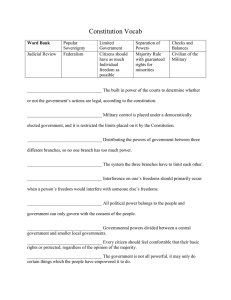
TOPIC 1.1- IDEALS OF DEMOCRACY 1. Identify the term associated with each of the following definitions. Natural Rights . Fundamental rights of all humans NOT received from a government Popular Sovereignty . The ideas that people are the source of governmental power and authority Social Contract . The idea that people create a government to protect the rights of the people . A form of government where people choose representatives to make public policy Republicanism 2. Identify two specific democratic ideals found in each of the following documents. Declaration of Independence U.S. Constitution Republicanism - Natural Rights Separation of Powers/Checks and Balances - Social Contract Limited Government and Popular Sovereignty TOPIC 1.2- TYPES OF DEMOCRACY 3. Describe the characteristics of each, provide contemporary examples, and identify one way the document supports that type of democracy. Characteristics Examples Document No. 1– state governments Supports - Broad participation in - Town Halls, Initiatives, Brutus Participatory where people can more directly politics and Referendums. Democracy influence government - Amendments that expand suffrage Pluralist Democracy - Group based influence of politics - Leads to competing factions - Interest Groups and States Elite Democracy - Limited participation by well-educated elites. - Supreme Court and the Electoral College - Political Parties - congressional representation, iron triangles, Super PAC's Federalist No. 10–Argues for a creation of a large republic so factions can compete to promote the pubic interest. U.S. Constitution– Creates EC and SC. Makes U.S. a representative republic. TOPIC 1.3- GOVERNMENT POWER AND INDIVIDUAL RIGHTS 4. Identify the Federalist and Anti-Federalist positions regarding the Constitution, the Bill of Rights, state sovereignty, and centralized power. Federalist Anti-Federalist - Supports the Constitution - Thinks of Bill of Rights is unnecessary - Want the states and fed government to share power (not ve sovereign) - Want more central power (to be effective) Do not Support the Constitution - Want of Bill of Rights - Like State sovereignty - Want central government to be weak (believe it would lead to tyranny) 5. According to Federalist No. 10, what was the biggest threat to the new nation, and what was the solution to the problem? Madison argued the biggest threat to the new nation were factions and that the solution was to create a large republic that would dilute the power of factions and promote the public interest. 6. According to Federalist No. 10, why will democracies always fail? Federalist No. 10 argues that pure democracies lead to mob rule where minorities (a small group of people) are oppressed. - Also believed that the people weren't educated enough to make the best laws and that it would be inefficient as the nation grew. 7. Identify three specific criticisms of the Constitution made in Brutus No. 1. Necessary and proper clause would lead to Congress having unlimited power (using it to justify creating any law they want) Supremacy Clause: lead to diminishing of state governments as the federal governments could strike down any law. - Tax, federal courts, standing army. © UltimateReviewPacket.com- Annual license required. Do not share or post online. Advanced Placement® and AP® are registered trademarks of the College Board. Page 1 of 3 TOPIC 1.4- CHALLENGES OF THE ARTICLE OF CONFEDERATION 8. Explain how Shays’ Rebellion highlighted the weaknesses of the Articles of Confederation. Congress couldn't send a militia to help Massachusetts deal with the rebellion and showed that Congress would need to have more power to help in the future. 9. Identify if each is a characteristic of the Articles of Confederation (AOC), the U.S. Constitution, or both. State sovereignty Shared sovereignty Congress has the power to tax Congress can create a currency States can create their own currencies ▢ AOC ▢ AOC ▢ AOC ▢ AOC ▢ U.S. Constitution ▢ U.S. Constitution ▢ U.S. Constitution ▢ U.S. Constitution ▢ AOC ▢ U.S. Constitution Congress can regulate interstate commerce ▢ AOC ▢ U.S. Constitution Congress can declare war and make treaties ▢ AOC ▢ U.S. Constitution States retain powers not delegated to the federal government ▢ AOC ▢ U.S. Constitution TOPIC 1.5- RATIFICATION OF THE U.S CONSTITUTION 10. The Virginia Plan favored states by making representation based on population. The Conneticut compromise, big though, established that the House would be based on population while the Senate would be equal per state. Electoral College 11. The chooses the president. At the Constitutional Convention, some advocated for the president to be chosen directly by the people while others wanted Congress to choose the president. 