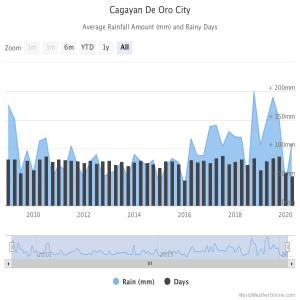
Writer: Pairat Group Members: Amora, Ecuacion, Ladao, Olape, Tampos Section: 11-Santos Score: Balancing Education: The Case for Banning Homework in Schools A Position Paper I. Introduction A. The debate on whether schools should ban homework has ignited discussions among educators, parents, and students. It is a topic that demands careful consideration and examination of its potential impacts on students' well-being and academic development. B. With changing educational landscapes and increasing concerns about student well-being, there is a need to critically examine the practice of assigning homework and its potential impacts on students. C. Thesis: In this position paper, we argue that schools should ban homework. By exploring the potential drawbacks of homework and considering its impact on students' well-being and learning experience, we will provide compelling evidence for the adoption of alternative approaches that promote a healthier, more balanced approach to education. II. Counter Argument A. Counterclaims: Opponents argue against banning homework, emphasizing its importance in reinforcing learning, fostering discipline, and preparing students for the future. They believe eliminating homework would hinder academic growth and independent study opportunities. B. Supporting Information: Supporters of homework argue that it plays a crucial role in reinforcing classroom learning. Homework provides students with an opportunity to review, practice, and solidify their understanding of the material. Engaging in independent study outside of the classroom further enhances their knowledge and academic performance. Homework fosters discipline, responsibility, and effective time management skills in students, preparing them for the demands of higher education and future careers. It equips them with the necessary skills and habits for success in autonomous learning environments. Additionally, homework encourages critical thinking, problem-solving, and creativity, skills that extend beyond academia and are essential for various professional fields. Proponents believe that homework serves as a valuable tool in reinforcing learning, fostering discipline, and preparing students for their educational and professional journeys. C. Refutation: However, it is important to recognize that excessive homework can lead to stress, exhaustion, and a negative impact on students' well-being. Assigning too much homework can also limit time for extracurricular activities, family interactions, and rest, which are crucial for a balanced and holistic development. D. Evidence: Multiple research studies, such as the meta-analysis conducted by Cooper, Robinson, and Patall (2006), have found a positive correlation between homework completion and academic performance. Furthermore, a study by Trautwein and Koller (2003) revealed that regular engagement in homework tasks enhances students' self-regulation skills, including time management and goal setting. Real-world examples of successful individuals also highlight the role of homework in developing perseverance, critical thinking, and problem-solving abilities. Additionally, countries with higher homework loads, like Finland and South Korea, consistently rank among the top performers in international assessments, providing further support for the argument that homework contributes to academic excellence. In conclusion, this evidence underscores the value of homework in enhancing academic achievement, fostering self-regulation, and cultivating essential skills for success. III. Our Argument A. Point #1: Reduces Stress and Mental Health Issues 1. Opinion: We firmly believe that homework causes excessive stress and it tends to have an effect on the students’ well-being. 2. Support: The pressure to complete multiple assignments within tight deadlines can lead to anxiety, sleep deprivation, and a decline in mental health. Additionally, chronic stress can lead to burnout, reduced motivation, and a negative attitude towards learning. By banning homework, schools can alleviate this unnecessary stress and promote a healthier learning environment that prioritizes student well-being and holistic development. B. Point #2: Promotes Student Independence and Accountability 1. Opinion: Encouraging student autonomy and responsibility is crucial for fostering independent learning and preparing students for future success. 2. Support: By getting rid of homework and using teaching methods that focus on student-centered approaches like projects and inquiry-based learning, students have the chance to take control of their education. They learn to set goals, manage their time well, and make choices about what they want to learn. This helps them develop self-discipline, learn to be accountable for their actions, and gain important skills for their future education and careers. When students are encouraged to be independent and responsible for their learning, they become active learners who can take charge of their education. C. Point #3: Encourages a Positive Work-Life Balance 1. Opinion: Banning homework allows students to have a healthier work-life balance. 