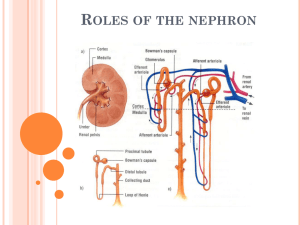
Summary of Urinary System Function and Fluid/Electrolyte Balance Concept Map By: Carol A. Gavareski, MS Bellingham Technical College 3028 Lindbergh Ave Bellingham, WA 98225 360-752-8431; cgavares@btc.ctc.edu Objective: Review processes of urine formation and fluid and electrolyte balance, and show how they inter-relate. Directions to student: You will work in groups of 2-4 students, without using books or notes. Your instructor will be available for input as needed. After you have submitted your concept map for instructor review, you may consult your notes (no textbook) to correct errors and complete the map. Most of the terms and phrases you will need are listed in the following table. You may select from these, or use your own words. Where appropriate, add your own wording to further describe something. Some terms and phrases will be used more than once, and possibly some not at all. Numbers in ( ) following some terms and phrases suggest how many times they may be used. Steps: 1. Fill in the boxes under NEPHRON STRUCTURES with the names of the various nephron parts and urinary structures (see Table- column 1). 2. Fill in the blanks numbered 1-3 with the 3 steps of urine formation. 3. Fill in the blanks under DESCRIPTIONS/FUNCTIONS with the proper substances involved (see Table- column 2) and/or phrases that further describe that structure or explain a process (see table column 3). 4. In the column under REGULATION/HOMEOSTASIS, fill in the proper terms or phrases that describe how that particular process is controlled (see Table- columns 23). 5. When you have finished step 4 above, add the following titles to the various sections you completed in step 4: a. Acid-base balance b. Potassium homeostasis c. Calcium homeostasis d. Maintenance of plasma volume and blood pressure homeostasis e. Osmoregulation © 2007 Carol Gavareski Structures Solutes, fluids, hormones, other substances Descriptions/functions Afferent arteriole Water (4) Glomerular filtration (2) Efferent arteriole Small solutes Tubular reabsorption (2) Glomerulus RBC’s Tubular secretion (2) Bowman’s capsule Protein Return of substances from tubular fluid to blood Distal convoluted tubule Glucose Movement of substances from blood into tubular fluid Proximal convoluted tubule Urea Uses counter-current exchange to establish osmotic gradient in kidney medulla Na+ (2) Glomerular blood pressure (2) Collecting duct K+ (2) Blood plasma osmotic pressure Loop of Henle Ca++ Capsular hydrostatic pressure Peritubular capillaries (2) H+ (3) HCO3- (2) Kidney “self-regulation” of glomerular blood flow to maintain relatively constant GFR Cl- Vasoconstriction of afferent arteriole to reduce GFR ADH (3) (Hypertonic or hypotonic?) blood plasma Aldosterone (3) (Too high or too low?) blood Ca++ PTH (Too high or too low?) blood pressure Venule Renal artery Renal vein Principal cells Intercalated cells Juxtaglomerular cells Renin (Too high or too low?) blood K+ Baroreceptors (intrarenal) Angiotensinogen (Increases or decreases?) K+ secretion Renal pelvis Angiotensin I (Increases or decreases?) Na+ reabsorption Ureter Angiotensin II Water follows Na+ by osmosis (2) Urinary bladder Angiotensin-converting enzyme (Increases or decreases?) Ca++ reabsorption Filtrate (Increases or decreases?) water permeability of collecting duct cells Tubular fluid (Increases or decreases?) water reabsorption by osmosis Urine (Increase or decrease?) blood plasma Ca++ to normal Hypertonic urine (Increase or decrease?) blood plasma K+ to normal Hypotonic urine Restore blood plasma volume Urethra Adrenal cortex (2) Posterior pituitary Parathyroid glands Restore blood plasma acid-base balance; pH = 7.35-7.45 Return blood plasma to isotonic condition © 2007 Carol Gavareski Blood enters kidney by way of _________________ (vessel) NEPHRON STRUCTURES DESCRIPTIONS/ FUNCTIONS Blood enters nephron via __afferent arteriole___ REGULATION/ HOMEOSTASIS NFP determined by 3 forces: _________________________ minus ____________________ minus ____________________ __________________ (1) (1) Process: ______________________ __________________ __________________ Fluid called: _____________ Consists of: ______________ and ____________________ Does not contain: _________ and __________ (2) Fluid flows into renal tubule system __________________ Fluid now called: ____________________ (3) Exchange between blood in ____________________ and fluid in renal tubules is “2-way” © 2007 Carol Gavareski GFR normally regulated by alterations of ____________________ (one of the forces listed above). Alterations accomplished in 2 ways: Autoregulation: __________________ _______________________________ Sympathetic stim: ________________ _______________________________ (2) Process: _________________________ Describe: _________________ _________________________ (3) Process: _________________________ Describe: _________________ _________________________ Consist of these regions: __________________ Reabsorption: 1. _______ 2. _______ 3. _______ 4. _______ 5. _______ 6. ____________ 7. (metabolic waste) ______ 8. other ions 9. _____ follows by osmosis Secretion: 1. _______ __________________ __________________ Function: _________________________ Reabsorption: 1. Ca++ 2. Na+ and other ions 3. ______ follows by osmosis Secretion: 1. ______ 2. ______ © 2007 Carol Gavareski Secreted by ________________ in response to ______________ (stimulus) Regulated by: ______________ (hormone) Has this effect: _________________________, which in turn helps to _________________________. Stimulus: _________________________ Receptors are ______________ located ___________________ Stimulates secretion of: _____________ by juxtaglomerular cells of the kidney. Mediates conversion of: _________________ (plasma protein produced by the liver) to ____________________ __________________ Consist of 2 cell types: (1) _____________________ (2) _____________________ Converted to: _____________________ in presence of ______________ located in endothelium of pulmonary capillaries. Stimulates _________________ to produce ________________ (hormone) Reabsorption of ____________ And this causes: __________________ © 2007 Carol Gavareski Regulated by: ______________ (hormone) Has this effect: _________________________ which in turn causes _________ which helps to _____________ Secreted by ________________ in response to ______________ (stimulus) Secretion of _______________ Regulated by: ______________ (hormone) Has this effect: _________________________ which in turn helps to _________________________ Secreted by ________________ in response to ______________ (stimulus) Reabsorption of ____________ Regulated by: ______________ (hormone) Has this effect on CD cells: _________________________ which results in: _________________________ Which in turn helps to Secrete either: _____ if plasma pH <7.4; or _____ if plasma pH > 7.4 © 2007 Carol Gavareski Has this effect: helps to _________________________ It is now _________ in its final form. Blood, its contents altered by these processes, now flows away from the nephron by way of _____________ (vessel type) Fluid is now at the end of the nephron tubule system. Consists of water and solutes added by processes of: _______________________ and _______________________ minus water and solutes removed by process of: ________________________. Concentration is: _____________________ in presence of _________ (hormone) Or __________________ in absence of __________. (hormone) It flows next into the _______________ (central collecting portion) of the kidney. Blood leaves kidney by way of _________________ (vessel) to re-enter general circulation into the inferior vena cava. © 2007 Carol Gavareski Eliminated from body through other urinary structures: ________________________ ________________________ ________________________