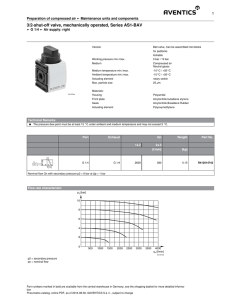
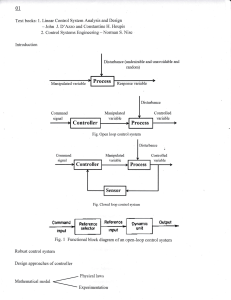
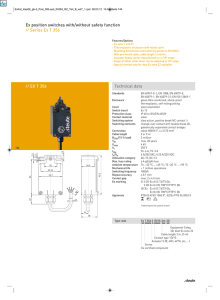
Approved by Order of the Federal Environmental, Industrial and Nuclear Supervision Service dated 21 March 2012 No. 176 FEDERAL RULES AND REGULATIONS IN THE FIELD OF ATOMIC ENERGY USE "RULES FOR ARRANGEMENT AND OPERATION OF ACTUATING MECHANISMS OF REACTIVITY MODIFICATION DEVICES" NP-086-12 I. Purpose and scope 1. These Federal Rules and Regulations in the Field of Atomic Energy Use "Rules for design and operation of actuating mechanisms of reactivity modification devices" (hereinafter referred to as the Rules) were developed in compliance with Federal Law dated 21 November 1995. No. 170-FZ "On Atomic Energy Use", Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation dated 1 December 1997 N 1511 "On approval of Regulations on development and approval of federal standards and regulations in the field of atomic energy use" (Code of the Russian Federation legislation, 1997, N 49, art. 5600; 2012, N 51, art. 7203). (p. 1 as revised by Rostechnadzor Order N 395 dated 28.09.2017) 2. These Rules contain requirements to the design, assembly, tests and operation of actuating mechanisms of reactivity modification devices (hereinafter referred to actuating mechanisms). (p. 2 as revised by Rostechnadzor Order N 395 dated 28.09.2017) 3. Requirements of these Rules apply to actuating mechanisms of reactor plants of nuclear power plants and research nuclear facilities of all types being designed, constructed, built and operated. Requirements of these Rules do not apply to reactivity modifiers of periodic pulse research reactors or to starters of periodic pulse research reactors. (as revised by Rostechnadzor Order N 395 dated 28.09.2017) The terms and definitions used are given in the Appendix to these Rules. 3(1). The procedure of bringing actuating mechanisms of reactivity modifiers of nuclear installations into compliance with these Rules including time limits and scope of all necessary measures shall be defined on case by case basis under the conditions of the siting, construction and operation license. (p. 3(1) is enacted by Rostechnadzor Order N 395 dated 28.09.2017) II. Requirements to actuating mechanisms Requirements to the design of actuating mechanisms 4. The design of actuating mechanisms must ensure compliance with quantitative values of the parameters established in the nuclear installation project: (as revised by Rostechnadzor Order N 395 dated 28.09.2017) working rate of travel of reactivity modifier; time of introduction of reactivity modifier exercising the emergency protection function into the core on onset of requirement for actuation of emergency protection; time of delay from issue of an emergency protection signal to the beginning of travel of reactivity modifier; reactivity modifier position measurement error. 5. The design of actuating mechanisms must ensure: damping movable parts of the actuating mechanism and reactivity modifier in case of actuation of the control and protection system on emergency protection signal; reliable engagement and disengagement of the coupling device with (from) the reactivity modifier; enabling control of engagement of the coupling link with the reactivity modifier on the shut down reactor, critical, subcritical assembly (visually, or by means of a special device); (as revised by Rostechnadzor Order N 395 dated 28.09.2017) enabling engagement with manual drives or special devices for moving the reactivity modifier; margin of travel of the reactivity modifier from the end switch to the limit stop (the maximum margin of travel is determined in technical documents for actuating mechanisms); operability of the mechanism in case of deviation of straightness or inclination angle of the process channel (duct) for travel of the reactivity modifier within the limits established in the project of the reactor plant, critical, subcritical stand; (as revised by Rostechnadzor Order N 395 dated 28.09.2017) enabling operation of its elements within the temperature range established in the project of the reactor plant, critical, subcritical stand; (as revised by Rostechnadzor Order N 395 dated 28.09.2017) compliance with technical characteristics (including reliability parameters) throughout the assigned service life, as required by technical documents; vibration resistance all across their operating conditions; enabling their being handled with hoisting mechanisms within the nuclear power plant, research reactor, the building accommodating a critical, subcritical stand; (as revised by Rostechnadzor Order N 395 dated 28.09.2017) enabling their decontamination following dismantling without causing damage to parts; enabling dismantling the actuating mechanism of the shut down reactor, a critical, subcritical assembly. (as revised by Rostechnadzor Order N 395 dated 28.09.2017) 6. The design of emergency protection actuating mechanisms must ensure: movement of the reactivity modifier from