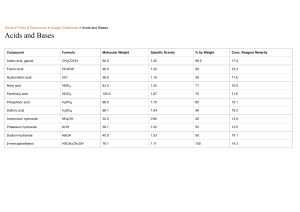
Classification ofMixtures I Pure Substance Mixture ~ - I ElementCompound deterogeneous homogeneous Uniform - components different throught phases Emulsion tekarsmayan · Two immisable liquids form heterogeneous mixture, called a · · They do dissolve each other even if as Ex:Olive oil-water, olive of vinegar emulsion. they not Dispersed phase and dispensing from are water, diesel of water gasoline shamened well- mayonnaise medium phase be seen with eyes may Suspension: solid which A is partially dispersed in a liquid withoutdissolving Solid particles suspense Ifa suspension is in the liquid and are usually left undisturbed, the particles Dispersed particles are larger than a suspension. Ex: Muddy water, sandy water, chalky water several fruitjoices, agram, Turkish coffee, soup visible. to settle down. likely are forms 10cm (1080nm) Aerosol: A solid liquid dispersed or An aerosol is a in a to form suspension offine solid heterogenous a mixture called liquid droplets or in a as Ex:fog, cloud, aerosol. ↳ gay. Colloid Particles size clordy and as very lone size, two opaque, some are of visible lom) · . can't be seen. light a colloid, itis permeable easy see bubbles, shaked egg, soap blood. (450 +ezsOrn). scattered randomly by the dispersed particles. This light scattering · efectcalled as onstanding I and · · Dontseparate can'tbe light from filter paper · Permeable ↳ not on 192 standing separated by filtration light (tyndall ect) & . · filter paper permeable paper heterogenous larger than 10(/runm) Particles settle daun can · · u their sizes are similar to the Suspensions · (Om (1 and Because Tyndall Efect. heterogeneous separated by filteration. Scatter · to not Ex: Cream, dyes, selly, Colloids don't separate Do not scatter 1200nm) - are dagimen smaller than 10m(1 nm) < · 11 and aer osal distant phases transparent homogenous can'tbe · or components o milk and Solutions · another phases of collodial mixtures When lightpasses through wavelength particles in between 10 and 10 cm (10m and Because oft he particle · Solid belirli componenti s dispersed One spray liquid across Smag, volcanic eruptions be separated by May scatter light, Not permeable - filtration but absorbs it. filter, paper paper How Compounds Dissolve in Water Ionic (NaCl) Compounds Molecular Substance form ions forming The generalization Nompolar substancy be schable Hexone, a in is stated simly be solvable in nompeter solvents;i cnic and paler solutes immiscible in water. Hexone is the top layer because A substance (such as Nall) whose aqueous solutions contain Concentration small of cons (icAzOs) thatdoesn't formions in it ions is solution is called called a an electrolyte. nonelectrolyte. (parts,per million) ppby billion 186 a the quantify Boiling-point Elevation Nonvolatile solute pointofthe Compound CH22O, t molecular compend - Mass 4 of in solo components mponent xO total mass of pain sal competion x lob volgofsoutexlof total mass volume of solution ofsolution pointand raising ofthe bailing pointare physical properties of solution solute particly called colligative properties the of a freezing a solution tempt pure substance's temp. ofa solution to be raised boiling point causes in comparison with the boiling pure solvent Freezing. PointDepression Addition of a solute to ↳ Because Nacl-ionic los Colligative Properties lowering on -> Solutions concentration to solute-dilute solution thatdepend likelyto less dense than water, is Large concentrationsto be concentrated ppm one more polar solvents. hydrocarbon, is substance (such as A methand "like dissolves like" as likely to are more (CH, OH) dissolves without the of depression solution temp a in solvent will < pure cause substance the freezing pointof the solventto be lowered the freezing point, the seawater does notfreeze as readily as freshwater lakes and rivers do. Vapor Pressure Lowering The vapor pressure ofa leads to boiling pure solvent is greater than the vapor pressure ofa solution containing nonvolatile liquid. This point. Osmotic Pressure The pressure a solution thatmustbe applied to the solution side to stop fluid movementwhen from pure water. a semipermeable membrane separates Separation ofMixtures 1. The difference in sizes of components Cheterogeneous) 1. Picking up I solid-solid) handpicking stone,wheat, - 4. yaylma like Diffusionofsmall