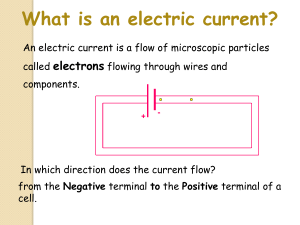
Thermal energy, internal energy and temperature 1 What is heat a measure of? Tick (✓) two boxes. the total kinetic energy of atoms and molecules in a substance part of the kinetic energy of atoms and molecules in a substance the potential gravitational energy of atoms and molecules in a substance the total movement energy of atoms and molecules in a substance 0 0 0 0 2 What 1s a temperature? Tick(✓) one box. an indication of how hot an object is an indication of how cold an object 1s an indication of how hot or cold an obJect Is on indication of how worm an object is □ D □ □ 3 A pan of water containing 50 cm3 of water is heated on a stove. a Would this water boil faster or slower than 100 cm3 water on the same stove? Circle your answer. - faster slower b What is this due to? Orcle your answer. - density mass substance temperature volume ■ PHYSICS Measuring the amount of thermal energy ~ 4 Rafiq is finding out how much energy 1s in a quantity of candle wax. He sets up the apparatus shown in the diagram. -1hermometer ,.,. ~ beake, water I candle He records the mass o f t he candle on a balance and records the temperature of the 500 m,3 of water In the beaker. He lights the candle, stirs the water and records the water temperature until 1t has nsen 10 'C. He puts out the burning candle and records its mass again. Here are his results. ; Mass of candle before burning 10g Temperature before heating 22'C Sg Temperature after heating 32•c Rise In temperature __ •c - Mass of candle after burning Loss of mass 1 - -9 a Complete t he two tables. b The energy in 1g of candle is found by using t he fallowing formula: 2.1 x rise In temperoture loss of moss =kJ/g Use the formula to find the energy in the candle wax that was burnt away by Rafiq. Show your working. ■ 12 Energy Joyo Is comparing the heat produced by two fuels. She uses each one 1n turn to heat the same volume of water for 10 minutes. Then she records the temperature every 2 minutes. The table shows he1 data. Time/minutes Fuel A temperaturer c Fuel B temperaturel"C 0 20 20 2 22 24 4 24 28 6 26 32 8 28 36 10 30 40 a Draw and label one line graph with a separate line for each fuel In the space below. b Use your graph to predict what the temperature of the water would be after 12 minutes. Mork your prediction with a dot on the graph. c Predict lhe temperature difference between l he two beakers of water after 12 minutes. ■ PHYSICS Conservation of energy 6 Explain in your own words what the phrase ·conservation of energy· means. ··-···......-....._.............._....._._,,.._..._._,...._.......... .._,._,,_..,,.....-......._._,_..........._,_, .. _. __ _ ___....... .... _,_,,, .. ,_,__ ,_,, __ ,.. Heat dissipation 7 Wh1d1 direcuon does heat (thermal) energy always tJovel 1n? Tick<✓) one box. from hotter to cooler O O cooler to halter 0 cold to hol 1l doesn't trove. cold to warmer □ □ 8 One end of the metal rod is heated using a Bunsen burner or heal source. The metal thumb tacks (drawing pins) are attached to the metal rod with wax. TrT a Predict what will happen as the metal rod IS heated b Describe how this equipment could be used to compare the conductivity of different metals. ■ 12 Energy 9 Explain how convection occurs when water 1s heated 1n a saucepan. Use these terms to help you: - convectJon current heat energy kinetic energy particles convection 10 a Describe how energy travels as rod1at1on. b Energy con travel through air. but what else can 1t travel through? ■ PHYSICS Evaporation 11 a On a warm day. after a rain shower, puddles of water remain an the ground. Explain the effect evaporation will hove on the puddles. b What state ls the water In when it 'disappears'? Circle your answer. - gas - liquid - solid c Describe another example of Lhis process happening 1n everyday life. d Do things become hotter or cooler when this process happens? Explain your answer. 