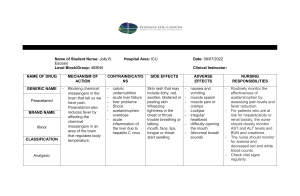
UNFOLDING Reasoning Simulation Cirrhosis Preparation for Care Activity Recognizing Clinical Relationships Review the medical history and home medications of this patient. For each home medication, identify the pharm. classification and expected outcome for this patient its most common side effect (SE). Finally, draw a line to determine which medication treats what condition. Medical History Hepatitis C Home Medications Ibuprofen 600 mg PO every 6 hours PRN for headache Pharm. Classification Expected Outcome Common SE nsaid pain relief gastric ulcers, upset stomach, impaired kidney function Part I: Developing Noticing and Interpreting Skills 1. Which findings from the present problem are most important and noticed by the nurse as clinically significant? Most Important Findings Clinical Significance Abdominal pain, nausea and vomiting, fatigue, decreased appitite, and Hep C diagnosis The presence of these symptoms, such as hepatic encephalopathy, ascites, or spontaneous bacterial peritonitis, in this patient might signify a severe complication linked to his hepatitis C or cirrhosis. They could indicate the progression of liver disease or indicate malnutrition, both of which can have negative effects on patients with liver disease. The recent diagnosis and treatment imply that the patients liver disease may not be effectively managed at this point. Additionally, these circumstances also increase the likelihood of adverse reactions to medications and potential interactions. 2. Which data from the social history is most important and noticed by the nurse as clinically significant? Most Important Findings Clinical Significance He serves as a caregiver for his wife who suffers from dementia while also working part-time at a convenience store. This situation could potentially lead to increased stress levels for the patient, impacting his ability to allocate time and energy towards maintaining his own health. It is possible that he has been neglecting proper nutrition and sufficient rest, which could further exacerbate his symptoms. Additionally, the financial burden he faces may contribute to physical exhaustion. His job at the convenience store exposes him to different individuals, potentially increasing the risk of infections, particularly given his compromised immune system due to liver disease. 3. What psychosocial/holistic care priority will guide how the nurse responds to formulate a plan of care? List interventions by priority and the expected outcome. Psychosocial/Holistic Care Priority Priority Interventions Rationale Expected Outcome Alleviating stress and reducing feelings of anxiety The well-being of individuals can be significantly impacted by the physical discomfort caused by their symptoms. Also, the presence of anxiety can exacerbate the experience of pain and overall discomfort. Pain relief and reduced anxiety © 2023 KeithRN LLC. All rights reserved. No part of this case study may be reproduced, stored in retrieval system or transmitted in any form or by any means, electronic, mechanical, photocopying, recording or otherwise, without the prior written permission of KeithRN UNFOLDING Reasoning Simulation 4. To provide compassionate holistic care for this patient, answer the following questions. They are probably facing considerable discomfort as a result of his physical symptoms, including abdominal pain, nausea, and vomiting. What is the patient likely Additionally, his lack of appetite and potential malnutrition may be causing fatigue and a general feeling of being unwell. Considering his diagnosis of hepatitis C, he may be experiencing anxiety and fear regarding what lies ahead, particularly given his role as a experiencing/feeling right now in recent caregiver for his wife with dementia. The juggling act of balancing his part-time job, caregiving responsibilities, and his own health might leave him feeling overwhelmed and stressed. this situation? What can you do to engage yourself with this patient's experience, and show that they matter to you as a person? Active listening: Dedicate time to actively listen to the the patient as they expresses his concerns, fears, and emotions. Encourage him to openly share his experiences, and provide reassurance that his feelings are acknowledged and respected. Empathy: Display empathy towards their situation, demonstrating understanding and compassion. Validate his feelings of stress and being overwhelmed, considering the challenges he currently faces. 