working and other intermediate position on an emergency protection signal and introduction of negative reactivity into the core of the reactor, critical, subcritical assembly, including cases of failures of electric motor, power cables, connectors, end switches and other electrical elements of the actuating mechanism; (as revised by Rostechnadzor Order N 395 dated 28.09.2017) availability of devices ensuring travelling of the reactivity modifier into the core so that the protective action initiated on an emergency protection signal is terminated; enabling examination and check of the mechanism on the shut down reactor, critical, subcritical assembly and control of its technical condition in the course of operation (scope and means of control are determined in the nuclear installation project and presented in the operation manual for actuating mechanisms). (as revised by Rostechnadzor Order N 395 dated 28.09.2017) 7. The design of actuating mechanisms is to prevent: spontaneous movement of the reactivity modifier resulting in introduction of positive reactivity, even in case of a failure in power supply of the actuating mechanism, as well as in case of internal emergency impacts and external natural and man-induced impacts; spontaneous disengagement of the actuating mechanism coupling device from the reactivity modifier during normal operation and in case of abnormal operation including design basis accidents; jamming of movable parts of the actuating mechanism during normal operation and in case of abnormal operation including design basis accidents; spontaneous relocation (withdrawal) of the emergency protection reactivity modifier after its insertion into the core on an emergency protection signal (for emergency protection actuating mechanisms). 8. The design of the actuating mechanism must provide for: means for control of reaching the limit stop by the reactivity modifier, or the coupling device; a device for removal of gas from the internal cavity of the actuating mechanism during operation (non-use of the gas removal device must be substantiated in the nuclear installation project); (as revised by Rostechnadzor Order N 395 dated 28.09.2017) enabling control over actuation of safety devices (for actuating mechanisms having such devices in their kinematic chain). 9. Neither a failure of end switches nor reaching the reactivity modifier limit stop by movable parts of the actuating mechanism must result in damage of the actuating mechanism. 10. The design of actuating mechanisms operating in the primary circuit medium must ensure: keeping the primary circuit sealed at normal operation and abnormal operation including accidents at nuclear installations, except for those, where the tightness of the primary circuit during normal operation and in case of abnormal operation, including accidents, is not stipulated by the project; (as revised by Rostechnadzor Order N 395 dated 28.09.2017) availability of electrical lead-ins into the internal cavity of the drive of actuating mechanism (for electromechanical actuating mechanisms). 11. For easier maintenance, the design of actuating mechanisms is based on a unit (modular) principle, which allows replacement of units (modules) (non-use of unit (modular) design must be substantiated in the nuclear installation project). (as revised by Rostechnadzor Order N 395 dated 28.09.2017) 12. When designing and manufacturing actuating mechanisms, materials and components must be used that are resistant to mechanical, thermal, physical-chemical and radiation impacts. 13. When designing, constructing, manufacturing and operating actuating mechanisms, it is necessary to meet the requirements of the quality assurance program. (p. 13 as revised by Rostechnadzor Order N 395 dated 28.09.2017) Electrical equipment of actuating mechanisms of reactivity modifiers 14. The design of electromechanical actuating mechanism must provide for: application of electric motors of a rated power sufficient for the traction force of actuating mechanisms with a margin substantiated in the technical documents; availability of position indicators ensuring control of end and intermediate positions, as well as end switches actuated directly from the reactivity modifier (should it be impossible to have a direct contact of the reactivity modifier with end switches, the correctness of operation of the actuating mechanism must be substantiated); availability of a safety device preventing damage of the electric motor of the actuating mechanism in case of jamming of the reactivity modifier, or non-actuation of end switches; devices preventing loss of information on the current position of the reactivity modifier; enabling physical separation of internal power and control lines of electrical elements of the actuating mechanism; preventing spontaneous travel of the reactivity modifier resulting in introduction of positive reactivity into the core of the reactor, critical, subcritical assembly in case of failures of electric motors, damage of cables, connectors. end switches or other electrical elements of the actuating mechanism. (as revised by Rostechnadzor Order N 395 dated 28.09.2017) 15. The technical documents for actuating mechanisms must specify the impedance of insulation of windings of electrical equipment of the actuating mechanism in all the operating conditions. 