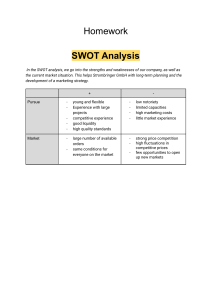
LESSON 2 ENVIRONMENTAL FORCES AND ENVIRONMENTAL SCANNING Organization and Management LEANING OBJECTIVES 1. Analyze various forces/elements influencing local and international business environments using PEST and SWOT strategies. ABM_AOM11- Ia-b-3 Organization and Management ACTIVITY 1 WHY IS THAT? • Identify what effect will be happened in each scenario. Organization and Management ACTIVITY 1 WHY IS THAT? • Identify what effect will be happened in each scenario. Organization and Management ACTIVITY 1 WHY IS THAT? • Identify what effect will be happened in each scenario. Organization and Management ACTIVITY 1 WHY IS THAT? • Identify what effect will be happened in each scenario. Organization and Management ACTIVITY 1 WHY IS THAT? • Identify what effect will be happened in each scenario. Organization and Management ACTIVITY 2 INVESTIGATE Organization and Management ACTIVITY 2 INVESTIGATE Organization and Management CHAPTER DISCUSSIONS ENVIRONMENTAL FORCES AND ENVIRONMENTAL SCANNING BUSSINESS ENVIRONMENT SWOT ANALYSIS, PORTER’S FIVE FORCES, AND PESTEL ANALYSIS. Organization and Management LESSON PRE-TEST Organization and Management Environmental Forces and Environmental Scanning The environment in which a business operates is a major consideration in determining an organization’s design structure. Considerations such as uncertainty, procurement, and competition are linked to the external environment. A company’s strategy and approach to operations must also be aligned with the limitations of its external environment. Definition of Terms 1. Environmental scanning means seeking for and sorting through data about the environment 2. External business environment refers to the factors/elements outside the organization which may affect, either positively or negatively, the performance of the organization. 3. Internal business environment refers to the factors/elements within the organization which may affect, either positively or negatively, the performance of the organization. BUSINESS ENVIRONMENT BUSINESS ENVIRONMENT Micro-environment includes those players whose decisions and actions have a direct impact on the company. Production and selling of commodities are the two important aspects of modern business. Accordingly, the micro-environment of business can be divided. Macro-environment is the condition that exists in the economy as a whole, rather than in a particular sector or region. In general, the macro environment includes trends in the gross domestic product (GDP, inflation,employment, spending, and monetary and fiscal policy. BUSINESS ENVIRONMENT • • • • • The various constituents of the micro-environment are as under: Suppliers of inputs: An important factor in the external microenvironment of a firm is the supplier of its inputs such as raw materials and components. Customers: The people who buy and use a firm’s products and services are an important part of the external micro-environment. Marketing intermediaries: In the firm's external micro-environment, marketing intermediaries play an essential role in selling and distributing its products to the final customers. Competitors: Different firms in an industry compete for the sale of their products. Publics: Finally, the public is an important force in the external microenvironment. Environmentalists, media groups, women’s associations, consumer protection groups, local groups, and Citizens Association are some important examples of publics that have an important bearing on the business decisions of the firm. BUSINESS ENVIRONMENT External Macro Environment • Economic Environment: Economic environment includes all those forces which have an economic impact on business. Accordingly, the total economic environment consists of agriculture, industrial production, infrastructure, and planning, basic economic philosophy, stages of economic development, trade cycles, national income, per capita income, savings, money supply, price level, and population. • Political-legal Environment: Business firms are closely related to the government. The political-legal environment includes the activities of three political institutions, namely, legislature, executive, and judiciary which usually play a useful role in shaping, directing, developing and controlling business activities. BUSINESS ENVIRONMENT • Technological Environment: Technological environment is exercising considerable influence on business. Technology implies the systematic application of scientific or other organized knowledge to practical tasks or activities. The business makes it possible for technology to reach people in a proper format. • Global or International Environment: Global environment plays an important role in shaping business activity. With the liberalization and globalization of the economy, the business environment of an economy has become different wherein it has to bear all shocks and benefits arising out of the global environment. BUSINESS ENVIRONMENT • Socio-cultural Environment: Social and cultural environment also influences the business environment indirectly. These include people’s attitudes to work and wealth, ethical issues, the role of family, marriage, religion, and education, and also social responsiveness of business. • Demographic Environment: The demographic environment includes the size and growth of the population, the life expectancy of the people, rural-urban distribution of the population, technological skills, and educational levels of the labor force. All these demographic features have an important bearing on the functioning of business firms. BUSINESS ENVIRONMENT • Natural Environment: influences business in diverse ways. Business in modern times is dictated by nature. The natural environment is the ultimate source of many inputs such as raw materials and energy, which firms use in their productive activity. • Ecological Environment: Due to the efforts of environmentalists and international organizations such as the World Bank the people have now become conscious of the adverse effects of depletion of exhaustible natural resources and pollution of the environment by business activity. BUSINESS ENVIRONMENT Internal Environment • The factors in the internal environment of a business are to a certain extent controllable because the firm can change or modify these factors to improve its efficiency. However, the firm may not be able to change all the factors. The various internal factors are 1. Value system: The value system of an organization means the ethical beliefs that guide the organization in achieving its mission and objectives. It is a widely acknowledged fact that the extent to which the value system is shared by all in the organization is an important factor contributing to its success. 