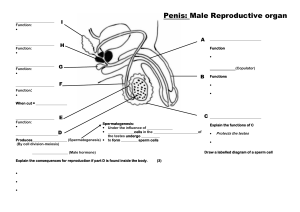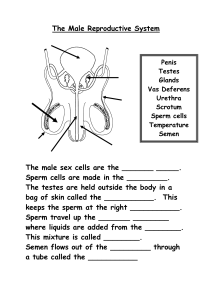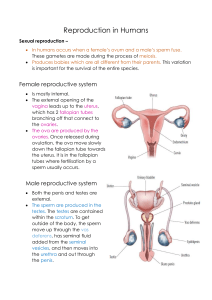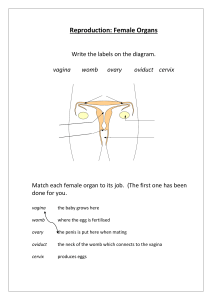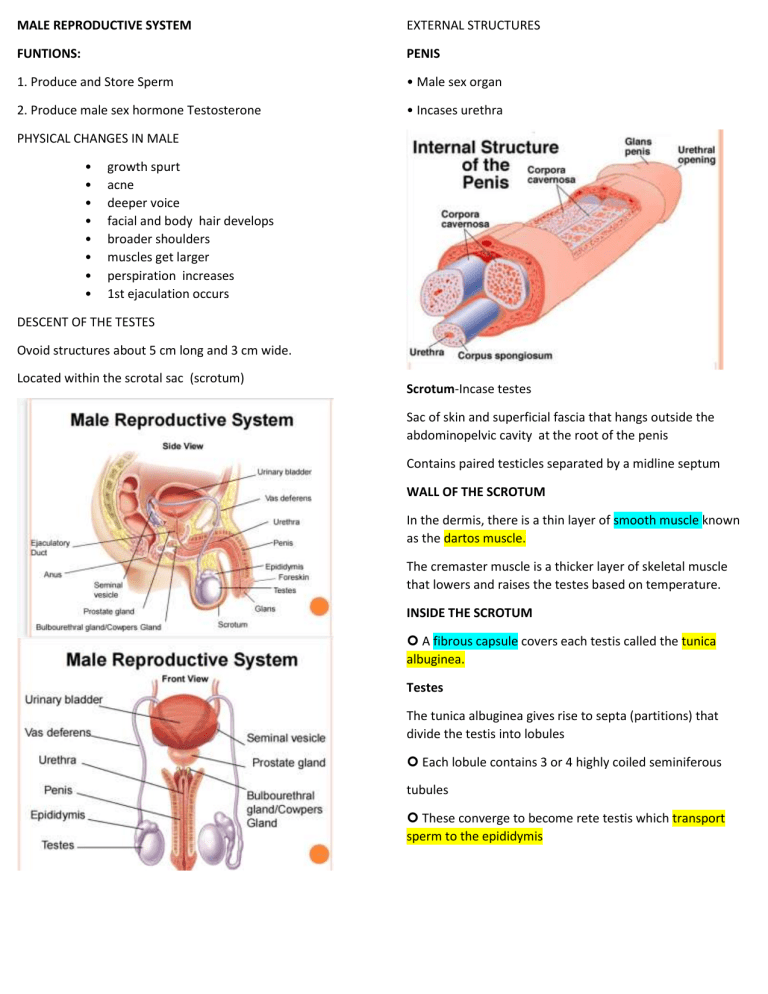
MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM EXTERNAL STRUCTURES FUNTIONS: PENIS 1. Produce and Store Sperm • Male sex organ 2. Produce male sex hormone Testosterone • Incases urethra PHYSICAL CHANGES IN MALE • • • • • • • • growth spurt acne deeper voice facial and body hair develops broader shoulders muscles get larger perspiration increases 1st ejaculation occurs DESCENT OF THE TESTES Ovoid structures about 5 cm long and 3 cm wide. Located within the scrotal sac (scrotum) Scrotum-Incase testes Sac of skin and superficial fascia that hangs outside the abdominopelvic cavity at the root of the penis Contains paired testicles separated by a midline septum WALL OF THE SCROTUM In the dermis, there is a thin layer of smooth muscle known as the dartos muscle. The cremaster muscle is a thicker layer of skeletal muscle that lowers and raises the testes based on temperature. INSIDE THE SCROTUM A fibrous capsule covers each testis called the tunica albuginea. Testes The tunica albuginea gives rise to septa (partitions) that divide the testis into lobules Each lobule contains 3 or 4 highly coiled seminiferous tubules These converge to become rete testis which transport sperm to the epididymis sperm per minute Testosterone - hormones produced by Testes - develop sexual characteristics Epididymis (on top of each testicle) • Sperm are stored and mature here Epididymis: Storage and maturation area for sperm Its head joins the efferent ductules and caps the superior aspect of the testis The duct of the epididymis has stereocilia that: Absorb testicular fluid Pass nutrients to the sperm Nonmotile sperm enter, pass through its tubes and become motile (propelled by peristalsis) Upon ejaculation the epididymis contracts, expelling sperm into the ductus deferens MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM Function: - produce and store sperm During 7th month, Testes can be seen Testes - 50,000