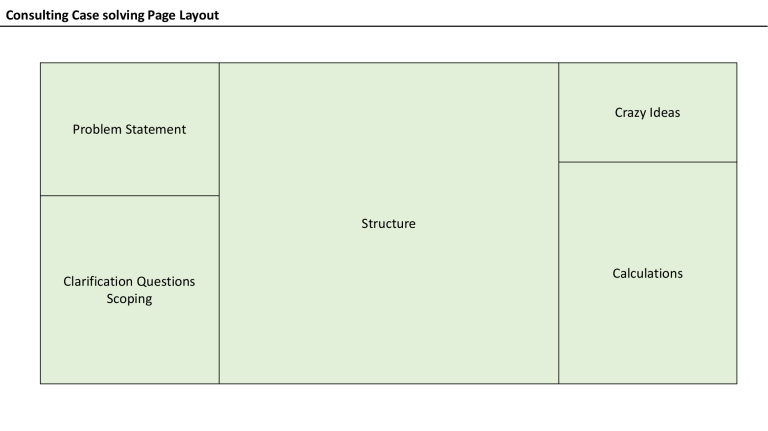
Consulting Case solving Page Layout Crazy Ideas Problem Statement Structure Clarification Questions Scoping Calculations Guesstimates (24/30 – A.A) Approach (Mix of both) Population approach Household Approach Direction Wise Top Down Quantity Wise Bottom Up Demand Side Supply Side Bottleneck Approach Duration & Unit Clarity Life / Replacement Start with Population and then filter Key Filters e.g. start with Delhi and use Proxy for other cities and add Urban-Rural When supply is abundant e.g. FMCG, white goods Age Income When Supply is constrained e.g. flights take-off, burgers @McD Gender Peak Time Analysis Occupancy Rate Ask Clarifying Questions Make MECE Basket First Define the structure and then add numbers at the end Create a formula Narrow the estimate e.g. AC (res or comm, new v/s used) Use replacement life + new addition Strategies Journey Map Prioritise Start End MECE 80:20 Rule Formula Approach (useful in identifying delay, giving solution) Data Centric Critical Comparison (data point. Abnormality) Customer Experience – Layout Structure Five Sense then (Aircraft Go Green Exampl) fill numbers Ear, Eye, Nose, Tongue, Touch Big Picture Scoping Questions Essential Methods MECE Process Mapping Business Framework Formula CCPC 7S Think of this, when it is Manufactured Products Product Time Price Quality Place Location Promotion Service Mix 5C 4P 5W & 1H 5 Why Packaging ……….. Positioning Essential Steps Services Unconventional Case Case Framework Breakdown Recommendation Matrix Must ask questions • Current objective & Any other objective • Issue occurring since when • