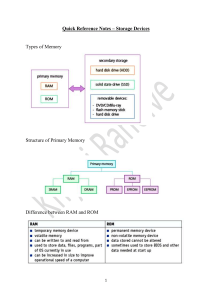
Information representation Magnitude Prefixes Binary Prefix Value Denary Prefix Value Kibi (Ki) Mebi (Mi) Gibi (Gi) Tebi (Ti) 1024 bytes 1024 KiB 1024 MiB 1024 GiB Kilo (k) Mega (M) Giga (G) Tera (T) 1000 bytes 1000 kb 1000 Mb 1000 Gb Binary Coded Decimal (BCD) In a BCD each character in a number is represented by a 4-bit binary number such as 8 is 1000 and 19 is 00011001. If a character is greater than 9 it cannot be represented in BCD. Used to represent numbers in calculators and counters It allows you to accurately measure fractions You can electronically code decimal numbers Hexadecimal Base 16 from 0-9 to A-F Used in MAC and IP Addresses Used to represent colors in HTML Used in error messages and memory dumps Character Sets The characters that a computer can use such as lowercase and uppercase letters, numbers, and symbols. Each character set has a unique code for each symbol. ASCII Extended ASCII Unicode American Standard Code for Information Interchange Contains 128 characters only from the English language. 7 bit Extended ASCII Contains 256 characters from most European languages including English. 8 bit Unicode Contains over 10,000 characters from a variety of languages and is the current standard. Up to 32 bit Bitmap Images A canvas filled with pixels that together represent an object Pixelates when enlarged Large file size Pixel The smallest unit of area in an image representing a single color File Header Data about the image i.e.; Image size Image resolution Color depth Number of colors Image Resolution Number of pixels per unit area of an image. Higher values increase file size Screen Resolution Number of pixels displayed by a screen at a time Bit Depth / Color Depth The number of bits used to represent each color i.e.; 4-bit color means 4 bits so 16 colors because 24 = 16 Higher values increase file size. “Image Size = Image Resolution x Color Depth” Lossy image compression can be done by; Reducing bit depth which means fewer bits are used to store each pixel in an image Reducing color palette which means less colors and therefore less bits per pixel Reducing image resolution which means fewer pixels per unit area so less space is needed Lossless image compression can be done by; Run length encoding (RLE) will look for series of consecutive pixels that store the same color and will index the color and the number of times it occurs Vector Images A series of geometric shapes made with mathematical formulas and their properties often used for logos that cannot be compressed Can be scaled without losing quality as it gets recalculated Has a relatively small file size as it stores equations not pixels Drawing List A list of shapes involved in a vector image i.e.; triangle, R, line Drawing Object An individual shape defined using math in a vector Property Data about the drawing object Line Color Line width Fill Color Shape Sounds The frequency/amplitude of the sound are recorded at regular intervals and are then converted into a histogram when the time comes to replay the sounds. Sampling The process of recording the amplitude and frequency of sound at regular intervals Sampling Rate The number of samples that are taken per unit time. Larger value means more accurate sound but higher file size as more samples are taken. Sampling Resolution The number of bits used to store each sample. Larger values mean more accurate reconstruction of sound but higher file size as more bits are used to store the sound. “Sound Size = Sampling Rate x Sampling Resolution x Time” Analogue Data Continuous real-world data Digital Data Discrete electrical data Compression The act of reducing the size of a file To reduce transfer time Save bandwidth Save storage space There are 2 types of compression techniques; Lossy Lossless Lossy File size compression where original data is lost and cannot be recovered Creates a much smaller file size than lossless Useful when significant size reduction is needed Significant loss in quality Lossless File size compression where original data is not lost and can be recovered Maintains quality Useful when all original data needs to be recovered Communication Networks Devices in a network are inter-connected and communicate between each other You can easily transfer data like files between devices Devices can share resources such as hardware like printers or same software You can store data in drives connected to the network There are two main types of networks Local Area Network Wider Area Network Geographical Region Ownership Medium Speed Congestion LAN Small Private Wi-Fi, Copper, Coaxial High Low WAN Large Public / Private PSTN or satellites Low High There are two types of models between computers on a network Client-Server Peer-to-Peer Client-Server In a client-server model the server stores all the data and performs the tasks requested by the client. The client computer sends requests to the server which will return the requested result back to the client. Such as when loading a webpage. Several requests can be made to the server at a time Some examples include; Sending and receiving emails A company storing files on a central server Print/file/web/proxy/email server There are pros and cons to this model Increased security as only the server has higher privileges Increased performance of individual computers they are not receiving any requests There is central management of data and software so there is always a backup and each device has consistent software Since all operations depend on the main server, if the server is down then the other devices are too It is difficult to scale and relatively expensive The speed of the network decreases exponentially