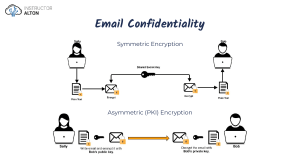
Remote User Authentication Using Asymmetric Encryption GROUP 21 Remote User Authentication Remote user authentication refers to the process of verifying the identity of a user accessing a system or network from a remote location. Objectives The key objectives of remote user authentication are to ensure secure access, prevent unauthorized entry, and protect sensitive information. Importance • Secure authentication is crucial in remote systems to safeguard against unauthorized access and potential data breaches. Digital Certificates • Definition: Digital certificates are electronic documents that bind the identity of a user or entity to a public key. They are issued by a trusted Certificate Authority (CA). • Authentication Usage: Digital certificates are used for authentication in remote systems. They provide a way to verify the identity of users or entities based on the trust placed in the issuing CA. • Role of Certificate Authority: The Certificate Authority verifies the identity of the certificate holder and signs the certificate, ensuring its authenticity and integrity. Authentication Process • Step 1: The user requesting access generates a random session key and encrypts it with the server's public key. • Step 2: The server receives the encrypted session key and decrypts it using its private key. • Step 3: Both the user and the server now share the session key securely for further communication Asymmetric Encryption • Asymmetric encryption, also known as public-key cryptography, is a cryptographic method that uses a pair of keys – a public key and a private key – for encryption and decryption. • Public and Private Keys: The public key is shared openly, while the private key is kept secret. Messages encrypted with the public key can only be decrypted using the corresponding private key. • Key Generation and Usage: Public and private keys are generated mathematically related to each other. The public key is used for encryption, while the private key is used for decryption. Public Key Infrastructure (PKI) • Introduction: Public Key Infrastructure (PKI) is a framework that manages the creation, distribution, and revocation of digital certificates, which are used for authentication and encryption. • Role in Remote User Authentication: PKI plays a crucial role in remote user authentication by providing a trusted infrastructure for issuing and managing digital certificates. • Components: PKI includes a Certificate Authority (CA), which is responsible for issuing and validating certificates, as well as other components like registration authorities and certificate repositories. Benefits and Challenges • Benefits: Using asymmetric encryption for remote user authentication offers several advantages, such as strong security, protection against eavesdropping, and non-repudiation. • Challenges: There are challenges to consider, including the need for a trusted infrastructure, performance impact due to encryption/decryption operations, and key management complexity. Real-World Examples • Example 1: Online Banking • Many banks employ remote user authentication using asymmetric encryption to ensure secure access to online banking systems. • Users are provided with digital certificates that authenticate their identity during login. • Asymmetric encryption guarantees secure communication between users and the banking servers, protecting sensitive financial transactions. Virtual Private Networks (VPNs) • VPN providers utilize asymmetric encryption for remote user authentication to establish secure connections. • Users authenticate themselves using digital certificates, ensuring secure access to the VPN infrastructure. • Asymmetric encryption guarantees the confidentiality and integrity of data transmitted over the VPN. Government Systems • Government agencies often implement remote user authentication using asymmetric encryption for secure access to sensitive systems. • Digital certificates issued by trusted authorities validate the identities of government employees and officials. • Asymmetric encryption ensures secure communication and protects classified information from unauthorized access.