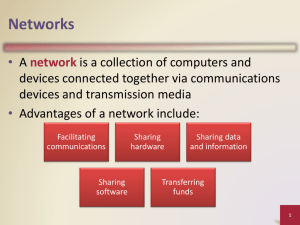
Module 1 – 5a Networked Systems Networked Systems: group of interconnected (via cable and/or wireless) computers and peripherals that are capable of sharing software and hardware resources between many users - Enables multiple users to share devices/data which saves time/money Basic Network Components Client - Computer or device on network that request resources or services from another computers/devices within network Host - Any computer or device on network that enables resources sharing Network Devices - Devices used to connect computers or other electronic devices together for sharing of files and resources Node - Any device connected to network other than networking cabling which has a unique address and capable of sending or receiving data o Ex. Printer Servers - Powerful computers that provide specific resources or services to other computers (clients) Transmission Media - Various channels through which data is transmitted and received Client Server Architecture Network architecture where each computer is configured either as a client or a sever Advantages - Easier organization/management of resources to include data updates and editing along with creating backups Monitoring access rights as well as defining rules for security which is meant to prevent any illegal/unauthorized access Disadvantages - More expensive in setup and maintenance due to specialized sever equipment and software Module 1 – 5a Networked Systems - When clients are added it increases the workload placed on the server; reduces network speed Should the server fail, the network could collapse. Clients need a server to function. A crash can loss all server data Server Types Application Server - Designed to run specific applications DHCP Server - Assigns each computer an IP address from a list of available addresses. Logs and tracks IP and network connections Domain Name System (DMS) Sever - Provides a translation of domain names into IP addresses Mail Server - Emails; transfers and stores mail over corporate networks thru LANS Proxy Server - Mediator between client and server Filtering device Virtual Servers - Data center shared by multiple web site owners Web Server - Provides content to a web browser by loading a file from a disk Types and Structure - Network comprised of computers connected for purpose of sharing resources Ability to share information over dissimilar networks known as internetworking Local Area Network (LAN) - Grouping computers and other devices a in single physical location Metropolitan Area Network (MAN) - Network physically covering an area larger than a Lan yet smaller than a WAN Wide Area Network Module 1 – 5a Networked Systems - Network covering a larger geographical area networks (LAN, MAN,WAN) together Global Area Network (GAN) Personal Area Network (PAN) Wireless Local Area Network (WLAN): - Lan without wires Network Topologies - the physical structure of a network, Stat topology Tress Hierarchical Topology - central node connecting multiple nodes to one another Mesh Topology Hybrid Topology Transmission Media - channel between Transmission Media Category Bounded Unbounded Twisted-Pair Cable Unshielded Shielded Fiber-Optic Cable Single Mode Fiber Multi-mode Finer Wireless Module 1 – 5a Networked Systems Factors selecting transmission media Distance Frequency (Bandwidth) Interface Cost Network Devices Network Interface Car (NIC) - card that allows computer to become a network node Switches - determines the proper path for traffic to take by saving routing info in an internal table limits network connections Bridges - connects 2 or more networks together may connect dissimilar physical topologies as well as wired or wireless Routers - intelligent network node connecting networking of different types intelligent devices maintaining routing table determining best path to destination node Repeaters - devices used to give data the extra extension to reach its destination Gateway - combinations of networking hardware and software connecting dissimilar networks Wireless Remote Access - end user has wireless NIC connecting to an access point (corporate LAN or Internet)