based on the number of devices connected Thin Client A thin client provides input to the server and receives an output from the server Thick Client A thick client carries out some processing on its own before/after sending/receiving data to the server Peer-to-Peer In a peer-to-peer network all devices on the network are of equal status. Each computer has access to all the data and resources of another device therefore each device is responsible for its own safety. The initial cost of the setup is very cheap Each device has complete access to any other device on the network No dependency on a central server Reduced security as the device is vulnerable to viruses from other devices on the network Reduced performance as other devices might be attempting to access the data on this computer No central backup of files so if one computer loses the data, they all might lose access to it Topologies The way of connecting devices on a network Bus Star Mesh Hybrid Bus All devices are connected to a central cable that has terminators at the end. Only one communication can take place at a time. Data terminators are needed to prevent a network crash from data collision Star All devices are connected to a central switch/router via its own route. Hence no collisions can occur and data can be sent out simultaneously. Alternatively, you can use hub instead of switch but its slower. Mesh All devices on a network are connected to each other. The internet itself is an example of mesh topology. Hybrid A combination of topologies used together Cloud Computing Applications and services that deliver over the internet. A third party hosts the data for the user that they can then use. Can exist for public, where it can be used by anyone online, and private use, where it is made specifically for use by a company. Free for small quantities Can access data from anywhere if you have internet Likely better security and recovery options Internet access is required to access it Long upload and download time limits access to data No control over security and backups Transmission Mediums Wired o Twisted Pair / Copper Cable o Fiber-optic cable Wireless o Radio waves o Micro waves o Satellites Copper Cable Twisted pair of copper wires that carry data as electrical signals Fiber Optic Glass/Plastic cables that rely on total internal reflection in order to transmit data as light Speed Distance Interference Security Durability Price Fiber Optic Cable Fast Long Low risk Safe Low High Copper Cable Slow Short; needs repeaters Higher risk Less safe High Low Radio Waves An electromagnetic wave that carries data wirelessly; Wi-Fi Micro Waves An electromagnetic wave that is used to communicate with satellites Satellites A communication device that orbits the Earth and sends/receives data Radio Wave Price Cheap Obstacles Other radio waves Distance Long Size Lower Micro Wave Expensive Physical Objects Shorter High LAN Hardware Certain hardware is used to support the LAN system; Switch Server Network Interface Card (NIC) Wireless Network Interface Card (WNIC) Satellites Expensive High risk Long High Wireless Access Point (WAP) Cables Bridge Repeater Switch Connects all devices on a network and simultaneously broadcasts information to those devices Server A specialized high-speed computer that handles requests from clients or other computers on the network Network Interface Card (NIC) A hardware component that provides each device with a unique MAC address so that it can be identified Wireless Network Interface Card (WNIC) A hardware component that provides each device with a unique MAC address so that it can be identified on a wireless network. It provides an interface by acting as an antenna to a Wi-Fi network. It receives analogue radio waves, that it decodes and converts into a digital data, and it sends digital data, that it encrypts and converts into analogue waves, via the antenna. It checks incoming transmission to see if they match the device’s IP/MAC address and ignores them if they are not. Wireless Access Point (WAP) Allows devices to connect to the network wirelessly that is usually built into a router; such as Wi-Fi Cables Physical means of sending and receiving data on a network Bridge A device that interconnects two or more LANs together and forwards data packets. Repeater A network device that amplifies or regenerates a signal to prevent it from being lost or corrupting Router The router is connected to the switch because it is connected to all devices on the network or to the server because the server acts as the proxy. The router has several functions Maintain a table of MAC and IP addresses Assign private IPs to devices on a network Route packets to their destination but does not direct packets to each device attached to it Receive packets Ethernet The most common form of wired connection used in LAN and WAN that is based on Bus topology Due to this it is possible for data collisions to occur, hence a Carrier Sense Multiple Access/Collision Detection (CSMA/CD) is used. A workstation listens to the communication channel, when it receives a request first it will check if the line is empty, if empty sends data. If a collision occurs because both devices checked if the line was empty at the same time, then the workstation will send an abort signal and the data will be sent back. And a random wait time is assigned to each device before resending. Speed Stability Security Movement Cabling Expandability Wired Faster More Stable More Secure Restricted High Hard a Internet Hardware Modem Public Switch Telephone Network (PSTN) Dedicated Lines Wireless Slower Less Stable Less Secure Free Less Easy Cell phone network Modem A device that allows users to connect to the