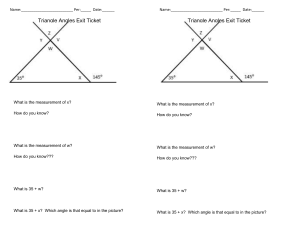
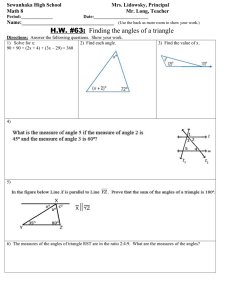
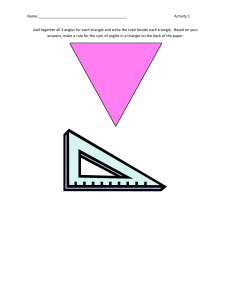
001a REFRESHER PLUMBING ARITHMETIC ELEMENTS ENGR. ROEL A. ABAO 1. For any two triangles, if an angle of one triangles is congruent to an angle of the other and if the two sides of one triangle are proportional to two sides of the other, they are what kind of triangles? a. b. c. d. Complementary Supplementary Similar Dissimilar 1. For any two triangles, if an angle of one triangles is congruent to an angle of the other and if the two sides of one triangle are proportional to two sides of the other, they are what kind of triangles? a. b. c. d. Complementary Supplementary Similar Dissimilar 2. An angle inscribe in a semi-circle is always? a. b. c. d. Unaligned More than 90 deg. Less than 90 deg. 90 deg. 2. An angle inscribe in a semi-circle is always? a. b. c. d. Unaligned More than 90 deg. Less than 90 deg. 90 deg. 3. A factor repeated to produce a power is? a. b. c. d. Numerator Square Quotient Root 3. A factor repeated to produce a power is? a. b. c. d. Numerator Square Quotient Root 4. A polygon with ten side is? a. b. c. d. Dodecagon Undecagon Decagon Tendicagon 4. A polygon with ten side is? a. b. c. d. Dodecagon Undecagon Decagon Tendicagon 5. Two angles having the same vertex and the side of one is the prolongation of the side of the other is? a. b. c. d. Acute angle Scalene angle Obtuse angle Vertical angle 5. Two angles having the same vertex and the side of one is the prolongation of the side of the other is? a. b. c. d. Acute angle Scalene angle Obtuse angle Vertical angle 6. The volume of the cube is equal to the cube of the measure of its? a. b. c. d. Angle Corner Edge Diagonal 6. The volume of the cube is equal to the cube of the measure of its? a. b. c. d. Angle Corner Edge Diagonal 7. If each two lines is perpendicular to the same line, then the lines are? a. b. c. d. Perpendicular Parallel Tangent Converging 7. If each two lines is perpendicular to the same line, then the lines are? a. b. c. d. Perpendicular Parallel Tangent Converging 8. Is a branch of mathematics dealing with integers and more generally, numeral computation? a. b. c. d. Algebra Trigonometry Geometry Arithmetic 8. Is a branch of mathematics dealing with integers and more generally, numeral computation? a. b. c. d. Algebra Trigonometry Geometry Arithmetic 9. The power to which a number is raised is indicated by a small superior figure called? a. b. c. d. Logarithm Increment Exponent Mantissa 9. The power to which a number is raised is indicated by a small superior figure called? a. b. c. d. Logarithm Increment Exponent Mantissa 10. A number that be exactly divided by two is? a. b. c. d. Real Odd Integer Even 10. A number that be exactly divided by two is? a. b. c. d. Real Odd Integer Even 11. A space that is devoid of matter and which the pressure is zero? a. b. c. d. Block hole Outer space Vacuum Inner space 11. A space that is devoid of matter and which the pressure is zero? a. b. c. d. Block hole Outer space Vacuum Inner space 12. Decrease in the value of a physical property due to the passage of time? a. b. c. d. Inflation Depletion Recession Depreciation 12. Decrease in the value of a physical property due to the passage of time? a. b. c. d. Inflation Depletion Recession Depreciation 13. We may classify an interest rate which specifies the actual rate of interest on the principal for one year as? a. b. c. d. Nominal rate Rate of return Exact interest rate Effective rate 13. We may classify an interest rate which specifies the actual rate of interest on the principal for one year as? a. b. c. d. Nominal rate Rate of return Exact interest rate Effective rate 14. The ratio of the interest payment to the principal for a given unit of time and usually expressed as a percentage of the principal? a. b. c. d. Interest Interest rate Investment Rate 14. The ratio of the interest payment to the principal for a given unit of time and usually expressed as a percentage of the principal? a. b. c. d. Interest Interest rate Investment Rate 15. Additional information of prospective bidders on contract documents issued prior to bidding date? a. b. c. d. Depict Escalate Assessment Bid bulletin 15. Additional information of prospective bidders on contract documents issued prior to bidding date? a. b. c. d. Depict Escalate Assessment Bid bulletin 16. The acceleration is ________ the mass of the object. a. b. c. d. Directly proportional to Inversely proportional to Directly proportional to the square of Inversely proportional to the square of 16. The acceleration is ________ the mass of the object. a. b. c. d. Directly proportional to Inversely proportional to Directly proportional to the square of Inversely proportional to the square of FORCE = MASS x ACCELERATION 17. Reduction in the level of national income and output usually accompanied by the fall in the general price level? a. b. c. d. Devaluation Deflation Inflation Depreciation 17. Reduction in the level of national income and output usually accompanied by the fall in the general price level? a. b. c. d. Devaluation Deflation Inflation Depreciation 18. It is a series of equal payment occuring at equal interval of time? a. b. c. d. Annuity Debt Amortization Deposit 18. It is a series of equal payment occuring at equal interval of time? a. b. c. d. Annuity Debt Amortization Deposit 19. The place where buyers and sellers come together? a. b. c. d. Market Business Recreation center Buy and sell section 19. The place where buyers and sellers come together? a. b. c. d. Market Business Recreation center Buy and sell section 20. A market whereby there is only one buyer of an item for which there are no goods substitute? a. b. c. d. Monopsony Oligopoly Monopoly Oligopsony 20. A market whereby there is only one buyer of an item for which there are no goods substitute? a. b. c. d. Monopsony Oligopoly Monopoly Oligopsony 21. It is a series of equal payments occurring at equal interval of time where the first payment is made after several periods, after the beginning of the payment? a. b. c. d. Perpetuity Ordinary annuity Annuity due Deferred annuity 21. It is a series of equal payments occurring at equal interval of time where the first payment is made after several periods, after the beginning of the payment? a. b. c. d. Perpetuity Ordinary annuity Annuity due Deferred annuity 22. The total income equal the total operating cost? a. b. c. d. Balance sheet In place value Check and balance Breakeven no gain loss 22. The total income equal the total operating cost? a. b. c. d. Balance sheet In place value Check and balance Breakeven no gain loss 23. Kind of obligation which has no condition attached. a. b. c. d. Analytic Pure Gratuitous Private 23. Kind of obligation which has no condition attached. a. b. c. d. Analytic Pure Gratuitous Private 24. Direct labor cost incurred in the factory and direct material costs of all materials that go into production. The sum of these two direct cost is known as: a. b. c. d. GS and A expenses Operating and Maintenance cost Prime cost O and M cost 24. Direct labor cost incurred in the factory and direct material costs of all materials that go into production. The sum of these two direct cost is known as: a. b. c. d. GS and A expenses Operating and Maintenance cost Prime cost O and M cost 25. An index of short term paying ability is called? a. b. c. d. Receivable turn over Profit margin ratio Current ratio Acid-test ratio 25. An index of short term paying ability is called? a. b. c. d. Receivable turn over Profit margin ratio Current ratio Acid-test ratio 26. An artificial expenses that spreads purchase price of an asset or another property over number of years. a. b. c. d. Depreciation Sinking fund Amnesty Bond 26. An artificial expenses that spreads purchase price of an asset or another property over number of years. a. b. c. d. Depreciation Sinking fund Amnesty Bond 27. Estimated value at the end of the useful life. a. b. c. d. Market value Fair value Salvage value Book value 27. Estimated value at the end of the useful life. a. b. c. d. Market value Fair value Salvage value Book value 28. Consist of the actual counting or determination of the actual quantity of the materials on hand as of a given date. a. b. c. d. Physical inventory Material update Technological assessment Material count 28. Consist of the actual counting or determination of the actual quantity of the materials on hand as of a given date. a. b. c. d. Physical inventory Material update Technological assessment Material count 29. A series of uniform accounts over a period of time. a. b. c. d. Depreciation Annuity Perpetuity Inflation 29. A series of uniform accounts over a period of time. a. b. c. d. Depreciation Annuity Perpetuity Inflation 30. The quantity of a certain commodity that is offered for sale at a certain price at a given place and time. a. b. c. d. Demand Supply Stocks Goods 30. The quantity of a certain commodity that is offered for sale at a certain price at a given place and time. a. b. c. d. Demand Supply Stocks Goods 31. Work-in process is classified as, a. b. c. d. An asset A liability An expenses An owner’s equity 31. Work-in process is classified as, a. b. c. d. An asset A liability An expenses An owner’s equity 32. What is the highest position in the corporation? a. b. c. d. President Board of Directors Chairman of the Board Stockholders 32. What is the highest position in the corporation? a. b. c. d. President Board of Directors Chairman of the Board Stockholders 33. Type of ownership in business here individuals exercise and enjoy the right in their own interest. a. b. c. d. Equitable Public Private Pure 33. Type of ownership in business here individuals exercise and enjoy the right in their own interest. a. b. c. d. Equitable Public Private Pure 34. Decrease in the value of a physical property due to the passage of time. a. b. c. d. Inflation Depletion Recession Depreciation 34. Decrease in the value of a physical property due to the passage of time. a. b. c. d. Inflation Depletion Recession Depreciation 35. An association of two or more individuals for the purpose of operating a business as co-owners for profit, a. b. c. d. Sole proprietorship Company Partnership Corporation 35. An association of two or more individuals for the purpose of operating a business as co-owners for profit, a. b. c. d. Sole proprietorship Company Partnership Corporation 36. Refers to the vertical speed at which the force of air resistance is just sufficient to the balance the body’s weight. a. b. c. d. Gravitational acceleration Terminal speed Drag Lift 36. Refers to the vertical speed at which the force of air resistance is just sufficient to the balance the body’s weight. a. b. c. d. Gravitational acceleration Terminal speed Drag Lift 37. It is defined to the capacity of a commodity to satisfy human want. a. b. c. d. Discount Luxury Necessity Utility 37. It is defined to the capacity of a commodity to satisfy human want. a. b. c. d. Discount Luxury Necessity Utility 38. It is the amount which a willing buyer will pay to willing seller for a property where each has equal advantage and is under no compulsion to buy or sell. a. b. c. d. Fair value Market value Book value Salvage value 38. It is the amount which a willing buyer will pay to willing seller for a property where each has equal advantage and is under no compulsion to buy or sell. a. b. c. d. Fair value Market value Book value Salvage value 39. This occurs in a situation where a commodity or service is supplied by a number of vendor by a number of vendors and there is nothing to prevent additional vendors entering the market. a. b. c. d. Perfect competition Oligopoly Monopoly Elastic demand 39. This occurs in a situation where a commodity or service is supplied by a number of vendor by a number of vendors and there is nothing to prevent additional vendors entering the market. a. b. c. d. Perfect competition Oligopoly Monopoly Elastic demand 40. These are products or services that are desired by human and will be purchase if money is available after the required necessities have been obtain, a. b. c. d. Utilities Necessities Luxuries Product goods and services 40. These are products or services that are desired by human and will be purchase if money is available after the required necessities have been obtain, a. b. c. d. Utilities Necessities Luxuries Product goods and services 41. These are products or services that are required to support human life and activities that will be purchased in somewhat the same quantity even though the price varies considerably, a. b. c. d. Utilities Necessities Luxuries Product goods and services 41. These are products or services that are required to support human life and activities that will be purchased in somewhat the same quantity even though the price varies considerably, a. b. c. d. Utilities Necessities Luxuries Product goods and services 42. A condition where only few individuals produce a certain product and that any action of one will lead to almost the same action of others. a. b. c. d. Oligopoly Semi-monopoly Monopoly Perfect competition 42. A condition where only few individuals produce a certain product and that any action of one will lead to almost the same action of others. a. b. c. d. Oligopoly Semi-monopoly Monopoly Perfect competition 43. Grand total of the assets and operational capability of a corporation. a. b. c. d. Authorized capital Investment Subscribed capital Money market 43. Grand total of the assets and operational capability of a corporation. a. b. c. d. Authorized capital Investment Subscribed capital Money market 44. The worth of the property equals to the original cost less depreciation. a. b. c. d. Scrap value Face value Market value Book value 44. The worth of the property equals to the original cost less depreciation. a. b. c. d. Scrap value Face value Market value Book value 45. Money paid for the use of borrowed capital. a. b. c. d. Discount Credit Interest Profit 45. Money paid for the use of borrowed capital. a. b. c. d. Discount Credit Interest Profit 46. Liquid assets such as cash and other assets that can be converted quickly into cash, such as accounts receivable and merchandise are called