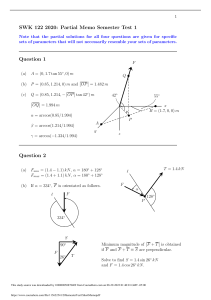
CHAPTER 7 Internet – A network of networks, which communicates using TCP/IP (Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol) World Wide Web – A system of interlinked (hyperlinked) documents accessible by use of HTTP (HyperText Transfer Protocol) Protocol – Convention or standard that controls and enables communication between two computers o Rules governing the syntax, semantics, and synchronization of communication Networking and Communication Trends Convergence o Telephone networks and computer networks converging into a single digital network using Internet-based standards o Cable companies now offer voice services Broadband – High-speed transmission technology; designates a single communications medium that can transmit multiple channels of data simultaneously Broadband Wireless o Voice and data communication and Internet access are increasingly taking place over broadband wireless platforms, such as cell phones and handheld digital devices Components of a Simple Network Two or more connected computers Network Interface Card (NIC) – Expansion card inserted into a computer to enable it to connect to a network Network Operating System (NOS) – Routes and manages communications on the network and coordinate network resources Server Computer – Performs important network functions for client computers Hubs – Simple devices that connect network components, sending a packet of data to all other connected devices Switch – Can filter and forward data to a specified destination on the network Router – Communications processor used to route packets of data through different networks, ensuring that the data sent gets to the right address Telecommunications and Networking in Today’s Business World Key Digital Network Technologies: o Client/Server Computing A distributed processing model in which some processing power is located within small, inexpensive client computers This study source was downloaded by 100000854186461 from CourseHero.com on 07-25-2023 13:24:40 GMT -05:00 https://www.coursehero.com/file/7692143/CHAPTER-7/ The clients are linked to one another through a network that is controlled by a network server computer The server sets the rules of communication for the network and provides every client with an address so others can find it on the network o Packet Switching Messages are first broken down into small bundles of data called packets Packets are sent along different communication paths as paths become available Packets are reassembled once they reach their destinations o TCP/IP and Connectivity TCP (Transmission Control Protocol) • Breaks information into small chucks called data packets • Manages the transfer of the packets from computer to computer • Reassembles data packets into a message at the destination IP (Internet Protocol) • Controls how data packets are formed • Addresses each packet with the source and destination address • A data packet conforming to the IP spec is called an IP datagram Communication Networks and Transmission Media Computers use digital signals (a binary waveform) to communicate a message while a telephone system uses an analog signal (continuous waveform) o To use analog telephone system to send digital data, must use device called modem Modem – Modulator-demodulator o Translates digital signals from a computer into analog form to be transferred over analog telephone lines o Translates analog signals back into digital form for the receiving computer Types of Networks o Local Area Network (LAN) o Campus Area Network (CAN) o Metropolitan Area Network (MAN) o Wide Area Network (WAN) Transmission Media – Wired o Twisted Pair (TP) – Two or more pairs of insulated copper wires twisted together and may be shielded (STP) or unshielded (UTP). It is the lowest capacity of the cable options This study source was downloaded by 100000854186461 from CourseHero.com on 07-25-2023 13:24:40 GMT -05:00 https://www.coursehero.com/file/7692143/CHAPTER-7/ Coaxial (COAX) – Contains a solid inner copper conductor surrounded by insulation and outer braided copper or foil shield. It has higher capacity than the twisted pair o Fiber-Optic – Made of light-conducting glass or plastic core, surrounded by more glass, called cladding, and a tough outer sheath. It is high capacity and used in high speed backbones o The Wireless Revolution Wireless computer networks and Internet access o Bluetooth, Wi-Fi, WiMax, Broadband cellular wireless services Cellular Phone – A two-way wireless communication that assigns unique frequencies to calls and can transmit in analog or digital Internet Access Telephone or Dial-Up Connection o Telephone Modem – A device that connects your computer to your phone line so that you can access another computer or network Modulates analog carrier signal to encode digital information Demodulates carrier signal to decode transmitted information Digital Subscriber Line (DSL) o A high-speed internet connection using phone lines, which allows you to use your phone for voice communications at the same time o Need to be close to the phone company to get a good connection speed Cable Modem o A device that uses your TV cable to deliver an Internet connection o More computers on the network ,the slower the transmission rate Internet Over o Satellite Modem – A modem that allows you to get Internet access from a satellite dish o Download using the satellite modem, but upload usually using phone Wireless o Fixed wireless access points allow computers with access cards to access ground-based networks o Mobile wireless devices can access networks using mobile wireless networks The Internet Internet Addressing and Architecture o Every device connected to the internet has a unique 32-bit numeric IP address o A Domain Name System (DNS) converts IP addresses to English-like domain names The domain name system