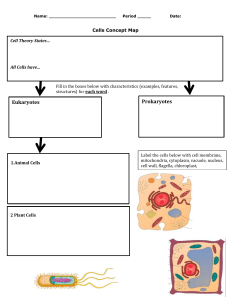
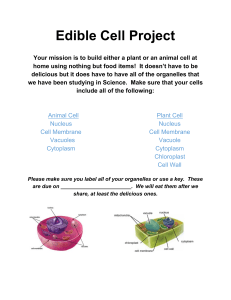
1. multicellular = containing many cells = humans unicellular = containing single cell = bacteria 2. The absence of a cell wall in animal cells means that they are more fragile and easily damaged. The fluid nature of the cytoplasm in animal cells makes it difficult to see the internal structures of the cell without staining them. 3. ribosomes, nucleus, chloroplast, cell wall, vacuole, cell membrane 4. ribosomes, nucleus, cell membrane 5. no 6. 1000 micrometers = 1 mm 7. no 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. B C B B a. i. shows cell walls; more rectangular ii. has nucleus iii. chloroplast b. i. contains genetic material (chromosomes which are made of DNA) to determine kind of protein made in the cell ii. for protein synthesis 6. a. no b. cytoplasm = a jelly-like substance where metabolic reactions occur cell membrane = a partially permeable membrane that controls what goes in and out of the cell nucleus = contains DNA to determine kind of protein made in cell c. to conduct electrical impulses 7. a. nucleus b. B = mitochondria, to provide energy from glucose so they can make protein molecules C = cytoplasm, for metabolic reactions, also has proteins dissolved in it