12. Identify the outcome of the following compromises. Three-fifths compromise Compromise on the importation of slaves 3/5's of the slave population was counted for representation in the House. States with more slaves were taxed more. The slave trade was abolished in 1808. But it wasn't touched until then. 13. Identify the two ways the Constitution can be amended. It can be proposed either by 2/3 vote in Congress of 2/3 of special state conventions 3/4 of the states need to ratify it (either through state legislatures or special state ratifying conventions) TOPIC 1.6- PRINCIPLES OF AMERICAN GOVERNMENT 14. Describe the main idea of Federalist No. 51. To keep the government from becoming tyrannical, power should be separated into three branches largely independent of each other. But they should have the power to check the power of the other branches. 15. Describe the difference between separation of powers and checks and balances. Separation of powers refers to the division of powers between the branches (e.g. only Congress can make laws) while checks and balances refers to the ability of each branch to stop the other from having too much power (e.g. impeachment, judicial review) TOPIC 1.7- RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN THE STATES AND FEDERAL GOVERNMENT 16. Define each term and provide examples of each type of power. Definition Delegated Powers given to the federal government by the powers Constitution. Reserved Powers only the states have powers Concurrent Powers both the federal and state government has powers © UltimateReviewPacket.com- Annual license required. Do not share or post online. Advanced Placement® and AP® are registered trademarks of the College Board. Examples - Declaring War - Coining Money - Regulating Commerce within a state - Policing/Education/Hospitals - making laws - taxation Page 2 of 3 TOPIC 1.7- RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN THE STATES AND FEDERAL GOVERNMENT (continued) Federalism 17. is the division of power between national, state, and local governments. 18. Compare dual federalism and cooperative federalism. Dual federalism - states and federal government competing Cooperative federalism - fiscal federalism. 19. Identify the term associated with each of the following definitions. Block Grants Unfunded Mandate Federal Funding Categorical Grants Dual Federalism - Both the states and the federal government are supreme in separate thing (there is NO overlap in power) Cooperative Federalism - the states and the central government share power. . Money provided to the states that can be spent within a broad policy area . A federal requirement that states take a specific action, without providing money to do so . Money provided to the states without any restrictions on how the money is spent Federal Revenue Sharing. . Federal money provided to the states to be spent for a specific purpose TOPIC 1.8- CONSTITUTIONAL INTERPRETATIONS OF FEDERALISM 20. Describe how each of the following constitutional clauses has increased federal power relative to the states. Commerce clause Supremacy clause Allows Congress to make laws on issues that tie to commerce (which is a lot of things) It gives federal laws more authority than state laws which increases the power of the federal government. 21. Explain how the Tenth Amendment and the necessary and proper clause create tension over the balance of state and federal power. The necessary and proper clause give significantly more power to the federal government by expanding the scope of Congress's power to unknown lengths. While the tenth amendment gives powers to the states which the federal government isn't allowed to do. But exactly what the federal government can't do is unclear due to the vagueness of the necessary and proper clause. 22. Compare the facts, holding, and constitutional principle in McCulloch v. Maryland (1819) and U.S. v. Lopez (1995). McCulloch v. Maryland (1819) U.S. v. Lopez (1995) - Maryland taxed a federal bank - McCulloch refused to pay it. - Constitution doesn't explicitly say Congress can create a bank. Facts Holding Principle The federal government could create a bank due to the necessary and proper clause and Maryland could not tax it due to the supremacy clause. Federalism (gave federal government more power) - Kid brings a gun to school and is charged under state law and then under federal law. Congress used the Commerce Clause to create that federal law. Congress couldn't use the commerce clause to make that law. The law was unconstitutional. Federalism (gave the states more power) TOPIC 1.9- FEDERALISM IN ACTION 23. Identify two advantages of federalism in the creation of public policy. - Multiple access points - States serve as "laboratories of democracy" - States can make policy w/o national consensus - Allows for uniform policy everywhere. - While allowing states to pass specific laws for their people. 24. Define each of the following and identify the constitutional support for each type of power. Enumerated powers Enumerated powers are the powers the Constitution explicitly lists Congress has. They are given in Article 1 Section 8 of the Constitution © UltimateReviewPacket.com- Annual license required. Do not share or post online. Advanced Placement® and AP® are registered trademarks of the College Board. Implied powers Implied powers are powers Congress has that aren't explicitly listed in the Constitution. Congress is implied to have these because they are needed to carry out the enumerated powers. The necessary and proper clause gives Congress these powers. Page 3 of 3