5. Which findings from the contextual factors are most important and noticed by the nurse as clinically significant? Most Important Findings Clinical Significance The unit is currently experiencing a shortage of staff, resulting in a busy day at the urgent care facility. The impact of these circumstances could potentially compromise the level of care provided to every patient. It raises the risk of errors, reduces the amount of time allocated to each patient, and may lead to delays in treatments and interventions. Patient Care Begins 6.Which vital sign findings are most important and noticed by the nurse as clinically significant? Most Important Data Clinical Significance Heart rate is 132 when he stands This reading significantly exceeds the typical range and suggests the presence of tachycardia. 6. What assessment data needs to be noticed as most important? Interpret clinical significance. Most Important Data Clinical Significance Abdominal pain, nausea, and vomiting The pain experienced by the patient might serve as an indication of a liver disease complication, such as ascites. This could imply a deterioration in his liver disease condition or possibly signify the presence of other gastrointestinal problems. © 2023 KeithRN LLC. All rights reserved. No part of this case study may be reproduced, stored in retrieval system or transmitted in any form or by any means, electronic, mechanical, photocopying, recording or otherwise, without the prior written permission of KeithRN UNFOLDING Reasoning Simulation Auscultate Breath Sounds Place a circle on the chest where the nurse would place the stethoscope to auscultate the right upper lobe. Click this link to listen. Identify what type of breath sounds are heard, and interpret their clinical significance. Breath Sounds Clinical Significance Stridor The clinical significance of stridor lies in its indication of a potentially critical respiratory issue that warrents urgent attention. Auscultate Heart Sounds Place a circle on the chest where the nurse would place the stethoscope to auscultate the apical pulse. Click this link to hear breath sounds. Identify what type of heart sounds are heard, and interpret their clinical significance. Heart Sounds Clinical Significance Normal sinus rhythem Heart appears healthy As you complete the head-to-toe assessment, you notice this softball-sized discoloration on his abdomen. 7. Which findings are most important and noticed by the nurse as clinically significant? Most Important Findings Clinical Significance Bruising The possibility of a coagulopathy arises, which is a bleeding disorder that may occur as a complication of advanced liver disease, characterized by reduced production of clotting factors. © 2023 KeithRN LLC. All rights reserved. No part of this case study may be reproduced, stored in retrieval system or transmitted in any form or by any means, electronic, mechanical, photocopying, recording or otherwise, without the prior written permission of KeithRN UNFOLDING Reasoning Simulation 8. Which findings are most important and noticed by the nurse as clinically significant? Most Important Findings Clinical Significance These spots might serve as indications of various conditions. Could be indicative of a clotting problem Lab Results Hematology: Complete Blood Count (CBC) WBC HGB PLTS % Neuts % Lymphs % Monos % Eosin Bands Which diagnostic findings are most important and noticed by the nurse as clinically significant? Most Important Data Clinical Significance TREND Improved/Declined/No Change White blood cells, hemoglobin, and platelet count The WBC count has risen from 9.5 to 12.8, which can be indicative of an infection or inflammation within the body. The hemoglobin level has decreased from 11.5 to 10.2, which signifies the presence of anemia. The platelet count has decreased from 126 to 75, a common occurrence in cirrhosis as a result of reduced production and increased destruction in the spleen, known as thrombocytopenia. All declined Metabolic Panel Na K Cl CO2 AG Gluc Ca BUN Creat GFR Which diagnostic findings are most important and noticed by the nurse as clinically significant? Most Important Data Clinical Significance TREND Improved/Declined/No Change 8 high Creatinine- 1.5 high An elevated BUN level may indicate reduced kidney function or dehydration, both of which are potential occurrences in cirrhosis. Similarly to BUN, an increased creatinine level can suggest impaired kidney function, which is commonly observed in advanced cirrhosis. Both declined © 2023 KeithRN LLC. All rights reserved. No part of this case study may be reproduced, stored in retrieval system or transmitted in any form or by any means, electronic, mechanical, photocopying, recording or otherwise, without the prior written permission