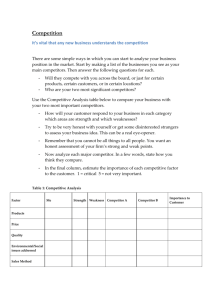
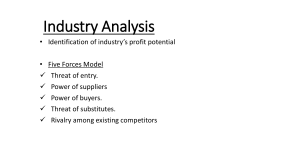
SESSION 4 WELCOME OBJECTIVE • This session is designed to impart learnings on: 1. Industry & competitor analysis, 2. Developing an effective Business model Industry Analysis Important considerations starting a new venture are: before 1. Is this the right industry to start a new venture? 2. Does the industry contain markets that are ripe for innovation or are underserved? 3. Are there positions in the industry that will avoid some of the negative attributes of the industry as a whole? Industry Trends • The two most important trends for entrepreneurs to evaluate are 1. Environmental Trends 2. Business Trends: The Five Forces Model Michael FIVE forces understanding porter model the designed framework structure of for an i n d u s t r y. T h e s e f o r c e s a r e : 1. The threat of substitute 2. The entry of new competitors 3. Rivalry among existing firms 4. The bargaining power of suppliers 5. The bargaining power of buyers All these forces have direct impact average rate of return for the firm. on The FIVE Forces Model 1. Threat of substitute: Industries are more attractive when the threat of substitutes is l o w. T h i s m e a n s t h a t p r o d u c t s o r s e r v i c e s from other industries can’t easily serve as substitutes for the products or services being m a d e a n d s o l d i n t h e f o c a l f i r m ’ s i n d u s t r y. 2. Threat of new Entrants: Industries are more attractive when the t h r e a t o f e n t r y i s l o w. T h i s m e a n s t h a t c o m p e t i t o r s c a n n o t e a s i l y e n t e r t h e i n d u s t r y. The six major sources of barriers to entry are: a. Economics of scale b. Product differentiation c. Capital requirements d. Cost advantage e. Access to distribution channel f. Government and legal barriers The FIVE Forces Model 3. Rivalry among existing firms: In most industries, the major determinant of industry profitability is the level of competition among t h e f i r m s a l r e a d y c o m p e t i n g i n t h e i n d u s t r y. There are four primary factors that determine the nature and intensity of the rivalry among existing firms in an industry: 1. Number and balance of competitors 2. Degree of difference between products 3. Growth rate of an industry 4. Level of fixed costs The FIVE Forces Model 4. Bargaining Power of Supplie rs: Industries are more attractive when the bargaining power of suppliers is low. Several factors have an impact on the ability of suppliers to exert pressure on buyers and suppress the profitability of the industries they serve. These include the following: 1. Supplier concentration 2. Switching costs 3. Attractiveness of substitutes 4. Threat of forward integration The FIVE forces Model 5. Bargaining pow er of buyers: Industries are more attractive when the bargaining power of buyers (a start-up’s c u s t o m e r s ) i s l o w. S e v e r a l f a c t o r s a f f e c t buyers’ ability to exert pressure on suppliers and suppress the profitability of t h e i n d u s t r i e s f r o m w h i c h t h e y b u y. T h e s e include the following: 1. Buyer group concentration 2. Buyer ’s costs 3. Degree of standardization of supplier ’s 4. Threat of backward integration products Industry Types The five most prevalent industry types are: • Emerging: An emerging industry is a new industry in which standard operating procedures have yet to be developed. The firm that pioneers or takes the leadership of an emerging industry often captures a first-mover advantage. • Fragmented: A fragmented industry is one that is characterized by many firms of approximately equal size. The primary opportunity for start-ups in fragmented industries is to consolidate the industry and establish industry leadership because of doing so • Mature: A mature industry is an industry that is experiencing slow or no increase in demand, has numerous repeat (rather than new) customers, and has limited product innovation. Entrepreneurs introduce new product innovations to mature industries Industry Types The five most prevalent industry types are: • Declining: A declining industry is an industry that is experiencing a reduction in demand. Typically, entrepreneurs shy away from declining industries. • Global: A global industry is an industry that is experiencing significant international sales. Many start-ups enter global industries and from day one try to appeal to international rather than just domestic markets. Competitor Analysis • After a firm has gained an understanding of the industry and the target market in which it plans to compete, the next step is to complete a competitor analysis. • A competitor analysis is a analysis of a firm’s competition. detailed • It helps a firm understand the positions of its major competitors and the opportunities that are available to obtain a competitive advantage in one or more area Competitor Analysis • The steps of competitor analysis are: 1. Identifying competitor a. Direct Competitor: Businesses offering identical or similar products b. Indirect competitor: substitute products Businesses offering close c. Future Competitor: Businesses that are not yet direct or indirect competitors but could be any time. 2. Gathering competitive intelligence: The information that is gathered by a firm to learn about its competitors is referred to as competitive intelligence. 