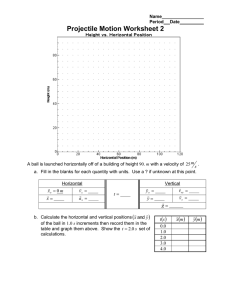
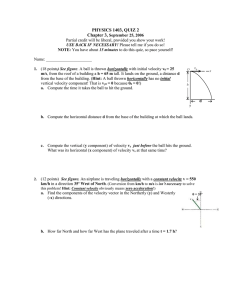
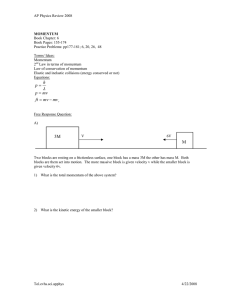
SPH 4U 2D Collision Problems Answer these questions using complete solutions including Designated direction(s) Vectors Formulae units 1. A grenade of mass 1.20 kg is at rest on a smooth, frictionless surface when it suddenly explodes into three pieces. A 0.50 kg piece flies off horizontally to the north at 3.0 m/s, and a 0.30 kg piece flies off horizontally to the southwest at 4.0 m/s. What is the horizontal speed and direction of the third piece? (2.7 m/s [E37˚S]) 2. Repeat the above problem, but this time assume that the grenade was moving at a constant velocity of 1.5 m/s [E] just before it exploded. (Assume that the final speeds and directions of pieces one and two remain the same.) (6.8 m/s [E14°S]) 3. A bomb initially at rest on a smooth, horizontal surface is exploded into three pieces. Two pieces fly off horizontally at a 60°angle to each other, a 2.0 kg piece at 20 m/s and a 3.0 kg piece at 12 m/s. The third piece flies off horizontally at 30 m/s. (a) Determine the direction of motion of the third piece. (148° CCW from the 3.0 kg piece) (b) What is its mass? (2.2 kg) 4. A 2000 kg car travelling east at 24 m/s enters an icy intersection and collides with a 3600 kg truck travelling south at 10 m/s. If they become coupled together in the collision, what is their velocity immediately after impact? (11 m/s [E37˚S]) 5. A nucleus, initially at rest, decays radioactively. In the process, it emits an electron horizontally to the east, with momentum 9.0 x 10-21 kg●m/s and a neutrino horizontally to the south, with momentum 4.8 x 10-21 kg●m/s. (a) In what direction does the residual nucleus move? (W28˚N) (b) What is the magnitude of its momentum? (1.0 x 10-20 kg●m/s) (c) If the mass of the residual nucleus is 3.6 x 10-25 kg, what is its recoil velocity? (2.8 x 104 m/s) 6. A steel ball of mass 0.50 kg, moving with a velocity 2.0 m/s, strikes a second ball of mass 0.30 kg, initially at rest. The collision is a glancing one, causing the first ball to be deflected by an angle of 30°, with a speed of 1.50 m/s. Determine the velocity of the second ball after the collision, giving both its speed and direction. (1.7 m/s [R47°D]) 7. A 3000 kg space capsule is travelling in outer space with a velocity of 200 m/s. In an effort to alter its course, it fires a 25.0 kg projectile perpendicular to its original direction of motion at a speed of 2000 m/s. What is the new speed of the space capsule? By what angle has its direction changed? (2.02 x 102 m/s, 4.76°) \sph4U\moment\40731531