internet via telephone line. It converts analogue signals into digital signals and vice versa. Public Service Telephone Network (PSTN) Full duplex form of communication over wire that passes through circuit switching centers that remains active during power outages Dedicated Lines A permanent connection for communication that is expensive but faster and more secure/consistent Faster connections Improved security Expensive to set up and maintain Disruption to line would leave no other options Cell phone Network A wireless connection that relies on mobile connection and cell towers that use radio waves Bit Streaming A video is compressed and is then sent as a continuous stream of bits. When it is downloaded the server sends the data to the buffer which then sends a continuous steam of data to the user. Higher bit-rate speed and broadband speed means users can stream the video faster and with less buffering There are two methods of bit-streaming; Real-time On-demand Real-Time Real-Time bit streaming is used when watching a live stream of events that are currently taking place. The event is captured live with a video camera connected to a computer, and it cannot be paused or rewound On-demand On-demand bit streaming is used when watching an event that has taken place in the past. Existing media are encoded to bit streaming format and uploaded to a server. It can be paused and rewound World Wide Web (WWW) The world wide web is the collection of websites that are available on the internet. When you access a website, you are using both the internet and the world wide web because the website is stored on WWW but the internet provides the necessary infrastructure. IP Address The unique address that identifies a device a network and to allow router to send data from the internet to the device. There are 2 formats for an IP address; IPv4 IPv6 – Invented because number of IPv4 addresses will run out Number of Groups Group Range Separator Size Example IPv4 4 0-255 . 32-bit 192.168. 1.1 IPv6 8 0-65535 : 64-bit fe80::d4a8:6435:d2d8:d9f3b11 :: can only show up once in each IPv6 Types of IP Addresses There are many types of IP addresses; Public Private Static Dynamic Public Assigned by the ISP that is visible to any device on the internet. Must be unique on the internet. Only the router has a public IP address, the devices on the network do not as all data passes through the router. This also protects the device from external threats Private Assigned by the router that is visible to devices on the network. Must be unique on that specific network. Static Remains constant whenever a device connects to the internet. Webpages need static IP addresses so that the DNS does not need to be updated every time which can cause delays and errors. Dynamic A new IP address is allocated every time a device connects to the internet Subnetting The practice of dividing a network into smaller groups. Reduces traffic More secure URL Uniform Resource Locator, an easier way to remember IP Addresses for websites. Google.com > 152.245.23.001 Domain Name Server (DNS) When you type a URL it is sent to the DNS. The DNS looks up the URL within a table and if it finds the corresponding IP Address, it is then returned to the client. If it cannot find the IP Address, the request is forwarded to a higher DNS. Hardware Primary Electrons are stored as volatile data in RAM. Volatile means the data is lost when the voltage is lost (turned off) Read Only Memory (ROM) Random Access memory (RAM) Secondary Non-volatile storage Magnetic/Hard Disk Drive (HDD) Solid State Drive (SSD) Read Only Memory (ROM) Non-volatile, write speed is slow and stores basic information that a device needs to operate/boot. ROM is used to store information that does not change or information that needs to be retained even when the device is turned off. There are 3 types of ROM; Programmable ROM (PROM) Erasable Programmable ROM (EPROM) Electronically Erasable Programmable ROM (EEPROM) Programmable ROM (PROM) A ROM chip that is initially empty but can be written to once Erasable Programmable ROM (EPROM) A ROM chip that can erased by using a UV light to heat up the circuit and erase it. Can be overwritten many times. EPROM needs to be completely erased before overwriting. Electronically Erasable Programmable ROM (EEPROM) A ROM chip that can be erased electronically using voltage. It is a type of flash memory that means it can be rewritten quickly and many times. EEPROM can be partially erased and overwritten. Random Access memory (RAM) Volatile with fast read and write speed that stores the current program in use. There are 2 types of RAMS; Static RAM (SRAM) Dynamic RAM (DRAM) Static RAM (SRAM) A type of RAM in which data remains constant if power is supplied. It is commonly used as CPU cache and buffers due to its lower storage capacity. Transistors are arranged as flip flops. Uses multiple transistors. Dynamic RAM (DRAM) A type of RAM that stores each bit on a capacitor and therefore needs to be constantly refreshed. DRAM is used for personal computers and webservers as its cheaper. Transistors are arranged as capacitors. Uses a single transistor and capacitor. ROM MBs False Slower Size Volatility Speed RAM GBs True Fast DRAM Cheap Slow High Low High Price Access Speed Power Use Heat Size SRAM Expensive Fast Low High Low Secondary Storage ⇌ DRAM ⇌ RAM ⇌ Microprocessor Size – Speed + Price + Magnetic/Hard Disk Drive A hard disk has one or more platters mounted on a spindle. The platter is divided into concentric tracks and sectors. It is spun at a very fast speed. A read and write head is mounted on an arm above the surface. The data is encoded as magnetic patterns. Cheaper than SSD Longer life span