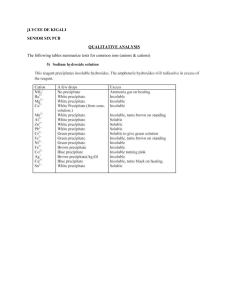
ASSUMPTION UNIVERSITY FACULTY OF ENGINEERING BASIC SCIENCE DEPARTMENT CHEMISTRY LABORATORY REPORT BG 14032 GENERAL CHEMISTRY LABORATORY EXPERIMENT (10) Cation Analysis Group (III) Submitted to: : A. Kyi Kyi Tin Submitted by: : Mr. Si Thu Tun (ID 6218135) Section :642 Date(4/4 / 2020) Semester (2/2019) I. Purpose of the experiment The purpose of inorganic qualitative analysis is to enable - The acquisition of powers of observation and deduction - The learning of reaction of inorganic chemistry - The development of practical chemical skills II. Introduction In many real situation, a chemist must gather observation to decide the chemical identity of an unknown sample. Given a totally “unknown” sample, how does go about determining what is actually present? This process is called “qualitative analysis” . Cations are classified into five groups on the basis of their behavior against some reagents by using groups reagents; we can decide presence or absence of groups of cations and can also separate these groups for further examination. The group reagents used for the classification of most common cations are hydrochloric acid, hydrogen sulphide , ammonium sulphide and ammonium carbonate. Classification is based on whether a cation reacts with these reagents by the formation of precipitates or not. Therefore, it can be said that classification of most common cations is based on the differences of solubilities of their chlorides. Sulphides and carbonates. The five groups are as follows: Group I… Cations from precipitates with dilute hydrochloric acid. Ions of this group are Lead Mercury(I), and Silver Group II. Cations do not react with hydrochloric acid, but from precipitates with hydrogen sulphide in dilute mineral acid medium. II A. Mercury (II), Copper , Bismuth, Cadmium Sulphides of II A are insouluble in (NH4)2S II B. Arsenic (III), Arsenic (V), Antimony (III), Antimony (V), Tin(II) and Tin(IV). Sulphides of II B are soluble in (NH4)2S. Group III Cations do not react either with dilute mineral acid medium. They form precipitates with ammonium sulphide in neutral or ammonical media. They are Cobalt(II), Nickel (II), Iron (II) Iron(III), Chromium (III), Aluminum, Zinc , and Mangenese(II). Group IV Cations do not react with the reagents of group I, II and III. They form precipitates with Ammonium carbonate in the presences of ammonium chloride in neutral or slightly acidic media Group V. Cations do not react with reagents of previous groups. They are Magnesium, Sodium, Potassium, Ammonium, Lithium, and Hydrogen ions. III. Experimental 3.1 Chemicals 3.2 Equipment 3.3 Procedure Take 5ml known solution sample in the test tube and follow instructions accordingly, and report your results in the table given below: Fe(III) ion Reagent 1(a).Add NH3 soln. Al(III)ion Reddish brown ppt White jelly ppt insoluble Insoluble Reddish brown ppt White jelly ppt insoluble soluble (NH4OH) 1-2 drops (b) excess NH3 soln. 2(a). Add NaOH soln. 1-2 drops (b) excess NaOH soln. 3. Add K4Fe(CN)6 soln. to Fe(III) ion sol 4. Add KSCN soln. to Fe n. (III) ion soll Deep blue n. Blood Red Equation FeCl (aq) + 3NH OH(aq) 3 3NH Cl(aq)+ Fe(OH) (s) 4 4 3 AlCl (aq) + 3NH OH(aq) NH Cl(aq) + Al(OH) (aq Fe(OH)3aq) + 3HCL(aq) FeCl3(aq) + 3NaCl(aq) 3 4 4 Al(OH) (aq) + 3HCl(aq) FeCl (aq) + 3NaOH(aq) Fe(OH)3(aq) + 3NaCl(aq) 3 3 3 2 FeCl3(aq) + 3H2O(l) Remark Group III cation present Reddish Brown ppt Clear solution Fe(OH)3, Al(OH)3 Group II to V ions Black brown ppt was formed Fe(OH)3 and (NaAlO2) Brown ppt Clear solution Fe(OH)3 NaAlO2 Residue II (Fe(OH3)was dissolved in minium volume of dil HCl sol and divided into two tube. KCNS solution was added to first tube with Fe(OH)3 Blood red suspension [Fe(SCN)3 Confirmed presence of Fe3 K Fe(CN)6]3 solution was added to second test tube with Fe(OH)3 Deep blue suspension (Fe4[Fe(CN)6]3 Confirmed presence of Fe3+ NH Cl solution was added to Filtrate II than stirred well and boiled. White suspension Al(OH)3 Co(N03)2 was added Blue suspension Confirmed presence of Al3+ n 3NaCl(aq)+2H2O(l)+NaAlO (aq) Fe(OH) (aq) + 3HCL(aq) observation Reddish brown ppt was formed Reddish Brown ppt. was washed with a small amount of distilled water and dissolved in minimum volume of dil HCL NaOH sol was added and boiled in hot water and filtered during hot. Residue II Filtrate II AlCl3(aq) + 2H2O(l) 3 AlCl (aq)+4NaOH(aq) 3 No Experiment 1 NH4Cl and NH4OH was added to mixture, than stirred ,boiled and filtered Residue I Filtrate I 3 n FeCl (aq) + 3KCNS(aq) 3 4FeCl3(aq) + 3K4Fe(CN)6 (aq) 12KCl(aq) Fe(CNS)3(aq) + 3KCl(aq) Fe[Fe(Cn)6]3(aq) + NaAlO2(aq) + NH4Cl(aq) + H2O(l) NaCl(aq) + NH3(g) + Al(OH)3(s) 2Al(OH)3(s) 3H2O(l) + Al2O3(s) Al2O3(s) O2(g) + 2Co(N03)2(aq) 2CoAl2O4(s) + 4NO2(g) + 4 4 4 IV. Results and discussions The given unknown salt mixture solution is found to be Cation Group(I) (i) Fe(III) ion is confirmed (ii) Al(III) ion is confirmed V. Conclusion The given unknown salt mixture solution is found to be Fe(III) ion and Al(III Form cation Group(III)