12 a After vigorous exerdse. we produce sweat on the skin surface. When we stop. the sweat evaporates. Whal effect does Lhis have on body temperature? b Explain why this happens. ■ Sound and vibrations 1 What happens when you 'twang' a ruler and move one end over the edge of a table and back? Tick(✓) two boxes. The sound goes higher as the vibrating length Increases. The sound goes lower as the vibrating length increases. □ □ The sound goes higher as the vibroling length decreases. [l The sound goes lower as the vibrating length decreases. □ 2 Explain in your own words what a vibration Is. 3 a When something vibrates In the air. what get squashed together? b What change in the air does this squashing cause? ......................................................................................... c When the squashing ends. what happens next?.......................................·-·············································· ........ d What alternating regions ore generated in the air? ■ PHYSICS e What do these alternating regions make as they move through the 01r? ·····-···-···---··--··-·--.........______ .,.. _____ ________......._,._______ ___ ____.__ , , , The features of a waveform 4 In the waveform for the sound wave shown below, what name 1s given to both the distances labeUed A ond both the d ,stances labelled B? A. A. B .............. -···-···· -···-···-··-······...···-····-···-····-···-····.. ·····-······. ····..····-··· ····-···-····-···-···· -····-··-····-···-· 5 Which of the waveforms represents the louder sound 1 Cirde your answer. • b 6 Whic.h statement best describes pitch? T1c1< (✓) one box P1tc.h Is how loud a sound 1s. P1td1 1s how high or low a musical note sounds. Pitch 1s how soft a musical note ,s. Pitch 1s how loog a sound can be heard. Pitch Is how many sounds con be heard In one minute. ■ D 0 D D D 13 Waves 7 a What 1s frequenry?. ·-····-····--····-·-·-·--········-··-·······--·-····-·-·····-·-··-····-··-···--·--·······---·--····-··... b Label diagrams A and B as being either a high-frequency sound or low•frequency sound. A .......-....-..........- ...........................................................- ....-...........·-···..·····---·......................................................... b B ...... _....·-···---. -···. -········..······· ··-··...·-··-··.....-...........-....._..... ·-..····· ..-········............................... --........··-· ·-·.. ·-··. c What units do we use to measure the frequency of a sound? Give its name and symbol. Name· ······-··..-···..······-·-····-··-......... _ .. __ .._ ......... _.......... _ ...... _. __ ...._ ............_, Symbol: - .... --· .........._....................-..............- ...--.-·---····..·····-···-····-·--····..····. . . When sound waves interact 8 a What 1s the term used to describe when two sounds waves meet? Tic► interfere resonate amplitude □ □ □ I✓ ) one frequency pitch box. □ □ b Give two words to define each description below. When two sound waves of the some frequency meet, producing a wave of greeter amplitude. - .......·-···-·····-···-····-··...·...................... and ·······-····..···-·····..··-···-··-..···..··-·····- ■ PHYSICS ii When two sound waves of the same frequency meet and produce a wave of smaller amplitude. ..................................................................... and ..................................................................... c Explain ,n your own words whal a · dead spot' ,s. Modelling sound waves (I,} 9 a What properties of waves are measured when using a ripple tank? Tick frequency amplitude D D wavelength current D D (✓) as many as apply. speed D b The ripple Lank is used to model sound waves. Describe the strengths and limitations of Lhis model. Strengths· ........................................................................................................................................................................... Um1tat1ons: ....................................................................................................................................................................... . ■ Circuits 1 Noveen sets up the c1rcu1t shown ,n the diagram. 0 w,n, a When he closes the switch. which of the following happens in the wire? Tick (✓} one box. The electrons move from the negative terminal to the positive terminal. The atoms move from the negative terminal to the positive terminal. The electrons move from the pos1t1ve terminal to the negative terminal. The atoms move from the pos1t1ve terminal to the negative terminal. D D D 0 b Where does the energy to aeate the current come from? Cirde your answer - wire - cell - lamp switch c As the current flows through the circuit. the wire In the lamp behoves differently from the other wires In the drcwl What happens to the wire? ......... ••••• .. ••••••••• .. ••• .. ••••••....