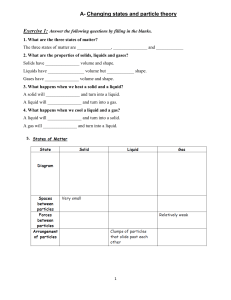
KINETIC PARTICLE THEORY By Mehrunnisa Qaisar SYLLABUS CONTENT 1.1-States of matter 1.2-Kinetic particle theory 1.3-Changes in state of matter and kinetic particle theory 1.4-Diffusion 1.1- STATES OF MATTER • Matter: Anything that occupies space and has mass is matter. • All living and non living things are matter. • Matter is 5 states: 1. Solid 2. Liquid 3. Gas 4. Plasma 5. Bose- Einstein Condensate • All these states are interchangeable if specific temperature and pressure conditions are provided to them. TABLE OF PROPERTIES PROPERTIES SOLID LIQUID GAS SHAPE FIXED NOT FIXED NOT FIXED VOLUME FIXED FIXED NOT FIXED COMPRESSIBILITY NOT COMPRESSABLE NOT COMPRESSABLE COMPRESSABLE 1.2- KINETIC PARTICLE THEORY • Kinetic particle theory: It states that all matter is made up of tiny particles and that these particles are in constant random motion. • This theory focuses on three points: 1. Describes the states of matter. 2. Explains the difference between the properties of solids, liquids and gases. 3. Explains the changes in state of matter. SOLID STATE • The particles are closely packed. • They vibrate at their fixed position. • They have high attractive forces between its particles. • All of that causes its shape to be fixed. • Solids can not be compressed as their particles can not be moved further close to each other. • This allows solids to have fixed volume. LIQUID STATE • Liquids have lesser attractive forces between its molecules. • They are usually found in clusters. • The particles roll over each other as they move. • This causes liquids to not have a fixed shape. • The liquid particles even though are not closely packed they still have very less space between them and hence can not be compressed. • This phenomena causes liquids to have a fixed volume. GAS STATE • The gas particles are always in random motion. • They move freely and are far apart from each other. • The gas particles have negligible forces of attraction between them. • This allows it to not have a fixed shape. • The vast space between the particles allows it to be compressed as pressure can cause particles to come together. • This compressibility factor allows gases to not have a fixed volume 1.3- CHANGES IN STATE OF MATTER AND THE KINETIC PARTICLE THEORY • All particles of matter have kinetic energy. • Moving down the list the kinetic energy decreases: 1. Gas 2. Liquid 3. Solid • When any matter is heated or is cooled, kinetic energy is either added or removed from it causing it to affect the motion of the particles. • This change in movement causes a change of state. • Melting: It is the process by which a substance changes from solid state to liquid state at a fixed temperature • Melting point: It is that temperature at which a solid becomes a liquid. • The temperature of the substance dose not change until all of the substance has changed it state completely. • Boiling: It is a process that occurs when a liquid substance changes its state to a gas at a fixed temperature. • Boiling point: It is the temperature at which a substance changes its state from a liquid to a gas. • The temperature remains constant until all of the liquid has been changed into a gas. • The boiling point of a substance is used to find the purity of any substance. • When a liquid boils, bubble can be observed that show the transition of liquid state to gas. • Evaporation: It is the process that occurs when a liquid state changes to a gaseous state at a temperature lower than its boiling point. • Some particles in a liquid have more energy and thus they easily escape the liquid surface. • Liquids that evaporate quickly are called volatile liquids. • Volatile liquids have their boiling points just above room temperature. BOILING EVAPRATION Occurs only at boiling point Occurs below boiling point Through out the liquid Only at the surface Bubbles are formed No bubbles formed HEATING CURVE: IT IS THE GRAPH THAT SHOWS THE CHANGE OF STATE WHEN A SUBSTANCE IS HEATED, IT IS PLOTTED AS TEMPERATURE AGAINST TIME. A: solid is heating Temperature change No state change State: solid Melting point B: the process of melting occurs No temperature change State change State: solid and liquid State change completed C: liquid is heating Temperature change No state change State: Liquid Boiling Point D: The process of boiling Occurs No temperature change State change State: liquid and gas state change completed E: gas is heating Temperature change No state change State: Gas • Freezing: It is the process in which a substance changes from liquid state to a solid state at fixed temp. • Freezing point: It is that temperature at which a substance changes from a liquid to a solid. • The freezing point and melting point are always the same. For example, ice melts and freezes at 0 degrees. • The temperature of the liquid substance stays constant until all liquid has converted to solid. • Condensation: It is a process in which a substance changes its state from a gas to a liquid at a fixed temp. • When gas touches a cold surface, condensation takes places and it changes from gas to a liquid. • It is the reverse of boiling. • Sublimation: It is the process in which a substance turns directly from a solid to a gas. • This occurs when the particles at the surface of the solid have enough energy to escape, they break free and thus convert to gas. • Desublimation: It is the process in which gas directly changes from a gas to a solid. COOLING CURVE: IT IS THE GRAPH THAT SHOWS THE CHANGE OF STATE WHEN A SUBSTANCE IS COOLED, IT IS PLOTTED AS TEMPERATURE AGAINST TIME. A B c D E A: temperature change state: Gas No state change condensation temperature B: condensation Temperature constant State change State: Gas/liquid all gas has converted to liquid C: temperature change State: liquid No state change freezing point D: freezing State change State: solid/liquid Temperature constant all liquid has converted to solid E: state: solid No state change Temperature change • Exothermic: The process that releases heat is called as an exothermic process. • Endothermic: The process that absorbs heat is called as an endothermic process. • The heating curve shows an endothermic process as it shows the absorption of heat. • The cooling curve shows an exothermic process as it shows the release of heat. 1.4- DIFFUSION • The movement of particles from a region of higher concentration to a region of lower concentration. • It is the evidence of the kinetic particle theory. • Diffusion in gases: 1. The rate at which a gas diffuses from higher concentration to lower concentration is with the help of its molecular mass. 2. Molecular mass of a gas is the mass of its particles. 3. It can be calculated by looking at the formulas of the particles BROWNIAN MOTION Brownian motion, also called Brownian movement, any of various physical phenomena in which some quantity is constantly undergoing small, random fluctuations. MOLECULAR MASS CALCULATION GAS RELATIVE MOLECULAR MASS Hydrogen (H2 ) 1+1=2 Helium (He) 4 Methane (CH₄) 12+1+1+1+1=16 Ammonia (NH3) 14+1+1+1=17 Carbon dioxide (CO₂) 12+16+16=44 Nitrogen (N₂) 14+14=28 Oxygen (O₂) 16+16=32 A 14+1+1+1=17 NH3 RATE OF DIFFUSION B C D DEMONSTRATION 1+35.5=36.5 HCl POROUS POT EXPERIMENT Fall: When X has a lower Mr than Y the gas X diffuses into the pot causing the water level at point Z to fall. Rise: When X has a higher Mr than Y the gas y diffuses out of the pot causing the water level at point Z to rise. Same: When both gas X and Y have similar Mr this causes the gases to have same rate of diffusion inside and out of the pot causing the level of water at point Z to remain unchanged. • Diffusion in liquids: 1. It is the same as that of gases as liquids move from higher concentration to a lower concentration. 2. The diffusion in liquids is much slower than that of gases. 3. The rate of diffusion increases as the temperature is increased. 4. This type of diffusion can be seen as a drop of ink is dropped into a glass of water. CONCEPT MAP THANKYOU!!! ADDITIONAL VIDEO FOR GENERAL KNOWLEDGE BOSE-EINSTEIN CONDENSATE ADDITIONAL VIDEO FOR GENERAL KNOWLEDGE PLASMA