of KeithRN UNFOLDING Reasoning Simulation Liver Panel Albumin Ammonia Total Bili Direct Bili InDirect Bili Alk Phos ALT AST Which diagnostic findings are most important and noticed by the nurse as clinically significant? Most Important Data Clinical Significance TREND Improved/Declined/No Change Low levels of albumin, a liver-produced protein, can indicate poor liver function, malnutrition, or absorption issues. This can contribute to fluid imbalance and edema, which are common complications of cirrhosis. In this case, the albumin level is significantly elevated, surpassing the normal range of approximately 0.1-1.2 mg/dL.High levels of bilirubin, a waste product processed by the liver, can indicate liver dysfunction or bile duct obstruction. This can result in jaundice, a condition characterized by yellowing of the skin and eyes.The alkaline phosphatase level is 285 IU/L, which exceeds the normal range of about 44-147 IU/L. Elevated alkaline phosphatase levels can occur in conditions that damage the liver or bile ducts, indicating liver dysfunction or bile duct disease. The ALT level is 128 U/L, indicating elevated levels compared to the normal range of about 7-55 U/L. ALT is an enzyme predominantly found in the liver, and increased levels can suggest liver damage. Similarly, the AST level is 124 U/L, also exceeding the normal range of approximately 8-48 U/L. Like ALT, AST is an enzyme present in the liver, and elevated levels can indicate liver damage Albumin Total bili Alk Phos ALT AST All have declined Coagulation Reference Range: Current Prior adm. INR 0.9-1.1 1.5 ! 1.1 PT 10-13 seconds -- aPTT 25-35 seconds -- Which diagnostic findings are most important and noticed by the nurse as clinically significant? Most Important Data Clinical Significance TREND Improved/Declined/No Change The current INR reading is 1.5, showing an increase from the prior admission's value of 1.1. The normal range for INR is 0.9-1.1. A high INR can signify an extended blood clotting time, potentially indicating a bleeding disorder or the influence of blood-thinning medication. This becomes particularly significant for patients with liver disease, as the liver plays a role in producing the necessary proteins for blood clotting. A rising INR in a cirrhosis patient may suggest a deterioration in liver function, as the liver's ability to produce these proteins diminishes, elevating the risk of bleeding. INR Declined Lab Planning Activity Identify the most important lab values to monitor for this patient. They can be normal or abnormal. Then record the normal range of each relevant lab value, the critical or red flag value, its physiologic significance and priority nursing assessments and/or interventions. Lab Name ALT Normal Range Critical Value Physiologic Significance Albumin, which is synthesized by the liver, plays a crucial role in maintaining osmotic pressure and preventing fluid leakage from blood vessels. A low albumin level can suggest malnutrition or poor liver function, contributing to fluid imbalance and edema. Nursing interventions involve monitoring for signs of fluid overload, such as peripheral edema, ascites, and shortness of breath. Regular assessment of nutritional status is necessary, and a high-protein, high-calorie diet should be provided as tolerated. Total Bilirubin: Normal Range: 0.1-1.2 mg/dL, Critical Value: >2.5 mg/dL. Bilirubin is a byproduct of red blood cell breakdown and is metabolized by the liver. Elevated levels can result in jaundice and indicate liver dysfunction. Nursing interventions include monitoring for signs of jaundice and changes in stool or urine color. Adequate hydration should be encouraged to facilitate bilirubin excretion. ALT and AST: Normal Range: ALT 7-55 U/L, AST 8-48 U/L, Critical Value: >3 times the upper limit of normal. These enzymes are released into the bloodstream when liver cells are damaged. Increased levels suggest liver damage or inflammation. Monitor for signs of liver dysfunction, including jaundice, dark urine, pale stools, and confusion or altered mental status. BUN and Creatinine: Normal Range: BUN 7-20 mg/dL, Creatinine 0.6-1.2 mg/dL, Critical Value: BUN >50 mg/dL, Creatinine >3 mg/dL. These waste products are cleared by the kidneys. Elevated levels can indicate impaired kidney function. Monitor for signs of fluid overload, changes in urine output, and alterations in electrolytes. Adequate hydration should be ensured. Priority Nursing Assessments Nursing interventions involve regular monitoring for indicators of fluid overload, such as peripheral edema, ascites, and difficulty breathing. Nutritional status should be consistently