ion
F, F“, 0
0, C, Li
Na, K, Rb
.
Least
—
middle - most
Ne, Be, Li
H, Li, Na
H, Li, Na
Explain using electrostatic forces each of the above trends.
11)
Use the following table to answer this question
Temperature
(°C)
Solubility
(Grams of solute/100g water)
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
14
'
23
35
46
62
80
100
Plot the graph with temperature on the x-axis. Label the chart properly and
put a title in the correct position.
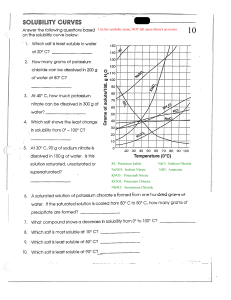
Estimate the solubility of this salt at 25 °C.
What is the lowest temperature at which 42 grams/ 100g HzO is saturated?
Is 38 grams
solution.
of this salt stirred in 50 grams H20
a saturated or unsaturated
How many degrees Centigrade must you heat 22 grams of Potassium
nitrate stirred in 35g of water to make it unsaturated? Assume the solution
to be at room temperature of 20 °C.
450 grams of a saturated solution is cooled from 60 degrees Celsius to 25.
How much precipitate will form? Also, calculate the mass of salt that will
end up in the filtrate (This is the salt that stays in solution).
£254.5-
"
12)
13)
Balance the following reactions and provide the states:
+
N20
nitrogen(
+
a)
Ammonia(
b)
CaSO4(
G)
How many litres of N20 can produce 8 litres of nitrogen gas?
)
)
+
~
H3PO4(
(g)
)—>
——>
Ca3PO4(
)
)
+
water(
)
HZSO4(aq)
What is the mass of B in this reaction
A +
125g
B
—>
C + D
240g 75g
14)
Find the mass of 3 moles of hydrogen sulphate
15)
325 ml of 6 M nitrous acid contains how many grams of anhydrous chemical?
16)
How many molecules are present in 14.5 g of CaSO4
17)
How would you prepare 285 ml of 3.28 M sodium sulphite solution?\
18)
What is the volume of 15g of NH3 at a pressure of 34 KPa and 200 °C?
19)
A 5 litre glass bottle of gas is sealed at high altitude where the pressure is 70 Kpa
and the temperature is 3°C.
a)
What will the internal pressure be if the bottle is moved to a place Where
the temperature is 30°C?
b)
What will the volume be?
20)
Hydrochloric acid and silicon dioxide can be produced from the reaction of
silicon tetrachloride with water.
a)
b)
C)
d)
19)
0.250 grams of NaOH is dissolved in 1.56 ml of water.
a)
b)
C)
d)
20)
How many moles of hydrogen chloride can be produced from 22.0 g of
water?
How many grams of silicon tetrachloride will react with 50 grams of
water?
How many moles of water will be needed to react with 13 moles of
sulphur tetrachloride?
How many grams of silicon dioxide can be produced from the reaction of
4.55 moles of silicon tetrachloride with 158 grams of water?
Calculate the molarity of this solution?
Determine the pH of this solution.
How many m1 of water must be added to the base to produce a 0.000625
molar solution?
How many ml of 0.3 M phosphoric acid can be neutralized with this
solution?
Lead (II) nitrate + potassium chromate
a)
b)
C)
60
—>
Complete the above equation (it leads to the formation of a precipitate)
Write the molecular equation
Write the ionic equation
Write the net ionic equation
21)
6.8 grams of sodium are placed in a solution containing 0.3 moles of
copper
nitrate. Determine the mass of the salt produced.
22)
28L of gas in an expandable container at 2.3 atm and 25 degrees C are moved to a"
place at 1.35 atm. If the volume becomes 140 L, then what is the temperature?
23)
.Sketch the following results on a graph to find out what an inverse relationship
looks like.
Pressure
Volume
(L)
(L)
100
2
50
4
40
5
20
10
10
20
5
40
4
50
100
2
60
'
40
w
20“
|
I
G
20
40
60
80
l
120
190
120
100
Now sketch the direct
relationship which exists
between volume and
temperature.