a. b. c. d. Total assets Fixed assets Current assets None of the above 46. Liquid assets such as cash and other assets that can be converted quickly into cash, such as accounts receivable and merchandise are called a. b. c. d. Total assets Fixed assets Current assets None of the above 47. The length of time which the property may be operated at a profit a. b. c. d. Physical life Economic life Operating life All of the above 47. The length of time which the property may be operated at a profit a. b. c. d. Physical life Economic life Operating life All of the above 48. The provision in the contract that indicates the possible adjustment of material cost and labor cost. a. b. c. d. Secondary clause Escalatory clause Contingency clause Main clause 48. The provision in the contract that indicates the possible adjustment of material cost and labor cost. a. b. c. d. Secondary clause Escalatory clause Contingency clause Main clause 49. The present worth of all depreciation over the economic life of the item is called a. b. c. d. Book value Capital recovery Depreciation recovery Sinking fund 49. The present worth of all depreciation over the economic life of the item is called a. b. c. d. Book value Capital recovery Depreciation recovery Sinking fund 50. Gross profit, sale less cost of good sold, as a percentage of sales is called a. b. c. d. Profit margin Gross margin Net income Rate of return 50. Gross profit, sale less cost of good sold, as a percentage of sales is called a. b. c. d. Profit margin Gross margin Net income Rate of return 51. Worth of the property as shown in the accounting records of an enterprise, a. b. c. d. Fair value Market value Salvage value Book value 51. Worth of the property as shown in the accounting records of an enterprise, a. b. c. d. Fair value Market value Salvage value Book value 52. Those funds that are required to make the enterprise or project a going concern, a. b. c. d. Initial investments Current accounts Working capital Subscribed capital 52. Those funds that are required to make the enterprise or project a going concern, a. b. c. d. Initial investments Current accounts Working capital Subscribed capital 53. A market situation where there is one seller with many buyer, a. b. c. d. Monopoly Monopsony Oligopoly Oligopsony 53. A market situation where there is one seller with many buyer, a. b. c. d. Monopoly Monopsony Oligopoly Oligopsony 54. A market situation where there is one seller and one buyer, a. b. c. d. Monopoly Monopsony Bilateral monopoly Bilateral monopsony 54. A market situation where there is one seller and one buyer, a. b. c. d. Monopoly Monopsony Bilateral monopoly Bilateral monopsony 55. A market situation where there are few sellers and few buyers, a. b. c. d. Oligopoly Oligopsony Bilateral oligopoly Bilateral Oligopsony 55. A market situation where there are few sellers and few buyers, a. b. c. d. Oligopoly Oligopsony Bilateral oligopoly Bilateral Oligopsony 56. A market situation where there are only two buyers with many sellers, a. b. c. d. Duopoly Oligopoly Duopsony Oligopsony 56. A market situation where there are only two buyers with many sellers, a. b. c. d. Duopoly Oligopoly Duopsony Oligopsony 57. Define as the future value minus the present value. a. b. c. d. Interest Rate of return Discount Capital 57. Define as the future value minus the present value. a. b. c. d. Interest Rate of return Discount Capital 58. If an object is thrown vertically upward, its acceleration. a. Is smaller than that of the object thrown vertically downward b. Is equal to that of an object thrown vertically downward c. Greater than that of the object thrown vertically downward d. Zero until the object reaches maximum point 58. If an object is thrown vertically upward, its acceleration. a. Is smaller than that of the object thrown vertically downward b. Is equal to that of an object thrown vertically downward c. Greater than that of the object thrown vertically downward d. Zero until the object reaches maximum point 59. Scrap value of an asset is sometimes known as, a. b. c. d. Book value Salvage value Replacement value Future value 59. Scrap value of an asset is sometimes known as, a. b. c. d. Book value Salvage value Replacement value Future value 60. A type of annuity where the payments are made at the end of payment period starting from the first period, a. b. c. d. Ordinary annuity Annuity due Deferred annuity Perpetuity 60. A type of annuity where the payments are made at the end of payment period starting from the first period, a. b. c. d. Ordinary annuity Annuity due Deferred annuity Perpetuity 61. Bond to which are attached coupons indicating the interest due and the date when such interest is to be paid, a. b. c. d. Registered bond Coupon bond Mortgage bond Collateral trust bond 61. Bond to which are attached coupons indicating the interest due and the date when such interest is to be paid, a. b. c. d. Registered bond Coupon bond Mortgage bond Collateral trust bond 62. “When free competition exists the price of a product will be that value where supply is equal to the demand” a. b. c. d. Law of diminishing return Law of supply Law of demand Law of supply and demand 62. “When free competition exists the price of a product will be that value where supply is equal to the demand” a. b. c. d. Law of diminishing return Law of supply Law of demand Law of supply and demand 63. The ratio of the net income to the owners equity is known as, a. b. c. d. Price-earning ratio Profit margin ratio Return of investment Gross margin 63. The ratio of the net income to the owners equity is known as, a. b. c. d. Price-earning ratio Profit margin ratio Return of investment Gross margin 64. Capitalized cost of any property is equal to the, a. b. c. d. Annual cost First cost + interest of the first cost First cost + cost of perpetual maintenance First cost + salvage value 64. Capitalized cost of any property is equal to the, a. b. c. d. Annual cost First cost + interest of the first cost First cost + cost of perpetual maintenance First cost + salvage value 65. Which of the following depreciation methods cannot have a salvage value of zero? a. b. c. d. Declining balance method Sinking fund method Straight line method SYD method 65. Which of the following depreciation methods cannot have a salvage value of zero? a. b. c. d. Declining balance method Sinking fund method Straight line method SYD method 66. The lessening of value of an asset due to the decrease in the quantity available preferring to the natural resources? a. b. c. d. Depreciation Depletion Inflation Incremental cost 66. The lessening of value of an asset due to the decrease in the quantity available preferring to the natural resources? a. b. c. d. Depreciation Depletion Inflation Incremental cost 67. An increase in the value of a capital asset is called a. b. c. d. Profit Capital gain Capital expenditure Capital stock 67. An increase in the value of a capital asset is called a. b. c. d. Profit Capital gain Capital expenditure Capital stock 68. Lands, buildings, plant and machinery are example of a. b. c. d. Current assets Trade investments Fixed assets Intangible assets 68. Lands, buildings, plant and machinery are example of a. b. c. d. Current assets Trade investments Fixed assets Intangible assets 69. An angle that measures from the horizontal upward to an object is called a. b. c. d. Right angle Acute angle Angle of elevation Angle of depression 69. An angle that measures from the horizontal upward to an object is called a. b. c. d. Right angle Acute angle Angle of elevation Angle of depression 70. Any number multiplied by _____ equals unity? a. b. c. d. e. Infinity Itself Its reciprocal Zero None of the above 70. Any number multiplied by _____ equals unity? a. b. c. d. e. Infinity Itself Its reciprocal Zero None of the above 71. A polygon with 15 sides is called a. b. c. d. Pentagon Dodecagon Pentadecagon nonagon 71. A polygon with 15 sides is called a. b. c. d. Pentagon Dodecagon Pentadecagon nonagon 72. The chord passing through the focus of the parabola and perpendicular to its axis is term as: a. b. c. d. Directrix Translated axis Latus rectum Asymptotes 72. The chord passing through the focus of the parabola and perpendicular to its axis is term as: a. b. c. d. Directrix Translated axis Latus rectum Asymptotes 73. For ordinary annuity, what is the value for periodic payment “A”? a. b. c. d. Fi / (1+ i)^ n - 1 Pi / (1+ i)^ n - 1 Fi / (1+ n)^ i - 1 Fi / 1+ (1+ i)^ n 73. For ordinary annuity, what is the value for periodic payment “A”? a. b. c. d. Fi / (1+ i)^ n - 1 Pi / (1+ i)^ n - 1 Fi / (1+ n)^ i - 1 Fi / 1+ (1+ i)^ n 74. In a regular polygon, the perpendicular line drawn from the center of the inscribed circle to any one of the sides is called: a. b. c. d. Radius Altitude Median Apothem 74. In a regular polygon, the perpendicular line drawn from the center of the inscribed circle to any one of the sides is called: a. b. c. d. Radius Altitude Median Apothem 75. For the flush tank type water closet, what is the main purpose of the tank? a. b. c. d. Serves as a back rest To give water surge To hold a supply of water For rim support 75. For the flush tank type water closet, what is the main purpose of the tank? a. b. c. d. Serves as a back rest To give water surge To hold a supply of water For rim support 76. The section of the sphere cut by a plane through its center is termed as: a. b. c. d. Small circle Semi-circle Big circle Great circle 76. The section of the sphere cut by a plane through its center is termed as: a. b. c. d. Small circle Semi-circle Big circle Great circle 77. The statement “a+b = b+a” is a, a. b. c. d. Associative law of addition Commutative law of addition Associative law of multiplication Commutative law of multiplication 77. The statement “a+b = b+a” is a, a. b. c. d. Associative law of addition Commutative law of addition Associative law of multiplication Commutative law of multiplication 78. Today is Monday. After 61 days, it will be: a. b. c. d. Wednesday Saturday Sunday Thursday 78. Today is Monday. After 61 days, it will be: a. b. c. d. Wednesday Saturday Sunday Thursday 79. If two bodies of different masses, initially at rest, are acted upon by the same force for the same time, then what will be the same in both bodies? a. b. c. d. Velocity Acceleration Kinetic energy Momentum 79. If two bodies of different masses, initially at rest, are acted upon by the same force for the same time, then what will be the same in both bodies? a. b. c. d. Velocity Acceleration Kinetic energy Momentum 80. What is so very special about the number 8549176320? a. b. c. d. It’s a cyclic number It’s a Fibonacci series It is the largest number yet enumerated orally It contains digits in an alphabetical order 80. What is so very special about the number 8549176320? a. b. c. d. It’s a cyclic number It’s a Fibonacci series It is the largest number yet enumerated orally It contains digits in an alphabetical order 81. A line segment joining two points on a circle is called: a. b. c. d. Arc Tangent Sector Chord 81. A line segment joining two points on a circle is called: a. b. c. d. Arc Tangent Sector Chord 82. The absorption of ink by blotting paper involves which phenomenon? a. b. c. d. Siphon action Diffusion of ink through the blotting Viscosity of ink Capillary action phenomenon 82. The absorption of ink by blotting paper involves which phenomenon? a. b. c. d. Siphon action Diffusion of ink through the blotting Viscosity of ink Capillary action phenomenon 83. Let a thin capillary tube be replaced with another tube of insufficient length then, what will happen to water? a. b. c. d. Depressed will overflow Change its meniscus Will not rise 83. Let a thin capillary tube be replaced with another tube of insufficient length then, what will happen to water? a. b. c. d. Depressed will overflow Change its meniscus Will not rise 84. Why metals electricity? a. b. c. d. are They contain free electrons The atoms are lightly packed They have high melting point All of the above good conductors of 84. Why metals electricity? a. b. c. d. are They contain free electrons The atoms are lightly packed They have high melting point All of the above good conductors of 85. On 8th Feb, 2005 it was Tuesday. What was the day of the week on 8th Feb, 2004? a. b. c. d. Tuesday Monday Sunday Wednesday 85. On 8th Feb, 2005 it was Tuesday. What was the day of the week on 8th Feb, 2004? a. b. c. d. Tuesday Monday Sunday Wednesday 86. A 5-pointed star is also known as: a. b. c. d. Pentagon Pentagram Pentatron Quintagon 86. A 5-pointed star is also known as: a. b. c. d. Pentagon Pentagram Pentatron Quintagon 87. The normal to a given plane is: a. b. c. d. Lying on the plane Coplanar Perpendicular to the plane Parallel to the plane 87. The normal to a given plane is: a. b. c. d. Lying on the plane Coplanar Perpendicular to the plane Parallel to the plane 88. A plane section cut from a right circular cone by a plane perpendicular to the base of the cone is: a. b. c. d. Parabola Circle Hyperbola Ellipse 88. A plane section cut from a right circular cone by a plane perpendicular to the base of the cone is: a. b. c. d. Parabola Circle Hyperbola Ellipse 89. Which of the following statements is true? a. All squares are rectangles and rhombuses. b. All rectangles are rhombuses, but not all rhombuses are rectangles. c. All squares are parallelograms, but not all squares are rectangles. d. All rhombuses are parallelograms and all parallelogram are rhombuses. 89. Which of the following statements is true? a. All squares are rectangles and rhombuses. b. All rectangles are rhombuses, but not all rhombuses are rectangles. c. All squares are parallelograms, but not all squares are rectangles. d. All rhombuses are parallelograms and all parallelogram are rhombuses. 