assessed, and a diet rich in protein and calories should be offered based on individual tolerance. © 2023 KeithRN LLC. All rights reserved. No part of this case study may be reproduced, stored in retrieval system or transmitted in any form or by any means, electronic, mechanical, photocopying, recording or otherwise, without the prior written permission of KeithRN UNFOLDING Reasoning Simulation Part II: Developing Responding Skills 1. Interpreting clinical data collected, list at least two problems that are possible for this patient? Which problem is the priority? Possible Problems Priority Problem Pathophysiology of Priority Problem Deteriorated liver function due to cirrhosis is evident, with potential ascites indicated by a notable discoloration on the abdomen, decreased albumin levels, and elevated bilirubin, AST, and ALT. There is a possibility of Hepatorenal Syndrome, as evidenced by elevated BUN and creatinine levels. Cirrhosis is an advanced phase of liver scarring that occurs as a result of various liver diseases and conditions, including hepatitis and chronic alcoholism. In this patient's case, the diagnosis of Hepatitis C suggests that it is likely the underlying cause of his cirrhosis. Decompensated cirrhosis follows the compensated stage and is characterized by the emergence of complications. The presence of a substantial discoloration on Darius's abdomen, along with his abdominal discomfort, raises significant concern for the development of ascites 2. What body system(s) will you assess most thoroughly based on the primary medical problem? What specific assessments will you implement? Priority Body System(s) Priority Assessments Consistently evaluate the size of the abdomen and diligently observe for any increases, as they may suggest a deterioration of ascites. Regularly track vital signs. Cirrhosis, particularly when accompanied by ascites, can lead to fluctuations in blood pressure and heart rate. Closely monitor urine output, as a decrease in urine production can be indicative of deteriorating renal function or the development of hepatorenal syndrome, a complication associated with cirrhosis. Gastrointestinal System Cardiovascular System Renal System Medical Management of Care 3. Identify the rationale for each provider order and its expected outcome. Provider Orders: Rationale: Establish peripheral IV The client is experiencing symptoms of nausea and vomiting, which NS 0.9% bolus of 1000 mL Ondansetron 4 mg IV every 4 hours PRN Recheck orthostatic BP following bolus. increase the risk of dehydration. Establishing IV access enables the administration of fluids and medications. This order is intended to restorethe client's fluid balance due to vomiting, potential decreased intake, and possible redistribution of fluids caused by ascites. Normal saline is an isotonic solution that maintains the body's electrolyte balance. Ondansetron is an antiemetic medication used to alleviate nausea. Given the client's persistent symptoms of nausea and vomiting, this medication can help manage these symptoms and prevent further disruptions in fluid and electrolyte levels caused by excessive vomiting. Orthostatic blood pressure measurement is employed to assess how the cardiovascular system responds to changes in body position. It can provide insight into volume depletion and dehydration. 4. For the order of ondansetron, complete the table below. Mechanism of Action Most Common Side Effects Ondansetron functions by inhibiting the action of serotonin, a natural substance in the body responsible for inducing vomiting. The most frequently observed adverse effects of ondansetron include headache, dizziness, drowsiness, and constipation. Expected Outcome: The anticipated outcome is to preserve and enhance the client's hydration level while establishing a means for medication delivery. The desired outcome is an improved hydration status, normalized blood pressure, and a reduced risk of additional kidney damage.The intended outcome is a decrease in nausea and vomiting, resulting in enhanced comfort, increased oral intake, and improved hydration status.The expected outcome involves consistent blood pressure readings, indicating a suitable cardiovascular response to the administered fluids. Client Education Before Administering Prior to administering ondansetron, it is essential to notify the client that this medication is employed to alleviate his symptoms of nausea and vomiting. He should be provided with information regarding potential side effects and instructed to promptly report any severe symptoms, such as blurred vision or irregular heartbeat. © 2023 KeithRN LLC. All