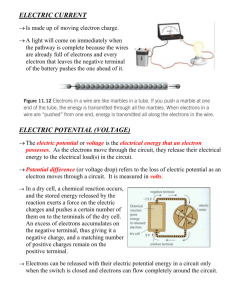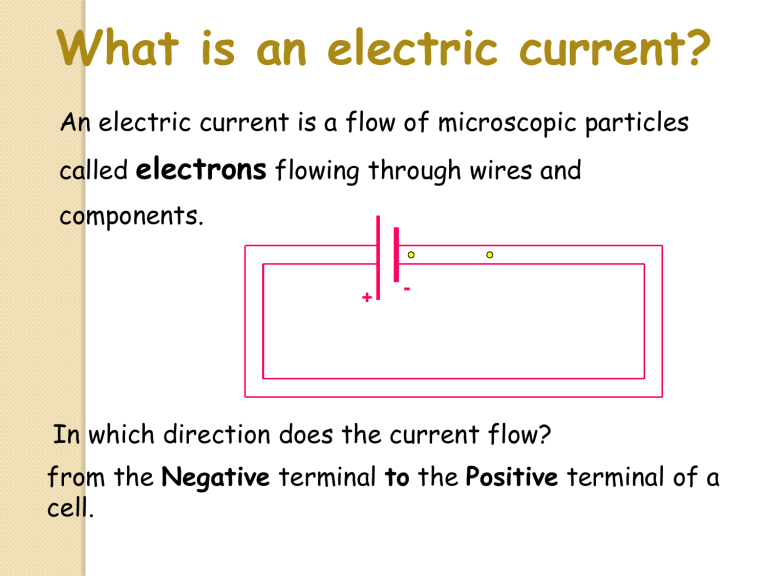
What is an electric current? An electric current is a flow of microscopic particles called electrons flowing through wires and components. + - In which direction does the current flow? from the Negative terminal to the Positive terminal of a cell. Electrical Charge and Current Learning Outcomes: 1. I can recall and apply the equation for charge 2. I can apply the equation for charge to show how we can increase or decrease current in a circuit 3. I can apply the equation for charge flow to an exam style question Electric current Electric current is a flow of electrical charge carried by electrons which move from the negative terminal to the positive terminal. The size of the electric current is the rate of flow of electrical charge. Electrical Charge Stand up and move around to make a circle around the room. Now start walking around in the circle. Stop – what are you in the circuit? Think about this analogy – if you are the electrons carrying the charge, how could you work out the charge? Charge Charge (Q) = Current (I) x Time (t) Q=It Units: ◦ Charge (Q) is in Coulombs (C) ◦ Current (I) is in Amps (A) ◦ Time (t) is in Seconds (s) Can you draw a formula triangle for this? Examples: 1. A current of 12A passes through a kettle for 20s. How much charge has flowed through the kettle? Answer: Q =It = 12 x 20 = 240C 2. A current of 200A passes through a hoover for 10minutes. How much charge has flowed through the kettle? Answer: Q=It = 200 x (10x60) =12,000C 3. A charge of 200C flows through an iron for 10s. What is the current? Answer: Q=It, I= Q/t = 200/10 = 20A Moving charges worksheet Have a go at the worksheet on charges and Q=It. Current If Q = It, how could we INCREASE or DECREASE the current in a circuit? Hint: Try rearranging the equation to make current the subject of the equation..... Answer... Q=It so I=Q/t. This means that the current increases if: 1. You INCREASE the charge, or 2. You decrease the time. (Thinking back to our moving round the room analogy – if you ran, you would pass the front more times, if you walked around a smaller room, you would too.) Exam question Have a go at the exam question on charge and current. Once you are done, write a question for the person next to you. Just a minute With the person next to you, you are going to play a game of just a minute... Rules: ◦ First person talks for a minute about current and charge without: ◦ ◦ 1. Repetition – repeating yourself 2. Hesitation – saying ‘erm’ or long gaps 3. Deviation – talking about something unrelated If you do any of this, and the other person buzzes you, the other person has the remaining time to talk about it. The person who is talking at the minute mark wins!