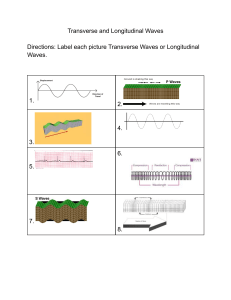
Waves Introduction • What Waves Are • Types of Waves • Transverse vs. Longitudinal Waves • Frequency, Hertz, Period • Amplitude • Crests, Troughs, and Wavelength • Universal Wave Equation How Your Lesson Works ØText that is bolded and underlined is blank on your student copy. When you see it, pause the video and copy it into your notes. ØWhenever a video is available, you will see the video icon and a number. Refer to your Additional Resource document to find the correct video link. While you’re watching the video, take a few jot notes on the main ideas that are covered. Waves • Waves are disturbances which transfer energy over a distance • They all originate from vibrations • i.e. dropping a pebble into water • Examples: • Water waves • Waves in a string • Earthquake waves Waves • The vibrating source supplies energy which is transported along the medium as a wave • This vibration can be caused by many things from moving a string, rubbing objects together or having an object impact the ground or water • i.e. seismic waves are waves of energy created by earthquakes which travel through the earth and are caused by tectonic plates moving against each other Waves • Waves pass their energy from one particle to another until it runs out of energy • Example: Water waves created from tectonic activity, volcanic eruptions, winds, impacts, etc. carry a lot of energy which can be used to inflict serious damage 1 2 Waves We will be discussing two main types of waves 1) Transverse Waves 2) Longitudinal Waves Transverse Waves The particles vibrate perpendicular to the direction of motion Longitudinal Waves The source vibrates parallel to the direction of motion Transverse vs. Longitudinal Waves 3 Terminology Regarding any kind of vibrating object: • One complete oscillation is called a cycle • The number of cycles per second is the frequency (f) • The unit for frequency is the hertz (Hz) • The time required for one full cycle is the period (T) • The unit is usually the second but can be days, months, years, etc. One complete cycle Frequency and Period They are reciprocals of each other therefore, 1 𝑓= 𝑇 1 𝑇= 𝑓 Amplitude The distance from rest position to maximum displacement is the amplitude Amplitude Check Your Understanding A mass hung from a spring vibrates 15 times in 12 s. Calculate a) the frequency. b) the period of the vibration. Check Your Understanding A mass hung from a spring vibrates 15 times in 12 s. Calculate a) the frequency. b) the period of the vibration. Answer: a) f = 1.3 Hz b) T = 0.80 s Check Your Understanding The amplitude of a child swinging on a swing is 1.2 m. What total distance does she travel after 3 complete cycles? Check Your Understanding The amplitude of a child swinging on a swing is 1.2 m. What total distance does she travel after 3 complete cycles? Answer: 14.4 m A Few More Terms • Crests - High section of the wave • Troughs - Low section of the wave • Wavelength (in m) Distance from crest to crest or from trough to trough Universal Wave Equation • Recall: • Regarding waves, the distance travelled is the wavelength (𝜆 in m) and the time is the period (T) which is the time to complete a wavelength in s therefore, • The wave equation works for all waves, visible and invisible Check Your Understanding The wavelength of a water wave in a ripple tank is 0.080 m. If the frequency of the wave is 2.5 Hz, what is its speed? Check Your Understanding The wavelength of a water wave in a ripple tank is 0.080 m. If the frequency of the wave is 2.5 Hz, what is its speed? Answer: 0.20 m/s Check Your Understanding The distance between successive crests in a series of water waves is 4.0 m and the crests travel 9.0 m in 4.5 s. What is the frequency of the waves? Check Your Understanding The distance between successive crests in a series of water waves is 4.0 m and the crests travel 9.0 m in 4.5 s. What is the frequency of the waves? Answer: 0.50 Hz Check Your Understanding The period of a sound wave from a piano is 1.18 × 10–3 s. If the speed of the wave in the air is 3.4 × 102 m/s, what is its wavelength? Check Your Understanding The period of a sound wave from a piano is 1.18 × 10–3 s. If the speed of the wave in the air is 3.4 × 102 m/s, what is its wavelength? Answer: 0.40 m