rights reserved. No part of this case study may be reproduced, stored in retrieval system or transmitted in any form or by any means, electronic, mechanical, photocopying, recording or otherwise, without the prior written permission of KeithRN UNFOLDING Reasoning Simulation Priority Setting 5. Determine the order of priority the nurse will implement each order and the rationale for the order you chose. Care Provider Orders Order of Priority Rationale 1. Establish peripheral IV IV, Normal Saline bolus, 2. NS 0.9% bolus of 1000 Ondansetron, Recheck mL BP 3. Ondansetron 4 mg IV every 4 hours PRN nausea 4. Recheck orthostatic BP This is the first priority as it allows for fluid and medication administration. It ensures a route for subsequent interventions and is crucial for addressing dehydration and potential medication needs. The administration of normal saline bolus is the next priority after establishing IV access. It aims to replenish fluid balance due to vomiting, reduced intake, and potential third spacing of fluids caused by ascites. Addressing dehydration is essential for maintaining overall stability. After addressing fluid balance, managing nausea is the subsequent priority. Ondansetron, as an antiemetic medication, helps control nausea and prevents further fluid and electrolyte imbalances due to excessive vomiting. Administering it on an as-needed basis provides symptom relief. Once the immediate interventions for fluid administration and symptom management are in progress, rechecking orthostatic blood pressure is the final priority. This assessment helps evaluate the cardiovascular response to position changes and provides insight into volume depletion, guiding further interventions if necessary. The order of priority ensures that immediate needs are addressed first followed by symptom management and a subsequent assessment to evaluate the effectiveness of interventions. Nursing Management of Care 6. After interpreting clinical data collected, identify the nursing priority and three priority interventions. For each intervention write the rationale and expected outcome. Nursing Priority Priority Intervention(s) Rationale Administer the prescribed fluid therapy of a 1000 mL bolus of normal saline Administer the prescribed medication Given the client's symptoms of nausea, vomiting, and potential dehydration, it is vital to restore his fluid and electrolyte balance. The anticipated outcome is to enhance his hydration status, increase blood volume, and support kidney function. Effectively managing the client's nausea will contribute to his overall comfort and may reduce further episodes of vomiting and associated fluid loss. The expected outcome is a reduction in nausea and vomiting, improved comfort, and an enhanced ability to consume oral intake. Expected Outcome Expected outcomes include improved hydration, increased blood volume, and enhanced kidney function. Problem Recognition 7. To prevent a complication based on the primary problem, answer each question in the table below. Based on the client's diagnosis of cirrhosis and his symptoms, the leading Identify the worst potential serious complication is likely hepatic encephalopathy, characterized by a deterioration in brain function caused by advanced liver possible/most likely disease. complication? What interventions can prevent this complication from developing? (if applicable) What clinical data will indicate this complication early? What nursing interventions will the nurse implement if the anticipated complication develops? Effective management of the client's hepatitis C and cirrhosis requires regular medical check-ups, monitoring of laboratory tests, and adherence to prescribed medications and dietary recommendations. Timely intervention is crucial to address potential triggers such as infections, gastrointestinal bleeding, or electrolyte imbalances.Vigilant monitoring and appropriate management of constipation are essential to prevent excessive ammonia absorption, a significant factor in the development of hepatic encephalopathy. Initial indications of hepatic encephalopathy may manifest as alterations in personality, mood, or sleep patterns, along with confusion, forgetfulness, decreased concentration, and reduced mobility. Advanced symptoms may encompass pronounced confusion, drowsiness, and in severe instances, loss of consciousness. The client's ammonia levels may elevate, and liver function tests may exhibit further decline. Promptly alert the healthcare provider: This situation necessitates immediate notification of the healthcare provider to facilitate urgent diagnostic assessments and treatment. Promote