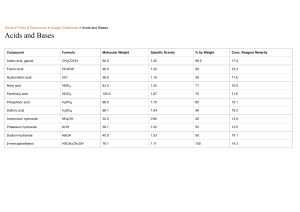
Lesson 1 Acids and Bases Focus Question How can you determine whether a solution is acidic or basic? Learning Objective The students will be able to: 1. Identify the properties and Uses of Acid and Base 2. Identify acid and base using Litmus paper. Review Vocabulary Electrolyte: a compound that breaks apart in water, forming ions that can conduct electricity Objective: U6 M22L1 – Acid and Base Determine whether a solution is acidic or basic Keywords • • • • • • Acid Base Litmus paper pH scale Hydronium ion----H3O+ Hydroxide ion-----OH- VOCABULARY Watch This! Acids • An acid is a substance that produces hydrogen ions (H+) in a water solution. • The H+ ions bind to water molecules to produce hydronium ions: H3O+. • Acids are corrosive and can burn your skin. • They can react strongly with metals such as zinc to produce hydrogen gas (H2). • Acids cause the sour taste in foods such as limes and pickles. • They tend to turn indicators red. Solutions of Acids • An acid ionizes in water, producing hydronium ions when the hydrogen ions from the acid become attracted to water molecules. • For example, when hydrogen chloride is added to water, a hydronium ion and a chloride ion are produced. Question: is this an example of ionization or dissociation? Critical Thinking Should you use a strong acid to clean out your metal drains? Why or why not? We shouldn’t use acids to clean out metal Answer drains because the acid can corrode the metal. Objective: Identify Acid and Base using Litmus paper and pH scale. Keywords: U6 M22L1 – Acid and Base Learning Check ACIDS Acid Base Sour Bitter Hydronium ion---H+ Hydroxyl ion----OH- • Taste sour • Are corrosive • Produce hydrogen gas when reacting with metals. • Produce hydronium ions H3O+ Acids Some Common Acids and Their Uses Name, Formula Use Other Information Acetic acid (CH3COOH) food preservation, commercial organic synthesis vinegar (about 5% acetic acid) Ascorbic acid (H2C6H6O6) antioxidant, vitamin Vitamin C; occurs naturally in some foods and is added to others Carbonic acid (H2CO3) carbonated drinks involved in cave formation and acid rain Hydrochloric acid (HCl) cleans steel in a process called pickling Gastric juice in the stomach is a solution of HCl and water. Sulfuric acid (H2SO4) car batteries; to manufacture fertilizers and other chemicals Dehydrating agent that extracts water from air. Watch This! Bases • Most bases contain an OH–, called a hydroxide ion, in their chemical formula. • A base is a substance that produces hydroxide ions when it is dissolved in water. • Also, a base is any substance that accepts H+ from acids. • In their pure state, many bases are crystalline solids. This is because they are ionic compounds like salts. • In solution, bases feel slippery and have a bitter taste. • They are corrosive and can burn skin. • Bases tend to turn indicators blue/purple. Solutions of Bases • Most bases are ionic compounds, made up of positive metal ions and hydroxide ions. In water, such bases dissociate, forming positive metal ions and hydroxide ions. • For example, when sodium hydroxide dissolves in water, a sodium ion and a hydroxide ion are produced. Solutions of Acids and Bases • Some bases are neutral compounds that accept H+ ions from acids, or even from water. • These types of bases can ionize other molecules to produce hydroxide ions in solution, even though they do not have an OH group. • For example, ammonia, NH3, reacts with water to produce hydroxide ions in solution. In this case, water acts as an acid. Common Bases • Sodium bicarbonate, NaHCO3 is a base used in baking. • Amines (compounds with an – NH2 group) are found in many foods. • Soaps and cleaners are generally bases, although limescale remover for your bathroom will contain a strong acid. • Sodium hydroxide (NaOH) is used in the paper industry to separate the cellulose fibers needed for paper from the wood pulp. • Aluminium hydroxide is used in water treatment plants. It’s sticky surface collects impurities, making them easier to remove. Bases Some Common Bases and Their Uses Name, Formula Use Other Information Aluminium hydroxide (Al(OH)3) color-fast fabrics, antacid, water purification sticky gel that collects suspended clay and dirt particles on its surface Calcium hydroxide (Ca(OH)2) to make leather, mortar and a.k.a slaked lime plaster; to lessen soil acidity Magnesium hydroxide (Mg(OH)2) laxative, antacid called milk of magnesia when it is mixed with water Ammonia (NH3) cleaners, fertilizer; to make rayon and nylon irritating odor that is damaging to nasal passages and lungs U6 M22L1 – Acid and Bases Keywords: Learning Check BASES Acid Base 1. Taste bitter Sour Bitter 2. Soapy to touch Hydronium ion---H3O+ Hydroxyl ion----OH- 3.Produce Hydroxide ions OH- Critical Thinking What ions do acids produce? What ions do bases produce? Do you notice anything interesting about these ions? H+ Answer -OH If you add them together, you get H2O Objective: Identify Acid and Base using Litmus paper and pH scale. U6 M22L1 – Acid and Bases Brain storming Keywords: Acid Base If you have two beakers: 1. With an acid 2. With a base Indicator Litmus paper pH scale How will you identify which beaker has acid and which has base? Objective: Identify Acid and Base using Litmus paper and pH scale. Keywords: U6 M22L1 – Acid and Bases Indicators: Litmus paper Acid Base Litmus paper pH scale We need something which can help us to identify between acid and base. We call them as indicators One of such indicator is Litmus paper Understand Objective: Identify Acid and Base using Litmus paper and pH scale. U6 M22L1 – Acid and Bases Understand Keywords: Acid Base Litmus paper pH scale Acid Base Objective: Identify Acid and Base using Litmus paper and pH scale. Word wall: Acid Base Litmus paper pH scale U6 M22L1 – Acid and Bases Understand and Apply Identify the Solution – Acid or base Quiz 1. Which is NOT characteristic of an acid? A tastes sour B feels slippery C turns blue litmus red D a source of H+ ions Quiz 2. Which is the term for H3O+? A hydroxide ion C trihydrogen oxide ion B hydronium ion D hydrogen ion Quiz 3. Which is NOT characteristic of bases? A produce OH– in water B corrosive and damaging to skin C turn blue litmus red D bitter-tasting Quiz 4. Which is an example of a base? A HCl B HNO3 C NH3 D H3PO4 Quiz 5. Unlike acids, bases made up of positive metal ions and hydroxide ions _______ in water. A dissociate C react B ionize D crystallize Lesson Summary • Acids are sour tasting and corrosive; they make the blue litmus paper turn red • Bases exist as crystals in the solid state, they are slippery, have a bitter taste, are corrosive and make the red litmus paper turn blue • Because water is polar, acids and bases can dissolve in it and produce ions Plenary https://quizizz.com/admin/quiz/629858bbbed47a001f 707f73/g8-acids-and-bases