Moving parts so it can be loud Slower Solid State Drive Blocks of transistors are arranged in a grid with two transistors at each intersection; the floating gate and the control gate. Memory cells stores 0s and 1s. Movement of electrons is controlled for read and write operations. Faster No moving parts Shorter life span Expensive Buffer A temporary storage usually in the RAM that is used due to speed incompatibility between devices. Such as a video buffer when steaming videos. Embedded Systems An integrated system with microprocessor within a larger system that performs one specific task. Compact and fast Consumes less power and is very reliable Cheap Tedious and difficult to upgrade Time needed to maintain it Hard to backup Not easily changed by device’s owner Input Output Devices Laser Printer 3D Printer Microphone Speaker Optical Disc Reader/Writer Touch Screen Virtual Reality Headset Laser Printer The drum has an initial charge. As it rotates, a laser bounces back and forth across the drum in certain areas to remove the charge. The drum is coated with a charged toner which sticks to the charged area. As a piece of electrostatically charged paper is rolled in, the toner sticks to it and the pattern is transferred. The ink is melted so that it continues to stick to the paper even after charge is removed by passing it into the fuser. Lastly the excess toner is collected. 3D Printer A 3D design is made using CAD. The design is split into layers that are transmitted one by one to the printer. The printer head can move in all cardinal directions squirting out material. This is repeated for every layer. After that it needs to be cured; either by removing excess material or letting the material dry/harden. Microphone As sound is passed into the diaphragm is vibrates. The diaphragm is connected to a circuit where the vibrations cause a change in the electrical signal. The analogue signal is then converted into a digital signal by an ADC. Speaker The digital signal is converted by a DAC. The analogue signal is then sent as current to a speaker. The current passes through the coil creating an electromagnet, which is attached to the diaphragm. Changes in the sound affect the direction of the current. The electromagnet is constantly being attracted/repelled by a permanent magnet causing the diaphragm to vibrate and produce sound. Optical Disc Reader/Writer An optical disc is spun on a spiral track, as it spins the pits and lands are read by a laser. The pits and bumps reflect light differently. The surface of the disc is coated in a reflective metal layer. The lens helps focus the laser onto the disc. The difference in the reflection of a pit and land is read as 0s and 1s Touch Screen There are two types of touch screens; Resistive Capacitive Resistive Two charged plates. When you press on the screen the two layers connect and complete a circuit. Point of contact is registered and the coordinates are used to calculate position. Capacitive A conductive layer stores charge. When touched charge is transferred to the finger. Sensors at the corner of the screen detect changes and the point of contact is registered and the coordinates are used to calculate position. Virtual Reality Headset A headset contains two eye pieces which are fed images from a controlling system which when looked through simulates being in a 3D environment. When the user moves their head or uses the controlling device they can move and look around in the environment. Sensors Sensors are input devices that provide data based on real-word data. Temperature Infrared Pressure Sound Actuators are used in tandem with sensors, they provide the output. When using sensors, there are two main types of systems; Monitoring Controlling Monitoring A system in which the sensors are used to detect changes, they cannot resolve the issue itself. For example, if a temperature gets too high, it will turn on a red light. Human intervention is needed Controlling A system in which the sensors are used to detect changes and resolve the issue. For example, if a temperature gets too high, it will turn on the air conditioning. No human intervention is needed. Logic Gates Not A 0 1 A NOT 1 0 OR AB 00 01 10 11 X 0 1 1 1 AB 00 01 10 11 X 0 0 0 1 AB 00 01 10 11 X 1 0 0 0 AND NOR NAND AB 00 01 10 11 X 1 1 1 0 AB 00 01 10 11 X 0 1 1 0 XOR Logic Circuit Logic Expression (A+B) ⊕ (A+B) Processor Fundamentals Fetch-Execute Cycle 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. The contents of the PC are copied to the MAR The PC is incremented by 1 The MAR fetches the data at the given address and loads it into the MDR The contents of the MDR are copied to the CIR The instructions are decoded by the CPU and executed by the CIR and the cycle repeats Register Notation MAR <- [PC] PC <- [PC] +1 MDR <- [[MAR]] CIR <- [MDR] Registers A register is the temporary storage of data that needs to be or has been processed. There are many registers in a computer such as; Program Counter (PC) Memory Data Register (MDR) Memory Address Register (MAR) Current Instruction Register (CIR) Index Register (IX) Accumulator (ACC) Status Register (SR) Program Counter (PC) Stores the address of the next instruction to be fetched Memory Data Register (MDR) Stores the data that has been received/transmitted from/to CIR/memory Memory Address Register (MAR) Stores the address where the data that needs to be fetched is located and sends to MDR Current Instruction Register (CIR) Stores the data received from the MDR Index Register (IX) Stores a value that is used to calculate an address Accumulator (ACC) Stores the values temporarily after an execution of instruction by ALU Status Register (SR) Contains independent