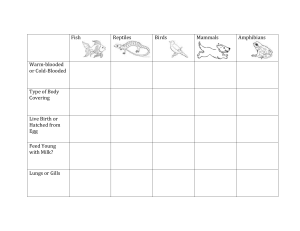
Vertebrates HAVE BACKBONES AND SKULL BONES B. Cole EDUC 730: Lesson Plan Animals such as fish, amphibians, reptiles, birds, and mammals have backbones B. Cole EDUC 730: Lesson Plan Scientist classify vertebrates into several main groups: Fish: • Jawless Fish • Cartilage Fish • Bony Fish B. Cole EDUC 730: Lesson Plan Amphibians Reptiles Birds Mammals Fish Three groups: 1. jawless fish 2. cartilage fish 3. bony fish A fish has: scaly skin, gills, heart with two chambers Most fish have fins. All fish live in water and are cold-blooded animals. cold-blooded: changes with the temperature of its environment scales: thin, overlapping pieces of bonelike material that covers the bodies of most fish. Forms a protective covering. B. Cole EDUC 730: Lesson Plan Amphibians Cold-blooded vertebrates Have a heart with three chambers Live part of their lives in water and part on land Lay eggs in water or in moist places Examples: Frogs, toads, newts and salamanders Young frogs are called tadpoles The change into adult frogs through different stages is metamorphosis. They eat large quantities of flies, mosquitoes and other insects B. Cole EDUC 730: Lesson Plan Reptiles Group of vertebrates that are more complex than amphibians Cold-blooded vertebrate Has dry, scaly skin Most have two pairs of legs with five toes on each leg Can run, crawl, climb, or paddle Breath with well developed lungs Most reproduce by laying eggs on land B. Cole EDUC 730: Lesson Plan Reptiles continued… 4 Main groups: Turtles Special shell covering for protection and movement Live on land, fresh water, ocean Lizards Live in many places cold regions, rainy regions, dry deserts The skin color of many lizards changes with surrounding conditions – camouflage B. Cole EDUC 730: Lesson Plan Reptiles continued… Alligators and Crocodiles: largest kind of reptile Strong jaws and sharp teeth Live in warm, swampy areas along streams, rivers, or lakes Snakes Some live on land, some in water No legs Body covered with dry scales Move by catching their scales on the ground and pushing forward with their muscles Do not tear or chew food, but swallow it whole B. Cole EDUC 730: Lesson Plan Birds Warm-blooded animal Have hearts with 4 chambers Have wings, which are used for flying Feathers are an important body covering Protects body of the bird Aids in balancing and flying Also helps to control a bird’s body temperature Many birds build nests in which they lay their hard- shelled eggs After the eggs hatch, the adult birds feed and protect the young B. Cole EDUC 730: Lesson Plan Birds continued… Birds live in different environments Penguins: cold, snowy areas Parrots: warm areas with much rain Ducks, geese, robins: change with season, when the weather turns cold and snowy, many migrate to warmer areas. Birds are an important food source for people B. Cole EDUC 730: Lesson Plan Mammals Most complex group of animals Examples: bats, moles, bears, horses, rats, cows, monkeys, kangaroos, rabbits, seals whales and humans A mammal is a vertebrate with a body covering of fur or hair, and special female organs that produce milk to feed its young. They care fore their young until they are able to care for themselves Live in nearly all kinds of habitats B. Cole EDUC 730: Lesson Plan Mammals continued… Mammals have more complex brains than other animals Humans are able to become skilled in the use of tools Other mammals produce eggs that develop in different ways A marsupial is a mammal that has a special pouch for carrying the undeveloped young B. Cole EDUC 730: Lesson Plan Comparison Chart Mammals Fish Constant warm body temperature Coverings of hair Cold body temperatures Coverings of scales Breath through lungs Carry their unborn young in their bodies Breath through gills Lay eggs B. Cole EDUC 730: Lesson Plan