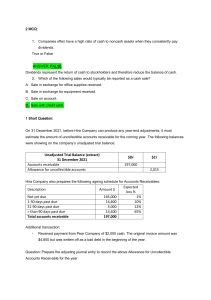
in financial accounting what is internal control Internal control in financial accounting refers to the policies, procedures, and processes implemented by a company to ensure the accuracy, reliability, and integrity of its financial reporting. The purpose of internal control is to help a company achieve its objectives by preventing and detecting errors and fraud in financial reporting. Internal control covers a wide range of activities that include: 1. Separation of duties: Assigning different responsibilities to different employees to ensure that no one person has complete control over a process or transaction. 2. Authorization and approval: Requiring approvals and authorizations for financial transactions to ensure they are legitimate and comply with company policies. 3. Segregation of assets: Separating assets and liabilities to ensure they are properly accounted for and protected from theft or loss. 4. Record keeping and documentation: Ensuring that financial transactions are properly recorded, classified, and documented to support the accuracy of financial statements. 5. Physical controls: Implementing controls such as locks, cameras, and security personnel to protect assets from theft or damage. Overall, internal control helps a company to achieve its goals by ensuring that financial reporting is accurate, complete, and reliable. Effective internal control also helps to prevent and detect fraud, error, and waste, which can harm a company's financial performance and reputation. in financial acccounting define control of cash how control of cash is done Control of cash refers to the procedures and processes a company uses to ensure the proper handling, security, and accounting of its cash. Effective control of cash is important to prevent loss, theft, or misappropriation of cash and to ensure the accuracy and reliability of financial statements. To control cash, a company may implement the following procedures: 1. Separation of duties: Different employees should be assigned responsibilities for handling cash to ensure that no one person has complete control over cash handling. 2. Segregation of functions: The functions of cash receipt, recording, and custody should be segregated to avoid errors or fraud. 3. Use of prenumbered documents: All cash receipts and disbursements should be recorded on prenumbered documents to provide a clear audit trail and to prevent unauthorized transactions. 4. Daily reconciliation of cash balances: The company should reconcile its cash balances on a daily basis to ensure that all cash transactions have been properly recorded and to detect any discrepancies. 5. Physical controls: Physical controls such as safes, locks, and surveillance cameras should be used to secure cash and protect it from theft or loss. 6. Authorized access: Only authorized personnel should have access to cash and only for authorized purposes. 7. Periodic audits: Regular internal and external audits should be conducted to ensure compliance with cash control policies and to identify any weaknesses or deficiencies in the system. Overall, control of cash is a critical component of a company's internal control system, and it requires a combination of procedures and controls to ensure the proper handling and accounting of cash. in financial acccounting define control of cash how control of cash is done Control of cash refers to the procedures and processes a company uses to ensure the proper handling, security, and accounting of its cash. Effective control of cash is important to prevent loss, theft, or misappropriation of cash and to ensure the accuracy and reliability of financial statements. To control cash, a company may implement the following procedures: 1. Separation of duties: Different employees should be assigned responsibilities for handling cash to ensure that no one person has complete control over cash handling. 2. Segregation of functions: The functions of cash receipt, recording, and custody should be segregated to avoid errors or fraud. 3. Use of prenumbered documents: All cash receipts and disbursements should be recorded on prenumbered documents to provide a clear audit trail and to prevent unauthorized transactions. 4. Daily reconciliation of cash balances: The company should reconcile its cash balances on a daily basis to ensure that all cash transactions have been properly recorded and to detect any discrepancies. 5. Physical controls: Physical controls such as safes, locks, and surveillance cameras should be used to secure cash and protect it from theft or loss. 6. Authorized access: Only authorized personnel should have access to cash and only for authorized purposes. 7. Periodic audits: Regular internal and external audits should be conducted to ensure compliance with cash control policies and to identify any weaknesses or deficiencies in the system. Overall, control of cash is a critical component of a company's internal control system, and it requires a combination of procedures and controls to ensure the proper handling and accounting of cash. components of internal cash control Internal cash control is a critical component of a company's overall internal control system. Effective internal cash control is essential for ensuring the accuracy and reliability of financial reporting and preventing fraud, errors, and other financial irregularities. The components of internal cash control typically include: 1. Separation of duties: This involves separating the responsibilities of cash receipt, recording, and custody to different employees to prevent any one person from having complete control over cash handling. For example, the person responsible for recording cash receipts should not also be responsible for handling cash. 2. Authorization and approval procedures: This involves establishing procedures for authorizing and approving all cash transactions, such as cash receipts and disbursements, to ensure that they are legitimate and authorized. 