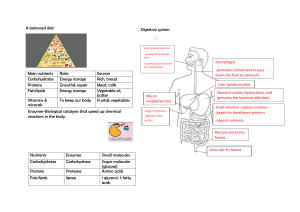
02. Food & Digestion Nutrients are chemical substances that keeps the body fit. They provide energy and materials that are responsible in making cells and other parts of the body. There are two types of nutrients. 1. Macro Nutrients – the nutrients that are consumed in excess quantities. E.g. – Carbohydrates, Lipids and proteins 2. Micronutrients – Nutrients that are consumed in very less quantities. E.g. – Vitamins and Minerals Nutrients Composition Building Categories Uses Major Source Elements Unit Monosaccharide Carbohydrates Carbon, Simple Provides energy Cereal, Whole Hydrogen, Sugars Glucose, Fructose (found in instantly Wheat, Rice, Oxygen fruits), Galactose (Dairy Yams Products) Disaccharides - Lactose (milk), Sucrose (sugar Cane) Polysaccharides - Starch (plant energy store), Cellulose (plant fiber), Glycogen (animal energy store) Lipids Carbon, Fatty 1. Solid Fats Formation of cell Chicken Liver, Hydrogen, acids and Animal Fat (Lard) membranes, Cheese, Nuts, Oxygen Glycerol 2. Liquid Fats stores excess Butter, Egg Plant fats (oils) amount of fats Yolk under the skin as heat insulation Proteins Carbon, Amino 20 types of amino acids Building Egg White, Hydrogen, Acids structures within Soya, Kidney Oxygen, the cells, beans, Nitrogen, at Formation of almonds, times Sulphur tissues and Sesame seeds, organs, for cheese, milk, growth and to meat, Fish repair worn out tissues, production of enzymes Vitamins and minerals – Micro-nutrients, doesn’t provide the body with energy, but required by the body for other functions of the body activities. Fiber – Dietary fiber cannot be digested, rather helps the food to be moved along the intestines. As the fiber moves along the large Intestine, bacteria feed on it and adds bulk to the food along with the fiber. This helps the muscle to push the food along, as it would have the most amount of water absorbed within, like a sponge, which makes the undigested foods to form the faeces soft and easy to be egested. Water – All the metabolic chemical reaction within the body takes place in the water. Blood is made up of water 55%, which allows the nutrients and other blood components to be transported throughout the body. Water also allows the body to maintain its temperature. 1|P ag e Test for Carbohydrates 1. Benedict’s Test (Test for sugars) Benedicts solution is composed of Sodium Carbonate, Sodium citrate and copper sulphate. Obtain a food sample that contains sugars, crush and grind using some amount of water. Filter and drain the water used to grind, into a test-tube. Add benedicts reagent (Blue in color). Immerse the food sample into a water bath and heat until the following series of color is been observed. Blue Green yellow Orange Red Brick Red Precipitate If we are using a sample of sucrose, since it is a disaccharide (non-reducing sugar), it has to be converted to monosaccharide (Reducing sugar), by adding diluted sulphuric acid and then neutralizing with an alkaline solution, add benedict’s reagent and then heat it in a water bath. 2. Test for Starch (Iodine Test) Obtain a food sample that contains starch (E.g. – A piece of bread), add diluted Iodine solution (yellowbrown color). If the bread piece turns into blue-black color, we can conclude that the food sample has starch in it. Balanced Diet – A diet that provides all the different nutrients in the appropriate quantities/right amount is known as balanced diet. Malnutrition – Malnutrition occurs when a person’s diet contains too many or too few nutrients than required. 1. Excess amounts of carbohydrates and fats can cause obesity. 2. Excess amounts of proteins, if consumed, part of it would be converted to glycogen and stored in the liver and the remaining part would be converted to ammonia and be excreted through the urine. Deficiency Diseases Nutrients Proteins Lipids Vitamin A Vitamin B1 Vitamin C Vitamin D Vitamin E Vitamin K Iron Calcium Iodine 2|P ag e Function in the body Growth of cells and tissues Thermal insulator Increased resistance to diseases and for proper visual senses Prevents digestive disorders and for proper functioning of nerves and muscles To prevent damages caused in the circulatory system To prevent weakening of bones and joints Protects body tissues from damages and prevents the person from aging. Prevents excess blood flow when wounded Helps oxygen to be transported throughout the body Buildup of strong bones and joints, teeth For production of thyroid hormone Disease Marasmus, Kwashiorkor Anorexia Nervosa Night blindness, Color Blindness Beri Beri Scurvy Rickets Less Fertility/hair loss Leukemia (Bone Marrow Cancer)/ Less blood Clotting Anemia Osteoporosis Goiter The breakdown of food – 2 major processes. 