90. When a solid (ice and snow) changes into water vapor (gas) without moving through the liquid phase, the process is called a. b. c. d. Condensation Evaporation Deposition Sublimation 90. When a solid (ice and snow) changes into water vapor (gas) without moving through the liquid phase, the process is called a. b. c. d. Condensation Evaporation Deposition Sublimation 91. Its is amount of energy needed to cool or heat 1 lb of water by one degree F. a. b. c. d. Celsius Rankine Btu Calories 91. Its is amount of energy needed to cool or heat 1 lb of water by one degree F. a. b. c. d. Celsius Rankine Btu Calories 92. One liter per second is equal to _____ gpm? a. b. c. d. 0.278 gpm 15.85 gpm 7.48 gpm 264 gpm 92. One liter per second is equal to _____ gpm? a. b. c. d. 0.278 gpm 15.85 gpm 7.48 gpm 264 gpm 93. One btu/hr is equal to ______ kJ/hr? a. b. c. d. 3.96 kJ/hr 1.055 kJ/hr 4.40 kJ/hr 3413 kJ/hr 93. One btu/hr is equal to ______ kJ/hr? a. b. c. d. 3.96 kJ/hr 1.055 kJ/hr 4.40 kJ/hr 3413 kJ/hr 94. 1 atm is equal to _____? a. b. c. d. e. 406.8 in. of water 76 cm Hg 101.3 KPa 14.7 psi All of the above 94. 1 atm is equal to _____? a. b. c. d. e. 406.8 in. of water 76 cm Hg 101.3 KPa 14.7 psi All of the above 95. 1 horsepower is equal to ____ ? a. b. c. d. e. 2545 btu/hr 550 ft-lb/s 178.1 cal/s 746 watts All of the above 95. 1 horsepower is equal to ____ ? a. b. c. d. e. 2545 btu/hr 550 ft-lb/s 178.1 cal/s 746 watts All of the above 96. One CMH is equal to _____ ? a. b. c. d. 0.588 cfm 4.4 gpm 0.278 lps All of the above 96. One CMH is equal to _____ ? a. b. c. d. 0.588 cfm 4.4 gpm 0.278 lps All of the above 97. One inch water column at 4 deg. C is equal ______? a. b. c. d. 0.036 psi 250 Pa 1.868 Torr All of the above 97. One inch water column at 4 deg. C is equal ______? a. b. c. d. 0.036 psi 250 Pa 1.868 Torr All of the above 98. One kilowatt is equal to ______? a. b. c. d. e. 1.34 hp 737.6 ft-lb/s 238.9 cal/s 3413 btu/hr All of the above 98. One kilowatt is equal to ______? a. b. c. d. e. 1.34 hp 737.6 ft-lb/s 238.9 cal/s 3413 btu/hr All of the above 99. One m3 is equal to ______? a. b. c. d. e. 35.3 ft3 264.04 gal 9.81 kPa 1000 li All of the above 99. One m3 is equal to ______? a. b. c. d. e. 35.3 ft3 264.04 gal 9.81 kPa 1000 li All of the above 100. One gpm is equal to ______? a. b. c. d. e. 0.063 lps 449 cfs 0.2272 cmh 1440 gpd All of the above 100. One gpm is equal to ______? a. b. c. d. e. 0.063 lps 449 cfs 0.2272 cmh 1440 gpd All of the above 101. Brake horsepower is: a. b. c. d. The power delivered by the motor to the pump. The power delivered by the pump. Always greater than the motor horsepower. Always less than the motor horsepower. 101. Brake horsepower is: a. b. c. d. The power delivered by the motor to the pump. The power delivered by the pump. Always greater than the motor horsepower. Always less than the motor horsepower. 102. What is the term for the combined efficiency of a pump and motor that is obtained by multiplying the pump efficiency by the motor efficiency? a. b. c. d. Total system efficiency Well efficiency Wire-to-water efficiency Motor-to-pipe efficiency 102. What is the term for the combined efficiency of a pump and motor that is obtained by multiplying the pump efficiency by the motor efficiency? a. b. c. d. Total system efficiency Well efficiency Wire-to-water efficiency Motor-to-pipe efficiency 103. Which of the following is the standard acceleration due to gravity in the English unit? a. b. c. d. 981 fps^2 32.2 fps^2 9.81 fps^2 32.2 ips^2 103. Which of the following is the standard acceleration due to gravity in the English unit? a. b. c. d. 981 fps^2 32.2 fps^2 9.81 fps^2 32.2 ips^2 104. What is the value of 1 radian in degrees? a. b. c. d. 57.3 deg. 89.55 deg. 60.3 deg. All of the above 104. What is the value of 1 radian in degrees? a. b. c. d. 57.3 deg. 89.55 deg. 60.3 deg. All of the above 105. How many degrees are 4800 mils? a. b. c. d. 180 deg. 270 deg. 90 deg. 360 deg. 105. How many degrees are 4800 mils? a. b. c. d. 180 deg. 270 deg. 90 deg. 360 deg. 106. The atomic weight of hydrogen is 1 gram per gram-atom. What is the mass of a hydrogen atom? a. b. c. d. 1.66 x 10^-24 g/atom 6.02 x 10^-23 g/atom 1 g/atom The mass is too small to calculate 106. The atomic weight of hydrogen is 1 gram per gram-atom. What is the mass of a hydrogen atom? a. b. c. d. 1.66 x 10^-24 g/atom 6.02 x 10^-23 g/atom 1 g/atom The mass is too small to calculate 107. The equation y = a1 + a2x is an algebraic expression for which of the following choices? a. b. c. d. Straight line Cosine expansion series Circle in polar form Projectile motion 107. The equation y = a1 + a2x is an algebraic expression for which of the following choices? a. b. c. d. Straight line Cosine expansion series Circle in polar form Projectile motion 108. One million gallons per day (mgd) is equal to ______? a. b. c. d. 684.04 kPa 694 gpm 1,000,000 li All of the above 108. One million gallons per day (mgd) is equal to ______? a. b. c. d. 684.04 kPa 694 gpm 1,000,000 li All of the above 109. One million gallons per day (mgd) is equal to ______? a. b. c. d. 1.547 cfs 449 gpm 3.785 li All of the above 109. One million gallons per day (mgd) is equal to ______? a. b. c. d. 1.547 cfs 449 gpm 3.785 li All of the above 110. One meter is equal to ______? a. b. c. d. 1.094 yard 39.37 in 3.28 ft All of the above 110. One meter is equal to ______? a. b. c. d. 1.094 yard 39.37 in 3.28 ft All of the above 111. One quarts is equal to ______? a. b. c. d. 0.946 li 449 cfs 0.2272 cmh All of the above 111. One quarts is equal to ______? a. b. c. d. 0.946 li 449 cfs 0.2272 cmh All of the above 112. Determine the value of each interior angle of a regular pentagon. a. b. c. d. 108 deg. 120 deg. 180 deg. 90 deg. 112. Determine the value of each interior angle of a regular pentagon. a. b. c. d. 108 deg. 120 deg. 180 deg. 90 deg. 113. Determine the first derivative with respect to x of the function: g(x) = 5 sq. rt. Of 10 – 35. a. b. c. d. 0 0.75 35 5 113. Determine the first derivative with respect to x of the function: g(x) = 5 sq. rt. Of 10 – 35. a. b. c. d. 0 0.75 35 5 114. Find the root mean square of 11,23 and 35. a. b. c. d. 25 27 26 24 114. Find the root mean square of 11,23 and 35. a. b. c. d. 25 27 26 24 115. Think of a number. Double the number. Subtract 6 from the result and divide the answer by 2. The quotient will be 20. what is the number you think? a. b. c. d. 12 20 23 32 115. Think of a number. Double the number. Subtract 6 from the result and divide the answer by 2. The quotient will be 20. what is the number you think? a. b. c. d. 12 20 23 32 116. How many permutation can be made out of the word ENGINEERING? a. b. c. d. 277,200 272,700 200,277 227,700 116. How many permutation can be made out of the word ENGINEERING? a. b. c. d. 277,200 272,700 200,277 227,700 117. What is the acid test ratio? a. The ratio of owner’s equity to the current liabilities. b. The ratio of all assets to actual current liabilities. c. The ratio of current assets (exclusive of inventory) to the total current liabilities. d. The ratio of gross margin to operating, sales, administrative expenses. 117. What is the acid test ratio? a. The ratio of owner’s equity to the current liabilities. b. The ratio of all assets to actual current liabilities. c. The ratio of current assets (exclusive of inventory) to the total current liabilities. d. The ratio of gross margin to operating, sales, administrative expenses. 118. How do call an energy required to move 1 coulomb of charge through an element? a. b. c. d. Current Voltage Power Resonance 118. How do call an energy required to move 1 coulomb of charge through an element? a. b. c. d. Current Voltage Power Resonance 119. This is a number sequence where the succeeding term is obtained by adding the last pair of preceding terms such as sequence (1,1,2,3,5,8…) how do you call this number sequence? a. b. c. d. Euler’s number Fermat number Fibonacci number Darsho’s number 119. This is a number sequence where the succeeding term is obtained by adding the last pair of preceding terms such as sequence (1,1,2,3,5,8…) how do you call this number sequence? a. b. c. d. Euler’s number Fermat number Fibonacci number Darsho’s number 120. If the roots of an equation are zero, then, how do you classify the solutions? a. b. c. d. Extraneous solutions Trivial solutions Conditional solutions Darsho’s solutions 120. If the roots of an equation are zero, then, how do you classify the solutions? a. b. c. d. Extraneous solutions Trivial solutions Conditional solutions Darsho’s solutions 121. In electricity, how do you call the rate of charge flow? a. b. c. d. Potential difference Current Voltage Power 121. In electricity, how do you call the rate of charge flow? a. b. c. d. Potential difference Current Voltage Power 122. This law in electrical circuits states, “The algebraic sum of currents entering a node (or a closed boundary) is zero”. How do you call this law? a. b. c. d. Kirchhoff’s current law Ohm’s law Kirchhoff’s voltage law Darsho’s law 122. This law in electrical circuits states, “The algebraic sum of currents entering a node (or a closed boundary) is zero”. How do you call this law? a. b. c. d. Kirchhoff’s current law Ohm’s law Kirchhoff’s voltage law Darsho’s law 123. This law in electrical circuits states, “The algebraic sum of all voltages around a closed path (or loop) is zero”. How do you call this law? a. b. c. d. Kirchoff’s current law Ohm’s law Kirchoff’s voltage law Darsho’s law 123. This law in electrical circuits states, “The algebraic sum of all voltages around a closed path (or loop) is zero”. How do you call this law? a. b. c. d. Kirchoff’s current law Ohm’s law Kirchoff’s voltage law Darsho’s law 124. In electrical, what is the SI unit of conductance? a. b. c. d. Ohm Siemens Ampere Darsho’s siemens 124. In electrical, what is the SI unit of conductance? a. b. c. d. Ohm Siemens Ampere Darsho’s siemens 125. Which of the following is the equivalent of 1 ampere? a. b. c. d. 1 coulomb per second 1 joule per second 1 darsho per second 1 kJ per second 125. Which of the following is the equivalent of 1 ampere? a. b. c. d. 1 coulomb per second 1 joule per second 1 darsho per second 1 kJ per second 126. This is the process of expressing a polynomial as the product of another polynomial or monomial of lower degree. What is this mathematical process? a. b. c. d. Rationalization Decomposition Factoring Darshoing 126. This is the process of expressing a polynomial as the product of another polynomial or monomial of lower degree. What is this mathematical process? a. b. c. d. Rationalization Decomposition Factoring Darshoing 127. This is a point where the concavity of a curve changes or when the slope of the curve is neither increasing nor decreasing. What is this point commonly called? a. b. c. d. Maximum point Minimum point Point of inflection Darsho’s point 127. This is a point where the concavity of a curve changes or when the slope of the curve is neither increasing nor decreasing. What is this point commonly called? a. b. c. d. Maximum point Minimum point Point of inflection Darsho’s point 128. How do you call the axis of the hyperbola that passes through the center, the foci and vertices? a. b. c. d. Transverse axis Conjugate axis Asymptote axis Major axis 128. How do you call the axis of the hyperbola that passes through the center, the foci and vertices? a. b. c. d. Transverse axis Conjugate axis Asymptote axis Major axis 129. What is the number, which could not be expressed as a quotient of two integers? a. b. c. d. Natural Rational Irrational Surd 129. What is the number, which could not be expressed as a quotient of two integers? a. b. c. d. Natural Rational Irrational Surd 130. How do you call the opposite of the prefix nano? a. b. c. d. Peta Tera Giga Gaga 130. How do you call the opposite of the prefix nano? a. b. c. d. Peta Tera Giga Gaga 131. What do you a triangle having unequal sides? a. b. c. d. Obtuse Oblique Scalene Isosceles 131. What do you a triangle having unequal sides? a. b. c. d. Obtuse Oblique Scalene Isosceles 132. How do you call the distance of a point from y-axis? a. b. c. d. Abscissa Ordinate Coordinate Polar distance 132. How do you call the distance of a point from y-axis? a. b. c. d. Abscissa Ordinate Coordinate Polar distance 133. This is the measure of central tendency defined as the most frequent score. How do you call this measure of central tendency? a. b. c. d. Median Mode Mean Deviation 133. This is the measure of central tendency defined as the most frequent score. How do you call this measure of central tendency? a. b. c. d. Median Mode Mean Deviation 134. One mil is equal to ______? a. b. c. d. .01 in .001 in .0001 in .00001 in 134. One mil is equal to ______? a. b. c. d. .01 in .001 in .0001 in .00001 in 135. A polygon with 10 sides is said to be: a. b. c. d. Dodecagon Decagon Decahadron Dodecahadron 135. A polygon with 10 sides is said to be: a. b. c. d. Dodecagon Decagon Decahadron Dodecahadron 136. Any number expressed in place value notation with the base 12 is known as: a. b. c. d. Duodecimal Deonite Decile Dedekind 136. Any number expressed in place value notation with the base 12 is known as: a. b. c. d. Duodecimal Deonite Decile Dedekind 137. Another name for derivative is said to be: a. b. c. d. Differential manifold Partial derivative Differential form Differential coefficient 137. Another name for derivative is said to be: a. b. c. d. Differential manifold Partial derivative Differential form Differential coefficient 138. Another name for rhombus is said to be: a. b. c. d. Dichotomy Diamond Bi-rectangular Bi-sexual 138. Another name for rhombus is said to be: a. b. c. d. Dichotomy Diamond Bi-rectangular Bi-sexual 139. A prefix denoting a multiple of 10 times any of the physical units of the system international. a. b. c. d. Deka Nano Hecto Exa 139. A prefix denoting a multiple of 10 times any of the physical units of the system international. a. b. c. d. Deka Nano Hecto Exa 140. The father of plane geometry. a. b. c. d. Euclid Pythagoras Aristotle Galileo 140. The father of plane geometry. a. b. c. d. Euclid Pythagoras Aristotle Galileo 141. This is the case of a solution of a plane triangle where the given data leads to two solutions. How do you call this case? a. b. c. d. Ambiguous case Quadratic case Extraneous case Darsho’s case 141. This is the case of a solution of a plane triangle where the given data leads to two solutions. How do you call this case? a. b. c. d. Ambiguous case Quadratic case Extraneous case Darsho’s case 142. It is a series of equal payments occurring at equal intervals of time where the first payment is made after several periods, after the beginning