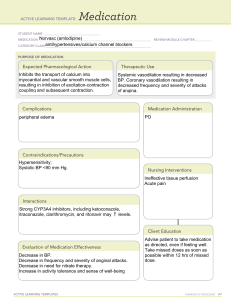
ACTIVE LEARNING TEMPLATE: Medication Brittney Pinckney STUDENT NAME______________________________________ Calcium Gluconate MEDICATION___________________________________________________________________________ REVIEW MODULE CHAPTER____________ Other; Calcium Salts CATEGORY CLASS__Antidotes, _____________________________________________________________________ PURPOSE OF MEDICATION Expected Pharmacological Action Maintain cell membrane and capillary permeability. Helps in transmission of nerve impulses and contraction of cardiac, skeletal, and smooth muscle. Essential for bone formation and blood coagulation. Therapeutic Use Replacement of calcium for deficiencies. Treatment of hyperkalemia, hyper-magnesia, and adjunct in cardiac arrest or calcium channel blocking agent toxicity Complications Little or no urination, swelling, rapid weight gain, lightheadedness, slow or irregular heartbeats, nausea, vomiting, constipation, increased thirst or urination, muscle weakness, bone pain, confusion, lack of energy, and feeling tired Medication Administration Calcium Gluconate should be administered intravenously either directly or by infusion. Adults: 500 mg - 2 grams (5-20 mL). Children: 200-500 mg (2-5 mL). Infants: not more than 200 mg (not more than 2 mL) Contraindications/Precautions Hypercalcemia, renal calculi, ventricular fibrillation, severe respiratory insufficiency patients, renal disease, cardiac disease, Interactions Calcium can decrease the absorption of other drugs such as bisphosphonates (for example, alendronate), tetracycline antibiotics (such as doxycycline, minocycline), estramustine, levothyroxine, and quinolone antibiotics (such as ciprofloxacin, levofloxacin). Certain foods (cereals, spinach) may decrease absorption Evaluation of Medication Effectiveness Increase in serum calcium levels. Decrease in the signs and symptoms of hypocalcemia. Decrease in the signs and symptoms of magnesium toxcity. Muscular issues resolved Nursing Interventions Monitor ECG and BP frequently. Administer infusion slowly. Monitor vital signs throughout infusion. If patient experiences side effects, halt infusion and resume slowly once symptoms stop Client Education Do not take any OTC medication without consulting physician. Maintain diet with adequate calcium levels. Separate other medications as recommended by physician with calcium supplements. Avoid alcohol and smoking. Watch for signs of drug interactions or hyper/hypocalcemia and report to physician immediately Source: ATI Medication Book and https://www.rxlist.com/consumer_calcium_gluconate_gluconate_ca/drugs-condition.htm#what_other_drugs_interact ACTIVE LEARNING TEMPLATES Therapeutic Procedure A7