2. Support: Excessive homework assignments can consume a significant amount of students' time outside of school, leaving them with little opportunity for relaxation, pursuing personal interests, or spending quality time with family and friends. By eliminating homework, schools can prioritize the overall well-being of students and ensure they have ample time for self-care, extracurricular activities, and fostering important relationships. This promotes a healthier work-life balance, which is crucial for students' mental and emotional well-being, as well as their overall development. IV. Conclusion A. Restate the argument: Eliminating homework helps students maintain a healthier work-life balance and minimizes stress and mental health problems while also fostering student autonomy and responsibility. B. Plan of action: By examining the negative impact of homework on work-life balance, stress levels, and mental health, it becomes evident that eliminating homework is a viable solution to promote a healthier and more balanced educational experience. Additionally, the argument for banning homework highlights the potential for fostering student autonomy, responsibility, and creativity through alternative approaches that prioritize meaningful learning experiences. By embracing this change, schools can create an environment that supports students' overall well-being, enhances their learning outcomes, and prepares them for a future that values a holistic and balanced approach to education. Writer: Ecuacion Groupmates: Amora, Ladao, Olape, Pairat, Tampos Section: 11 - SANTOS Score: Brave New World By Aldous Huxley A Book Review “Brave New World” by Aldous Huxley is a story about the future of mankind, 600 years into the future. Aldous Huxley was an English writer and philosopher, novelist, born July 26, 1894. His works were notable for their wit and satire on society. Although this story may be set 600 years into the future, the future Aldous Huxley imagined reveals the horrors of how the things we admire most in our society can destroy the very society we live in if we are not careful. This story tells us to be cautious when we pursue the things we value in our society, as we may lose our very humanity in the process . The book mainly follows Benard Marx, Helmholtz Watson, and John the Savage as they navigate the society of the World State, 600 years after the creation of the Model T Automobile. They explore a world where, in the pursuit of progress, science, and efficiency, the world has totally transformed, and turned to crush individualism, love, poetry, and what it means to be human. By the end of the story, in retribution for their defiance of the societal norms of their world, Bernard and Helmholtz are exiled to the Falkland Islands, and John is used for research, where he ultimately escapes and kills himself. The society of Brave New World has sought progress and science above all else, and in doing so crushed the very essence of humanity. In the perfectly engineered society of the World State, everything about the way a person goes through life has been engineered. From their very genetic makeup, the way they were born, all the way to the occupation. This seemingly utopian world was built upon the erasure of our very individuality. In the story, the World State keeps the world compliant with its control through the use of "soma", a drug that keeps the user in a blissful state of mind, unable to feel pain, and only being able to feel pleasure. In pursuit of order and perfection, people take in drugs that suppress how they truly feel for the sake of societal stability. Generally, the book asks us "what should society value more? Happiness, or freedom?". We can see in the story that the people who live within the setting are indeed, very happy. Everybody is contented with the engineered lives they live, nobody experiences pain through soma, nobody suffers from disease, nobody fears old age, and nobody starves. Seemingly a perfect world. But this setting also has no room for intimate love, as it would produce more happiness if everybody were promiscuous. There are also no mothers, or fathers, as the structure of the family unit can cause societal instability. There is no poetry, no art, as the pleasure that would be given by these works of art is easily accessible through "soma". In the pursuit of happiness and progress, we have lost our humanity. But, in a utilitarian sense, the setting of "Brave New World" is a legitimate paradise. No hunger, no disease, no pain. Everybody lives in harmony with each other, and everybody, no matter their social status within their caste system, is wholeheartedly content with the way everything is. The book asks us "is this world desirable? And if so, was the means to get there justifiable?". Brave New World is often compared to another dystopian novel of its age, namely George Orwell’s 1984. Both books have become almost synonymous with dystopian literature, but each book goes around it differently. 