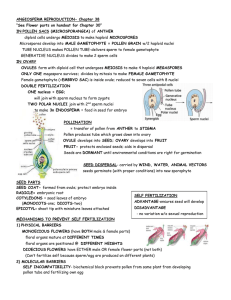
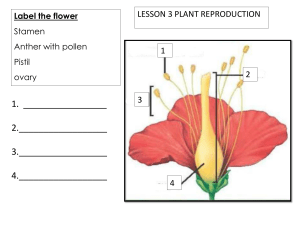
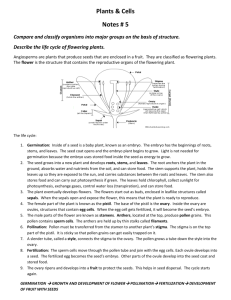
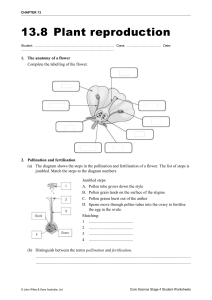
Chapter6: Flower Plant Reproduction structure I it is " p female reproductive a (carpel) sepal peduncle plants thathave Carpel - Stamen- both to male and female produce embryo produces number sac pollen of stamens are organs are called hermaphrodites. (offspring) differentfor different species of plants Stamen pollen pyjobe each · the 1) anther has · sac each lobes 4 lobe has pollen sac microspore a pollen sac has (diploid, 2n) mother cells filament fetrad (4 microspore cells) - meiosis, . microspore - ↳ mother cell microspore cell (n) (2n) develop(grow) become to V pollen grains (n) thicker wall mitosis . fube ⑳ 3 generative · pollen grain tube nucleus (n) mature nucleus generative nucleus nucleus - - pollen grain to form the to form pollen the male fertilisation tube after garnetes, pollination used for Carpel ovule-formed - more the inside than -attached to ovary inside I the ovary the placenta through called structure a funicle the in ovary - -placenta -inside a) supplies nutrients to the the ovule, we have nucellus - - type tissue tissue) into (form of develop ovule (parenchyma integumenttissue the skin of seeds) b) embryo sac-formed - from itcontains (diploid, nucallus the megaspore mother cell In) 1 style embricans placenta it aange (t micropyle:allows air andwater to enter seed during germination megaspore cells (n) - meiosis ⑧ ⑧ 7 . - will develops megaspore degenerate (diel (grow) mother cell (2n) W divides through mitosis to 8 o 3 times produce nuclei -> ·8 o -> mitosis 3 times produces 8 = (2 8) ⑧ · · . I antipodal I polar nuclei I embryo two cells synergic cells and one egg sac antipodal cells egg cell provide nutrients to two synergic cells guides the pollen - - polar nucleiand forms egg cell- involved forms diploid zygote triploid endosperm O tube with fertilisation with male nuclei with male nuclei(3n) (2n) cell pollination fertilisation and transfer pollination:the -done tube nucleus · gametes (n) · 0 ⑧ ⑧ egg cell (n) . to be agentcauses pollen transferred from other to stigma pollinating tube nucleus ⑧. the male · bodies (n) from degenerates the pollen the sac down, I haploid pollen tube reaches degenerates ganetes male of the ovary ovary, enter the (embryo the (n) tube embryo sac female nuclei), where fertilisation tube gametes ovary moves gametes nucleus stigma male tube nucleus in nucleus when · ↓ ovule to · 3 an pollen tube that a generative itdivides by mitosis form as . polar generates grows towards · e embren insects, wind, water) ene Tolleare male pollen from anther to stigmar pollinating agents (animals, by ⑧. severative of contains occurs fertilisation:fusion plants, in there male 2 are 12 it 2nd and of male male female nuclei nucleiand female 3 32 polar ganetes) nuclei legg cell) nucleiand becomes gamete male male ganete egg (n) + (n) 2 + cell (n) polar > nuclei diploid (2n) zygote >triploid (n),(n) zygote:the offspring, develops :develop endosperm cell into a endosperm tissue embryo into plantifthe ovule (now called seed) is planted. endosperm tissue help with embryo development(either before develop into :to seed is planted or after the seed is germination occurs). provides nutrition allows the to seed endosperm cell plantsurvival (and therefore the the planted, when embryo survive to planted ... nucleus becomes fertilisation double embryo (3n) endosperm - - double for long periods before fertilisation] is is it needed for Seed FruitDevelopment and ⑱See After fertilisation: becomes 1) Ovule 2) seed > becomes Ovary fruit 3 terminal mitosis ⑳ cell -> 8 embryo c. basal zygote structure cell seed zygote a) divides terminal b) basal by form two mitosis to cells: embryo thatconsists form cell:develop to 1) plumule:immature leaf/shoot 2) radicle:immature 3) cotyledon:food storage cell:develops root tissue suspensor. The into embryo embryo to sac of: suspensor attaches (like umbilical cord humans) what 1) happens the of female flower: fall off petals 2) stigma 3) sepal and style degenerate or may 4) integumentwill 3) parts other to wall Ovary a) may degenerate not form will seed form coat pericarp. (skin) Pericarp has 3 layers: exocarp-skinof fruits b) mesocarp c) endocarp - - where the flesh the fruitis of layer surrounding seeds fruits of in Importance seeds for of Importantfeatures of that allow chance for seeds 1) large numbers 2) may be better -> dormantfor by 3) surrounded 4) cotyledon provides 5) 6) seed testor breaks for germination. seed structure damaging. (testal coat when (presence is small, to survive. survival which seed conditions water of firm to it and still long periods nutrients only survival and survive protects seed embryo are favourable breaks the testal able to resistspoiling or