“
50‘
4-0—
20“
Volume (L)
0
20
40
50
80
100
120
temp (K)
24)
An atmosphere on a distant planet has the following composition:
20% NH3, 50% N2, 30% Ar
If the total pressure is two atmospheres, what is the pressure exerted by each gas?
a)
NH3
b)
N2
Ar
Which law are you applying in your calculations?
If the total volume
is 5.00L, and the temperature is 25 °C, then determine
the number of moles of each gas.
Achemistry student carried out a volumetric titration. She found that 40ml of
phosphoric acid was neutralised by 15 ml of 0.20 M sodium hydroxide. What15
the molarity of the acid and what is the mass of sodium hydroxide used?
Using examples, explain how the electronegativity of two different elements
determines the type of bond that forms between them.
25)
26)
4
Determine the atomic mass of Bromine when 50. 69 % of the naturally occurring
isotopes are Br-79 and the rest are Br- 81
Which postulates of Dalton’s atomic theory are
27)
correct
correct if you add “in a chemical reaction”
not correct
»
28)
Determine the percentage mass of phosphorus in sodium phosphate
29)
Determine how many grams of oxygen there are in 187 grams of sodium
phosphate.
30)
A hydrocarbon containing 92. 3% carbon occupies 22 4 L at standard temperature
and 202. 6 kPa. If the mass of the gas is 52 grams then what15 the empirical and
the molecular formula.
31)
Determine the mass of the salt produced when 325 mL of 0.35 M sulphuric acid
is reacted with 458 ml of 0. 222 M sodium hydroxide.
32)
y
250 ml of calcium nitrate solution is made by using 48.3 g of calcium nitrate.
Let’s call this solution A. Solution B is made by taking 100 ml of solution A and
adding 150 m1 of water. Solution C is made by taking 100 ml of solution A and
adding 10 more grams of calcium nitrate.
a)
b)
c)
d)
What is the concentration of solution
What is the concentration of solution
What is the concentration of solution
What is the nitrate ion concentration
with 40 m1 of solution C?
A?
B?
C?
when 25 ml of solution B is mixed
v“,
33)
Write the formula of the following:
ammonium sulfide
nickel(II) iodide
calcium nitrate tetrahydrate
mercurous oxide
cupric bromide
plumbous chlorite
aluminum sulfate
dinitrogen monoxide
potassium nitrate
iron(II) bisulfite
ferrous carbonate
magnesium nitrate hexahydrate
lead(H) phosphate
iron(III) chromate
diphosphorus pentoxide
iron(II) chromate
cupric hydroxide
copper(II) hydroxide
calcium fluoride
cuprous carbonate
iickel(II) nitrate
sulphurous acid
tetraphosphorus decoxide
calcium chlorate
ammonium bicarbonite
aluminium bisulphite
calcium hypobicarbonite
carbonous acid
ammonium sulfite
ammonium oxide
zinc sulfate
aluminum perchlorate
tin(H) chloride
hydrobromic acid
carbonic acid
zinc bicarbonate
antimony(III) chloride
hydrogen peroxide
hypotellurous acid
sodium phosphate
silver sulfide
silver hypochlorite
magnesium hydroxide
chloric acid
Ammonia
ammonium phosphate
ammonium carbonate
ferrous chlorite
nickel(II) acetate
potassium sulfide
aluminium chromate
barium peroxide
rubidium peroxide
aluminium peroxide
magnesium dichromate
sodium chromate
perfluoric acid
nitrous acid
tin(IV) bromide
hydrosulphuric acid
calcium bicarbonite
potassium permanganate
magnesium persulfate
silver perchlorate
ferrous phosphate
hydrophosphoric acid
silicic acid
potassium phosphate
calcium sulfate dihydrate
chromic hyposulphite
chromic acetate
Magnesium peroxide
Sodium peroxide
58
Sulphur
a)
b)
c)
d)
e)
f)
35)
P4
Write balanced chemical equations for the following (For double-displacement
reactions, also write the net ionic equation:
34)
»
phosphorous
g)
h)
-
The
The
The
The
The
The
The
The
combustion of butane C4H10
combustion of 2-butene C4H3
combustion of 2-butyne C4H6
reactions of phosphoric acid and barium hydroxide
reaction between potassium carbonate and phosphoric acid
reaction between potassium carbonate and cupric iodide
reaction between sodium oxide and sulphur dioxide
reaction between sodium oxide and water
Solution A generally becomes more soluble with temperature. Solution B
generally becomes less soluble with temperature. Sketch the two solubility curves
on the same graph. Explain how you separate and purify a mixture of the salts A
and B.