1. Physical breakdown – food been broken down from larger pieces to smaller pieces using the teeth is called physical breakdown of food. Human beings have 32 teeth and have 4 types of teeth. Incisors – to bite soft foods like fruits. Canines – to tear hard food like meat. They are pointed and sharp to carry out the function. Molars and premolars – to grind/crush the food into smaller pieces physically. Part Function Enamel Hard covering, contains Calcium Dentine Contains living cells, not hard as the enamel Gum Protects the teeth and the underlying bone Pulp cavity Contains blood vessels and nerves Fibers Holds the tooth in the jawbone Jawbone Helps in handling the food by biting, chewing etc. Blood vessels Supplies blood What are the causes for holes in your tooth? too many sugary or acidic foods and drinks a poor oral hygiene routine, such as failing to brush or floss daily not getting enough fluoride (Mineral) dry mouth (when salivary glands in your mouth don’t produce enough saliva) eating disorders, such as anorexia and bulimia (fear of gaining weight) acid reflux disease (If the circular muscle is weak or doesn’t tighten properly, the acid from your stomach can move backward into your oesophagus), which can result in stomach acid wearing down your tooth enamel. 2. Chemical breakdown of food Carbohydrates, proteins and lipids are all made up of large molecules which contains of basic building units. These large molecules cannot be absorbed by the body as it is not soluble in water. For it to become soluble in water, and be absorbed by the body, it has to be broken down into smaller molecules by the action of chemical reactions that uses enzymes. Enzymes are chemical substances that allows a reaction to be fastened, without being used up. Therefore, digestive enzymes helps the process of chemical breakdown to occur faster. 3|P ag e . Digestion begins in your mouth. Saliva plays a major role in digestion of food, especially carbohydrates. Saliva is made up of 99% of water, a slimy substance called mucin and an enzyme called amylase. We have three pairs of salivary glands named as – Parotid, Submaxillary and Sublingual. Muscles can contract but will not be able to lengthen/expand on their own. For this purpose, the oesophagus is composed of two layers of muscle cells. The outer layer is called longitudinal muscle and the inner layer is called the circular muscle. The Circular muscles contract in order to squeeze the food down the gullet, the longitudinal muscles will contract in order to lengthen the circular muscles. This continuous wave of muscular contraction and expansion is called peristalsis. Part of the Digestive System Mouth Oesophagus Stomach Small Intestine 4|P ag e Name of the Enzyme Nutrient Digested Type of Enzyme Functions (If Any) Amylase from Saliva _ Carbohydrates Carbohydrase Carbohydrates Sugars _ _ Hydrochloric Acid _ _ Pepsin Bile (from gall Bladder in liver) Pancreatic Juice (from Pancreas) Proteins Fats Protease Lipase Passing the food from the mouth to the stomach by a process named peristalsis. Breaks down hard bones into smaller pieces. Provides an acidic medium for pepsin to begin its function. Protein Amino Acids Lipids Fatty acids + glycerol Fats Carbohydrates Proteins Lipase Carbohydrase Protease Lipids Fatty acids + glycerol Carbohydrates Sugars Protein Amino Acids Large Intestine _ _ _ Absorbs water along with vitamins and minerals that are dissolved in it and passes undigested food through. Digestion is a chemical reaction, as one substance is changed into a different substance. For this chemical reaction to occur, enzymes are present within the alimentary canal. Enzymes are substances/chemicals that speeds up a chemical reaction without being used up. Enzymes belongs to a larger category called Catalyst. Catalyst or biological catalysts usually work in the form of a lock and key model. It can be explained as follows. 5|P ag e