bits/flags where each flag is set based on an event Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU) Part of the processor that carries out arithmetic and logical operations like input and output Control Unit (CU) Sends and receives signals to control operations like input and output. And helps coordinate actions of different components. Immediate Access Store (IAS) The components that directly addressed by the processor System Clock Generates the timing signals that synchronize the components on the motherboard Number of Cores Each core processes one instruction per clock pulse so more cores means more than one instruction can be processed Clock Speed Each instruction is executed on a single clock pulse so the faster the clock speed the more instructions that can be executed per second Bus Width The number of directly addressable memory locations to transfer data between Cache Stores frequently/recently used information so that it can be quickly accessed Universal Serial Bus (USB) Fast data transfer for large files like videos and supports plug and play so no need to install drivers Video Graphics Array (VGA) Transfers high resolution image display without sound High Definition Multimedia Interface (HDMI) Transmits high quality videos and sound Data Bus Carries data between processor and memory, it is bidirectional Control Bus Transmits control signals between CU and other components, it is bidirectional Address Bus Carries addresses from MAR to memory location, it is unidirectional Interrupts An interrupt is a signal from a device telling the processor that its attention is needed Printer is out of paper Runtime error User interaction Input or output request At the start and end of every fetch and execute cycle the processor checks for interrupts, if an interrupt is found it identifies the source and priority. If lower priority than current task it continues the cycle else if it is higher priority than the current task, the current task is pushed to stack and the Interrupt Service Routine (ISR) is called. After the interrupt is serviced, it checks to make sure there are no interrupts of high priority that need to be serviced then the task is pulled from the stack and the fetch execute cycle continues. Assembly Language A low-level language that is used to directly instruct the registers and microprocessors. There are 5 categories of instructions. Data Movement Input and Output Arithmetic Operations Conditional and Unconditional Jumps Comparison Data Movement LDM <#n/Bn/&n> // Loaded to ACC LDD <address> // Contents of address loaded to ACC LDI <address> // Contents of address of address loaded to ACC LDX <address> // Content of IX added to address to form a new address and data from there is loaded to ACC LDR <#n/Bn/&n> // Loaded to IX MOV <register> // Move contents of ACC to <register> STO <address> // Store contents of ACC at <address> Input and Output IN <> // Store the ASCII value of the char in the ACC OUT <> // Output the character based on the ASCII value in the ACC Arithmetic Operations ADD <#n/Bn/&n> // Add to ACC SUB <#n/Bn/&n> // Subtracts from ACC INC <register> // Increment register DEC <register> // Decrement register Conditional and Unconditional Jumps JMP <address> // Jump to given address JPE <address> // Jump if true; after comparison JPN <address> // Jump if false; after comparison Comparison CMP <#n/Bn/&n> // Checks if ACC is equal to value CMI <address> // Check if contents of address of the address is equal to ACC # Represents a decimal number B Represents a binary number & Represents a hexadecimal number Immediate The operand is the value used in the instruction Direct The value of the address is used in the instruction Indirect The operand stores an address that points to another address that stores the data Indexed The operand is added to the index and the data at the address is used Relative The operand is added to a set address to calculate where to read value from; offsets. It is used to allow for relocatable code as all addresses are base + offset. Assembler The assembler runs in two phases. In the first phase it reads the instructions, when it sees a symbolic address, it checks if it is in the symbol table, if it is not then it is added to the table. If it is already in the table, it checks if the absolute address is known, if yes, it is entered else it is marked as unknown. During the first run it also removes comments and expands macros. During the second run the code is executed/generation of object code. Code is read in both runs. Logical Shift LogicalShiftLeft (LSL) multiples the number by 2 to the power n LogicalShiftReft (LSR) divides the number by 2 to the power n LSR <#n> // Move towards right; empty spaces are 0s LSL <#n> // Move towards left; empty spaces are 0s Arithmetic Shift Works like the logical shift except that most significant bit stays the same, i.e., the number stays positive/negative. Absolute Address A numerical address that points directly to a memory location Symbolic Address A word or symbol that represents a memory location System Software Operating System An operating system is a piece of system software that facilitates communication between the user and the hardware Need To provide a means of communication between hardware and user To provide an environment for the execution of software To manage system resources Tasks Memory Management File Management Security Management Hardware/Input Output/Peripheral Management Process Management Error detection and Management User Interface Memory Management Allocates memory to processes when they need to run Releases memory when a process stops so that it can be recycled and reused Makes use of virtual memory when