••••• .. •-••••.. •••••••••• .. •-•••• ..•••••• ....••••••• .... ••• .. • ..•••-•••-•••u••-• ............................................,-,.. •••• .. ••••.. •-•• Noveen leaves the circuit on for some time and later observes that the current has become weaker, d How con he tell Just by looking at the orcuit? ■ PHYSICS e What has caused this change in the current? f Naveen opens the switch. What happens to the rurrent? ii Explain your answer. 2 Here ore the symbols far the components m Noveen's c1rcu1t. The one on the lefl 1s for the cell. a Put o cross(•) next to the side which hos the negouve terminal. b Make a circuit diagram of Naveen's Circuit using these symbols. ■ 14 Electrical circuits c Naveen adds another cell in senes to the circuit. Drow the circuit dt0gram for th,s new c1rcu1t. d Naveen switches on the drcu1L How does the appeoronce of the lamp change? ii Explain your answ<?r. 3 The connection of the wire to the lamp breaks. Arunl suggests putting a piece of aluminium foil across the gap. Naveen disagrees and says a puxe of wood ,s all that is needed. a Who 1s correct 7 ···-·-·········-····-··· ....- .••• _.................................................._._._ ...........................- ..........................._..... b Explain your answer. ■ PHYSICS 4 Here are the symbols of three components of orcu,ts. Name them. A B C A 5 An electric current is flowing through a wire then the wtre splits into two to form a parallel circuit. What happens to the current? T,ck (✓ I one box. It~~All of 1t flows down one w,re and none of ,t flows through the other wire. It splits up and flows equally through both wtres. ll splits up but more of lhe cu11ent flows through one w,re than the other. 0 0 0 0 Measuring current 6 Which p,ece of equipment ,s used to meosu,e current In a orcutt? Circle you, answer. - ammete, - buuer - cell - lamp - voltmeter 7 An 01nmeter hos its pos,t,ve terminal marked in red. When adding on ammeter to a c11cu1t. which Instruction should you follow? Tick (✓ ) one box. Connect the red terminal to the pos,t,ve terminal or the cell. Connect the red terminal to the negative terminal of the cell. Connect the red terminal to either terminal of the cell. Connect the red terminal too lamp. ■ 0 0 0 0 14 Electrical circuits 8 Och1 sets up the orcuit shown in the diagram. She connects the ammeter at point A and then at point B. B A What does she find? Tick (✓ ) one box. □ □ □ The reading at A 1s lower than at B. The reading at A IS higher than at B. The reading al A is lhe same as al B. 9 Koh sets up the circuit shown 1n the drogrom. a How many places 1n Lhe orcu1l should she check w1Lh the ammeter? Cirde your answer. - 2 - i. - 3 - 5 b Mork the places on Lhe circuit d10grom. Measuring voltage 10 'vVhat does voltage measure? T1d. o difference In potentJal energy a difference 1n current speed o difference in resistance a d,fference In lamp brightness ✓) one box. D D D D ■ PHYSICS ~ 11 The diagram shows the symbol for the voltmeter and o simple circuiL .------------1 ~ Drow how you would connect the voltmeter lo the circuit to measure the voltage across the lamp. Resistance ~ 12 a What unit IS used to measure resistance? Give its name and symbol. b What 1s the equation that 1s used to calculate res1Stance? \11/nte 1t in both word and symbol form. Words· ···-···..···············..··-·-····-..······--·-·············-············-·..····-····-····-..·····-··-..···-···-··-··-··-···-····-·······-·-· Symbols· ..............................-· -·--.........................................................._.......... _._.........................................__ ....... _..... ■ 14 Electrical circuits c What 1s the resistance of a lamp when the voltage across 1t is 12 V and the current is measured OS 3A? d If the lamp is replaced with a different component that hos a resistance of 6.0 and the voltage remains 12V, what will be the new current? ■