of the payment, how do you call this payment? a. b. c. d. Deferred annuity Ordinary annuity Annuity due Simple annuity 142. It is a series of equal payments occurring at equal intervals of time where the first payment is made after several periods, after the beginning of the payment, how do you call this payment? a. b. c. d. Deferred annuity Ordinary annuity Annuity due Simple annuity 143. What do you think is the negotiation of wage rates, conditions of employment ,etc. by representatives of the labor force and management? a. b. c. d. Union trade Union rally Collective bargaining Cooperative 143. What do you think is the negotiation of wage rates, conditions of employment ,etc. by representatives of the labor force and management? a. b. c. d. Union trade Union rally Collective bargaining Cooperative 144. How do you call a type of bond where the corporation’s owner name is recorded and the interest is paid periodically to the owners with their asking for it? a. b. c. d. Registered bond Preferred bond Bail bond Incorporator’s bond 144. How do you call a type of bond where the corporation’s owner name is recorded and the interest is paid periodically to the owners with their asking for it? a. b. c. d. Registered bond Preferred bond Bail bond Incorporator’s bond 145. How do you call the integral of any quotient whose numerator is the differential of the denominator? a. b. c. d. Co-logarithm Logarithm Product Derivative 145. How do you call the integral of any quotient whose numerator is the differential of the denominator? a. b. c. d. Co-logarithm Logarithm Product Derivative 146. What is a regular polygon that has 27 diagonals? a. b. c. d. Nonagon Hexagon Pentagon Heptagon 146. What is a regular polygon that has 27 diagonals? a. b. c. d. Nonagon Hexagon Pentagon Heptagon 147. How do you call the formula used to compute the value of n factorial, which is in symbolic form(!), where n is large number? a. b. c. d. Stirling’s approximation Matheson formula Darsho’s formula Diophantine formula 147. How do you call the formula used to compute the value of n factorial, which is in symbolic form(!), where n is large number? a. b. c. d. Stirling’s approximation Matheson formula Darsho’s formula Diophantine formula 148. What is the reason why an ivory soap floats in water? a. b. c. d. All mater has mass. The specific gravity of ivory soap is greater than of water. The density of ivory soap is unity. The specific gravity of ivory soap is less than of water. 148. What is the reason why an ivory soap floats in water? a. b. c. d. All mater has mass. The specific gravity of ivory soap is greater than of water. The density of ivory soap is unity. The specific gravity of ivory soap is less than of water. 149. When two planes intersect with each other, the amount of divergence between the two planes is expressed by measuring the: a. b. c. d. Reflex angle Dihedral angle Polyhedral angle Plane angle 149. When two planes intersect with each other, the amount of divergence between the two planes is expressed by measuring the: a. b. c. d. Reflex angle Dihedral angle Polyhedral angle Plane angle 150. What do you think is the output or sales at which is insufficient to equal operating cost? a. b. c. d. Breakeven point Depreciation Investment Cash flow 150. What do you think is the output or sales at which is insufficient to equal operating cost? a. b. c. d. Breakeven point Depreciation Investment Cash flow 151. What is the estimate of assets net market value at the end of its estimated life? a. b. c. d. Book value Depreciation Salvage value Cash flow 151. What is the estimate of assets net market value at the end of its estimated life? a. b. c. d. Book value Depreciation Salvage value Cash flow 152. What do you think is the lessening of the value of an asset due to the decrease in the quantity available as a coal, oil and timber in forests? a. b. c. d. Depletion Amortization Depreciation Investment 152. What do you think is the lessening of the value of an asset due to the decrease in the quantity available as a coal, oil and timber in forests? a. b. c. d. Depletion Amortization Depreciation Investment 153. What can you say about the present worth of all depreciation over the economic life of the item? a. b. c. d. Maintenance Capital recovery Depreciation recovery Annuity 153. What can you say about the present worth of all depreciation over the economic life of the item? a. b. c. d. Maintenance Capital recovery Depreciation recovery Annuity 154. What do you think is the provision in the contract that indicates the possible adjustment of material cost and labor cost? a. b. c. d. Secondary clause Specification Escalatory clause General 154. What do you think is the provision in the contract that indicates the possible adjustment of material cost and labor cost? a. b. c. d. Secondary clause Specification Escalatory clause General 155. This is the process of determining the value of certain property for specific reasons. Guess, what is this? a. b. c. d. Amortization Investment Appraisal Depreciation 155. This is the process of determining the value of certain property for specific reasons. Guess, what is this? a. b. c. d. Amortization Investment Appraisal Depreciation 156. How do you call those products or services that are directly used by the people to satisfy their wants? a. b. c. d. Consumer goods and services Producer goods and services Necessity products and services Luxury products and services 156. How do you call those products or services that are directly used by the people to satisfy their wants? a. b. c. d. Consumer goods and services Producer goods and services Necessity products and services Luxury products and services 157. These are uses to produce consumer good and services. Guess, what are these? a. b. c. d. Consumer goods and services Producer goods and services Necessity products and services Luxury products and services 157. These are uses to produce consumer good and services. Guess, what are these? a. b. c. d. Consumer goods and services Producer goods and services Necessity products and services Luxury products and services 158. What do you think are those products and services that are required to support human life and activities that will be purchased in somewhat the same quantity even though the price varies considerably? a. b. c. d. Consumer goods and services Producer goods and services Necessity products and services Luxury products and services 158. What do you think are those products and services that are required to support human life and activities that will be purchased in somewhat the same quantity even though the price varies considerably? a. b. c. d. Consumer goods and services Producer goods and services Necessity products and services Luxury products and services 159. How do you call a cylinder with elliptical cross section? a. b. c. d. Ellipsoid Cylindroid Hyperboloid Paraboloid 159. How do you call a cylinder with elliptical cross section? a. b. c. d. Ellipsoid Cylindroid Hyperboloid Paraboloid 160. How do you call a market whereby there is only one buyer of an item for which there are no goods for substitutes? a. b. c. d. Monopoly Monopsony Oligopoly Oligopsony 160. How do you call a market whereby there is only one buyer of an item for which there are no goods for substitutes? a. b. c. d. Monopoly Monopsony Oligopoly Oligopsony 161. Which statement about a charge placed on a dielectric material is true? a. The charge increases the conductivity of the material b. The charge is confined to the region in which the charge was placed. c. The charge is immediately lost to the atmosphere. d. The charge is instantly carried to the material’s surface. 161. Which statement about a charge placed on a dielectric material is true? a. The charge increases the conductivity of the material b. The charge is confined to the region in which the charge was placed. c. The charge is immediately lost to the atmosphere. d. The charge is instantly carried to the material’s surface. 162. Which of the following is not a property of magnetic lines? a. b. c. d. Magnetic field lines have no beginnings and no ends. The lines cross themselves only at right angles. The line intersect surfaces of equal intensity at right angles. The field is stronger where the lines are closer together. 162. Which of the following is not a property of magnetic lines? a. b. c. d. Magnetic field lines have no beginnings and no ends. The lines cross themselves only at right angles. The line intersect surfaces of equal intensity at right angles. The field is stronger where the lines are closer together. 163. Tesla is a unit of which of the following? a. b. c. d. Magnetic induction Inductance Capacitance Magnetic flux 163. Tesla is a unit of which of the following? a. b. c. d. Magnetic induction Inductance Capacitance Magnetic flux 164. What is a pole pitch? a. b. c. d. The angle at which the pole windings are wound. The space on the stator allocated to two poles. The space on the stator allocated to one pole. The mica used to insulate the poles from each other. 164. What is a pole pitch? a. b. c. d. The angle at which the pole windings are wound. The space on the stator allocated to two poles. The space on the stator allocated to one pole. The mica used to insulate the poles from each other. 165. How do you call a polygon with 10,000 sides? a. b. c. d. Hectogon Chilliagon Myriagon Octacontagon 165. How do you call a polygon with 10,000 sides? a. b. c. d. Hectogon Chilliagon Myriagon Octacontagon 166. Any line segment joining a vertex of a triangle to a point on the opposite side is called as: a. b. c. d. Newton line Secant Cevian Euclidian line 166. Any line segment joining a vertex of a triangle to a point on the opposite side is called as: a. b. c. d. Newton line Secant Cevian Euclidian line 167. It is any influence capable of producing a change in the motion of the object. a. b. c. d. Force Acceleration Friction Velocity 167. It is any influence capable of producing a change in the motion of the object. a. b. c. d. Force Acceleration Friction Velocity 168. How do you call the amount needed at the beginning of operations and permits the enterprise to begin functioning before it receives any income from the sales of its product and service. a. b. c. d. Initial working capital Regular working capital Equity Annuity 168. How do you call the amount needed at the beginning of operations and permits the enterprise to begin functioning before it receives any income from the sales of its product and service. a. b. c. d. Initial working capital Regular working capital Equity Annuity 169. In the problem of writing the equation of a certain curve with respect to another axes in which the new axes are parallel to the original axes and similarly directed is known as: a. b. c. d. Translation of axes Reversal of axes Notation of axes Darsho’s axes 169. In the problem of writing the equation of a certain curve with respect to another axes in which the new axes are parallel to the original axes and similarly directed is known as: a. b. c. d. Translation of axes Reversal of axes Notation of axes Darsho’s axes 170. How do you call a ring shaped surface or solid obtained by rotating a circle about a coplanar line that does not intersect? a. b. c. d. Torus Annulus Circoloid Darsho’s annular 170. How do you call a ring shaped surface or solid obtained by rotating a circle about a coplanar line that does not intersect? a. b. c. d. Torus Annulus Circoloid Darsho’s annular 171. If the eccentricity is less than one, the curve is known as: a. b. c. d. Ellipse Hyperbola Parabola Circle 171. If the eccentricity is less than one, the curve is known as: a. b. c. d. Ellipse Hyperbola Parabola Circle 172. What can you say to the following statement: “the volume of a circular cylinder is equal to the product of its base and altitude”? a. b. c. d. Postulate Corollary Theorem Axiom 172. What can you say to the following statement: “the volume of a circular cylinder is equal to the product of its base and altitude”? a. b. c. d. Postulate Corollary Theorem Axiom 173. What is the study of the properties of figures of three dimensions? a. b. c. d. Physics Solid geometry Plane geometry Trigonometry 173. What is the study of the properties of figures of three dimensions? a. b. c. d. Physics Solid geometry Plane geometry Trigonometry 174. A type of bond, without any security behind them except a promise to pay by the issuing corporation is known as: a. b. c. d. Collateral trust bond Mortgage bond Debenture bond Joint bond 174. A type of bond, without any security behind them except a promise to pay by the issuing corporation is known as: a. b. c. d. Collateral trust bond Mortgage bond Debenture bond Joint bond 175. A situation whereby payment is made for work not done. The term also applies to the case where more workers are used than a reasonable requirement for efficient operation. a. b. c. d. Downtime pay Check-in-pay Feather bidding Moon lighting 175. A situation whereby payment is made for work not done. The term also applies to the case where more workers are used than a reasonable requirement for efficient operation. a. b. c. d. Downtime pay Check-in-pay Feather bidding Moon lighting 176. The difference between what a negotiable paper is worth in the future and its present worth is known as: a. b. c. d. Book value Salvage value Sunk value Discount 176. The difference between what a negotiable paper is worth in the future and its present worth is known as: a. b. c. d. Book value Salvage value Sunk value Discount 177. The temperature to which the air must be cooled at constant temperature to produce saturation. a. b. c. d. Absolute temperature 273 K Dew point Critical temperature 177. The temperature to which the air must be cooled at constant temperature to produce saturation. a. b. c. d. Absolute temperature 273 K Dew point Critical temperature 178. A net force that will give to a mass of one gram an acceleration of 1 cm/s2 is said to be: a. b. c. d. Newton Darsho Ergs Dyne 178. A net force that will give to a mass of one gram an acceleration of 1 cm/s2 is said to be: a. b. c. d. Newton Darsho Ergs Dyne 179. A change in position, specified by a length and a direction is said to be: a. b. c. d. Displacement Acceleration Velocity