1984, the more well known of the two, presents a dystopia wherein an external, oppressive force enslaves humanity. The sheer control of Big Brother in the story is almost akin to reality-bending, where if the party so chooses to, people can be erased, events forgotten, and history rewritten. Brave New World, on the other hand, presents a world where humanity has become enslaved by what it loves. The pursuit of happiness and progress resulted in a world where individualism no longer exists, where everybody is too busy chasing pleasure and drugs to be able to even think of what was or what will be.Where the pursuit of love is replaced by the thrill of constant sex. Basically, the world of Brave New World can be thought of as the “Pleasure Cube” made real. Brave New World and 1984 both portray dystopian worlds, 1984 shows us a dystopia caused by things we fear, and Brave New World shows us a dystopia caused by things we love. In summary, Brave New World cautions us about the consequences of our endless pursuit of progress, tells a tale of how we may lose our humanity if we become careless. It asks us if a world full of comfort, pleasure, and happiness, but devoid of the challenge, creativity, love, and pain that comes with being human is really worth it. The book itself doesn’t give us an answer to this question, leaving the reader to ponder and reevaluate what they value most in society. Brave New World is recommended for those who enjoy books that criticize the way modern society is structured, and as well for those who would like to explore the merits of utilitarian philosophy at its very extremes. To the everyday person, who can benefit through the questioning of the value of comfort and changing their lives. Writer: Ladao Group Members: Amora, Ecuacion, Olape, Pairat, Tampos Section: 11-Santos Score: Chapter 2 Literature Review This chapter contains the review of related literature relevant to the study. The literature and studies introduced and discussed within this chapter covers the concepts, generalizations, background, and findings that can be utilized as the foundation guiding the study’s development. Arrowhead plant (Syngonium Podophyllum) The arrowhead plant is a native or an ornamental aquatic house plant identified as an evergreen climbing vine that usually grows around 3-6 feet long. Its juvenile leaves are notably heart-like in shape with silver coloration (Balasubramanian, 2023). In terms of distribution, it is a plant first native to Central and parts of South America. Then, was introduced to Pacific countries such as Borneo, Singapore, and Malaysia. (Syngonium Podophyllum Schott | Plants of the World Online | Kew Science, 2023). Although recently, it has been introduced to the Philippines. They can be found in tropical forests, thriving in damp, fertile soils, and are also known to grow in sandy and loam soils under shady (Global Invasive Species Database, 2023). In terms of plant care, the arrowhead plant can survive or cope in temperatures of at least 60-85 ºF (15-29 ºC), and although it may sufficiently manage the temperature of 50 ºF (10 ºC), any temperature below will kill the plant (Arrowhead Plant - Syngonium Podophyllum, 2013). Within Cagayan De Oro City, its high temperatures range around 83-87 ºF, while its low temperatures range around 65-68 ºF (Climate and average monthly weather in Cagayan de Oro (Mindanao), Philippines, 2023). The temperatures of the city are within the required range for the plant to grow. This plant is capable of withstanding Philippine temperatures, especially in the summer. Syngonium Podophyllum is identified as an air purifier by means of having macrophytes as Syngonium Podophyllum is also identified as an aquatic plant. The most diverse group having macrophytes are aquatic plants (Kumar et al., 2022). Syngonium Podophyllum can also act as an anti-pollutant that cleanses the air. It reduces the presence of air pollutants and it also increases humidity. Moreover, Syngonium Podophyllum was approved to be as an air purifier that tops in the list of plant purifiers by Researchers from NASA (#1 the Syngonium, 2016). The surface area of the Syngonium Podophyllum increases with reducing the air pollutants as the absorption of air pollutant components increases. Most aquatic plants are commonly used in indoor places to remove the said air pollutant components that are present in the air (International Journal of Petrochemistry & Natural Gas, 2022). On the lists of ornamental plants, Syngonium Podophyllum is said to be top on the list as an air purifier (#1 the Syngonium, 2016). Furthermore, in an article by Mung et al (2006), Syngonium Podophyllum was reported with other ornamental plants that after it was tested for the absorption of air pollutants indoors, it was found and confirmed that Syngonium Podophyllum has the ability to absorb gasses by purifying the air (International Journal of Petrochemistry & Natural Gas, 2022). Aquatic plants are identified as macrophytes that grow in water or near in water (United States Environmental Protection Agency, 2022). Aquatic plants have natural-based solutions to provide the treatment of polluted waters by the ability of macrophytes that is naturally present in aquatic plants (Fletcher, 2020). Phytoremediation Phytoremediation of air is a process where airborne pollutants such as particulate matter (PM) and volatile organic compounds (VOCs) are absorbed by plants and filtered out, resulting in purifying the surrounding air. It usually involves a mechanism called phytovolatilization, where both inorganic and organic contaminants absorbed by plants are broken down and dispersed into the atmosphere through the plant’s stomata. The contaminants can remain as air pollutants, albeit less toxic than before, due to the degradation by hydroxyl radicals (Lee et al., 2021). The airborne pollutants namely, PM and VOC, are still prevalent in most establishments in the present, as they are byproducts of everyday items used by people as they go through their different lifestyles. Particulate matter (PM) refers to any type of solid or liquid particles uniformly distributed in the aerosol system (Wei et al., 2021). Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs) are chemicals that readily evaporate at room temperature, and their concentrations are higher than other pollutants in indoor air. Some of its sources are Aerosols, cleaning agents, polishes, varnishes, paints, pressed-wood products, and pesticides (Bandehali et al., 2021). It is commonly known that part of the process of photosynthesis shows how plants absorb carbon dioxide to create oxygen and promote the breakdown of VOCs by interacting with microorganisms in the rhizosphere and absorbing atmospheric particles through leaf adsorption (Wei et al., 2021). But, photosynthesis only focuses on converting Carbon Dioxide (CO₂), and does not include other gaseous substances. Whereas, phytoremediation in air is the most suitable model for enhancing air quality and reducing air pollutants in terms of costeffectiveness, due to its non-invasiveness and sustainability. The process already existing before the engineered air remediation technologies were developed also adds a reason why it is a much cheaper method. Additionally, plants decrease the mobility, harmfulness, and volume of the contaminants through various processes, such as accumulation, immobilization, volatilization, and degradation. In this way, phytoremediation is seen as a complementary technology for air purifiers (Lee et al., 2021). Although, some conditions may affect the factors of the purification in plants, namely light intensity, stomatal conductance, temperature, and microbial species, throughout the process of remediating air. Furthermore, the efficiency of phytoremediation depends on the species of the plant and its specific metabolism, it includes air absorption and photosynthesis, soil microbial diversity, and heavy metal uptake (Wei et al., 2021). Population Density Population density is defined as the total mean of the population of land per square kilometer. It is taken by dividing the population of the area by the total land area in square kilometers (Internet Geography, 2022, May 12). This is how we determine if a population is high or low in density, but of course, it is relative to the size of the land area and the population and may vary in interpretation. In the context of Cagayan De Oro City, according to the reports of the Philippine Statistics Authority (2020), Cagayan ranks 9th out of 17 cities outside of the National Capital Region, with a total population of 728, 402; a land square area of 412.80 square kilometers; and a population density of 1,675 persons per square kilometer of land. It is one of the more densely populated cities outside NCR, thus being a more urbanized city and highly dense in population. The arrowhead plant is a native or an ornamental aquatic house plant identified as an evergreen climbing vine that usually grows around 3-6 feet long. Its juvenile leaves are notably heart-like in shape with silver coloration (Balasubramanian, 2023). Within Cagayan De Oro City, its high temperatures range around 83-87 ºF, while its low temperatures range around 65-68 ºF (Climate and average monthly weather in Cagayan de Oro (Mindanao), Philippines, 2023). The temperatures of the city are within the required range for the plant to grow. This plant is capable of withstanding Philippine temperatures, especially in the summer. Syngonium Podophyllum is identified as an air purifier by means of having macrophytes as Syngonium Podophyllum is also identified as an aquatic plant. The most diverse group having macrophytes are aquatic plants (Kumar et al., 2022). Phytoremediation of air is a process where airborne pollutants such as particulate matter (PM) and volatile organic compounds (VOCs) are absorbed by plants and filtered out, resulting in purifying the surrounding air. It usually involves a mechanism called phytovolatilization, where both inorganic and organic contaminants absorbed by plants are broken down and dispersed into the atmosphere through the plant’s stomata. The contaminants can remain as air pollutants, albeit less toxic than before, due to the degradation by hydroxyl radicals (Lee et al., 2021). In the context of Cagayan De Oro City, according to the reports of the Philippine Statistics Authority (2020), Cagayan ranks 9th out of 17 cities outside of the National Capital Region, with a total population of 728, 402; a land square area of 412.80 square kilometers; and a population density of 1,675 persons per square kilometer of land.