3. Preparing competitive analysis grid: A competitive analysis grid is a tool for organizing the information a firm collects about its competitors BUSINESS MODEL BUSINESS MODEL • A business model is a firm’s plan or diagram for how it competes, uses its resources, structures its relationships, interfaces with customers, and creates value to sustain itself based on the profits it earns. • There is no standard business model, no hardand-fast rules that dictate how a firm in a particular industry should compete. • A firm’s business model is developed after the feasibility analysis stage of launching a new venture. Traditional vs. Innovative Business Model VALUE CHAIN • The value chain is the string of activities that moves a product from the raw material stage, through manufacturing and distribution, and ultimately to the end user. • The value chain consists of primary activities and support activities. • The primary activities have to do with the physical creation, sale, and service of a product or a service, while the support activities provide reinforcement for the primary activities. A business model consisting of the following components: Components of Business Model Core strategy (how a firm competes) Strategic resources (how a firm acquires and uses its resources) Partnership network (how a firm structures and nurtures its partnerships) Customer interface (how a firm interfaces with its customers Core Strategy • The first component of a business model is the core strategy, which describes how a firm competes relative to its competitors. • Mission Statement: The primary elements of a core strategy are the firm’s mission statement, the product/market scope, and the basis for differentiation. A firm’s mission statement, describes why it exists and what its business model is supposed to accomplish. • Product/Market Scope: A company’s product/market scope defines the products and markets on which it will concentrate. The choice of product has an important impact on a firm’s business model • Basis for Differentiation: A new venture should differentiate itself from its competitors in some way that is important to its customers and is not easy to copy. A firm typically choose one of two generic strategies • Cost leadership • Differentiation) Strategic Resources • A firm is not able to implement a strategy without adequate resources. A firm's most important resources are: • Core competencies: A core competency is a resource or capability that serves as a source of a firm’s competitive advantage over its rivals. It is a unique skill or capability that transcends products or markets, makes a significant contribution to the customer’s perceived benefit, and is difficult to imitate. • Stategic assets: Strategic Assets Strategic assets are anything rare and valuable that a firm owns. Companies ultimately try to combine their core competencies and strategic assets to create a sustainable competitive advantage. Partnership Network A firm’s network of partnerships is the third component of a business model. New ventures, in particular, typically do not have the resources to perform all the tasks required to make their businesses work, so they rely on partners to perform key roles. A firm’s partnership network includes suppliers and other partners. • Suppliers: A supplier (or vendor) is a company that provides parts or services to another company. • Other Key Relationships: Along with its suppliers, firms partner with other companies to make their business models work. Strategic alliances, joint ventures, networks, and trade associations are common forms of these partnerships. Customer Interface How a firm interacts with its customers—is the fourth component of a business model. The type of customer interaction depends on how a firm chooses to compete. The three elements of a company’s customer interface are target market, fulfilment and support, and pricing structure. Target Market: A firm’s target market is the limited group of individuals or businesses that it goes after. The target market a firm selects affects everything it does, from the strategic resources it acquires to the partnerships it forges to its promotional campaigns. Fulfilment and Support: Fulfilment and support refers to the channels a company uses and what level of customer support. Pricing Structure: A third element of a company’s customer interface is its pricing structure. Pricing structures vary, depending on a firm’s target market and its pricing philosophy Thank you