molecules waste and (elek) sieve Dialysis (diyaliz) J. Solid-solid presagill rice, Sieving (eleme) 2. (ayllama) - excess water (Solid-liquid)(sclid-gas) members from heterogeneous sem & Dialysis vermeable of blood Filtration(sizmel Mostcommon 2. The components of densities in (ayirma hunisi) Cliqued-liquid) & liquids immiscible 2. Floatation saidsolid putina liquid dissolve ↓ diff densities any Precipitation (Gaktrme) Two solutions form solid called is aprecipitates dx 3. The difference in solubility solid crystalic - - salty in dif evaporated its . · bolling in 1. Simple distillation Salty - Sugar in diff heated Nach, NoN, in temperatures can bailing points · boiling alcohol water olution are gathered distillation Precipitation only solid can be separated lower than salt be water in Sugar melting points Shnemogenous 25°C. fractionating are component from are solventto cheese is extracted from sugar beet. 6. The difference magnetic rater Distillation It's apparatus has to its Both solid and liquid Transferring other. saltfrom sea water /Ayrimsal damitmal point. I vapor ofitcondensed to form don'tchange. the liquid again. Solids - crystalize which or moremiscible liquids has damitmal Solid-riquid is 2 fractional points components (homogeneous Mumi Liquid differentsolubility Isolid liquid) (liquid-liquid) same values in S. The difference of Basit Dissolves in the soda and water 4. The difference 3.Extraction (ru aikarme) separated evaporates, salt crystalizes) sugar solution washing kristallenderne) temperatures. t Solids dissol agein water (water Crystallization layrimsal solventbuthave solution cooled down solution 2. Fractional /Solid-solid) increased atthe dissolved solid crystalizes. - I ↑ production ( solubilities hot Liquid party water wine · a water Crystallization (Kristall endin /Solid-liquid) ⑧ gold · dliq dY to sediment purification in maste components (heterogeneus) & liquid differentbecker from its sinks, dsolution removal iron ions in water 2. of them. One of them Put the precipitate. (Gocelti) ·removal ofphosphate of (liquid-solid) doesit sand-strat a insoluable an > (aktarmal 3. Decantation floats the other 4. (yizdurme) from insoluble solid an (heterogenous) funnel separatory By 1. difference technique separate liquid to column Solid-solid (alloys) homogenous One has lower iren-tie alloy zinc-copper alloy or melting bronze in components of heterogenous mixtures point property ↓ of in components Magnetization/minatis/amal heterogeneous solid-solid Distinction between magnetic and nonmagnetics sagrim) coin . iron particles attracted in mixture to the fe, Co, Ni i ron of and sulphur are magnetand separable. ane Perromagnetic elements. A cid and Acids we use Bases sour taste, daily life in Tartaric acids Properties:yprandirmak in queous solutions ofitionize grapes in lemons and orange folic acid in strawberries Reactwith metals to have I gas -bases, phenolphthalein formic acid in stinging Lactic acid in milk Acetic acid in vinegar ANO, Nitric vitamin C vinegar 5-8% acetic we use in daily life · Lime Bleach-beyazlaticl (NAS) Iye((a0Au) (NaltCOz Tooth Paste Washing Soda Shampoo (NazCOS HCOOH -> Formic acid electrolytes Bitter taste - found food less strong drugs a solution of 3.6% LiOHe Lithium hydroxide NaOH* Sodium hydroxide kOlt- Potassium hydroxide BalOH)z- Barium hydroxide Sea water is bases Phenopthalein Dark chocolate Milk ofmagnesia (MgCOH(aa) Strong Acetic acid Ca(CH),Calcium hydroxide React NactI with acid to pink. produce water and with ones react amphoteric acid - ·Red litmus turns blue Drain opener detergent) Blood Bleach HC10 Perchloric acid turns acid HCN- Cyanic acid CH,COOH Aqueous solution ofitis ph> 7 Stomach - H2SO4 sulfuric acid ionize added to water · · soda - H2SOt sulfurous acid ·corrosive Cooking Hf hydrofluoric acid HyPO Phosphoric acid properties Soap Ammonia Weak Acids HzCO,-Carbonic HCl hydrochloric acid HBr ->hybromic acid Al-hydroiodic acid * Bases colorless low ph values o, 1 or 2 Citric acid in lemonade in red turns strong acids well lonizes completely - conductelectric pickle suice in salt and water ph 7 nettle Lisirganotul acid in soda Ascorbic acid litmus turns Blue Malic acid in apples Acetic acid -electrolytes - Citric acid Carbonic corrosive A salt metals Weak bases. NAs ammonia AgOHeSilver hydroxide Mg(OH)-Magnesium hydroxide Fr ali,n . an Enternee