Plate Tectonics Presentation: Earth Structure & Plate Movement
advertisement

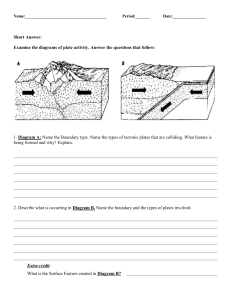
Plate tectonics by Alexander Jankovics Plate Tectonics At the end of the lesson, students will be able to: describe the structure of the Earth and the characteristics of the different layers explain the theory of plate tectonics sketch a labelled drawing of the Earth structure and a world map with the major tectonic plates . STARTER Engage the Brain What’s the difference? Mt Fuji Mt Everest VS . In pairs, you have 3 minutes to discuss what you think the main difference is in how Mt Fuji was formed, compared to the Mt Everest STARTER Engage the Brain Can you remember the layers of the Earth? ?? ?? ?? ?? This is the basic structure of the earth which you might have been shown before. At IGCSE you need to know a more detailed version of this… MAIN ACTIVITIES Gain knowledge & show understanding A cross-section of the Earths structure Crust 0-100 km thick Make your own diagram in your notebook! MAIN ACTIVITIES Gain knowledge & show understanding The Crust The Earth’s crust is very thin compared to the diameter of the planet. Think of it like the skin on an apple. MAIN ACTIVITIES Gain knowledge & show understanding The Crust The crust is made up of sections, called plates, ranging from the very small to the size of an entire continent. Continental crust is much thicker than oceanic crust. Oceanic crust is more dense than continental crust. MAIN ACTIVITIES Gain knowledge & show understanding The Crust Annotate the diagram in your notebook! Continental Crust Oceanic Crust • Below land • Thicker • Below ocean • Thinner • Less dense • More dense • Granite rock • Basaltic rock (35-100 km) (lighter) • (large crystals) (5-10 km) (heavier) • (black/dark grey) The crust is moving!!! Convection heat transfer MAIN ACTIVITIES Gain knowledge & show understanding Crust Convection Currents Mantle *THINK* Convection Cell Convection Currents MAIN ACTIVITIES Gain knowledge & show understanding Core Convection Cell Theory of plate tectonics Tectonic theory People once thought that the oceans and the continents were formed by shrinkage from when the Earth cooled down after being formed. Alfred Wegener proposed something different. Consider Africa and South America: These continents look like they “fit” together. They also have similar rock patterns and fossil records. These two pieces of evidence led me to believe that there was once a single land mass. This is my TECTONIC THEORY. Forming mountains The formation of mountain ranges can be explained by tectonic theory. Consider the Himalayas at the top of India: This is where India is now This is where India was millions of years ago The intense heat and pressure from this process causes the rocks to change structure into metamorphic rocks. The Evidence: Tectonic theory 1) Some continents look like they used to “fit” together 2) Similar rock patterns and fossil records The Problems: Wegener couldn't explain how continental drift happened so nobody believed him The Answer: 1) Scientists discovered 50 years later that the Earth generates massive amounts of heat through radioactive decay in the core. This heat generated convection currents in the mantle causing the crust to move 2) We also now know that the sea floor is spreading outwards from plate boundaries Conclusion – scientists now believe Wegener’s Tectonic Theory MAIN ACTIVITIES Gain knowledge & show understanding With your partner Name that plate! ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? Tectonic Plates MAIN ACTIVITIES Gain knowledge & show understanding North American Caribbean Pacific Cocos Nazca Eurasian Pacific Arabian Philippine African South American IndoAustralian Antarctic Tectonic Plates MAIN ACTIVITIES Gain knowledge & show understanding North American Caribbean Pacific Cocos Nazca Eurasian Pacific Arabian Philippine African South American IndoAustralian Antarctic Map of Plate Boundaries Exit ticket Answer these exam style questions: a)What is a plate? b)What causes plates to move? c)How fast do plates move? 4 minutes