is a hierarchical system with a root domain, top-level domains, second-level domains, and host computers at the third level This study source was downloaded by 100000854186461 from CourseHero.com on 07-25-2023 13:24:40 GMT -05:00 https://www.coursehero.com/file/7692143/CHAPTER-7/ Internet Architecture o Internet backbone connects to regional networks, which in turn provide access to Internet service providers, large firms, and government institutions o Network Access Points (NAP) and metropolitan area exchanges (MAE) are hubs where the backbone intersects regional and local networks and where the backbone owners connect with one another Internet Services and Communication Tools o E-mail o Usenet newsgroups – discussion groups on electronic boards o Chatting and instant messaging o Voice over IP – delivers voice in digital form over the internet o Unified communications – integrates all communications into one stream to allow user to switch back and forth o Virtual Private Networks (VPN) – a secure, encrypted private network for use internally to an organization Intranets and Extranets o Intranet – An internal organizational network that provides access to data across the enterprise; protected from public visits by firewalls o Extranet – Authorized visitors are given limited access to an internal intranet Client/Server Computing on the Internet o Client computers running web browser and other software can access an array of services on servers over the Internet o These services may all run on a single server or on multiple specialized servers VoIP Digitizes and breaks up a voice message into data packets that may travel along different routes before being reassembled at the final destination o A processor nearest the call’s destination, called a gateway, arranges the packets in the proper order and directs them to the telephone number of the receiver or the IP address of the receiving computer VPN o A private network of computers linked using a secure “tunnel” connection over the Internet o Protects data transmitted over the public internet by encoding the data and ‘wrapping” them with the IP o By addressing a wrapper around a network message to hide its content, organizations can create a private connection that travels through the public internet The World Wide Web o This study source was downloaded by 100000854186461 from CourseHero.com on 07-25-2023 13:24:40 GMT -05:00 https://www.coursehero.com/file/7692143/CHAPTER-7/ HTTP – Communications standard used for transferring web pages o Uniform Resource Locators (URL) – Addresses of web pages o Web Servers – Software for locating and managing web pages Searching for Information on the Web o Search Engines Started in early 1990s as relatively simple software programs using keyword indexes Today, major source of Internet advertising revenue via search engine marketing, using complex algorithms and page ranking techniques to locate results o Shopping Bots Uses intelligent agent software for searching internet for shopping information How Google works: o The user enters query o Google’s Web servers receive the request and Google uses PCs linked together and connected to the Internet to handle incoming requests and produce the results o Request is sent to Google’s index servers that describe which pages contain the keywords matching the query and where those pages are stored on the document servers o Using the PageRank software, the system measures the importance or popularity of each page by solving a complex equations o Small text summaries are prepared for each Web page o Results are delivered to the user o Emerging Internet Technologies and Issues Web 2.0 o Blogs, wikis, RSS, mash-ups, social software Web 3.0 – The future web o Semantic web The Future Internet: IPv6 and Internet 2 o IPv6 – Allows 128 bit addresses, a quadrillion possible addresses o Internet2 – Consortia of agencies working to provide a new robust and highbandwidth version of the Internet o CA*net4 infrastructure Based on optical networking technologies to promote the fastest speeds available over the Internet Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) This study source was downloaded by 100000854186461 from CourseHero.com on 07-25-2023 13:24:40 GMT -05:00 https://www.coursehero.com/file/7692143/CHAPTER-7/ Uses tiny tags with embedded microchips containing data about an item and location, and antenna Tags transmit radio signals over short distances to special RFID readers, which send data over network to computer for processing Active RFID – Tags have batteries, data can be written, range is hundreds of feet, more expensive Passive RFID – Range is shorter, smaller, less expensive, powered by radio frequency energy How it works: o A microchip holds data including an identification number, the rest of the tag is an antenna that transmits data to a reader o The RFID reader has an antenna that constantly transmits. When it senses a tag, it wakes it up, interrogates it, and decodes the data. Then it transmits the data to a host system over wired or wireless connections o The host computer processes the data from the tag that have been transmitted by the reader Wireless Sensor Networks Networks of hundreds of thousands or thousands of interconnected wireless devices embedded into physical environment to provide measurements of many points over large spaces Used to monitor building security, detect hazardous substances in air, monitor environmental changes, traffic, or military activity Devices have build-in processing, storage, and radio frequency sensors and antennas Require low-power, long-lasting batteries and ability to endure in the field without maintenance This study source was downloaded by 100000854186461 from CourseHero.com on 07-25-2023 13:24:40 GMT -05:00 https://www.coursehero.com/file/7692143/CHAPTER-7/ Powered by TCPDF (www.tcpdf.org)