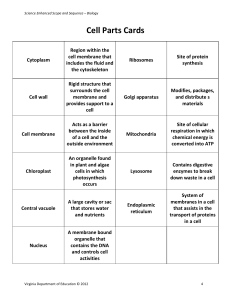
Sally and Khivaan Organelle + Description Function Cell Membrane ● Lipids and protein ● Phospholipid bilayer constantly in motion diameter of around 10 nm ● Found on the surface of animal cells and just inside the cell wall of other cells ● Partially permeable Controls the exchange of materials between the internal cell environment and the external environment. Cell Wall ● Rigid structure that surrounds cells in plants, algae and fungi. ● Formed outside of the cell membrane ● Freely permeable to most substances ● In plant and algae cells: made mainly of carbohydrate cellulose ● In fungi: chitin Offer structural support for cell. Nucleus ● Contains chromatin (a complex of DNA and histone proteins) which is the genetic material of the cell ● Present in all eukaryotic cells ● Largest organelle ● Separated from the cytoplasm by a double Controls cell activity through transcription of DNA, which contain instructions to make protein. Receptor molecules on the membrane allow it to respond to chemicals like hormones. Structural support is provided by the polysaccharide cellulose in plants, and peptidoglycan in most bacterial cells. Illustration ● membrane (the nuclear envelope) Contains chromosomes made from protein-bound linear DNA and one or more structures called nucleolus Nucleolus ● Darkly stained regions Produces ribosomes. Nuclear Envelope ● Has many nuclear pores Has channels for allowing mRNA and ribosomes to travel out of the nucleus, as well as allowing enzymes (eg. DNA polymerases) and signalling molecules to travel in. Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum ● A system of membranes that enclose a fluid-filled space ● Surface covered with ribosomes ● Formed from continuous folds of membrane continuous with the nuclear envelope RER folds and processes the proteins that have been produced at the ribosomes. Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum ● A system of membranes that enclose a fluid-filled space ● No ribosomes SER synthesises, processes and stores lipids, carbohydrates and steroids. Vacuole ● Bound by membrane called tonoplast which is selectively permeable ● Usually large ● Permanent organelle ● Found in the cytoplasm of plant cells ● Vacuoles in animal cells are temporary and small ● Contain a weak solution of sugars and salts called cell sap Help to maintain pressure inside the cell and keep it rigid. Involved in isolating unwanted chemicals in the cell. Golgi Body (Golgi Apparatus or Golgi Complex) ● A series of fluid filled, flattened membrane sacs ● Membrane sacs similar to the smooth endoplasmic reticulum Processes and packages new lipids and proteins. Modifies proteins and packages them into vesicles or lysosomes. Mitochondria (including the presence of small circular DNA) ● Oval/Rod-shaped organelle ● Has a double membrane ● Inner membrane is folded to form cristae ● Exists in eukaryotic cells ● Found in large numbers in very active cells and require a lot of energy Mitochondria are the site of aerobic respiration where ATP is produced. Ribosomes ● Smallest and most numerous of the cell organelles ● Either float free in the cytoplasm of all cells or are attached to the rough endoplasmic reticulum in eukaryotic cells ● Composed of almost equal amounts of RNA and protein ● Not surrounded by a membrane ● Formed in the nucleolus ● The ‘s’ stands for svedburgs - unit for measuring how fast molecules move in a centrifuge Site of translation (protein synthesis proteins are made) Inside is the matrix, which contains enzymes involved in respiration Small circular pieces of DNA (mitochondrial DNA) and ribosomes are also found in the matrix (needed for replication). Ribosomes 80s - large, denser - found in eukaryotic cells - Settles first Ribosomes 70s - smaller - found in prokaryotes and in mitochondria and chloroplasts of eukaryotes. Lysosomes ● Small, round organelles ● Surrounded by a membrane ● No clear internal structure ● Type of Golgi vesicle ● Contain the digestive enzymes lysozymes (hydrolytic enzymes). ● Rarely found in plant cells The enzymes are kept separate from the cytoplasm by the membrane and can be used to digest invading cells or break down worn out cell components. Centrioles ● Centrioles hollow cylinder about 500 nm long ● Formed from a ring of short microtubules ● Paired structures that lie just outside the nucleus of nearly all animal cells and some lower plants ● Two centrioles at right angles to each other form a centrosome ● Each centriole contains nine triplets of microtubules ● Not found in flowering plants and fungi Their function in most cells still isn’t known but they do act as microtubule-organizi ng centre (MTOC) in the flagella and cilia of bacteria. Break down waste materials such as worn-out organelles, used extensively by cells of the immune system and in apoptosis (programmed cell death). Microtubules ● Make up part of the cell cytoskeleton ● About 25 nm in diameter ● Made of α and β tubulin combined to form dimers, the dimers are then joined into protofilaments (thirteen protofilaments in a cylinder make a microtubule) Involved with the movement of vesicles and some organelles. Cilia ● Allows the movement of substances over the cell surface. Hair-like projections made from microtubules Spindle fibres which pull part chromosomes during cell division are microtubules. The cytoskeleton is used to provide support and movement of the cell. Microvilli ● Cell membrane projections Increases the surface area for absorption. Chloroplasts (including the presence of small circular DNA) ● Found in green parts of a plant ● Small, flattened structure ● Surrounded by a double membrane ● Membrane-bound compartments called thylakoids containing chlorophyll stack to form structures called grana ● Grana are linked together by lamellae - thin, flat pieces of thylakoid membrane ● Larger than mitochondria Chloroplasts are the site of photosynthesis: - The light-depend ent stage takes place in the thylakoids. - The light-indepen dent stage (Calvin Cycle) takes place in the stroma thick liquid found in chloroplasts. Also contain small circular pieces of DNA and ribosomes used to synthesise proteins needed in chloroplast replication and photosynthesis. Plasmodesmata ● Microscopic channels in plant and some algal cell walls Allow the rapid diffusion of materials between cells.