Dynamic equilibrium 179. A change in position, specified by a length and a direction is said to be: a. b. c. d. Displacement Acceleration Velocity Dynamic equilibrium 180. The process of one substance mixing with another because of molecular motion is known as: a. b. c. d. Adhesion Diffusion Cohesion Confusion 180. The process of one substance mixing with another because of molecular motion is known as: a. b. c. d. Adhesion Diffusion Cohesion Confusion 181. Those cost that arise at the result of a change in operation or policy or it is the ratio of a small increment cost and a small increment of output. a. b. c. d. Increment cost Differential cost Marginal cost Promotion cost 181. Those cost that arise at the result of a change in operation or policy or it is the ratio of a small increment cost and a small increment of output. a. b. c. d. Increment cost Differential cost Marginal cost Promotion cost 182. The index that gives the rate earned per share based on current price per share is called as: a. b. c. d. Price-earning ratio Operating expense ratio Dividend yield Equity ratio 182. The index that gives the rate earned per share based on current price per share is called as: a. b. c. d. Price-earning ratio Operating expense ratio Dividend yield Equity ratio 183. A regular polyhedron having 12 regular pentagons is called as: a. b. c. d. Octahedron Dodecahedron Tetrahedron Darshohedron 183. A regular polyhedron having 12 regular pentagons is called as: a. b. c. d. Octahedron Dodecahedron Tetrahedron Darshohedron 184. Two angles whose sum is 360 deg. is called: a. b. c. d. Explementary angles Complimentary angles Supplementary angles Elementary angles 184. Two angles whose sum is 360 deg. is called: a. b. c. d. Explementary angles Complimentary angles Supplementary angles Elementary angles 185. What is an annuity? a. b. c. d. The future worth of a present amount A series of uniform amounts over a period of time The present worth of a future amount. An annual repayment of a loan. 185. What is an annuity? a. b. c. d. The future worth of a present amount A series of uniform amounts over a period of time The present worth of a future amount. An annual repayment of a loan. 186. When using net present worth calculations to compare two projects, which of the following could invalidate the calculation? a. b. c. d. Use of the same discount rate for each period. Differences in the magnitude of the projects. Evaluating over different time periods. Mutually exclusive projects. 186. When using net present worth calculations to compare two projects, which of the following could invalidate the calculation? a. b. c. d. Use of the same discount rate for each period. Differences in the magnitude of the projects. Evaluating over different time periods. Mutually exclusive projects. 187. Which of the following is true regarding the minimum attractive rate of return used in judging proposed investments? a. It is smaller than the interest rate used to discount expected cash flows from investments. b. It is frequent a policy decision made by an organization’s management. c. It is larger than the interest rate used to discount expected cash flow from investments. d. It is not relevant in engineering economy studies. 187. Which of the following is true regarding the minimum attractive rate of return used in judging proposed investments? a. It is smaller than the interest rate used to discount expected cash flows from investments. b. It is frequent a policy decision made by an organization’s management. c. It is larger than the interest rate used to discount expected cash flow from investments. d. It is not relevant in engineering economy studies. 188. In a trajectory, air resistance decreases. a. b. c. d. Speed Maximum height Range of projectile All of the above 188. In a trajectory, air resistance decreases. a. b. c. d. Speed Maximum height Range of projectile All of the above 189. A leak from a faucet comes out in separate drops. Which of the following is the main cause of this phenomenon? a. b. c. d. Air resistance Gravity Surface tension Viscosity of the fluid 189. A leak from a faucet comes out in separate drops. Which of the following is the main cause of this phenomenon? a. b. c. d. Air resistance Gravity Surface tension Viscosity of the fluid 190. Which of the following elements and compounds is unstable in its pure form? a. b. c. d. Hydrochloric acid Carbon dioxide Sodium Helium 190. Which of the following elements and compounds is unstable in its pure form? a. b. c. d. Hydrochloric acid Carbon dioxide Sodium Helium 191. What is the actual geometric shape of the methane molecule? a. b. c. d. Tetrahedral Pyramidal Square planar Linear 191. What is the actual geometric shape of the methane molecule? a. b. c. d. Tetrahedral Pyramidal Square planar Linear 192. A substance is oxidized when which of the following occurs? a. b. c. d. It losses electrons. It becomes more negative. It gives off heat. It absorbs energy. 192. A substance is oxidized when which of the following occurs? a. b. c. d. It losses electrons. It becomes more negative. It gives off heat. It absorbs energy. 193. Reactions generally proceed faster at higher temperatures because of which of the following? a. b. c. d. The molecules are less energetic. The activation energy is less. The molecules collide more frequently. Both b and c. 193. Reactions generally proceed faster at higher temperatures because of which of the following? a. b. c. d. The molecules are less energetic. The activation energy is less. The molecules collide more frequently. Both b and c. 194. What are the valence electrons? a. b. c. d. The electrons of complete quantum shells. Electrons with positive charge. The outer-shell electrons. The k-quantum shell electrons. 194. What are the valence electrons? a. b. c. d. The electrons of complete quantum shells. Electrons with positive charge. The outer-shell electrons. The k-quantum shell electrons. 195. How do you call the strong bond between hydrogen atoms? a. b. c. d. Ionic and metallic bonds The covalent bond The ionic bond The metallic bond. 195. How do you call the strong bond between hydrogen atoms? a. b. c. d. Ionic and metallic bonds The covalent bond The ionic bond The metallic bond. 196. What are Van der Waals forces? a. b. c. d. Forces present only in gases. Forces not present in liquids. Primary bonds between atoms. Weak secondary bonds between atoms. 196. What are Van der Waals forces? a. b. c. d. Forces present only in gases. Forces not present in liquids. Primary bonds between atoms. Weak secondary bonds between atoms. 197. What do you call the replacement of the original cost of an investment? a. b. c. d. Pay off Return on investment Breakeven Capital recovery 197. What do you call the replacement of the original cost of an investment? a. b. c. d. Pay off Return on investment Breakeven Capital recovery 198. If f” (x1) = 0, then the point (x1, y1) is called: a. b. c. d. Minimum point Maximum point Inflection point Critical point 198. If f” (x1) = 0, then the point (x1, y1) is called: a. b. c. d. Minimum point Maximum point Inflection point Critical point 199. Adding more solute to an already saturated solution will cause the excess solute to settle to the bottom of the container. What is this process called? a. b. c. d. Precipitation Hydration Dehydration Saturation 199. Adding more solute to an already saturated solution will cause the excess solute to settle to the bottom of the container. What is this process called? a. b. c. d. Precipitation Hydration Dehydration Saturation 200. The length of time at which the original cost of capital used to purchase a unit has already been recovered. a. b. c. d. Economic life Write off period Physical life Salvage life 200. The length of time at which the original cost of capital used to purchase a unit has already been recovered. a. b. c. d. Economic life Write off period Physical life Salvage life 201. The actual interest earned by a given principal is known as: a. b. c. d. Compound interest Simple interest Effective interest Nominal interest 201. The actual interest earned by a given principal is known as: a. b. c. d. Compound interest Simple interest Effective interest Nominal interest 202. A book is at rest on top of a table. Which of the following is correct? a. b. c. d. There is no force acting on the book. The book has no inertia. There is no force acting on the table. The book is in equilibrium. 202. A book is at rest on top of a table. Which of the following is correct? a. b. c. d. There is no force acting on the book. The book has no inertia. There is no force acting on the table. The book is in equilibrium. 203. The property of a moving object to continue moving is what Galileo called: a. b. c. d. e. Velocity Speed Acceleration Inertia Direction 203. The property of a moving object to continue moving is what Galileo called: a. b. c. d. e. Velocity Speed Acceleration Inertia Direction 204. According to Newton’s First Law of Motion, a. An object at rest eventually begins to move b. An object in motion moves in a parabolic trajectory unless acted upon by a net force. c. An object at rest always remain at rest. d. An object at rest remains at rest unless acted upon by a net force. 204. According to Newton’s First Law of Motion, a. An object at rest eventually begins to move b. An object in motion moves in a parabolic trajectory unless acted upon by a net force. c. An object at rest always remain at rest. d. An object at rest remains at rest unless acted upon by a net force. 205. If an object is moving, then the magnitude of its ____ cannot be zero. a. b. c. d. Velocity Speed Acceleration A and B 205. If an object is moving, then the magnitude of its ____ cannot be zero. a. b. c. d. Velocity Speed Acceleration A and B 206. A body drop in free fall a vacuum, a. Will drop the same distance during each second of its fall. b. Will have the same average speed during each second of its fall. c. Will have a constant velocity during each second of its fall. d. Will not be accelerated during its fall. e. Will have the same acceleration during second of it fall. 206. A body drop in free fall a vacuum, a. Will drop the same distance during each second of its fall. b. Will have the same average speed during each second of its fall. c. Will have a constant velocity during each second of its fall. d. Will not be accelerated during its fall. e. Will have the same acceleration during second of it fall. 207. A bowling ball at a height of 36 meters above the ground is falling vertically at a rate of 12 meters per second. Which of these best describes its fate? a. It will hit the ground in exactly three seconds at a speed of 12 m/s. b. It will hit the ground in less than three seconds at a speed greater than 12 m/s. c. It will hit the ground in more than three seconds at a speed less than 12 m/s. d. It will hit the ground in less than three seconds at a speed less than 12 m/s. 207. A bowling ball at a height of 36 meters above the ground is falling vertically at a rate of 12 meters per second. Which of these best describes its fate? a. It will hit the ground in exactly three seconds at a speed of 12 m/s. b. It will hit the ground in less than three seconds at a speed greater than 12 m/s. c. It will hit the ground in more than three seconds at a speed less than 12 m/s. d. It will hit the ground in less than three seconds at a speed less than 12 m/s. 208. The speedometer in your car tells you the ____ of your car. a. b. c. d. e. Velocity Average speed Acceleration Inertia Instantaneous speed 208. The speedometer in your car tells you the ____ of your car. a. b. c. d. e. Velocity Average speed Acceleration Inertia Instantaneous speed 209. To report the ____ of an object, we must specify both its speed and its direction. a. b. c. d. e. Velocity Speed Acceleration Inertia Direction 209. To report the ____ of an object, we must specify both its speed and its direction. a. b. c. d. e. Velocity Speed Acceleration Inertia Direction 210. The ____ of an object on the Earth’s surface are directly proportional to each other. a. b. c. d. e. Velocity and force Speed and velocity Acceleration and mass Mass and weight Direction and weight 210. The ____ of an object on the Earth’s surface are directly proportional to each other. a. b. c. d. e. Velocity and force Speed and velocity Acceleration and mass Mass and weight Direction and weight 211. The moon’s gravity is 1/6 of the Earth’s gravity. The weight of a bowling ball on the Earth would be ____ its weight on the moon. a. b. c. d. Equal to 1/6 of 6 times 36 times 211. The moon’s gravity is 1/6 of the Earth’s gravity. The weight of a bowling ball on the Earth would be ____ its weight on the moon. a. b. c. d. Equal to 1/6 of 6 times 36 times 212. A falling object is said to reach terminal speed, a. b. c. d. When it lands on the ground. When its air resistance equals the force of gravity on it. When there is no air resistance acting on it. When there is no gravitational force acting on it. 212. A falling object is said to reach terminal speed, a. b. c. d. When it lands on the ground. When its air resistance equals the force of gravity on it. When there is no air resistance acting on it. When there is no gravitational force acting on it. 213. For every action there is an equal and opposite reaction. This is a statement of, a. b. c. d. Newton’s First Law of Motion Newton’s Second Law of Motion Newton’s Third Law of Motion Newton’s Law of Action 213. For every action there is an equal and opposite reaction. This is a statement of, a. b. c. d. Newton’s First Law of Motion Newton’s Second Law of Motion Newton’s Third Law of Motion Newton’s Law of Action 214. _____ are examples of vector quantities. a. b. c. d. Velocity and acceleration Volume and velocity Acceleration and mass Mass and volume 214. _____ are examples of vector quantities. a. b. c. d. Velocity and acceleration Volume and velocity Acceleration and mass Mass and volume 215. A green ball moving to the right at 3 m/s strikes a yellow ball moving to the left at 2 m/s. If the balls are equally massive and the collision is elastic, a. The green ball will move to the left at 3 m/s while the yellow ball moves right at 2 m/s. b. The green ball will move to the left at 2 m/s while the