Cambridge Lower Secondary Science Year 8 - Chapter 1.1 & 1.2
advertisement

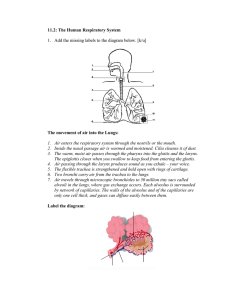
RESPIRATION Chapter 1 LEARNING OUTCOMES 1.1 1.2 The Human Respiratory System Gas Exchange 1.1 The Human Respiratory System Respiration A series of chemical reactions that happens inside every living cell Produces energy Aerobic respiration • • • The type of respiration that usually occurs inside our cells Aerobic = uses oxygen Cells produce carbon dioxide as a waste product Aerobic respiration • • • • • Breathe → air goes into lungs Some oxygen from air enters blood Blood delivers oxygen to cells → respiration Cells produce carbon dioxide Blood delivers carbon dioxide back to lungs Human Respiratory System Pathway of Air into Lungs 1) 2) 3) 4) 5) 6) Entrance to nose/mouth Larynx (voicebox) Trachea (windpipe) Bronchus Bronchiole Alveoli (air sacs) Emily Loves To Bake Brownies Always Larynx (voicebox) • • • • Contains vocal cords Vocal cords: bands of muscle that stretch across larynx When vocal cords vibrate → produce sound Like guitar strings Trachea (windpipe) Nose and mouth connect to trachea • Has strong rings of cartilage around it • Rings of cartilage: ➢ Keep trachea open and preventing it from collapsing → air can keep moving in and out of body • Bronchus • • • • • Plural: bronchi Has cartilage to provide support One bronchus goes to each lung Carries air deep into lungs Divides into smaller tubes: bronchioles Bronchioles & Alveoli (air sacs) Bronchioles: allow air to reach deeper into lungs • Branch into alveoli (air sacs) • Alveoli (air sacs): ➢ Where oxygen goes into blood ➢ Where carbon dioxide comes out • 1.2 Gas Exchange Structure of Alveoli (air sacs) Air sacs = alveoli Singular: alveolus Tiny blood vessels wrapped around alveoli → capillaries • Wall of air sacs and capillaries are made up of one layer of cells • • • Lung under microscope Structure of an Alveolus Gas Exchange in Alveolus • • • Gas exchange: oxygen from air goes into blood, carbon dioxide from blood goes into air Gas exchange occurs through diffusion Diffusion: movement of particles from an area of higher concentration to lower concentration Gas Exchange in Alveolus Alveolus • High oxygen • Low carbon dioxide • • • • Blood in capillary • Low oxygen • High carbon dioxide Blood in capillary comes from organs in the body Organs contain cells that undergo respiration → use up oxygen and produce carbon dioxide Blood in capillary contains little oxygen but a lot of carbon dioxide Air in alveolus contains a lot of oxygen but little carbon dioxide Gas Exchange in Alveolus Alveolus • High oxygen • Low carbon dioxide • • • • Blood in capillary • Low oxygen • High carbon dioxide Diffusion: movement of particles from an area of higher concentration to lower concentration There are only 2 very thin cells between air and blood Oxygen moves easily from air → thin-walled cells → blood (diffusion) Oxygen particles move from where there are a lot of them (air) to where there are fewer of them (blood) Gas Exchange in Alveolus Alveolus • High oxygen • Low carbon dioxide Blood in capillary • Low oxygen • High carbon dioxide • Oxygen dissolves when it gets into blood → goes into red blood cells → combines with haemoglobin • Carbon dioxide diffuses from the blood into the alveolus THE END. Questions?