2. Mission and objectives: The business domain of the company, director of development, business philosophy, business policy, etc. are guided by the mission and objectives of the company. The objective of all firms is assumed to be the maximization of profit. The mission is defined as the overall purpose or reason for its existence which guides and influences its business decision and economic activities. BUSINESS ENVIRONMENT 3. Organization structure: The organizational structure, the composition of the board of directors, the professionalism of management, etc. are important factors influencing business decisions. The nature of the organizational structure has a significant influence on the decision-making process in an organization. Efficient working of a business organization requires that the organization structure should be conducive to quick decision-making. 4. Corporate culture: Corporate culture is an important factor in determining the internal environment of any company. In a closed and threatening type of corporate culture, the business decisions are taken by top-level managers while the middle-level and lowerlevel managers have no say in business decisionmaking. BUSINESS ENVIRONMENT 5. Quality of human resources: The quality of employees that is of human resources of a firm is an important factor in the internal environment of a firm. The characteristics of human resources like skill, quality, capability, attitude, and commitment of its employees, etc. could contribute to the strength and weaknesses of an organization. 6. Labor unions: Labor unions collectively bargain with the managers for better wages and better working conditions for the different categories of workers. For the smooth working of a business firm, good relations between management and labor unions are required. 7. Physical resources and technological capabilities: Physical resources such as plant and equipment and technological capabilities of a firm determine its competitive strength which is an important factor for determining its efficiency and unit cost of production. BUSINESS ENVIRONMENT Specific Components of the External Business Environment Stakeholders, Customers, Suppliers, Pressure groups, Organization’s investors or owners, and Employees. Component of the Internal Business Environment 1. Resources – financial, physical, mechanical, technological, and human resources must be subjected to internal analysis (SWOT) SWOT ANALYSIS 1. What Is a SWOT Analysis? A SWOT analysis is a technique used to determine and define your Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats (SWOT). SWOT analyses can be applied to an entire company or organization, or individual projects within a single department. Most commonly, SWOT analyses are used at the organizational level to determine how closely a business is aligned with its growth trajectories and success benchmarks, but they can also be used to ascertain how well a particular project – such as an online advertising campaign – is performing according to initial projections Organization and Management SWOT ANALYSIS PORTER’S FIVE FORCES ANALYSIS Porter’s Five Forces analysis is a framework that helps analyze the level of competition within a certain industry. It is especially useful when starting a new business or when entering a new industry sector. According to this framework, competitiveness does not only come from competitors. Rather, the state of competition in an industry depends on five basic forces: the threat of new entrants, the bargaining power of suppliers, the bargaining power of buyers, the threat of substitute products or services, and existing industry rivalry. Organization and Management PORTER’S FIVE FORCES ANALYSIS PESTEL ANALYSIS A PESTEL analysis or PESTLE analysis (formerly known as PEST analysis) is a framework or tool used to analyze and monitors the macroenvironmental factors that may have a profound impact on an organization’s performance. This tool is especially useful when starting a new business or entering a foreign market. It is often used in collaboration with other analytical business tools such as the SWOT analysis and Porter’s Five Forces to give a clear understanding of a situation and related internal and external factors. PESTEL is an acronym that stands for Political, Economic, Social, Technological, Environmental and Legal factors. Organization and Management PESTEL ANALYSIS PESTEL ANALYSIS Considering future business scenarios – by realistic consideration of both worst-case scenarios or unfavorable future conditions, as well as middle ground possible conditions, you will have an idea of what to do in the future. Business prediction (also known as business forecasting) – is a method of predicting how variables in the environment will alter the future of a business. It could be used in making decisions regarding offshoring, branching out locally, and expanding or downsizing the company. However, the accuracy of such business predictions cannot always be assured. Organization and Management PESTEL ANALYSIS Benchmarking – the process of measuring or comparing one’s own products, services, and practices with those of recognized industry leaders in order to identify areas for improvement. Organization and Management INDIVIDUAL TASK Organization and Management THANK YOU!