yellow ball moves right at 3 m/s. c. The green ball will stop while the yellow ball moves left at 2 m/s. d. Both balls will stick together and move to the right at 1 m/s. 215. A green ball moving to the right at 3 m/s strikes a yellow ball moving to the left at 2 m/s. If the balls are equally massive and the collision is elastic, a. The green ball will move to the left at 3 m/s while the yellow ball moves right at 2 m/s. b. The green ball will move to the left at 2 m/s while the yellow ball moves right at 3 m/s. c. The green ball will stop while the yellow ball moves left at 2 m/s. d. Both balls will stick together and move to the right at 1 m/s. 216. The buoyant force on a block of wood floating in water, a. Is equal to the weight of a volume of water with the same volume as the wood. b. Is equal to the weight of the wood. c. Is greater than the weight of the wood. d. Is less than the weight of the wood. 216. The buoyant force on a block of wood floating in water, a. Is equal to the weight of a volume of water with the same volume as the wood. b. Is equal to the weight of the wood. c. Is greater than the weight of the wood. d. Is less than the weight of the wood. 217. An object with a mass of 1 kg displaces 700 ml of water. Which of the following is true? a. b. c. d. The weight of this object is 10 N. The weight of this object is 7 N. The weight of this object is 3 N. The weight of this object is 17 N. 217. An object with a mass of 1 kg displaces 700 ml of water. Which of the following is true? a. b. c. d. The weight of this object is 10 N. The weight of this object is 7 N. The weight of this object is 3 N. The weight of this object is 17 N. 218. An object with a mass of 1 kg displaces 0.6 kg of water. Which of the following is true? a. b. c. d. The buoyant force on this object is 10 N. The buoyant force on this object is 6 N. The density of this object is 3 N. The weight of this object is 17 N. 218. An object with a mass of 1 kg displaces 0.6 kg of water. Which of the following is true? a. b. c. d. The buoyant force on this object is 10 N. The buoyant force on this object is 6 N. The density of this object is 3 N. The weight of this object is 17 N. 219. The water pressure in a lake behind a dam depends on, a. The volume of lake water behind the dam. b. The surface area of the lake. c. The distance from the dam at which the pressure is measured. d. The depth below the surface at which the pressure is measured. 219. The water pressure in a lake behind a dam depends on, a. The volume of lake water behind the dam. b. The surface area of the lake. c. The distance from the dam at which the pressure is measured. d. The depth below the surface at which the pressure is measured. 220. When air is removed from a metal can be vacuum, the can buckles inwards and is crushed. This occurs because a. The air pressure on the inside of the can is greater than the air pressure on the outside of the can. b. The air pressure on the outside of the can is greater than air pressure on the inside of the can. c. The loss air molecules from inside the can weakens the metal. d. The opposite sides of the empty can strongly attract each other. 220. When air is removed from a metal can be vacuum, the can buckles inwards and is crushed. This occurs because a. The air pressure on the inside of the can is greater than the air pressure on the outside of the can. b. The air pressure on the outside of the can is greater than air pressure on the inside of the can. c. The loss air molecules from inside the can weakens the metal. d. The opposite sides of the empty can strongly attract each other. 221. Bernoulli’s principle explains why, a. b. c. d. A hot air balloon rises. Liquid rises in a drinking straw Airplanes fly Dead fish float 221. Bernoulli’s principle explains why, a. b. c. d. A hot air balloon rises. Liquid rises in a drinking straw Airplanes fly Dead fish float 222. In order to decrease the pressure in an automobile tire, one normally a. b. c. d. Decrease the temperature of the tire. Increases the volume of the tire. Increases the density of air in the tire. Decreases the number of air molecules in the tire. 222. In order to decrease the pressure in an automobile tire, one normally a. b. c. d. Decrease the temperature of the tire. Increases the volume of the tire. Increases the density of air in the tire. Decreases the number of air molecules in the tire. 223. It is the branch of mathematics which deals with the study of formal manipulations of equations involving symbols and numbers. a. b. c. d. Arithmetic Algebra Plane geometry Trigonometry 223. It is the branch of mathematics which deals with the study of formal manipulations of equations involving symbols and numbers. a. b. c. d. Arithmetic Algebra Plane geometry Trigonometry 224. Is an entity describing the quantity or position of a mathematical object or extensions of these concepts. a. b. c. d. Exponent Number Cardinal number Ordinal number 224. Is an entity describing the quantity or position of a mathematical object or extensions of these concepts. a. b. c. d. Exponent Number Cardinal number Ordinal number 225. It describes the size or quantity of the collections of objects like 1,2,3….1000 and so on & so forth. a. b. c. d. Exponent Number Cardinal number Ordinal number 225. It describes the size or quantity of the collections of objects like 1,2,3….1000 and so on & so forth. a. b. c. d. Exponent Number Cardinal number Ordinal number 226. It refer to the position relative to an ordering such as first, second, third etc. a. b. c. d. Exponent Number Cardinal number Ordinal number 226. It refer to the position relative to an ordering such as first, second, third etc. a. b. c. d. Exponent Number Cardinal number Ordinal number 227. It is the sum of real and imaginary numbers which expressed in “x+yi”. a. b. c. d. Real number Irrational number Rational number Complex number 227. It is the sum of real and imaginary numbers which expressed in “x+yi”. a. b. c. d. Real number Irrational number Rational number Complex number 228. Is the number that cannot be expressed into ratio of two integers. a. b. c. d. Real number Irrational number Rational number Complex number 228. Is the number that cannot be expressed into ratio of two integers. a. b. c. d. Real number Irrational number Rational number Complex number 229. Is any positive integer (excluding 1) having no integral factors other than itself and unity. a. b. c. d. Imaginary number Real number Ordinal number Prime number 229. Is any positive integer (excluding 1) having no integral factors other than itself and unity. a. b. c. d. Imaginary number Real number Ordinal number Prime number 230. What do you call this laws or properties of equality in algebra, xy = yx ? a. b. c. d. Commutative Law of Multiplication Associative Law of Multiplication Left Distributive Law Right Distributive law 230. What do you call this laws or properties of equality in algebra, xy = yx ? a. b. c. d. Commutative Law of Multiplication Associative Law of Multiplication Left Distributive Law Right Distributive law 231. What do you call this laws or properties of equality in algebra, x + y = y + x ? a. b. c. d. Commutative Law of Addition Associative Law of Addition Left Distributive Law Right Distributive law 231. What do you call this laws or properties of equality in algebra, x + y = y + x ? a. b. c. d. Commutative Law of Addition Associative Law of Addition Left Distributive Law Right Distributive law 232. What do you call this laws or properties of equality in algebra, (x+y) + z = x + (y+z) ? a. b. c. d. Commutative Law of Multiplication Associative Law of Addition Left Distributive Law Commutative Law of Addition 232. What do you call this laws or properties of equality in algebra, (x+y) + z = x + (y+z) ? a. b. c. d. Commutative Law of Multiplication Associative Law of Addition Left Distributive Law Commutative Law of Addition 233. What do you call this laws or properties of equality in algebra, (xy)z = x(yz) ? a. b. c. d. Commutative Law of Multiplication Associative Law of Multiplication Left Distributive Law Right Distributive law 233. What do you call this laws or properties of equality in algebra, (xy)z = x(yz) ? a. b. c. d. Commutative Law of Multiplication Associative Law of Multiplication Left Distributive Law Right Distributive law 234. What do you call this laws or properties of equality in algebra, x + 0 = x ? a. b. c. d. Additive Inverse Property Additive Identity Property Reflexive Property Symmetric Property 234. What do you call this laws or properties of equality in algebra, x + 0 = x ? a. b. c. d. Additive Inverse Property Additive Identity Property Reflexive Property Symmetric Property 235. What do you call this laws or properties of equality in algebra, x + (-x) = 0 ? a. b. c. d. Additive Inverse Property Additive Identity Property Reflexive Property Symmetric Property 235. What do you call this laws or properties of equality in algebra, x + (-x) = 0 ? a. b. c. d. Additive Inverse Property Additive Identity Property Reflexive Property Symmetric Property 236. What do you call this laws or properties of equality in algebra, x = x ? a. b. c. d. Additive Inverse Property Additive Identity Property Reflexive Property Symmetric Property 236. What do you call this laws or properties of equality in algebra, x = x ? a. b. c. d. Additive Inverse Property Additive Identity Property Reflexive Property Symmetric Property 237. What do you call this laws or properties of equality in algebra, x = y and y = x ? a. b. c. d. Additive Inverse Property Additive Identity Property Reflexive Property Symmetric Property 237. What do you call this laws or properties of equality in algebra, x = y and y = x ? a. b. c. d. Additive Inverse Property Additive Identity Property Reflexive Property Symmetric Property 238. It is a sequence of numbers or quantities in which there is always the same relation between each quantity and the one succeeding it. a. b. c. d. Geometry Progression Probability Rational number 238. It is a sequence of numbers or quantities in which there is always the same relation between each quantity and the one succeeding it. a. b. c. d. Geometry Progression Probability Rational number 239. It is a sequence of numbers in which each term (except the first term is obtained from the previous by adding a constant known as the common difference. a. b. c. d. Geometric progression Arithmetic progression Harmonic progression Permutation 239. It is a sequence of numbers in which each term (except the first term is obtained from the previous by adding a constant known as the common difference. a. b. c. d. Geometric progression Arithmetic progression Harmonic progression Permutation 240. It is a sequence of numbers, each of which each, after the first is obtained by multiplying the preceding term by a fixed number called the common ratio, known as the common difference. a. b. c. d. Geometric progression Arithmetic progression Harmonic progression Permutation 240. It is a sequence of numbers, each of which each, after the first is obtained by multiplying the preceding term by a fixed number called the common ratio, known as the common difference. a. b. c. d. Geometric progression Arithmetic progression Harmonic progression Permutation 241. It is a sequence of numbers in which the reciprocals form an arithmetic progression. a. b. c. d. Geometric progression Arithmetic progression Harmonic progression Permutation 241. It is a sequence of numbers in which the reciprocals form an arithmetic progression. a. b. c. d. Geometric progression Arithmetic progression Harmonic progression Permutation 242. It is an ordered arrangement of any element in a set. a. b. c. d. Probability Arithmetic progression Combination Permutation 242. It is an ordered arrangement of any element in a set. a. b. c. d. Probability Arithmetic progression Combination Permutation 243. It is an equation when the number of equations is less than the number of unknown. a. b. c. d. Deophantine Equation Quadratic Equation Darsho’s Equation Theory of Sets 243. It is an equation when the number of equations is less than the number of unknown. a. b. c. d. Deophantine Equation Quadratic Equation Darsho’s Equation Theory of Sets 244. Who was the first person of whose systematic use of trigonometry which have documentary evidence. a. b. c. d. Euclid Hipparchus Galileo Aristotle 244. Who was the first person of whose systematic use of trigonometry which have documentary evidence. a. b. c. d. Euclid Hipparchus Galileo Aristotle 245. It is the space between intersecting rays or lines. a. b. c. d. Line Revolution Angle Side 245. It is the space between intersecting rays or lines. a. b. c. d. Line Revolution Angle Side 246. Are angles which are non-right and nonstraight such as acute angles and obtuse angles. a. b. c. d. Right angle Oblique angles Reflex angles Darsho’s angle 246. Are angles which are non-right and nonstraight such as acute angles and obtuse angles. a. b. c. d. Right angle Oblique angles Reflex angles Darsho’s angle 247. It is a triangle with two sides equal. a. b. c. d. Scalene triangle Oblique triangle Isosceles triangle Equilateral triangle 247. It is a triangle with two sides equal. a. b. c. d. Scalene triangle Oblique triangle Isosceles triangle Equilateral triangle 248. It is a triangle with no equal sides. a. b. c. d. Scalene triangle Oblique triangle Isosceles triangle Equilateral triangle 248. It is a triangle with no equal sides. a. b. c. d. Scalene triangle Oblique triangle Isosceles triangle Equilateral triangle 249. It is a triangle without a 90 deg. angle. a. b. c. d. Scalene triangle Oblique triangle Isosceles triangle Equilateral triangle 249. It is a triangle without a 90 deg. angle. a. b. c. d. Scalene triangle Oblique triangle Isosceles triangle Equilateral triangle 250. It is a triangle that all sides are equal. a. b. c. d. Scalene triangle Oblique triangle Isosceles triangle Equilateral triangle 250. It is a triangle that all sides are equal. a. b. c. d. Scalene triangle Oblique triangle Isosceles triangle Equilateral triangle 251. The following are the primary (basic) SI (metric) units, except a. b. c. d. Length Mass Time Force 251. The following are the primary (basic) SI (metric) units, except a. b. c. d. Length Mass Time