patient safety: In the event of confusion or drowsiness, precautions must be implemented to prevent potential falls or harm. Monitor vital signs and neurological condition: Consistent monitoring allows for the evaluation of condition advancement and treatment efficacy. Administer prescribed medications: Medications like lactulose and rifaximin may be administered to lower blood ammonia levels. Education/Discharge Planning 8. To prepare this client for discharge, what educational topics need to be included in a teaching plan for this patient and/or family? Priority Topics Rationale Understanding of cirrhosis, hepatitis C and medication management Offer comprehensive information about these conditions, their consequences, progression, and common symptoms to be vigilant about. This will enhance the client and his family's comprehension of his condition and the rationale behind his care plan. Provide instruction on each medication, including its intended purpose, timing, and possible side effects. This encompasses his antiviral therapy and any prescribed medications to address symptoms or complications associated with cirrhosis. © 2023 KeithRN LLC. All rights reserved. No part of this case study may be reproduced, stored in retrieval system or transmitted in any form or by any means, electronic, mechanical, photocopying, recording or otherwise, without the prior written permission of KeithRN UNFOLDING Reasoning Simulation 9. Which interprofessional team member would the nurse need to consult and collaborate with to promote and maintain health after discharge? Team Member Rationale Part III: Developing Evaluation Skills Darius was discharged from the emergency department following fluid resuscitation and resolution of his nausea and vomiting. Today, six months later, he arrives in the emergency department via EMS after being found unresponsive by his son. Current VS: • T: 99.5 F/37.5 C (oral) • P: 118 (regular) • R: 22 • BP: 92/50 • O2 sat: 95% room air When you remove his shirt to place Darius in a gown, this is what you notice: 1. From this picture, which two assessment findings are most important and noticed by the nurse as clinically significant? Most Important Findings Ascites Altered mental status Clinical Significance Ascites refers to the buildup of fluid in the abdominal cavity, often caused by portal hypertension associated with cirrhosis. The client's significant ascites indicates the progression of his liver disease, potentially leading to worsened liver function and decompensated cirrhosis. It can cause discomfort, limited mobility, and respiratory difficulties due to pressure on the diaphragm. The severity of his ascites suggests a high risk for complications such as spontaneous bacterial peritonitis or hepatorenal syndrome. The client's unresponsiveness, as reported earlier, is a critical observation. It can be indicative of hepatic encephalopathy, a complication of advanced liver disease like cirrhosis. Hepatic encephalopathy occurs when the liver fails to adequately remove toxins from the blood, resulting in the accumulation of toxins that impair brain function. It can manifest as mild confusion, complete unresponsiveness, or even coma. © 2023 KeithRN LLC. All rights reserved. No part of this case study may be reproduced, stored in retrieval system or transmitted in any form or by any means, electronic, mechanical, photocopying, recording or otherwise, without the prior written permission of KeithRN UNFOLDING Reasoning Simulation Current Assessment: GENERAL SURVEY PAIN NEUROLOGICAL HEAD RESPIRATORY CARDIAC ABDOMEN GENITOURINARY INTEGUMENTARY Disheveled, appears unkempt, lying in bed, eyes closed, no response to external environment Unable to assess Speech mumbled, marked confusion Head normocephalic. No obvious injury. Non-labored respiratory effort Warm & dry, 2+ pitting edema lower extremities, heart sounds regular, pulses strong, equal with palpation at radial/pedal/post-tibial landmarks Abdomen grossly distended, firm to touch, bowel sounds inaudible per auscultation Small amount of brown, foamy urine Skin integrity intact, color normal for patient ethnicity. Sclera yellow bilaterally. 