16. Connectors for connection of actuating mechanisms to external electric circuits must ensure sealing of the contact connection and unambiguous identification of the joint (coupled) position. III. Development of documents and testing of actuating mechanisms; 17. Actuating mechanisms are supplied along with a package of technical documents comprising cover documentation including a passport (certificate) filled in by the manufacturer, with specification of the assigned service life of the actuating mechanism. 18. Technical documents for actuating mechanisms include engineering documents (including technical specifications), process documents for assembling of actuating mechanisms, operational documents (operation manual for actuating mechanisms). (as revised by Rostechnadzor Order N 395 dated 28.09.2017) 19. Engineering documents must be prepared in compliance with a quality assurance program developed and approved subject to an established procedure. 20. Technical documents for actuating mechanisms (as well as amendments introduced thereto) shall be developed by the manufacturer, or a specialized organization involved by the manufacturer in compliance with requirements of these Rules and shall be approved by the developer of the actuating mechanism. (p. 20 as revised by Rostechnadzor Order N 395 dated 28.09.2017) 21. Operation documents shall be developed based on engineering documents and approved by the operating organization subject to an established procedure. 22. Prototypes of actuating mechanisms are manufactured for confirmation of compliance of actuating mechanisms with design requirements. 23. Prototypes of actuating mechanisms shall be subject to the following types of tests: preliminary tests (for determination of compliance of the actuating mechanism prototype with requirements of technical documents, and for determination of readiness for acceptance tests); factory acceptance tests (for confirmation of compliance of the actuating mechanism prototype with requirements of technical documents in conditions close to operating conditions), including service life tests (for confirmation of operability of the actuating mechanism within the assigned service life); operating tests within the control and protection system on an operating nuclear installation (for confirmation of compliance of the actuating mechanism prototype with requirements of technical documents in normal operation conditions). (as revised by Rostechnadzor Order N 395 dated 28.09.2017) 24. Programs and methods of tests must be developed for testing of actuating mechanisms (the scope and the required quantity of actuating mechanisms for tests must be substantiated in technical documents for the actuating mechanisms). 25. Actuating mechanisms on a nuclear installation shall undergo the following operating tests: (as revised by Rostechnadzor Order N 395 dated 28.09.2017) pre-assembly tests on a pre-assembly test bench with reactivity modifier simulators for compliance of the main characteristics of actuating mechanisms with requirements of technical documents; comprehensive tests on the reactor installation, critical, subcritical stand under a startup & adjustment program. (as revised by Rostechnadzor Order N 395 dated 28.09.2017) 26. Tests of actuating mechanisms on the reactor, critical, subcritical assembly shall include: (as revised by Rostechnadzor Order N 395 dated 28.09.2017) test of engagement and disengagement of the actuating mechanism coupling devices with/from the reactivity modifier for each mechanism (it is not allowed to carry out work on engagement or disengagement of the actuating mechanism with/from the reactivity modifier with devices that are either malfunctioning, or have not passed scheduled checks of devices; at engagement or disengagement of the actuating mechanism with/from the reactivity modifier, immediate termination of lifting the reactivity modifier and its introduction into the core must be allowed); test of the reactivity modifier travel value for compliance with the value substantiated in the project of the reactor plant, critical, subcritical stand. (as revised by Rostechnadzor Order N 395 dated 28.09.2017) 27. Serially manufactured actuating mechanisms shall be subjected to factory bench tests simulating the conditions of operation of the actuating mechanism in a nuclear installation (channel corridor, medium parameters, coupling link). The scope and conditions of tests must be presented in the testing program. (as revised by Rostechnadzor Order N 395 dated 28.09.2017) 28. Assembling on the reactor, critical, subcritical stand may only be performed with actuating mechanisms, whose main