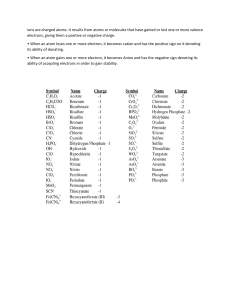
Ionic and Covalent Bonding ● Electronegativity Differences ○ If less than 0.4, then the bond is nonpolar covalent ○ If from 0.4-1.7, then the bond is polar covalent ■ Much weaker than ionic bonds ● Requires less energy to break ■ Much lower melting point than ionic bonds ■ Very poor conductivity / very poor solubility in water ○ If greater than 1.7, then the bond is ionic ■ Very strong bonds ■ Very high melting point ■ Low conductivity when solid ● Very high conductivity when dissolved in water or melted ○ This is due to the solid lattice structure causing electricity to be unable to move when the molecule is solid. When dissolved, however, the atoms have very high conductivity. ● Bond energy is the amount of energy needed to break a bond Lewis Structures & Exceptions to the Octet Rule ● Exceptions ○ Boron tends to form 3 covalent bonds ○ Elements in period 3 and beyond can exceed the octet rule ■ This happens often for sulfur and phosphorus ■ Extra electrons get placed on the central atom ○ Atoms in molecules with an odd number of electrons cannot form stable octets ■ Octet priority goes towards more electronegative atoms Resonance Formal Charges, and Chemical Nomenclature ● Resonance occurs when there are multiple valid Lewis structures for a single molecule ○ Represented by double headed arrows ● Formal charge is the charge assigned to an atom in a molecule ○ Sum of all formal charges must equal overall charge of molecule ■ FC = V (valence electrons) - N (non bonding electrons) - B (bonds) ● Atoms in molecules prefer formal charges close to zero ○ Any negative formal charges should reside on the more electronegative atoms ■ Major contributor ● Most favorable lewis structure ○ No charge, all formal charges are zero ■ Contributes most to what the molecule looks like in reality ● Naming ○ Binary ionic compounds ■ Cation named first, then anion ■ Name of cation is unchanged ■ Anion contains suffix “-ide” ● E.g. Potassium Iodide ■ Some atoms can form different types of ions ● Identify the charge on the metal ion using roman numerals ● Exceptions: Zn2+, Ag+, Cd2+, Groups 1, 2, Al ○ Polyatomic Ions ■ Ion Name Hg22+ Mercury (I) NH4+ Ammonium NO2- Nitrite NO3- Nitrate SO32- Sulfite SO42- Sulfate HSO4- Bisulfate/Hydrogen Sulfate OH- Hydroxide CN- Cyanide PO43- Phosphate HPO42- Hydrogen Phosphate H2PO4- Dihydrogen Phosphate SCN- or NCS- Thiocyanate CO32- Carbonate ○ Binary Covalent Compounds ■ First element is named ■ Second element contains the suffix “-ide” ■ Use prefixes to denote number of atoms present ● Mono is never used for the first element ○ Naming Acids ■ If the anion ends in -ide, the acid is named with the prefix hydro- and the suffix -ic ● E.g. Hydrochloric Acid ■ If the anion ends in -ate, the suffix -ic is added to the root name ● E.g. Sulfuric Acid ■ If the anion ends in -ite, the -ite is replaced by -ous ● E.g. Nitrous Acid VSEPR Model, Bond Polarity, Dipole Moments ● Thalidomide ○ Drug that helped with nausea, morning sickness, and a range of other conditions in pregnant women but when consumed as the S-isomer, thalidomide would hinder fetal growth ● VSEPR Model ○ Used to predict the structure of molecules ● Electron Arrangement vs. Molecule Structure ○ Electron arrangement describes the general structure of the molecule ○ Molecular structure is determined by the location of the atoms ■ Tetrahedral has 109.5 degree bond angle ■ Trigonal Pyramidal has 107 degree bond angle due to electron pair on central atom ■ Bent has 104.5 degree bond angle due to 2 electron pairs on central atom ● AXnEm notation ○ 2-3 electron groups ■ AX2 - linear ■ AX3 - trigonal planar ■ AX2E1 - Bent ○ 4 electron groups ■ AX4 - tetrahedral ○ ○ ■ AX3E1 - trigonal pyramidal ■ AX2E2 - bent 5 electron groups ■ AX5 - Trigonal bipyramidal ■ AX4E1 - Seesaw ■ AX3E2 - T-shape ■ AX2E3 - Linear 6 electron groups ■ AX6 - Octahedral ● ● ● ■ AX5E1 - Square Pyramidal ■ AX4E2 - Square Planar Determining Molecule Structure ○ Draw lewis structure for the molecule ○ Count number of electron groups around central atom ○ Arrange the atoms/groups of atoms around the central atom in a way that maximizes the distance between them ○ Determine the name of the molecule structure Bond Polarity and Dipole Moments Covalent bonds are polar if electronegativity difference is between 0.4 and 1.7