3. Physical control of cash: This involves implementing physical controls, such as secure storage facilities, locks, safes, and surveillance cameras, to safeguard cash and prevent theft or loss. 4. Reconciliation of cash balances: This involves regularly reconciling cash balances, such as comparing cash on hand to the cash balance in the accounting system, to detect any discrepancies and prevent errors. 5. Monitoring and review: This involves ongoing monitoring of cash transactions and reviewing the effectiveness of internal cash control procedures to identify any weaknesses or deficiencies in the system and make improvements. 6. Audit trail: This involves establishing an audit trail for all cash transactions, such as using prenumbered documents, to provide a clear record of all cash transactions and to help identify any discrepancies or unauthorized transactions. Overall, the components of internal cash control work together to establish a system of policies, procedures, and processes that aim to ensure the proper handling, accounting, and safeguarding of cash resources. Effective internal cash control is essential for maintaining the integrity and accuracy of financial reporting and preventing fraud or other financial irregularities. highlight internal controls for E-commerce Effective internal controls are critical for the success and security of ecommerce businesses. The unique aspects of e-commerce, such as online transactions and data security, require specific internal controls to ensure that transactions are processed accurately and securely, and to prevent fraud, errors, and other financial irregularities. The internal controls for ecommerce typically include: 1. Access controls: This involves establishing appropriate access controls for e-commerce systems, such as password protection, multi-factor authentication, and role-based access control. This ensures that only authorized personnel have access to e-commerce systems and sensitive data. 2. Data security: This involves implementing data security controls, such as encryption, firewalls, intrusion detection, and antivirus software, to protect sensitive customer information and prevent data breaches. 3. Fraud prevention: This involves establishing fraud prevention controls, such as real-time transaction monitoring, anomaly detection, and order verification procedures, to prevent fraudulent transactions and unauthorized access to customer data. 4. Payment processing controls: This involves implementing controls for payment processing, such as secure payment gateways, PCI compliance, and reconciliation of payments, to ensure that all payments are processed accurately and securely. 5. Inventory management controls: This involves implementing controls for inventory management, such as real-time inventory tracking, order fulfillment processes, and periodic inventory reconciliation, to prevent errors and ensure accurate inventory reporting. 6. Internal audit and review: This involves conducting periodic internal audits and reviews of e-commerce systems and processes to identify any weaknesses or deficiencies in the internal control system and make improvements. Overall, effective internal controls for e-commerce require a comprehensive approach that addresses the unique aspects of online transactions and data security. E-commerce businesses must establish appropriate access controls, data security, fraud prevention, payment processing, inventory management, and internal audit and review procedures to ensure the accuracy and security of online transactions and to maintain the trust of customers. How effective is the bank account as control device How effective is the bank account as control device Bank accounts are an effective control device for businesses because they provide a number of benefits in terms of internal control. Some of the key benefits of using bank accounts as a control device include: 1. Cash management: Bank accounts allow businesses to manage their cash more effectively by consolidating cash into a single account and tracking incoming and outgoing cash flows. This makes it easier for businesses to monitor their cash balances and ensure that they have sufficient funds to cover their expenses. 2. Fraud prevention: Bank accounts can help prevent fraud by providing a paper trail for all transactions and ensuring that transactions are authorized before funds are released. Additionally, many banks offer fraud prevention services that can help detect and prevent fraudulent activity. 3. Reconciliation: Bank accounts make it easier to reconcile cash balances by providing a statement of all transactions and balances. This can help identify errors or discrepancies in the accounting records and ensure that the financial statements accurately reflect the company's financial position. 4. Security: Bank accounts provide a secure way to store cash, reducing the risk of theft or loss. Additionally, electronic payments and online banking services can reduce the need for physical cash and checks, further improving security. 5. Audit trail: Bank accounts provide an audit trail for all transactions, which can be useful in the event of an audit or investigation. However, it's important to note that bank accounts alone are not enough to provide effective internal control. Other internal control measures, such as separation of duties, authorization and approval procedures, and regular monitoring and review, should also be implemented to ensure effective control of cash and other assets. Additionally, it's important to select a reputable and trustworthy bank and to regularly review and monitor bank account activity to ensure that it aligns with the business's financial goals and objectives. define and explain the process of bank reconciliation Bank reconciliation is the process of comparing the balance in a company's accounting records to the balance on the bank statement to identify and explain any differences. The goal of bank reconciliation is to ensure that the cash balance in the accounting records is accurate and complete. The process of bank reconciliation typically involves the following steps: 1. Obtain the bank statement: The first step in bank reconciliation is to obtain a copy of the bank statement for the period being reconciled. This statement will show all transactions that have been processed by the bank during that period, including deposits, withdrawals, and fees. 2. Compare transactions: The next step is to compare the transactions on the bank statement to the transactions recorded in the company's accounting records. This involves matching each transaction on the bank statement to the corresponding transaction in the company's records. 