Azure Cloud Fundamentals: IaaS, PaaS, SaaS, Deployment Models
advertisement
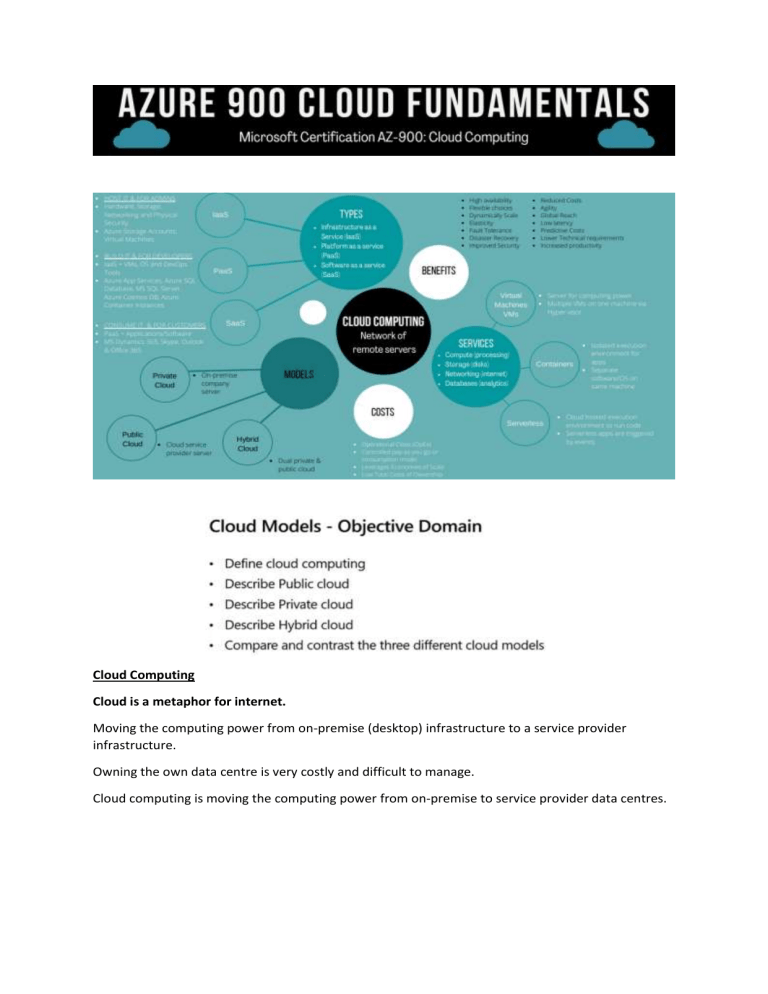
Cloud Computing Cloud is a metaphor for internet. Moving the computing power from on-premise (desktop) infrastructure to a service provider infrastructure. Owning the own data centre is very costly and difficult to manage. Cloud computing is moving the computing power from on-premise to service provider data centres. Cloud Computing Service delivery model over the internet (cloud). This includes but is not limited to compute power meaning servers such as windows, Linux, hosting environments, etc. storage like files and/or databases networking in azure but also outside when connecting to your company network analytics services for visualization and telemetry data. Information like who is visiting my websites, Alerts, loads, how much memory is needed etc. In this world everything’s comes under 2 things BUY OR SELL. Product (Person is sole owner) and Services (Bounded by contract) In Cloud everything is a service Key concepts scalability is the ability to scale, so allocate and deallocate resources at any time elasticity is the ability to scale dynamically agility is the ability to react fast (scale quickly) fault tolerance is the ability to maintain system uptime while physical and service component failures happen disaster recovery is the process and design principle which allows a system to recovers from natural or human induced disasters high availability is the agreed level of operational uptime for the system. It is a simple calculation of system uptime versus whole lifetime of the system. availability = uptime/(uptime + downtime) Key Concepts in detail: Scalability Elasticity A system ability to scale dynamically is called Elasticity. Agility Fault Tolerance Disaster recovery High Availability CapEx vs OpEx Payment method in Azure Economies of Scale The principle of economies of scale states that as the companies grow they become more effective at managing shared operations. Be that HR and hiring, taxes, accounting, internal operations, marketing, big purchases via contracts meaning better discounts, etc. etc. Because of those, companies can save/earn more which in return allows for reduction in cost of their services to their customers. This is so called ‘price per unit’. It’s not possible to go to 0 because in the end some underlying infrastructure needs to run to provide the services. But the larger the scale the more benefits can be passed to customers. In fact, in the current scale, Microsoft can already offer multiple services for free due to how small a fraction of the cost it is for them. IaaS vs PaaS vs SaaS cloud service models Deployment method Cloud Deployment Model is simple a separation which describes where are the company resources deployed. Whenever this is in public cloud provider environment or private datacenter. Public cloud Owned by the cloud services or hosting provider. Pay as you go model Provide resources and services to multiple organisations & users. Accessed via secure network connection (Typically over the internet) Isolation Application can be quickly provisioned and deprovisioned. Private cloud Organisation create a cloud environment in their data-center. Organization is responsible for operating the services they provide. Does not provide access to users outside of the Organisation. Organization are responsible for hardware maintenance& updates. Costly but secure. Hybrid cloud Combines private/ On-Premise and public clouds to allow applications to run in the most appropriate location. MS-Azure is most famous in this category. Application which people should access, can be kept in the public cloud and those application when execute can connect to SQL DB and that SQL Db is kept/ Running in the onpremise data center. Most of the organisation are adapting it. Provide the most flexibility. Organization control security, compliance or legal requirements. Layer Cloud Provider Own Datacenter Public ✅ ✖ Hybrid ✅ ✅ Private ✖ ✅ Core Azure architectural components Azure is OS which manages the datacentre of Microsoft Data Center Regions Multiple Data centres connected with internet is called regions or Regions are made up of one or more data centres in close proximity. The region is a geographic location from where the cloud service provider operates. Provides flexibility and scale to reduce the customer latency. Preserve data residency with a comprehensive compliance offering. The closure you are near to region the lesser the latency. Can check the speed on the website. Also, not all services are available on all the location/region. Availability zone AZ are designed to protect from data centre failure. Availability zones can have one or more data centres. Pointers :The cloud service provider will tell you where as a region, but they will not tell you where exactly is the zones located inside the region. You will basically know it's in Mumbai, but they will never tell you in which location is the zones. And in zone, how many data centres we are having, they will not tell you that. All AZs will be under 100 km boundary.