the main memory is under struggle due to a small capacity Controls movement of data to/from RAM Memory protection to make sure that 2 programs do not use the space File Management Allocates space to a given file Allows use of copy, paste, cut, delete, open, close and create. Maintains and creates directory structure Provides file naming conventions like it cannot contain illegal characters like ‘/’ Provides access rights to prevent certain users on the device from accessing the files Security Management Performs automatic backups in case of accidental deletions Sets up user accounts and implements access rights per user like ‘Administrator’ Provides a system restore when needed by the user Authenticates the username and passwords of the different accounts on the device Hardware Management Automatically installs necessary drivers when the device is plugged in Handles the interrupts and signals sent to/from the device including the device buffer Sends control signals in order to manipulate the device, such as start printing a document Process Management Manages the scheduling of different tasks in order to allow for multitasking Prevents interferences between different processes such as over resources Manages the resources which the process requires Error Detection Management Handles interrupts Provides safe mode boot up in case of a major error Provides error diagnostic messages and reports on the health of the system Saves system restore points User Interface Allows the user to communicate with the hardware by providing a CLI or GUI Provides facility for the user to input and output data to/from the hardware Utility Software Software that is installed by default on every computer just as a virus checker. A photo editor is not an example of utility software Disk Formatter Virus Checker Defragmentation Software Disk Repair and Analysis Software File Compression Backup software Disk Formatter The disk formatter prepares the hard disk for its initial use by creating logical partitions usually on a previously used disk. Virus Checker The virus checker scans the files stored on the system and files that newly enter the system for malicious code. It does this on a regular schedule. If a file is found it can be quarantined and deleted. Defragmentation Software Reorganizes the individual files on the system to ensure that they are stored in contiguous blocks to speed up access times. Disk Repair and Analysis Software Scans the disk for corrupt/bad sectors and marks them as unusable. It will resolve any errors and provide reports to the user File Compression Reduces the size of the file to optimize storage space by using an algorithm such as RLE, which can be lossy or lossless. Backup Software Creates copies of the content of the disk usually on schedule. Allows the user to decide what data is stored and when needed allows the user to restore the saved data Program Libraries A collection of pre-written code that can be linked to the main program to perform complex tasks Saves time as you can refer to the library instead of writing the code yourself Allows you to perform complex tasks without needing to understand how it works It has been thoroughly tested so you can use it without error checking Dynamic Link Library A collection of self-contained programs that have already been compiled. These are linked to the main program for execution Library program’s code is separate from the .exe file which means the library file is loaded at run time when it is needed A DLL file can be used by multiple programs at the same time and it can be automatically be updated Only loaded when needed so that means the executable’s size can be smaller Changes made to the DLL are separate from the executable so it does not need to be recompiled and it can be updated automatically Saves time as you can refer to the library instead of writing the code yourself Allows you to perform complex tasks without needing to understand how it works It has been thoroughly tested so you can use it without error checking Executable will not work if the DLL is corrupt External changes to the DLL could cause the executable to stop working The DLL needs to be present for the executable to work Translator A software that is used to convert higher level programming languages to a different form, usually machine code Compiler Interpreter Assembler Interpreter An interpreter requires the source code to be present when it reads line by line and stops whenever there is an error. Allows for easier debugging as the errors are outputted one at a time whenever they are encountered Compiler It reads the entire program and reports all errors in the end. Produces an executable file allowing for redistribution without the source Some high-level languages like Java are partially interpreted and partially compiled. Programs can be interpreted on different platforms Extra CPU resources may be needed as program needs to be interpreted on the user’s device which may run slowly Integrated Development Environment (IDE) An IDE is a software that helps programmers work more efficiently. They come bundled with many features Context sensitive prompts that auto complete what you are typing based on what has been typed out Dynamic syntax checking which highlights all syntax errors for you Pretty print which uses colors and automatic indentation to make the code more presentable Breakpoints which allow you to pause the program at certain points in execution to ensure line by line that everything is working Report window which outputs the contents of variables and data structures Single stepping which executes one line of code and stops Security, privacy, and data integrity Data Security Prevents accidental or malicious data loss Firewall Access Rights Passwords / Biometrics / 2FA Data Privacy Prevents unauthorized access to data Security Measures It is important to protect both data and the computer system User Accounts Authentication Digital Signature Firewall Anti-virus Encryption User Accounts Allows the administrator to specify different permissions for the users such as read and write access so that unauthorized actions cannot be carried out. Each user has an account with a password and username which helps prevent access to the system without a valid username and password Authentication Using a strong password with a unique combination of letters, numbers and symbols makes it hard to crack. Additionally using biometric data such as face id or fingerprint makes it even more difficult. 