3. Identify differences: Any differences between the bank statement and the accounting records are then identified. These differences may be due to timing differences, errors, or other discrepancies. 4. Adjust accounting records: If the differences are due to errors in the accounting records, the records should be adjusted to reflect the correct balance. For example, if a deposit was recorded in the accounting records but was not included on the bank statement, the accounting records should be adjusted to include the deposit. 5. Prepare reconciliation statement: Once all differences have been identified and resolved, a bank reconciliation statement is prepared to summarize the reconciliation process. The reconciliation statement will typically include the balance per bank, the balance per company records, and any adjustments made to the records. 6. Investigate outstanding items: If any differences cannot be resolved, they are considered outstanding items and may require further investigation. Outstanding items may include checks that have not cleared the bank, deposits that have not been credited, or errors that require additional review. By performing bank reconciliation on a regular basis, businesses can ensure that their accounting records accurately reflect their cash position, identify any errors or discrepancies, and prevent fraud or other financial irregularities. explain bank reconciliation method Bank reconciliation is a process of comparing the company's accounting records of cash transactions with the bank statement, in order to identify and resolve any differences or discrepancies. The purpose of bank reconciliation is to ensure that the company's accounting records of cash transactions match the bank's records of the same transactions. The method for bank reconciliation typically involves the following steps: 1. Obtain a copy of the bank statement: The first step in bank reconciliation is to obtain a copy of the bank statement. This statement shows all transactions processed by the bank during the period being reconciled, including deposits, withdrawals, and fees. 2. Update the company's accounting records: The next step is to update the company's accounting records to reflect any transactions that have not been recorded in the accounting system. These transactions may include checks written by the company that have not yet cleared, deposits made by the company that have not yet been credited, and bank fees or charges. 3. Compare the bank statement to the company's accounting records: The bank statement is then compared to the company's accounting records to ensure that all transactions have been properly recorded. Any discrepancies are identified and investigated. 4. Record any necessary adjustments: If discrepancies are found, any necessary adjustments are made to the company's accounting records. For example, if a check was recorded in the company's records but did not clear the bank, the check may need to be voided in the accounting system. 5. Prepare a reconciliation statement: Finally, a reconciliation statement is prepared to summarize the bank reconciliation process. This statement shows the beginning and ending balances for the bank account and the company's accounting records, and any adjustments made during the reconciliation process. The bank reconciliation method is an important process for ensuring the accuracy of a company's accounting records and identifying any discrepancies or errors. By performing bank reconciliation on a regular basis, businesses can prevent fraud and other financial irregularities, ensure the accuracy of their financial statements, and maintain good relationships with their banks. write a short note on internal control over cash payments Internal control over cash payments is a process of managing the flow of cash out of a business, in order to prevent fraud, errors, and other financial irregularities. The objective of internal control over cash payments is to ensure that all cash disbursements are properly authorized, supported by appropriate documentation, and accurately recorded in the company's accounting records. Some of the key components of internal control over cash payments include: 1. Segregation of duties: To prevent fraud or other financial irregularities, it's important to ensure that the process of cash payments is properly segregated from other accounting functions, such as cash receipts, bookkeeping, and financial reporting. 2. Approval processes: All cash disbursements should be authorized by an appropriate level of management, such as a supervisor or manager, and supported by appropriate documentation, such as purchase orders, invoices, or receipts. 3. Payment controls: Payment controls should be in place to ensure that cash payments are made in accordance with company policies and procedures, such as verifying the accuracy of invoices and checks, reviewing and approving payment requests, and ensuring that payments are made only to authorized vendors. 