10
36)
A mixture of 20g of sodium sulphate is mixed with 20 g of potassium chloride.
a) At what temperature are they equally soluble?
b) What is the solubility of these salts at this temperature?
How much water is needed to get both salts just into solution?
How much potassium chloride can be precipitated. State both the
temperature and the mass of the precipitate?
e) How much sodium sulphate can be precipitated. State both the
temperature and the mass of the precipitate?
o)
(1)
37)
How many grams of calcium nitrate tetrahydrate are required to make 58 ml of
0.155 M solution?
38)
What is the concentration of 670 ml of calcium nitrate when 130 grams of the
hydrate is used to make the solution?
39)
The formulas for ethanol and ammonium nitrate are C2H50H and NH4NO3. In
what respects are these formulae and compounds different and the same?
40)
2 moles
41)
Name the following binary compounds of the nonmetals:
of ammonia are mixed 25g of oxygen in a 3.5 L container. Calculate
the partial pressure exerted by each gas and the total pressure at 25 °C.
IFS
SiCl4
GeH4
P4010
N2H4
S4N4
CSz
SF6
PCls
OFz
Cle7
IF7
42)
What is the percent by mass of nitrogen in ammonium nitrate?
43)
Anhydrous lithium perchlorate (4.78 g) was dissolved in water and re—crystallized.
Care was taken to isolate all the lithium perchlorate as its hydrate. The mass of the
hydrated salt obtained was 7.21 g. What is the formula of the hydrate?
44)
An element has an atomic mass of 78.3 a.m.u . A mass spectrometer finds three
isotopes of mass 75,77 and 80 a.m.u. If the heaviest isotope has four times the
abundance of the middle isotope, then what is the abundance of each isotope?
11
45)
A LOO-liter flask contains 0.100 moles of solid NH4Clat 300 K. All of the air has
been pumped out so the pressure is essentiallyzero. The flask is heated to 600 K,
decomposing some of the solid, andthe total pressure is found to be 3.00 atm.
(There is NO NH4Clin the vapor phase).
What is the partial pressure of ammonia?
What is the partial pressure of HCl?
46)
The element A has 3 isotopes, A-25,A-26 and A-27. The abundance of A—25 is x
%. The abundance of A-26 is (x + 10)%. What is the abundance of A—27? If the
atomic mass is 25.8 amu, then what is the abundance of each isotope?
You are reminded to set your working correctly on the exam. There will be mark
deductions for omitting units and statements from your answers. Chemical
explanations ought to involve electrostatic forces or the behaviour of microparticles.
If I cannot read and understand your answer within a reasonable period of time,
then you will be awarded a zero for that answer.
12
150
140
130
120
W
,,/
/
/
f
K:
11.0
Solubility“ Curve
N3N0‘3
100
,
90
50
f'
1
1
“k
x.
70
‘ '- N
a
"\
“a
40
-
f
£7”
20‘m_ I
/"h
10
h
h
~
________,
0
o
1
0
f
f/
//
gases
sulids
20
'
"‘
k
“455911
E
-
r’
-
/
~
..._
30
“
filv/
x/J“Mb/1,7;
'-
H
KC!
~
..--F "H...“
ff"
\,
,f'/
i
51111401
f h“ “H
{a
m
.
/
/ Afi’:
\
m
y/ L
HCI
“a... L
50
30
//
‘
“1 ”H3
xx
Magma“
6“
/
/
f
r/
,
//f
if
h“ ...
..,
40
‘~
fiffi/
f
..
{ch10 3
‘Kx‘wu.
‘\-
“I.
so 2
a
n
1" “
"'
~---_-.{_+______.___see
Temperature
13
:
,/<“*~ ~
an
(QC?)
70
30
90
1130