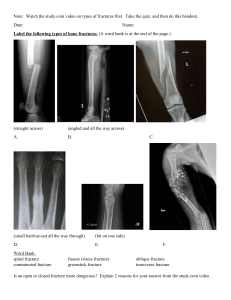
Patho Exam 2: UE Dysfunction Study online at https://quizlet.com/_bdxgfp 1. - pain S/Sx's associated with UE dysfunction - edema - decreased ROM - inflammation - mm guarding/weakness - decreased endurance 2. Impairments associ- The following lists examples of what? ated with UE dysfunc- - joint immobilization from inactivity tion - prolonged mm weakness/paralysis - inability to perform self care, ADL's, & access the community - worker's cant perform functional activities 3. - a dependent extrem- What are 3 specific issues associated with UE dysity function - hangs to gravity - potential for subluxation 4. subacromial impinge- also referred to as rotator cuff tendinopathy; refers to ment syndrome (SIS) pain and weakness experienced with movements of shoulder external rotation and elevation. 5. Primary: supraspina- What two conditions lead to subacromial impingetus tendon compres- ment syndrome SIS sion/decreased subacromial space Secondary: GH instability/tensile overload of Rcuff resulting in poor control of humeral head. 6. Scapular Dyskinesis an alteration in the normal position or motion of the scapula during scapulohumeral movements. scapular winging 1/8 Patho Exam 2: UE Dysfunction Study online at https://quizlet.com/_bdxgfp - Poor muscle use/recruitment strategies - Poor biomechanics 7. depth of tendon tear Rotator Cuff tears are defined by what factor? 8. Acromioplasty procedure that relieves pain associated with friction of the acromion 9. Subacromial Decom- procedure used to remove the cause of the impingepression Surgery ment of the humeral head and undersurface of the (SAD) acromion, thereby allowing freer movement. 10. Traditional open RC repair surgery technique that involves a vertical incision over the anterior shoulder, deltoid is split, and an anterior and inferior acromioplasty is performed 11. Neer's Impingement Test Test - patient is seated. clincian stabilizes scapula with one hand and forces the patients arm into maximal elevation with other hand. positive RC tear if pain is produced. 12. Glenohumeral Insta- abnormal symptomatic motion of the GH joint that bility affects normal joint kinematics and results in pain, subluxation, or dislocation of the shoulder 13. Anterior GH Instabili- most common instability of the GH joint and occurs ty when the patient has pain with overhead movements; present pain in positions of abduction and external rotation. 14. Bankart Lesion an avulsion of the capsule and GH labrum with anterior dislocation 15. T T or F: Shoulder dislocations can become recurrent 16. 2:1 ratio What is the ratio for scapulohumeral motion? A. 3:1 B. 2:1 17. 1 degree 2/8 Patho Exam 2: UE Dysfunction Study online at https://quizlet.com/_bdxgfp For every 2 degrees of GH flexion or abduction, after the first 30 degrees of shoulder motion, the scapula must rotate upward _ ___. 18. Adhesive Capsulitis also known as "frozen shoulder," condition that causes decreased shoulder ROM, pain, inflammation, fibrous synovial adhesions and reduction of the joint cavity. Can effect the shoulder, cervical and scapulothoracic mm's. (Primary or Secondary) 19. Acromio-Clavicular Sprain sprain commonly seen in the athletic population; can be acute traumatic or chronic and classified into 6 types. Types 1&2 involve ligament sprains and Types 3-6 involve ligament tears, and dislocations. 20. Scapular Fractures Rare and due to blunt force trauma 21. Clavicle Fractures Fracture that results from a FOOSH injury or less commonly a direct blow. patients have difficulty elevating their arm above 60 degrees. treatment involves acquiring and maintaining a reduction & managing immobilization. AROM and PROM exercises for the shoulder is initiated 1 week after sling fitting. 22. Proximal Humeral Fracture the most common fracture of the upper arm and typically results from a FOOSH injury. Classified as displaced or non-displaced. causes swelling and redness. depending on severity of fracture, could require ORIF. 23. Total Shoulder Arthroplasty the humeral head and glenoid capsule are replaced with artificial components to restore function and relieve pain. indicated for patients with bone tumors, PA, OA, fracture dislocations, paget's disease, and avascular necrosis of the humeral head. 24. Unconstrained TSA involves a shallow glenoid component with a stemmed humeral component; provides the greatest shoulder freedom but little stability; most widely used 3/8 Patho Exam 2: UE Dysfunction Study online at https://quizlet.com/_bdxgfp 25. Reverse TSA consists of a concave humeral socket that slides on a glenoid component that is a baseplate with a glenosphere; creates a mechanical advantage for deltoid muscles to compensate for lacking RC muscle. 26. Supraspinatus Tendonitis Inflammation of the supraspinatus tendon and surrounding rotator cuff tissues. 27. Bicipital Tenosynovi- inflammation of the biceps tendon and its surrounding tis tendon sheath just below its attachment on the front part of the scapula (shoulder blade). 28. Erb's Palsy a paralysis of the arm that most often occurs as an infant's head and neck are pulled toward the side at the same time as the shoulders pass through the birth canal 29. Ruptured Biceps Brachii also known as "Popeye arm"; commonly occurs when there is an unexpected force applied to the bicep muscle. effects elbow flexion and supination. 