4. Recordkeeping: Accurate and complete recordkeeping is essential for internal control over cash payments. This includes maintaining detailed records of all cash disbursements, as well as reconciling these records with bank statements and other financial records. By implementing effective internal control over cash payments, businesses can minimize the risk of fraud and errors, ensure the accuracy of their financial records, and maintain the trust of their customers, suppliers, and other stakeholders. give brief introduction of account receivables in financial accounting Accounts receivable is a term used in financial accounting to refer to the money owed to a company by its customers or clients for goods or services that have been sold or provided on credit. In other words, accounts receivable represents the company's right to receive payment from its customers for the products or services they have purchased, but have not yet paid for. Accounts receivable is considered an asset on a company's balance sheet, as it represents the company's expectation of receiving payment in the future. To record accounts receivable, a company creates invoices for each sale or service provided, which specify the amount due, the payment terms, and the due date. Once the invoice has been sent to the customer, it becomes a receivable until the customer pays. Managing accounts receivable is an important part of financial accounting, as it affects a company's cash flow, profitability, and overall financial health. Companies need to monitor their accounts receivable to ensure that customers are paying on time and to identify any delinquent accounts. To manage accounts receivable effectively, companies may use various strategies such as offering discounts for early payment, establishing credit policies, and utilizing collection efforts for overdue accounts. explain account receivable accounting with example Accounts receivable accounting is the process of managing and recording the money owed to a company by its customers for goods or services sold on credit. The accounting for accounts receivable involves tracking the balances due from customers, managing the credit terms and payment schedules, and recognizing revenue when the products or services are delivered. Here is an example of accounts receivable accounting: Suppose a company sells $10,000 worth of goods to a customer on credit with payment terms of 30 days. The company would record the sale as follows: Debit: Accounts Receivable $10,000 (to record the amount owed by the customer) Credit: Sales Revenue $10,000 (to recognize the revenue earned from the sale) At the end of the 30-day payment period, the customer pays the invoice in full. The company would record the payment as follows: Debit: Cash $10,000 (to record the receipt of cash) Credit: Accounts Receivable $10,000 (to reduce the amount owed by the customer) If the customer does not pay the invoice within 30 days, the company may need to take collection actions to recover the amount owed. The company may send reminder notices, make phone calls, or even take legal action to collect the debt. To manage accounts receivable, companies may also establish credit policies, such as requiring credit checks, setting credit limits, and establishing payment terms. Companies may also use aging schedules to monitor the status of their accounts receivable and identify delinquent accounts. In summary, accounts receivable accounting is an important part of managing a company's financial health. By effectively managing their accounts receivable, companies can improve their cash flow, profitability, and customer relationships. define with example allowance method in account receivables The allowance method is a method used in accounting to estimate and record the amount of uncollectible accounts receivable. It involves creating an allowance account on the balance sheet, which is used to offset the accounts receivable balance, resulting in a net accounts receivable balance. Here is an example of the allowance method in accounts receivable: Suppose a company has $100,000 in accounts receivable, but the company estimates that 2% of these accounts will be uncollectible. The company would create an allowance account for $2,000 (2% of $100,000) on the balance sheet. At the end of the accounting period, the company reviews its accounts receivable and identifies a specific customer with an outstanding balance of $5,000 that is deemed uncollectible. The company would record the following journal entry: Debit: Bad Debt Expense $5,000 (to recognize the expense of the uncollectible account) Credit: Allowance for Doubtful Accounts $5,000 (to reduce the allowance account) This entry reduces the balance in the allowance account by the amount of the uncollectible account, resulting in a net accounts receivable balance of $98,000 ($100,000 - $2,000 - $5,000). The allowance method is a way for companies to account for the risk of uncollectible accounts and to ensure that their financial statements accurately reflect the value of their accounts receivable. By estimating and recording a reserve for bad debts, companies can better manage their cash flow, maintain their creditworthiness, and reduce the risk of financial losses. the direct write off method in accountreceivables with example The direct write-off method is a method used in accounting to account for uncollectible accounts receivable. Under this method, a company waits until a specific account is deemed uncollectible before recording the bad debt expense. This method is simple and straightforward, but it does not match expenses to revenues and can distort financial statements. Here is an example of the direct write-off method in accounts receivable: Suppose a company has a customer with a balance of $5,000 that is deemed uncollectible. The company would record the following journal entry: Debit: Bad Debt Expense $5,000 (to recognize the expense of the uncollectible account) Credit: Accounts Receivable $5,000 (to reduce the accounts receivable balance) This entry reduces the accounts receivable balance by the amount of the uncollectible account, resulting in a net accounts receivable balance that does not reflect the potential risk of future uncollectible