characteristics meet the requirements of technical documents as based on results of tests on a pre-assembly test bench. (as revised by Rostechnadzor Order N 395 dated 28.09.2017) 29. Following assembling of an actuating mechanism on the reactor, critical, subcritical assembly, the actuating mechanism must be tested with a regular, or simulated core and with a regular control arrangement under the startup & adjustment program. (as revised by Rostechnadzor Order N 395 dated 28.09.2017) 30. The program for testing of actuating mechanisms on the reactor, critical, subcritical assembly must be approved by the operating organization in coordination with developers of technical documents for actuating mechanisms. Testing results are executed with an act (report). (as revised by Rostechnadzor Order N 395 dated 28.09.2017) 31. Actuating mechanisms are operated in compliance with manuals on operation of actuating mechanisms developed subject to requirements of the technological regulations on operation of a power unit of nuclear power plant, technological regulations and a manual on operation of a research reactor, a manual on operation of critical, subcritical stand. (p. 31 as revised by Rostechnadzor Order N 395 dated 28.09.2017) 32. During operation it is necessary to exercise control over operation of the actuating mechanism based on readings of instruments in the main control room and the standby control room (if available) (the scope and means of control are established in the design of the nuclear installation and are presented in the manual on operation of actuating mechanisms). (p. 32 as revised by Rostechnadzor Order N 395 dated 28.09.2017) 33. During operation of actuating mechanisms, it is necessary to register failures and malfunctions (with specification of the factory number of the service life of the actuating mechanism) stating the nature, place, time and causes thereof; measures taken for elimination and prevention. 34. Actuating mechanisms must on a regular basis, throughout the operation period, be examined for compliance with requirements of technical documents. Requirements to the frequency of tests must be substantiated in technical documents for actuating mechanisms. Appendix to Rules on Design and Operation of Actuating Mechanisms of Reactivity Modifiers, approved by order of the Federal Environmental, Industrial and Nuclear Supervision Service dated ___ ________ 20__, N ____ TERMS AND DEFINITIONS The following terms and their definitions are used in this document: Vibration resistance is the ability of an article to retain its strength, stability, air-tightness and operability during and after vibration impact. Position indicator is a device for issue of signals on the position of the reactivity modifier. (as revised by Rostechnadzor Order N 395 dated 28.09.2017) Actuating mechanism of reactivity modifier (actuating mechanism) is a device made up of a drive and coupling elements and intended for changing the position and holding reactivity modifiers. Comprehensive tests of actuating mechanism are tests of actuating mechanism within the control and protection system on the reactor installation, critical, subcritical stand. (as revised by Rostechnadzor Order N 395 dated 28.09.2017) End switch is a device for issue of information signals on reaching of extreme working positions by the reactivity modifier, as well as a signal on switching off the drive of the actuating mechanism. Reactivity modifier is a device comprising hard elements, which, with their position changing, ensure a change in the reactivity of the core of the reactor, critical, subcritical assembly. (as revised by Rostechnadzor Order N 395 dated 28.09.2017) Movable parts of actuating mechanism are elements of the actuating mechanism moving along with the reactivity modifier. Manual drive is a portable device for manual relocation of the reactivity modifier. Connector is a device for connection or disconnection of an electric cable. The paragraph has been repealed. - Rostechnadzor Order N 395 dated 28.09.2017. Working travel rate is the speed of travel of the reactivity modifier on change of reactivity of the reactor, critical, subcritical assembly for managing the power of the reactor, critical, subcritical assembly during normal operation. (as revised by Rostechnadzor Order N 395 dated 28.09.2017) Coupling link (coupling device) are elements of the actuating mechanism connecting movable parts with the reactivity modifier. Pre-assembly test bench is a device for adjustment, regulation and testing of actuating mechanism. Safety device is a device for protection of elements of electromechanical actuating mechanisms from electric overload. Limit stop (mechanical limit stop of actuating mechanism) is a limiter of travel of movable parts of actuating mechanism. Working travel is a value of displacement of reactivity modifier within the extreme working positions. Electrical lead-in is a device for entry of a cable into the electric drive of actuating mechanism.