2. For each finding, determine if it indicates the patient's condition has improved, has not changed, or has declined. Assessment Finding Improved No Change Declined x Marked confusion, mumbled speech x Non-labored respiratory effort x Abdomen grossly distended x Brown, foamy urine x Sodium 127 mEq/L x Potassium 2.9 mEq/L x Creatinine 1.9 x INR 2.6 nmol/L Ammonia 78 mcgl/dL x 3. Is the overall status of your client: DECLINED a. Improved b. Declined c. No change 4. After evaluating the patient, identify the current nursing priority and which action(s) should the nurse take. List interventions by priority and the expected outcome. Nursing Priority Priority Interventions: Provide a detailed update to the healthcare provider and administer the prescribed medications for hepatic encephalopathy. Addressing hepatic encephalopathy and associated complications while closely monitoring for any worsening signs and symptoms. Rationale: The client is displaying severe hepatic encephalopathy symptoms and worsening conditions, necessitating urgent medical intervention. The healthcare provider will promptly devise an action plan. Administer the prescribed medications for hepatic encephalopathy. These medications aid in lowering blood ammonia levels, a common contributor to hepatic encephalopathy, resulting in decreased confusion and improved consciousness. Expected Outcome: Reduced BUN level © 2023 KeithRN LLC. All rights reserved. No part of this case study may be reproduced, stored in retrieval system or transmitted in any form or by any means, electronic, mechanical, photocopying, recording or otherwise, without the prior written permission of KeithRN UNFOLDING Reasoning Simulation 5. Identify the rationale for each provider order and its expected outcome. Provider Orders Rationale Lactulose 200 g/300 mL Lactulose is effective in reducing blood ammonia levels. rectal x1 NOW Elevated ammonia levels can contribute to hepatic encephalopathy, which could be responsible for the client's confusion and unresponsiveness. There is a Potassium Chloride 10 mEq deficiency in potassium levels. This treatment aims to IVPB (x4) each dose over 1 restore potassium levels and restore electrolyte balance. hour. Recheck potassium per Considering the client's critical clinical state, close hospital protocol monitoring and the potential need for immediate intervention make an ICU setting the most suitable option. Transfer to ICU Expected Outcome The client experiences a reduction in confusion, an improvement in consciousness, and a decrease in blood ammonia levels. Potassium levels are normalized, potentially alleviating cardiac irregularities and muscle weakness. Enhanced monitoring allows for early detection of complications and prompt intervention in case of worsening condition. 6. For the new order of lactulose and potassium, apply your knowledge to complete the table below. Mechanism of Action Most Common Side Effects Client Education Before Administering Inform the client that lactulose is administered to alleviate confusion by reducing ammonia Lactulose Diarrhea, bloating, gas, stomach levels. Provide information about the potential side effects, with particular emphasis on diarrhea. cramps Potassium Chloride 10 mEq IVPB Nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and abdominal discomfort, and phlebitis at the IV site Educate the client about the administration of potassium to address low blood levels. Discuss the typical side effects and emphasize the close monitoring of the infusion. Instruct them to promptly report any IV discomfort to the healthcare team. The nurse has implemented all orders. 7. Five hours later, the potassium IVPBs are complete, and you reassess your patient. You complete a redraw of the BMP and collect the following assessment data: Assessment Finding Improved No Change Declined x Alert to self, incomprehensible speech x Non-labored respiratory effort x Abdomen grossly distended x Brown urine x The patient has had 2 loose bowel movements x Sodium 132 mEq/L x Potassium 3.1 mEq/L x Creatinine 2.0 x Ammonia 70 mcgl/dL 8. Write a concise narrative nurse's note to document what was most important at the end of your shift in the medical record. The client was reevaluated following the completion of potassium IVPBs. The patient remains awake, but their speech remains unintelligible. Respiratory effort remains unchanged and non-labored.Abdominal distension persists and is firm to the touch, with no audible bowel sounds on auscultation. The patient has experienced two loose bowel movements since the last assessment, possibly due to the effects of lactulose. The patient's urine continues to appear brownThe latest laboratory results after potassium replacement reveal a sodium level of 132 mEq/L, potassium level of 3.1 mEq/L, creatinine level of 2.0, and a decrease in ammonia levels to 70 mcgl/dL.These findings indicate an improvement in the patient's electrolyte imbalances; however, concerns remain regarding hepatic function and renal indices. Continuous monitoring and reassessment of the patient's neurological status and overall condition