accounts. The direct write-off method is not generally used in practice because it violates the matching principle in accounting, which requires that expenses be recognized in the same period as the related revenues. The allowance method is preferred because it estimates the amount of uncollectible accounts and records the bad debt expense in the same period as the related revenues. what is credt card and debit card .how sales are done with the help of these cards respectively A credit card and a debit card are two different types of payment cards that allow consumers to make purchases or transactions without using cash. A credit card is a payment card that allows the cardholder to borrow funds from the issuing bank or financial institution up to a certain credit limit. The cardholder must pay back the borrowed amount plus any interest charged by the bank or financial institution. When a credit card is used to make a purchase, the cardholder is essentially borrowing money from the issuer of the credit card to make the purchase. On the other hand, a debit card is a payment card that allows the cardholder to access funds from their bank account to make purchases or transactions. The cardholder can only spend the available balance in their bank account, and transactions made with a debit card are immediately deducted from the cardholder's account. When a sale is made with a credit card, the seller or merchant receives the payment from the credit card issuer or processor, and the amount of the sale is added to the cardholder's credit card balance. The cardholder will then need to pay off the balance on the credit card, either in full or with interest charges added over time. When a sale is made with a debit card, the seller or merchant receives the payment directly from the cardholder's bank account. The amount of the sale is immediately deducted from the available balance in the cardholder's account. In both cases, the use of credit cards and debit cards allows for fast, convenient, and secure payment transactions, and they are widely used in a variety of settings such as online shopping, in-person retail, and bill payments. what do you mean by notes receivables Notes receivable is a type of financial instrument that represents a written promise by a borrower to pay a specific sum of money to a lender at a future date or on demand. It is a type of asset that a company can hold on its balance sheet, and it represents an amount owed to the company by a borrower. A note receivable is similar to a loan, where a lender provides funds to a borrower in exchange for the borrower's promise to repay the amount borrowed plus interest by a specified date. The borrower is typically required to make regular payments of both principal and interest until the note is paid in full. Notes receivable may be secured or unsecured, depending on whether the borrower has provided collateral to the lender. For example, a company may provide a loan to a customer in the form of a note receivable, which specifies the amount borrowed, the interest rate, and the repayment terms. The customer may be required to make regular payments until the note is paid in full, and the company would record the payments as a reduction in the notes receivable balance on its balance sheet. Notes receivable are an important component of a company's assets and are commonly used to finance business operations or provide financing to customers. The valuation and management of notes receivable require careful consideration and analysis to ensure that the company is adequately compensated for the risk associated with lending money. How accounting information is used for decision making in account receivables How accounting information is used for decision making in account receivables Accounting information related to accounts receivable can be used to make important decisions related to a company's cash flow, credit management, and customer relationships. The following are some ways in which accounting information related to accounts receivable can be used for decision-making: 1. Cash flow management: Accounting information related to accounts receivable can be used to determine the amount and timing of expected cash inflows. This information can be used to make important decisions related to cash flow management, such as determining when to invest in new projects, pay suppliers, or pay dividends to shareholders. 2. Credit management: Accounting information related to accounts receivable can be used to evaluate the creditworthiness of customers and to assess the risk associated with extending credit. This information can be used to make important decisions related to credit management, such as determining credit limits, setting payment terms, and deciding when to take action against delinquent accounts. 3. Customer relationship management: Accounting information related to accounts receivable can be used to track customer payment history and to identify opportunities to improve customer relationships. This information can be used to make important decisions related to customer relationship management, such as identifying loyal customers for special promotions or offering payment plans to customers experiencing financial difficulties. 4. Performance evaluation: Accounting information related to accounts receivable can be used to evaluate the performance of the accounts receivable function and to identify areas for improvement. This information can be used to make important decisions related to performance evaluation, such as setting performance targets, identifying training needs, and allocating resources. In summary, accounting information related to accounts receivable can be used for various decision-making purposes, including cash flow management, credit management, customer relationship management, and performance evaluation. By using this information effectively, companies can improve their financial position, reduce risk, and enhance customer relationships.