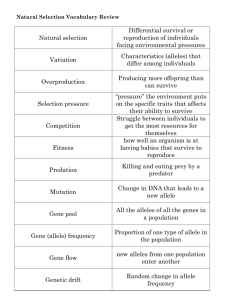
What are the key words and definitions for this external - Genetic Variation Feel free to edit definitions if you think you can improve them .Gene - A section of DNA that codes for a particular trait Allele - An alternative form of a gene (found on the same place on a chromosome) Allele frequency- The percentage of a population of a species that carries a particular allele on given chromosome locus. Mutation - A sudden and permanent change in the base sequence of an organism's genome (genetic sequence) Mutagen - An agent that can induce or increase the frequency of mutations in an organism eg. radiation, UV light, chemicals Meiosis - A type of (reduction) cell division in which one diploid cell splits into 4 haploid cells that are genetically different. (That produces gametes/sex cells; sperm or egg) Homologous pairs - Chromosome pairs that have the same structure and code for the same trait. Homologous Chromosomes – are similar but not identical. Each carries the same genes in the same order, but alleles for each train may not be the same. Crossing over - The process in meiosis when homologous pairs trade sections of DNA to increase variation (resulting in gametes that have chromosomes with different combinations of alleles to each other) Independent assortment - The process in Meiosis when homologous pairs randomly line up along the equator of the cell. (Therefore only one chromosome from each homologous pair is placed into the gametes) Segregation - The separation of homologous chromosomes during meiosis so that only one chromosome of each pair is placed into each gamete (during segregation the alleles from each gene are therefore separated so that each gamete carries one allele for each gene) (When the lines up homologous pairs separate to opposite poles of the cell, and then divide into 4 gamete cells, what chromatid ends up in each gamete is up to chance therefore increasing variation) Genetic variation - Variation in the allele frequency or genome between members of the species; or between groups of species What are the key words and definitions for this external - Genetic Variation Feel free to edit definitions if you think you can improve them Pure breeding - When two organisms with homozygous genotypes for a particular trait breed, resulting in an organism with the same homozygous genotype Test cross - Is when an animal/plant in question (of unknown genotype) is bred with a homozygous recessive individual, to find out whether or not it is purebred. Dominance - A relationship in which one allele is completely dominant over another (the phenotype of the allele is always expressed) Incomplete dominance - A condition in which a trait in an individual is intermediate between the phenotype of the individual’s parents because each allele is unable to express itself fully Co-dominance - When an individual which is heterozygous for two co-dominant alleles expresses the phenotypes associated with both the alleles. Recessive: an allele that is masked by a dominant allele. Only expressed when two copies of the allele are present. Multiple alleles - A gene with three or more alleles Lethal alleles - Alleles whose phenotypic effect can cause the death of an organism. Linked genes - Genes that are close together on the same chromosome and are usually inherited as a unit. Unlinked genes – Genes that are found on different chromosomes or far apart on the same chromosome and therefor unlikely to be inherited together. Gene pool - All of the alleles in all the individuals that make up a population. Total sum of different alleles available in an interbreeding population Genetic diversity - The total number of genetic characteristics in a populations (including different alleles, all of the genes and the frequency of each) Allele frequency - How often an allele appears in a gene pool compared to the alleles for the same gene in the pool Migration - When individuals move into (immigration) or out of (emigration) a population Evolution - A change in characteristics of a species over an extended period of time Natural selection - The process in which individuals who are best adapted (‘fit’) to the environment survive and reproduce, therefore passing on favourable (‘fit’) alleles to their offspring Genetic drift - Change in the allele frequency due to random chance (bottlenecking/ founders effect) Founder effect - When a subset of individuals emigrate from a larger population or become isolated and form a new population. What are the key words and definitions for this external - Genetic Variation Feel free to edit definitions if you think you can improve them Or Gene pool of a population that was established from a (subset) of a larger population. Population bottleneck (bottlenecking) - A proportion of the population is randomly eliminated resulting in a population that reflects the genetics of the survivors.