Force 252. The following are the secondary SI (metric) units, except a. b. c. d. Temperature Pressure Force Energy 252. The following are the secondary SI (metric) units, except a. b. c. d. Temperature Pressure Force Energy 253. Which of the following is not an intensive property? a. b. c. d. Temperature Pressure Mass Density 253. Which of the following is not an intensive property? a. b. c. d. Temperature Pressure Mass Density 254. Which of the following is not an extensive property? a. b. c. d. Mass Weight Volume Specific volume 254. Which of the following is not an extensive property? a. b. c. d. Mass Weight Volume Specific volume 255. The mass of the substance per unit volume is, a. b. c. d. Density Specific gravity Specific weight Force per unit 255. The mass of the substance per unit volume is, a. b. c. d. Density Specific gravity Specific weight Force per unit 256. The weight of the substance per unit volume is, a. b. c. d. Mass Density Force per unit Specific weight 256. The weight of the substance per unit volume is, a. b. c. d. Mass Density Force per unit Specific weight 257. The ratio of specific weight to acceleration of gravity is, a. b. c. d. Density Specific gravity Specific volume Viscosity 257. The ratio of specific weight to acceleration of gravity is, a. b. c. d. Density Specific gravity Specific volume Viscosity 258. The reciprocal of density is, a. b. c. d. Specific weight Specific gravity Specific volume Viscosity 258. The reciprocal of density is, a. b. c. d. Specific weight Specific gravity Specific volume Viscosity 259. It occurs when a decrease in selling price result in a greater than proportionate increase in sales. a. b. c. d. Elastic demand Inelastic demand Unitary elasticity of demand Darsho demand 259. It occurs when a decrease in selling price result in a greater than proportionate increase in sales. a. b. c. d. Elastic demand Inelastic demand Unitary elasticity of demand Darsho demand 260. It occurs when a decrease in the selling price produces a less than proportionate increase in sales. a. b. c. d. Elastic demand Inelastic demand Unitary elasticity of demand Darsho demand 260. It occurs when a decrease in the selling price produces a less than proportionate increase in sales. a. b. c. d. Elastic demand Inelastic demand Unitary elasticity of demand Darsho demand 261. It occurs when the mathematical product of volume and price is constant. a. b. c. d. Elastic demand Inelastic demand Unitary elasticity of demand Darsho demand 261. It occurs when the mathematical product of volume and price is constant. a. b. c. d. Elastic demand Inelastic demand Unitary elasticity of demand Darsho demand 262. It is calculated using principal only, ignoring any interest that had been accrued in preceding periods. a. b. c. d. Simple interest Compound interest Interest rate Effective rate 262. It is calculated using principal only, ignoring any interest that had been accrued in preceding periods. a. b. c. d. Simple interest Compound interest Interest rate Effective rate 263. It is the interest for an interest period is calculated on the principal plus total amount of interest accumulated in previous periods. a. b. c. d. Simple interest Compound interest Interest rate Effective rate 263. It is the interest for an interest period is calculated on the principal plus total amount of interest accumulated in previous periods. a. b. c. d. Simple interest Compound interest Interest rate Effective rate 264. Which of the following is not a vector quantity? a. b. c. d. Mass Torque Displacement Velocity 264. Which of the following is not a vector quantity? a. b. c. d. Mass Torque Displacement Velocity 265. The product of force and the time during which it acts is known as: a. b. c. d. Impulse Momentum Work Impact 265. The product of force and the time during which it acts is known as: a. b. c. d. Impulse Momentum Work Impact 266. The property of the body which measures its resistance to change in motion. a. b. c. d. Acceleration Weight Mass Rigidity 266. The property of the body which measures its resistance to change in motion. a. b. c. d. Acceleration Weight Mass Rigidity 267. The study of motion without reference to the forces which causes motion is known as: a. b. c. d. Kinetics Dynamics Statics Kinematics 267. The study of motion without reference to the forces which causes motion is known as: a. b. c. d. Kinetics Dynamics Statics Kinematics 268. The point through which the resultant of the distributed gravity force passes regardless of the orientation of the body in space is known as: a. b. c. d. Center of inertia Center of gravity Center of attraction Moment of inertia 268. The point through which the resultant of the distributed gravity force passes regardless of the orientation of the body in space is known as: a. b. c. d. Center of inertia Center of gravity Center of attraction Moment of inertia 269. The loss of weight of a body submerged in a fluid is: a. b. c. d. Proportional to the weight of the body Proportional to the depth of submergence Equal to the weight of the fluid displaced Independent of the volume of the body 269. The loss of weight of a body submerged in a fluid is: a. b. c. d. Proportional to the weight of the body Proportional to the depth of submergence Equal to the weight of the fluid displaced Independent of the volume of the body 270. One Joule of work is done by a force of one Newton acting through a distance of: a. b. c. d. 1 cm 1 in 1m 1 ft 270. One Joule of work is done by a force of one Newton acting through a distance of: a. b. c. d. 1 cm 1 in 1m 1 ft 271. The path of the projectile is: a. b. c. d. A parabola An ellipse A part of a circle A hyperbola 271. The path of the projectile is: a. b. c. d. A parabola An ellipse A part of a circle A hyperbola 272. One mole of a gas at standard temperature and pressure (STP) conditions occupies a volume equal to: a. b. c. d. 22.4 li 9.81 li 332 li 2274.5 li 272. One mole of a gas at standard temperature and pressure (STP) conditions occupies a volume equal to: a. b. c. d. 22.4 li 9.81 li 332 li 2274.5 li 273. This implies the resistance to shock or difficulty of breaking and expresses the work per unit volume required to fracture a material. a. b. c. d. Toughness Malleability Hardness Ductility 273. This implies the resistance to shock or difficulty of breaking and expresses the work per unit volume required to fracture a material. a. b. c. d. Toughness Malleability Hardness Ductility 274. The reciprocal of bulk modulus of elasticity of any fluid is called: a. b. c. d. Compressibility Volume strain Volume stress Shape factor 274. The reciprocal of bulk modulus of elasticity of any fluid is called: a. b. c. d. Compressibility Volume strain Volume stress Shape factor 275. Used as a guide to selecting the most efficient centrifugal pump: a. b. c. d. Specific speed Impeller type Bernoulli’s Equation Overall efficiency 275. Used as a guide to selecting the most efficient centrifugal pump: a. b. c. d. Specific speed Impeller type Bernoulli’s Equation Overall efficiency 276. Heat transmission carried by the movement of heated fluids away from a hot body, as in the heating of water by a hot surface: a. b. c. d. Radiation Convection Conduction Absorption 276. Heat transmission carried by the movement of heated fluids away from a hot body, as in the heating of water by a hot surface: a. b. c. d. Radiation Convection Conduction Absorption 277. An instrument temperature gases: a. b. c. d. Plenometer Manometer Anemometer Pyrometer for measuring high 277. An instrument temperature gases: a. b. c. d. Plenometer Manometer Anemometer Pyrometer for measuring high 278. The equilibrium temperature that a regular thermometer measures if exposed to atmospheric air is: a. b. c. d. Dry bulb temperature Degrees Celsius Wet bulb temperature Dew point 278. The equilibrium temperature that a regular thermometer measures if exposed to atmospheric air is: a. b. c. d. Dry bulb temperature Degrees Celsius Wet bulb temperature Dew point 279. Momentum = Force x ______. a. b. c. d. Time Velocity Velocity2 ½ velocity 279. Momentum = Force x ______. a. b. c. d. Time Velocity Velocity2 ½ velocity 280. An instrument for measuring specific gravity of fluids: a. b. c. d. Hygrometer Flowmeter Psyhcrometer Hydrometer 280. An instrument for measuring specific gravity of fluids: a. b. c. d. Hygrometer Flowmeter Psyhcrometer Hydrometer 281. The recorded current value of an asset is known as: a. b. c. d. Scrap value Book value Salvage value Present worth 281. The recorded current value of an asset is known as: a. b. c. d. Scrap value Book value Salvage value Present worth 282. A method of depreciation whereby the amount to recover is spread over the estimated life of the asset in terms of the periods or units of output is called: a. b. c. d. SOYD method Declining balance method Straight line method Sinking fund method 282. A method of depreciation whereby the amount to recover is spread over the estimated life of the asset in terms of the periods or units of output is called: a. b. c. d. SOYD method Declining balance method Straight line method Sinking fund method 283. The method of depreciation where a fixed sum of money is regularly deposited at compound interest in a real or imaginary fund in order to accumulate an amount equal to the total depreciation of an asset at the end of the asset’s estimated life is know as: a. b. c. d. Straight line method SOYD method Declining balance method Sinking fund method 283. The method of depreciation where a fixed sum of money is regularly deposited at compound interest in a real or imaginary fund in order to accumulate an amount equal to the total depreciation of an asset at the end of the asset’s estimated life is know as: a. b. c. d. Straight line method SOYD method Declining balance method Sinking fund method 284. The amount received from the sale of an additional unit of a product is termed as: a. b. c. d. Marginal cost Marginal utility Marginal unit Marginal revenue 284. The amount received from the sale of an additional unit of a product is termed as: a. b. c. d. Marginal cost Marginal utility Marginal unit Marginal revenue 285. An accounting book where the original record of all transactions is ordinarily recorded. a. b. c. d. Journal Log book Credit entry Transaction record 285. An accounting book where the original record of all transactions is ordinarily recorded. a. b. c. d. Journal Log book Credit entry Transaction record 286. An interest-earning fund in which equal deposits are made at equal intervals of time for the purpose of gradually accumulating a specific sum of money required at some future date. a. b. c. d. Amortization Sinking fund Annuity Capitalized cost 286. An interest-earning fund in which equal deposits are made at equal intervals of time for the purpose of gradually accumulating a specific sum of money required at some future date. a. b. c. d. Amortization Sinking fund Annuity Capitalized cost 287. Refers to cost of merchandise which excludes freight and insurance costs: a. b. c. d. Freight on board Sunk cost Debentures Book value 287. Refers to cost of merchandise which excludes freight and insurance costs: a. b. c. d. Freight on board Sunk cost Debentures Book value 288. The worth of property which is equal to the original cost less depreciation: a. b. c. d. Scrap value Earning value Book value Face value 288. The worth of property which is equal to the original cost less depreciation: a. b. c. d. Scrap value Earning value Book value Face value 289. A line which is perpendicular to the x-axis has a slope equal to: a. b. c. d. Zero -1 1 infinity 289. A line which is perpendicular to the x-axis has a slope equal to: a. b. c. d. Zero -1 1 infinity 290. In an ellipse, a chord which contains a focus and is in a line perpendicular to the major axis is a: a. b. c. d. Latus rectum Minor Focal width Conjugate axis 290. In an ellipse, a chord which contains a focus and is in a line perpendicular to the major axis is a: a. b. c. d. Latus rectum Minor Focal width Conjugate axis 291. An angle more than ∏ radian (180⁰) but less than 2∏ (360⁰) radians is: a. b. c. d. Straight angle Obtuse angle Oblique angle Reflex angle 291. An angle more than ∏ radian (180⁰) but less than 2∏ (360⁰) radians is: a. b. c. d. Straight angle Obtuse angle Oblique angle Reflex angle 292. An angle more than 90⁰ but less than 180⁰. a. b. c. d. Oblique angles Obtuse angles Full angle Reflex angle 292. An angle more than 90⁰ but less than 180⁰. a. b. c. d. Oblique angles Obtuse angles Full angle Reflex angle 293. An angles which are non-right and nonstraight which are acute and obtuse angles is called: a. b. c. d. Perigon Full angles Reflex angles Oblique angles 293. An angles which are non-right and nonstraight which are acute and obtuse angles is called: a. b. c. d. Perigon Full angles Reflex angles Oblique angles 294. Are opposite angles formed between two intersecting lines that are equal. a. b. c. d. Vertices Vertical angles Explementary angles Complementary angles 294. Are opposite angles formed between two intersecting lines that are equal. a. b. c. d. Vertices Vertical angles Explementary angles Complementary angles 295. In trigonometry, one revolution is equal to, except a. b. c. d. e. 400 gons 400 grads 6400 mils 360 degress Pi radians 295. In trigonometry, one revolution is equal to, except a. b. c. d. e. 400 gons 400 grads 6400 mils 360 degress Pi radians 296. It can be defined as the set of all points in the plane the sum of whose distance from two fixed points is a constant. a. b. c. d. Circle Ellipse Hyperbola Parabola 296. It can be defined as the set of all points in the plane the sum of whose distance from two fixed points is a constant. a. b. c. d. Circle Ellipse Hyperbola Parabola 297. The area of the region bounded by two concentric circles is called: a. b. c. d. Washer Ring Annulus Circular disk 297. The area of the region bounded by two concentric circles is called: a. b. c. d. Washer Ring Annulus Circular disk 298. An arc length, which is equal to the radius of the circle is called: a. b. c. d. 1 degree 2 pi radians 1 radian 1 pi radian 298. An arc length, which is equal to the radius of the circle is called: a. b. c. d. 1 degree 2 pi radians 1 radian 1 pi radian 299. Each