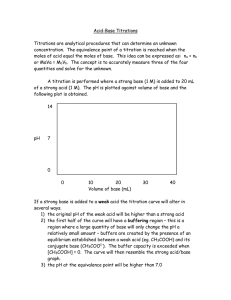
Use of Indicators • Indicators are weak acids that have a different color than their conjugate base form. • Each indicator has its own pH range over which it changes color. Most have a useful range of about 2 pH units • An indicator can be used to estimate the equivalence point in a titration as long as it changes color in the small volume change region where the pH rapidly changes. Aqueous Equilibria © 2015 Pearson Education, Education Inc. Aqueous Equilibria © 2015 Pearson Education Titration of a strong base and a strong acid • Rapid change occurs from pH 3 – 11 • Any indicator that changes colour in this pH region can be used • Both phenolphthalein and methyl red change color in the rapid-rise portion of the titration curve. Is methyl red a suitable indicator when you are titrating a strong acid with a strong base? Explain your answer. Aqueous Equilibria © 2015 Pearson Education, Education Inc. Titration of a weak acid with a strong base • Choice of an indicator is important when titrating a weak with a strong base and vice-versa. Why? Aqueous Equilibria © 2015 Pearson Education, Education Inc. Titrating a weak base with a strong acid Why is phenolphthalein not a suitable indicator when titrating a weak base with a strong acid? © 2015 Pearson Education, Education Inc. Aqueous Equilibria What is important about Thymol blue? Out of Interest Which compound is responsible for the colour change in litmus paper? Identify the structure of the compounds responsible for colour change in each indicator Aqueous Equilibria © 2015 Pearson Education Titrations of Polyprotic Acids • A polyprotic acid is an acid that has more than one ionizable hydrogen (H) atom Examples of polyprotic acids include H2SO4 , H2CO3 and H3PO4. Dissociation of H3PO4. Aqueous Equilibria © 2015 Pearson Education, Education Inc. Dissociation of H3PO4. Simplified version: What can you observe about Ka1, Ka2 and Ka3 values? © 2015 Pearson Education, Education Inc. Aqueous Equilibria Titrations of Polyprotic Acids When a polyprotic acid is titrated with a base, there is an equivalence point for each dissociation or for each acidic H. Why? - the neutralization reaction occurs in stages. The most acidic proton (Ka1) is titrated first, followed by the next most acidic (Ka2), and so forth The pH titration curve will show various equivalence points corresponding to each neutralization step. For example, H2SO4 will have 2 equivalence points. How about H3PO4? And H2CO3? © 2015 Pearson Education, Education Inc. Aqueous Equilibria Titrations of H2SO4 with NaOH Aqueous Equilibria © 2015 Pearson Education Titrations of H2CO3 with NaOH Aqueous Equilibria © 2015 Pearson Education Titrations of H3PO4 with NaOH 3rd equivalence point is not easy to detect via titration with 0.1M NaOH. Why? Aqueous Equilibria © 2015 Pearson Education Important information from a pH titration curve of a weak polyprotic acid The pH titration curves of the weak polyprotic acid helps us predict the pKa values of the acid. What is pKa? Lets consider the pH titration curve of H3PO3 . Why are we considering only two equivalence points when H3PO3 is suppose dto have 3 equivalence points? Write the pH expression for each equilibrium system Aqueous Equilibria © 2015 Pearson Education What would be the expression when [H2PO3-] = H3PO3]? What would be the expression when [HPO32-] = H2PO3-]? When [H2PO3-] = H3PO3], pH = pKa1 When [HPO32-] = H2PO3-], pH = pKa2 At which stage does this occur? - half way before the equivalence point. This point is Aqueous known as the half-equivalence Equilibria © 2015 Pearson Education Identifying the mid-points pH = pKa3 Why is the 3rd equivalence point difficult to identify using titration with NaOH? pH = pKa2 pH = pKa1 Aqueous Equilibria © 2015 Pearson Education, Education Inc. What are the implications? We can estimate the pKa values from the pH titration curve Estimate the pKa values of H3PO4 using the pH titration curve against NaOH Compare with the actual values (find the actual values on Google) Aqueous Equilibria © 2015 Pearson Education, Education Inc. Estimate the pKa values of H2SO3 using the pH titration curve against NaOH Aqueous Equilibria © 2015 Pearson Education, Education Inc.