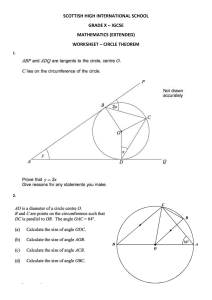
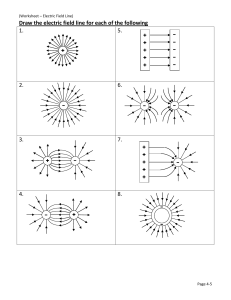
CAMBRIDGE IGCSE™ PHYSICS: CHAPTER 16 WORKSHEET ANSWERS Worksheet answers – Chapter 16 Worksheet 16A Question Answer 1 The nail is unmagnetised, because otherwise one end (of the nail) would repel from one of the poles of the magnet / the force of attraction would be weaker from one end than the other; the N and S poles of the magnet have equal strength. 2 induced magnetism 3 B 4a 4b plotting compass / magnetic compass 5 loses its magnetism easily / easily demagnetised (not stops being magnetic) Cambridge IGCSE™ Physics – Smyth © Cambridge University Press 2021 1 CAMBRIDGE IGCSE™ PHYSICS: CHAPTER 16 WORKSHEET ANSWERS Worksheet 16B Question Answer 1 Bring each end of the nail up to one pole of the magnet / bring each pole of the magnet up to one end of the nail. If there is attraction at one end and repulsion (or less attraction) at the other then the nail is magnetised. If there is equal attraction at both ends then the nail is unmagnetised. 2a induced magnetism 2b north 3 B 4a 4b where the lines are closer together 4c plotting compass / magnetic compass 5 The hard material keeps its magnetism, so the permanent magnet last for longer. The soft material loses its magnetism easily / easily demagnetised (not stops being magnetic) so the electromagnet can be switched off. Cambridge IGCSE™ Physics – Smyth © Cambridge University Press 2021 2 CAMBRIDGE IGCSE™ PHYSICS: CHAPTER 16 WORKSHEET ANSWERS Worksheet 16C Question Answer 1 Bring each end of the nail up to one pole of the magnet / bring each pole of the magnet up to one end of the nail. If there is attraction at one end and repulsion (or less attraction) at the other then the nail is magnetised. If there is equal attraction at both ends then the nail is unmagnetised. 2a induced magnetism 2b A north pole is induced at the end of both nails. Like poles repel so the nails are pushed apart. 3 B 4a 4b where the lines are closer together 4c plotting compass / magnetic compass 4d 5 The hard material keeps its magnetism so the permanent magnet last for longer. The soft material loses its magnetism easily / easily demagnetised (not stops being magnetic) so the electromagnet can be switched off. Cambridge IGCSE™ Physics – Smyth © Cambridge University Press 2021 3