of the faces of a regular hexahedron is a: a. b. c. d. Square Triangle Hexagon Circle 299. Each of the faces of a regular hexahedron is a: a. b. c. d. Square Triangle Hexagon Circle 300. In a conic section, if the eccentricity e > 1, the locus is: a. b. c. d. Ellipse Hyperbola Parabola Circle 300. In a conic section, if the eccentricity e > 1, the locus is: a. b. c. d. Ellipse Hyperbola Parabola Circle 301. In a conic section, if the value of discriminant B2 – 4AC > 0 that is called: a. b. c. d. Ellipse Hyperbola Parabola Circle 301. In a conic section, if the value of discriminant B2 – 4AC > 0 that is called: a. b. c. d. Ellipse Hyperbola Parabola Circle 302. In a conic section, if the value of discriminant B2 – 4AC = 0 that is called: a. b. c. d. Ellipse Hyperbola Parabola Circle 302. In a conic section, if the value of discriminant B2 – 4AC = 0 that is called: a. b. c. d. Ellipse Hyperbola Parabola Circle 303. In a conic section, if the value of discriminant B2 – 4AC < 0 (if A is not equal to C) that is called: a. b. c. d. Ellipse Hyperbola Parabola Circle 303. In a conic section, if the value of discriminant B2 – 4AC < 0 (if A is not equal to C) that is called: a. b. c. d. Ellipse Hyperbola Parabola Circle 304. In a conic section, if the value of discriminant B2 – 4AC < 0 (if A is equal to C) that is called: a. b. c. d. Ellipse Hyperbola Parabola Circle 304. In a conic section, if the value of discriminant B2 – 4AC < 0 (if A is equal to C) that is called: a. b. c. d. Ellipse Hyperbola Parabola Circle 305. In a conic section, if the eccentricity e < 1, the locus is: a. b. c. d. Ellipse Hyperbola Parabola Circle 305. In a conic section, if the eccentricity e < 1, the locus is: a. b. c. d. Ellipse Hyperbola Parabola Circle 306. In a conic section, if the eccentricity e = 1, the locus is: a. b. c. d. Ellipse Hyperbola Parabola Circle 306. In a conic section, if the eccentricity e = 1, the locus is: a. b. c. d. Ellipse Hyperbola Parabola Circle 307. In analytic geometry that if the line is vertical, the slope (m) is? a. b. c. d. Infinity zero positive negative 307. In analytic geometry that if the line is vertical, the slope (m) is? a. b. c. d. Infinity zero positive negative 308. In analytic geometry that if the line is horizontal, the slope (m) is? a. b. c. d. Infinity zero positive negative 308. In analytic geometry that if the line is horizontal, the slope (m) is? a. b. c. d. Infinity zero positive negative 309. In analytic geometry that if the line is inclined right, the slope (m) is? a. b. c. d. Infinity zero positive negative 309. In analytic geometry that if the line is inclined right, the slope (m) is? a. b. c. d. Infinity zero positive negative 310. When two lines are perpendicular, the slope of one is: a. b. c. d. Equal to the other Equal to the negative of the other Equal to the reciprocal of the other Equal to the negative reciprocal of the other 310. When two lines are perpendicular, the slope of one is: a. b. c. d. Equal to the other Equal to the negative of the other Equal to the reciprocal of the other Equal to the negative reciprocal of the other 311. How many degrees are 4,800 mils? a. b. c. d. 180⁰ 315⁰ 90⁰ 270⁰ 311. How many degrees are 4,800 mils? a. b. c. d. 180⁰ 315⁰ 90⁰ 270⁰ 4800 mils (1 degree / 17.78 mils) = 270⁰ 312. Determine the value of each interior angle of a regular pentagon. a. b. c. d. 108⁰ 120⁰ 98⁰ 135⁰ 312. Determine the value of each interior angle of a regular pentagon. a. 108⁰ b. 120⁰ c. 98⁰ d. 135⁰ (no. of sides – 2 / no. of sides)(180⁰) = (5 - 2 / 5)(180⁰) = 108⁰ 313. How do you call the distance of a point from the y-axis? a. b. c. d. Polar distance Coordinate Abscissa Ordinate 313. How do you call the distance of a point from the y-axis? a. b. c. d. Polar distance Coordinate Abscissa Ordinate 314. How do you call the x-coordinate? a. b. c. d. Polar distance Coordinate Abscissa Ordinate 314. How do you call the x-coordinate? a. b. c. d. Polar distance Coordinate Abscissa Ordinate 315. How do you call the y-coordinate? a. b. c. d. Polar distance Coordinate Abscissa Ordinate 315. How do you call the y-coordinate? a. b. c. d. Polar distance Coordinate Abscissa Ordinate 316. A formal organization of producers within an industry forming a perfect collusion purposely formed to increase profit and block new comers from the industry. a. b. c. d. Cartel Monopoly Corporation Competitors 316. A formal organization of producers within an industry forming a perfect collusion purposely formed to increase profit and block new comers from the industry. a. b. c. d. Cartel Monopoly Corporation Competitors 317. The set of all points in the plane, the sum of whose distances from two fixed points, called the foci, is a constant. a. b. c. d. Parabola Ellipse Hyperbola Semi-circle 317. The set of all points in the plane, the sum of whose distances from two fixed points, called the foci, is a constant. a. b. c. d. Parabola Ellipse Hyperbola Semi-circle 318. The set of all points in the plane, the difference of whose distances from two fixed points, called the foci, remains constant. a. b. c. d. Parabola Ellipse Hyperbola Semi-circle 318. The set of all points in the plane, the difference of whose distances from two fixed points, called the foci, remains constant. a. b. c. d. Parabola Ellipse Hyperbola Semi-circle 319. The set of all points in the plane whose distances from a fixed points, called the focus, and a fixed line, called the directrix, are always equal. a. b. c. d. Parabola Ellipse Hyperbola Semi-circle 319. The set of all points in the plane whose distances from a fixed points, called the focus, and a fixed line, called the directrix, are always equal. a. b. c. d. Parabola Ellipse Hyperbola Semi-circle 320. Find the volume generated by revolving a rectangle of sides ‘a’ and ‘b’ about the side ‘a’. a. b. c. d. ∏ ba2 ∏ ab2 /2 ∏ ba2 / 2 ∏ ab2 320. Find the volume generated by revolving a rectangle of sides ‘a’ and ‘b’ about the side ‘a’. a. b. c. d. ∏ ba2 ∏ ab2 /2 ∏ ba2 / 2 ∏ ab2 321. The capillary rise in a tube is obtained by equating: a. b. c. d. Cohesive and adhesive forces gravitational force to shear force Surface tension force to weight of liquid Pressure forces to gravitational forces 321. The capillary rise in a tube is obtained by equating: a. b. c. d. Cohesive and adhesive forces gravitational force to shear force Surface tension force to weight of liquid Pressure forces to gravitational forces 322. The fluid property which contributes cavitation is: a. b. c. d. atmospheric pressure Vapour pressure Cavitation number Suction head 322. The fluid property which contributes cavitation is: a. b. c. d. atmospheric pressure Vapour pressure Cavitation number Suction head 323. The shear stress is directly proportional to viscosity for liquids which are Newtonian such as: a. b. c. d. Water Milk Paint Honey 323. The shear stress is directly proportional to viscosity for liquids which are Newtonian such as: a. b. c. d. Water Milk Paint Honey 324. Pascal Law is applicable when: a. b. c. d. Fluid is at rest Fluid is compressible Fluid is in motion Fluid is incompressible 324. Pascal Law is applicable when: a. b. c. d. Fluid is at rest Fluid is compressible Fluid is in motion Fluid is incompressible 325. A perfect gas is one which: a. b. c. d. Obeys characteristics equation Zero viscosity Zero specific heat Highly compressible 325. A perfect gas is one which: a. b. c. d. Obeys characteristics equation Zero viscosity Zero specific heat Highly compressible 326. Cavitation cannot occur in: a. b. c. d. Francis turbine Piston pump Centrifugal pump Pelton wheel 326. Cavitation cannot occur in: a. b. c. d. Francis turbine Piston pump Centrifugal pump Pelton wheel 327. A draft tube is a must in: a. b. c. d. Francis turbine Axial pump Pelton turbine Centrifugal pump 327. A draft tube is a must in: a. b. c. d. Francis turbine Axial pump Pelton turbine Centrifugal pump 328. The pressure difference measured at the two ends of Pitot tube is: a. b. c. d. Static pressure Stagnation pressure Dynamic pressure Total pressure 328. The pressure difference measured at the two ends of Pitot tube is: a. b. c. d. Static pressure Stagnation pressure Dynamic pressure Total pressure 329. Piezometer head is equal to: a. b. c. d. Sum of elevation head and velocity head Sum of pressure head at velocity head Sum of pressure head and elevation Pressure head 329. Piezometer head is equal to: a. b. c. d. Sum of elevation head and velocity head Sum of pressure head at velocity head Sum of pressure head and elevation Pressure head 330. The coefficient of discharge of a venturi meter is approximately equal to: a. b. c. d. 0.98 0.6 0.75 1 330. The coefficient of discharge of a venturi meter is approximately equal to: a. b. c. d. 0.98 0.6 0.75 1 331. Bernoulli’s equation is derived based on the following assumptions: a. b. c. d. Flow is incompressible, steady and irrotational Flow is steady, compressible and irrotational Flow is steady, incompressible and rotational Flow is unsteady, incompressible and irrotational 331. Bernoulli’s equation is derived based on the following assumptions: a. b. c. d. Flow is incompressible, steady and irrotational Flow is steady, compressible and irrotational Flow is steady, incompressible and rotational Flow is unsteady, incompressible and irrotational 332. When two pumps are connected in PARALLEL the following relation holds good: a. b. c. d. Q = Q1 + Q2 H = H1 + H2 Q1 = Q2 Q1 / Q2 = H1 / H2 332. When two pumps are connected in PARALLEL the following relation holds good: a. b. c. d. Q = Q1 + Q2 H = H1 + H2 Q1 = Q2 Q1 / Q2 = H1 / H2 333. The highest overall efficiency is possible in: a. b. c. d. Hydropower stations Gas turbine power stations Steam power stations Combine cycle power stations 333. The highest overall efficiency is possible in: a. b. c. d. Hydropower stations Gas turbine power stations Steam power stations Combine cycle power stations 334. A hydropower station is constructed because of: a. b. c. d. Head Head and flow Flow Nearest to river 334. A hydropower station is constructed because of: a. b. c. d. Head Head and flow Flow Nearest to river 335. Consider of the following flows and state which one is one dimensional. a. b. c. d. Flow around a rocket Flow around an automobile Flow through an artery Flow through a vein 335. Consider of the following flows and state which one is one dimensional. a. b. c. d. Flow around a rocket Flow around an automobile Flow through an artery Flow through a vein 336. Indicate which one flows is unsteady: a. b. c. d. Flow through a irrigational channel Flow near the entrance of a pipe Flow around an automobile Flow through human heart 336. Indicate which one flows is unsteady: a. b. c. d. Flow through a irrigational channel Flow near the entrance of a pipe Flow around an automobile Flow through human heart 337. When two pumps are connected in SERIES the following relation holds good: a. b. c. d. H = H1 + H2 Q = Q1 + Q2 H1 = H2 Q1 / Q2 = H1 / H2 337. When two pumps are connected in SERIES the following relation holds good: a. b. c. d. H = H1 + H2 Q = Q1 + Q2 H1 = H2 Q1 / Q2 = H1 / H2 338. Which of the following liquids is classified as Newtonian fluid? a. b. c. d. Honey Petrol Glycerine Paint 338. Which of the following liquids is classified as Newtonian fluid? a. b. c. d. Honey Petrol Glycerine Paint 339. It is a prime number that exceeds 10,000. a. b. c. d. Clock prime Cousin prime Gigantic prime Sexy prime 339. It is a prime number that exceeds 10,000. a. b. c. d. Clock prime Cousin prime Gigantic prime Sexy prime 340. Prime number that differs from another prime number by four. a. b. c. d. Clock prime Cousin prime Gigantic prime Sexy prime 340. Prime number that differs from another prime number by four. a. b. c. d. Clock prime Cousin prime Gigantic prime Sexy prime 341. Prime number obtained by reading digits around an analog clock. a. b. c. d. Clock prime Cousin prime Gigantic prime Sexy prime 341. Prime number obtained by reading digits around an analog clock. a. b. c. d. Clock prime Cousin prime Gigantic prime Sexy prime 342. It is a British word for “Billion”. a. b. c. d. Killiard Milliard Killord Millord 342. It is a British word for “Billion”. a. b. c. d. Killiard Milliard Killord Millord 343. A theory containing criteria for an old theory. a. b. c. d. Metatheory Betatheory Megatheory Millitheory 343. A theory containing criteria for an old theory. a. b. c. d. Metatheory Betatheory Megatheory Millitheory 344. A number of digits of prime number factorization is less than the digits of the number. a. b. c. d. Amicable number Economical number Wasteful number Natural number 344. A number of digits of prime number factorization is less than the digits of the number. a. b. c. d. Amicable number Economical number Wasteful number Natural number 345. It refers to a large number. a. b. c. d. Billion Zillion Million Trillion 345. It refers to a large number. a. b. c. d. Billion Zillion Million Trillion 346. A square which can be dissected into a number of smaller squares with no to equal. a. b. c. d. Medial triangle Perfect square Prime square Cousin number 346. A square which can be dissected into a number of smaller squares with no to equal. a. b. c. d. Medial triangle Perfect square Prime square Cousin number 347. The degree of peakedness of a distribution. a. b. c. d. Cardiod Limacon Kurtosis Stochastic 347. The degree of peakedness of a distribution. a. b. c. d. Cardiod Limacon Kurtosis Stochastic 348. Trigonometry formulas that convert a product of functions into a sum or difference. a. b. c. d. Prostaphaeresis formulas Apoapis Fouries series Demlo numbers 348. Trigonometry formulas that convert a product of functions into a sum or difference. a. b. c. d. Prostaphaeresis formulas Apoapis Fouries series Demlo numbers 349. A skew polygon such that every two consecutive sides belong to a face of a regular polyhedron. a. b. c. d. Petrie polygon Cevian polygon Periapsis Spinode 349. A skew polygon such that every two consecutive sides belong to a face of a regular polyhedron. a. b. c. d. Petrie polygon Cevian polygon Periapsis Spinode 350. Polygon with infinite sides. a. b. c. d. Perigon Apeirogon Centigon Zilliogon 350. Polygon with infinite sides. a. b. c. d. Perigon Apeirogon Centigon Zilliogon