2 Factor/Step verification using an external device can help make sure no one access your account while you are away. Digital Signature Encrypted data that is electronically attached to files to verify it is from a trusted source A digital signature is created by producing a digest by putting the content through a hashing algorithm. The digest is encrypted with the sender’s private key and can only be decrypted by using their public key. Firewall Monitors incoming and outgoing traffic against a given criteria and will block anything suspicious that does not meet the requirement. It maintains blacklist of Ip address. It also has log of all traffic Anti-Virus It scans the files stored on the system and files that newly enter the system for malicious code. It does this on a regular schedule. If a file is found it can be quarantined and deleted. Encryption It is the process of converting a given input into an unreadable format using a key. If the file is accessed without the key its useless. A decryption key is needed to unscramble the data Security Threats Virus Spyware Hackers Phishing Pharming Virus A piece of malicious code that self-replicates itself with the intention of harming a computer system by corrupting data Spyware A piece of malicious software installed on the victim’s device that records keypresses and relays them to a third party without the user’s knowledge Hackers Unauthorized access to the victim’s device with malicious intent such as to steal sensitive information Phishing The user is redirected to a fake link usually through email that attempts to gain sensitive personal information Pharming The user is redirected to a fake website that appears legitimate to gain access to sensitive information Data integrity Ensures data is accurate and up to date Validation Verification Data Validation A method of checking if the data entered is valid but not accurate Range Check Format Check Length Check Prescence Check Existence Check Check digit Range Check Data must be between a given range i.e.; 1-100 Format Check Data must match a given format i.e.; DD/MM/YY Length Check Data must match a given length i.e.; have 25 characters or below Prescence Check Data must not be left empty Existence check Data must exist i.e.; if you are inputting a file name that file needs to exist Check Digit An arithmetic operation is carried out on the given input and the data must match the answer i.e.; international standard book number Data Verification A method of checking that data is the same as the original during entry and transfer Entry o Visual check / Proofreading o Double entry Transfer o Checksum o Parity Check Visual Check / Proofreading Data must be manually compared by the user to ensure it is correct Double Entry Data must be entered twice and then both inputs are compared to each other Checksum Data entered is passed through an algorithm to produce the checksum, the checksum is then sent along with the data. The checksum is recalculated and compared Parity Check Each row and column have even/odd parity, an even/odd number of 1 bit, depending on what is chosen. An additional parity byte is sent to ensure there is parity horizontally and vertically. The intersection of the row and column where the parity is broken is the error bit. Parity check fails when multiple bits transmitted incorrectly as they might cancel out. Ethics and Ownership Copyright It is the formal/legal right to ownership and protection of intellectual property. It allows you legal action against those who misuse it and restrict its usage. Ethical Body A group of people entrusted with maintaining operations of a legitimate occupational business. Provide ethical guidelines so the employee does not need to make decisions on his own Provide help and support such as legal advice when needed Provide training courses to ensure the employee’s skills are always polished IEEE Code of Ethics Public – Software engineers shall act consistently with the public interest. Client and Employer – Software engineers shall act in a manner that is in the best interests of their client and employer consistent with the public interest. Product – Software engineers shall ensure that their products and related modifications meet the highest professional standards possible. Judgement – Software engineers shall maintain integrity and independence in their professional judgment. Management – Software engineering managers and leaders shall subscribe to and promote an ethical approach to the management of software development and maintenance. Profession – Software engineers shall advance the integrity and reputation of the profession consistent with the public interest. Colleagues – Software engineers shall be fair to and supportive of their colleagues. Self – Software engineers shall participate in lifelong learning regarding the practice of their profession and shall promote an ethical