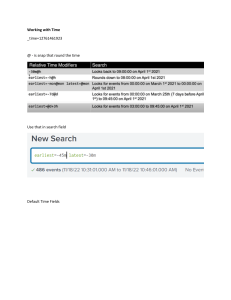
Splunk Enterprise Administration q What is SIEM • SIEM stands for Security information and event management • It collects the logs from various devices such as network devices, security devices, servers, applications, databases etc. • Once it collects the logs it normalize to the common SIEM format, in Splunk it is called as CIM (Common information model) and store the logs on the SIEM for long time • It enables long time logs retention and searching and reporting • It enabled you real-time time monitoring correlation and alerting q Why SIEM Required? • All the devices logs we can search from SIEM no need to login on each and every devices • Events stored on the SIEM are on the normalized format which is easy to understand unlike raw logs on the end devices • No need to analyze each and every logs instead we can write correlation rules on the SIEM which will trigger once any matching condition found q SIEM Players Available in Market • Splunk • Arcsight • Qradar • Logrithm • Azur Sentinel etc q Pros and Cons of the various SIEM • Arcsight: Good is Realtime correlation, Higher cost • Splunk: Very good in dashboard and visualization, Moderate cost • Qradar: Simplicity, easy to deploy and easy to manage, comparatively low cost q Splunk • Splunk Inc. is an American technology company based In San Francisco • Founded in 2003 • Cofounded by Michael Baum, Rob Das and Eric Swan q Splunk • Splunk is not only and SIEM tool but more on data analytics • SIEM is the one part of Splunk • Splunk can receive the logs for any device or machine which generate the data • Here in the class we are going to discuss how to use Splunk as an SIEM tool • As an SIEM we have to achieve 2 motives from SPLUNK Ø Collecting the Realtime logs from various device such as network devices, security devices, servers, applications, databases etc. Ø Realtime monitoring, correlation and alerting • What Is Splunk? q How is Splunk Deployed? Splunk Enterprise • Splunk components installed and administered on-premises Splunk Cloud • Splunk Enterprise as a scalable service • No infrastructure required Splunk Light • Solution for small IT environments q Search Heads also provide tools to enhance the search experience such as reports, dashboards and visualization q Types for Forwarders 1. Universal forwarder 2. Heavy forwarder Universal forwarder: • Installs on the end systems or servers and collects the logs locally • Light weight and required minimal resources Heavy Forwarder: • It’s a full flag Splunk Enterprise which act as a heavy forwarder • It collects the logs remotely from the end devices • Its does the parsing of the logs, we can apply the logs filtering on the forwarder q Splunk Installation Platforms • Splunk Enterprise - Windows - Linux(.rpm, .deb, .tgz) - Mac • Universal Forwarder - Windows - Linux - Solaris - Mac - AIX • Practical • Amount of storage required—refer slide 76 • 1)500GB/per day of data searchable for 1 years=500*365*.5+50b=91Tb • 2) 800GB/per day of searchable for 2 years • Create a • new index of XYZ • set a limit of 400GB • Upload the new licnes • Create a new pool of 5GB on the indexer # Practical • Create a new index = xyz and upload some logs there. • Create a new user and role for sales team and restrict the searches to the index=xyz • Create a new role “system admin” and assign him the can_delete and delete the data inside the index=xyz through the delete command #Practical Splunk Data Administration In Majority of the IT network from SIEM perspective will support either of the blow 2 types of log formats 1. Syslog 2. Windows Syslog: • Linux, Unix, IOS systems or servers or the devices hosted on these platforms support syslog • Syslog works on push mechanism that means the end device itself will push the logs to SIEM, In the end device we need to configure the IP address, port number and protocol to forward the logs to SIEM Windows: • Windows systems and servers supports Windows logs format • Windows works on pull mechanism that means SIEM will pull the logs from the Windows devices • We have to configure IP address or Host name of the device on the Splunk to pull the logs Windows Devices Integration with Splunk Windows devices can be integrated in 2 ways 1. By installing a Universal Forwarder on the windows device 2. Using Windows WMI Mechanism Integration Of Windows and Syslog Devices Using Universal Forwarder