Grade 7 EMS Lesson Plan: History of Money & Traditional Societies
advertisement
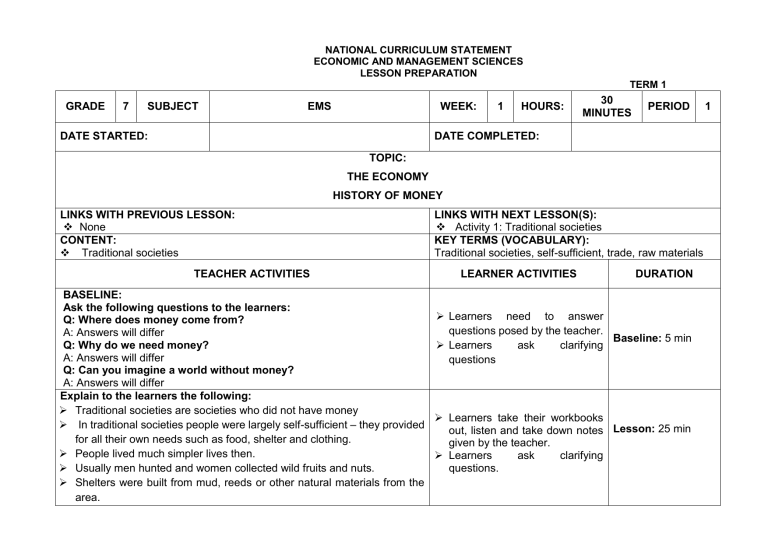
NATIONAL CURRICULUM STATEMENT ECONOMIC AND MANAGEMENT SCIENCES LESSON PREPARATION TERM 1 GRADE 7 SUBJECT EMS WEEK: DATE STARTED: 1 HOURS: 30 MINUTES PERIOD DATE COMPLETED: TOPIC: THE ECONOMY HISTORY OF MONEY LINKS WITH PREVIOUS LESSON: None CONTENT: Traditional societies TEACHER ACTIVITIES LINKS WITH NEXT LESSON(S): Activity 1: Traditional societies KEY TERMS (VOCABULARY): Traditional societies, self-sufficient, trade, raw materials LEARNER ACTIVITIES DURATION BASELINE: Ask the following questions to the learners: Learners need to answer Q: Where does money come from? questions posed by the teacher. A: Answers will differ Baseline: 5 min Q: Why do we need money? Learners ask clarifying A: Answers will differ questions Q: Can you imagine a world without money? A: Answers will differ Explain to the learners the following: Traditional societies are societies who did not have money Learners take their workbooks In traditional societies people were largely self-sufficient – they provided out, listen and take down notes Lesson: 25 min for all their own needs such as food, shelter and clothing. given by the teacher. People lived much simpler lives then. Learners ask clarifying questions. Usually men hunted and women collected wild fruits and nuts. Shelters were built from mud, reeds or other natural materials from the area. 1 Clothes were made from animal skins or women from local plant fibres. There are still some small traditional societies in remote areas in the world today For example, the San people of southern Africa, who are sometimes referred to as hunter-gatherers (because they hunted animals and gathered plants), have lived in traditional societies without money for thousands of years. There are examples of these traditional societies in places like the Amazon jungle in Brazil and in northern Canada where the Inuit people live. The Inuit people built shelters from snow and ice, and hunted seals for their furs and meat. Initially, they had no need for money, but gradually, like most other traditional societies, they began to trade. At first they traded by exchanging things among themselves. Later they traded with other societies who had raw materials and goods that they did not have, such as iron. They needed iron to make knives and steel tips for their spears, which are called harpoons. They traded seal skins for the iron that they needed. Today there are very few Inuit who live traditionally and although they still hunt, they sell seal skins for money to buy things that they need. TEACHING STRATEGY/ METHODOLOGY Co- operative learning Discussion Lecture / Direct instruction Visual/ Practical Demonstration Explanation Observation Simulation Use of technology and instructional resources Question and answer Other : Role playing Other: ASSESSMENT FORM TOOL Memorandum METHOD Baseline Data Response Poster Project Class work Case Study Homework Checklist Formal Informal Control Test Assignment Observation Sheet Educator Examinations Class Test Other: Self Drama Other : Rubric with criteria Other : RESOURCES: OHP/Whiteboard/ Chalkboard/Worksheets/Hand-outs, pencils, pens, Textbook(s), Charts, class notes. TEACHER REFLECTION EXPANDED OPPORTUNITIES/ ENRICHMENT Assist learners who are struggling with the concepts.