30. Lateral Epicondylitis "Tennis Elbow" inflammation of the lateral epicondyle of the elbow - Repetitive overuse of forearm extensors. specifically effects mm's involved in wrist extension & radial deviation. 31. Medial Epicondylitis 4/8 Patho Exam 2: UE Dysfunction Study online at https://quizlet.com/_bdxgfp "Golfer's Elbow" inflammation of medial epicondyle of the elbow - Repetitive overuse of forearm flexors. specifically effects flexor carpi-radialis & pronator teres. 32. Medial Valgus Stress ligament sprain of the medial (ulnar) collateral ligaOverload ments; insufficiency of valgus and external rotation forces as seen in tennis serves and baseball pitching; causes inflammation and pain over the medial elbow and possible irritation of the ulnar nerve. 33. Olecranon Bursitis presents as a swelling over the olecranon process easily bruised through direct trauma or irritated through repetitive grazing and weight bearing. patients often note decreased ROM in elbow and inability to wear long sleeves 34. - distal humerus - supracondylar What are the 2 types of elbow fractures? 35. Supracondylar Frac- fractures caused by direct trauma to the arm or shoulture der, OR by axial loading through the elbow. fracture pattern is produced related to the degree of elbow flexion and the direction and magnitude of force applied; surgery indicated to restore anatomy and prevent further injury 36. distal humerus frac- (intercondylar fracture) one of the most difficult of ture all fractures to manage; typically occurring following high-energy injury and can lead to significant functional impairment. treatment ranges from no treatment to extensive ORIF. 5/8 Patho Exam 2: UE Dysfunction Study online at https://quizlet.com/_bdxgfp 37. Volkmann's ischemic a permanent shortening (contracture) of forearm contracture muscles, usually resulting from injury, that gives rise to a claw-like deformity of the hand, fingers, and wrist. 38. Radial Head Fracture/Dislocations injuries typically resulting from trauma (FOOSH) with force of impact transmitted up the hand, through the wrist and forearm to the radial head. must be treated adequately to prevent disability from stiffness, deformity, post-traumatic arthritis and nerve damage. 39. Olecrannon Fracture fracture that can be a high or low energy injury; usually a fall backward onto the elbow or a FOOSH. 40. Elbow Dislocation ulna is displaced anteriorly or posteriorly in relation to the distal humerus. 41. colles fracture fracture of the distal radius at the wrist with posterior displacement of the distal fragment; typically caused by a FOOSH; treated with a closed reduction and cast in most cases. 6/8 Patho Exam 2: UE Dysfunction Study online at https://quizlet.com/_bdxgfp 42. smiths fracture a complete fracture of the distal radius with palmer displacement of the distal fragment; typically caused by a fall on the back of a flexed hand. classified into 3 types: Type 1: transverse fracture through the distal radius Type 2: oblique fracture through distal shaft Type 3: oblique fracture beginning farther down articulating surface of radius 43. scaphoid fracture what is the most common and commonly missed fracture of the carpal bones? if diagnosis is delayed it can result in significant long term pain, loss of mobility and decreased function 44. Metacarpal Fracture (Boxer's Fracture) fracture to the metacarpal bone (4th/5th metacarpals), striking an object; localized tenderness/swelling, Loss of knuckle prominence 45. Finger Fractures the most common fractures of the hand & wrist divided into base, shaft, neck, and head fractures. sometimes require surgical intervention or external fixation 46. Ulnar Collateral Ligament Sprain of the Thumb also known as gamekeepers thumb, skiers thumb, and breakdancer's thumb. involves injury to the UCL of the MCP joint of the thumb and is the most common injury of the hand. Most common cause is an acute abducting force on the thumb. 47. De Quervain Disease a repetitive motion injury that is characterized by tenosynovitis (inflammation of the tendon sheath) of the thumb side of the wrist; chronic inflammation, pain and loss of function in the wrist/thumb 48. Dupuytren Contracture progressive thickening and contracture of palmar fascia that leads to loss of extension and ABduction of 7/8 Patho Exam 2: UE Dysfunction Study online at https://quizlet.com/_bdxgfp digits. can be corrected by surgical release of tissue (cutting palmar fascia) 49. Carpel Tunnel Syndrome Caused by pressure on the wrist of the median nerve. loss of blood supply and grip strength; S/sx: decreased sensation, pain, tingling, motor problems; loss of thenar intrinsic mm's and 1 & 2 lumbricals. Etiology: OA, RA, fractures, cysts, diabetes, hypothyroidism, aging, pregnancy, overuse, vibration, & cumulative trauma 50. Complex Regional Pain Syndrome (CRPS) Aka "Reflex Sympathetic Dystrophy" an syndrome occurring after tissue damage with or without obvious nerve lesion; can result in visceral disease, CNS lesions without obvious cause, etiology unknown. 51. S/Sx's of CRPS - pain in injured extremity to light touch, air, clothing - trophic changes (shiny skin, tight skin, hair & nail growth) - Autonomic disturbances (abnormally warm or cold; pale, blue, pink, red) - functional impairment (loss of use of entire extremity) 8/8