are advised. Further management will be continued in the ICU according to the healthcare provider's instructions. © 2023 KeithRN LLC. All rights reserved. No part of this case study may be reproduced, stored in retrieval system or transmitted in any form or by any means, electronic, mechanical, photocopying, recording or otherwise, without the prior written permission of KeithRN UNFOLDING Reasoning Simulation Your patient is being transferred to ICU. Write out your SBAR report to the nurse who will be caring for your patient. Situation: Name/age: Darius, a 67-year-old male with a history of Hepatitis C, was brought to the emergency department by EMS after being discovered unresponsive by his son. While his condition was stabilized in the ED, his lab results have shown BRIEF summary of primary problem: changes, and persistent abdominal distension necessitates his transfer to the intensive care unit for vigilant monitoring and comprehensive care. Day of admission/post-op #: Background: Primary problem/diagnosis: RELEVANT RELEVANT Six months ago, Darius was hospitalized to address fluid resuscitation and alleviate symptoms of nausea and vomiting. During this current admission, he presented with confusion, a visibly distended abdomen, foamy brown urine, and abnormal past medical history: significant laboratory findings. Currently, his sodium level is 132 mEq/L, potassium level is 3.1 mEq/L, creatinine level is 2.0, and ammonia level is 70 mcg/dL. In the emergency department, he background data: received Lactulose and Potassium Chloride. Subsequently, he experienced two instances of loose bowel movements following the administration of Lactulose. Assessment: Current vital signs: RELEVANT body system nursing assessment data: RELEVANT lab values: TREND of any abnormal clinical data (stable/increasing/decreasing): Throughout his stay in the emergency department, the patient's condition has remained stable, although he continues to experience incomprehensible speech and abdominal distension. There have been no indications of labored respiratory effort. However, there is evidence of deteriorating renal function, as reflected by the presence of brown urine and elevated creatinine levels. Although the administration of lactulose has resulted in a slight reduction in ammonia levels, they still remain elevated. How have you advanced the plan of care? Patient response: INTERPRETATION of current clinical status (stable/unstable/worsening): Recommendation: Darius requires diligent monitoring of his renal function and electrolyte levels. Given his recent episode of confusion, regular assessments of his mental status are necessary. It is important to closely observe his response to Lactulose and monitor the frequency and consistency of his bowel movements, as Lactulose is being used to address his hyperammonemia. Given his distended abdomen, it is crucial to monitor for signs of rising intra-abdominal pressure and related complications. Lastly, his history of Hepatitis C requires careful management. © 2023 KeithRN LLC. All rights reserved. No part of this case study may be reproduced, stored in retrieval system or transmitted in any form or by any means, electronic, mechanical, photocopying, recording or otherwise, without the prior written permission of KeithRN UNFOLDING Reasoning Simulation Nurse Reflection To strengthen your clinical judgment skills, reflect on your knowledge and the decisions made caring for this patient by answering the reflection questions below. Reflection Question As you worked through this simulation, how did it make you feel? What did you already know and do well on this simulation? Nurse Reflection I was frustrated a few times becuase the text boxes were sometimes uncooperative, but other than that it wasn't too terrible. What areas do you need to develop/improve? I need to improve on my ability to put my thoughts into words that make sense in a medical sense. What did you learn? How will you apply what was learned to improve patient care? I learned that liver issues can cause a wide variety of other problems that can be challening to deal with as a healthcare worker. I think this can be applied in my own life by teaching me the importance of looking beyond what is the pricniple problem I was kinda familiar with cirrhosis becuase it is what killed my grandfather, but this let me dive deeper into it. © 2023 KeithRN LLC. All rights reserved. No part of this case study may be reproduced, stored in retrieval system or transmitted in any form or by any means, electronic, mechanical, photocopying, recording or otherwise, without the prior written permission of KeithRN