approach to the practice of the profession. Software License Free Software Opensource Shareware Commercial Free Software The source code comes with the software. If the software is modified, the edited source code must be released under the same conditions as the original software. Opensource Software is released with the source code. Users can edit and redistribute it. Usually, free. Allows users to edit code Allows users to fix errors Allow for collaboration Shareware Software that needs to be bought on a subscription model, usually free for a limited amount of time. You may re-distribute. Do not have access to the source code Commercial Software that needs to be purchased. A key is needed to install it. Source code is not provided. No unauthorized redistribution Can earn money by charging a fee Allows program to be copyrighted Prevents illegal access and changes to the program Artificial Intelligence Artificial intelligence can be trained to perform tasks much faster than humans. It can be trained by putting it through that situation multiples times and passing in different arguments based on the situation allowing the processor to decide accordingly. It can store the results of choices and determine if they are helpful and analyze the helpful ones and repeat them in order to succeed. Databases Item A single entry Fields/Attributes The headers of the table Tuples/Record Combination of interrelated fields Table A collection of records Databases A collection of tables Data Dictionary Stores metadata about the database like relationships, primary and foreign keys Logical Scheme The overview of the database structure using methods like an ER diagram Primary Key A field that is unique for every record, it cannot be repeated or null like an ID Composite Key When multiple fields are used to make a primary key Secondary Key A candidate key but not a primary key. An alternative field to the primary key when primary key is unknown Foreign Key A field which is common between two tables and hence is used to link them Candidate Key A field which has the potential to be a primary key but is not as only one primary key is needed. First Normal Form Figuring out key fields and their dependencies from the flat file to create multiple tables to avoid data repetition. Contains no data repetition. Second Normal Form Creating relationships between tables while avoiding partial dependencies and many-to-many relationships, an extra table might be needed. Contains no partial dependencies. Third Normal Form Figuring out non key fields and their dependencies to create an extra table and avoid data repetition. Contains no transitive dependencies. Flat File The file that keeps the data of all entities Master File The file which holds the basic data of an entity that does not need to be repeated Transactional File The file which keeps data of all entities during a transactional period which may change during the next transactional period Partial Dependency When a field only depends on one part of the composite primary key Transitive Dependency When a value does not depend on primary key and depends on another value instead like in TABLE(PetID, Owner, Number) number depends on Owner not PetID Referential Integrity Referential Integrity is making sure that tables do not try to refer to values that do not exist. A primary key cannot be updated or deleted unless all dependent values are deleted/updated. Every foreign key needs to have a corresponding primary key value with the same data type. ERD Entity relationship diagrams One to One One to Many Many to Many Primary to primary Primary to non-primary Non-primary to nonprimary SQL Structured Query Language DDL Data Definition Language DML Data Manipulation Language CREATE DATABASE Name CREATE TABLE Student (ID INT, Name VARCHAR(25), Address TEXT, Number INT, Birthday DATE, PRIMARY KEY (ID)); ALTER TABLE Student ADD PRIMARY KEY (ID); ALTER TABLE Student ADD PRIMARY KEY (ID, ID2); ALTER TABLE Student ADD FOREIGN KEY (ID) REFERENCES Grades(ID); ALTER TABLE Student ADD COLUMN Class VARCHAR(2); ALTER TABLE Student DROP Class; INSERT INTO Student VALUES(1, “Ali”, “ABC”, 123, 1/1/1); INSERT INTO Student (ID, Name, Birthday) VALUES(2, “Asim”, 2/2/2) DELETE FROM Student WHERE ID = 2; UPDATE Student SET Number = 456 WHERE ID = 2; SELECT ID, Birthday, Name FROM Student SELECT Name FROM Student WHERE Name LIKE “123*” SELECT Name, Rating FROM Movie INNER JOIN Timings ON Movie.ID = Timings.ID WHERE Movie.Name = “Monster”; SELECT ID, Birthday FROM Student ORDER BY Name ASC/DESC GROUP BY Class; SELECT COUNT(Name) FROM Student; SELECT SUM(ID) FROM Student; SELECT AVG(Percentage) FROM Student; File Based Approach There is more data redundancy because the same data is being stored in multiple different places Worse data integrity because duplicate data might be stored differently in certain places Lack of privacy as all users have equal access to it Difficult to perform complex searches as a new program must be written each time Relational Database Multiple tables are linked together which improves data integrity and reduces data redundancy Complex queries can easily be used to find very specific data User permissions can be setup to improve security and data privacy by preventing them from seeing data they should not Database Management System Serves as the interface between the user and the database Developer Interface to create interactive features and generate reports Query processor to design new SQL queries Password and biometrics to protect against unauthorized access User accounts to restrict what a user can do (read/write) Automatic backups in case of data loss Encryption to make data incomprehensible to people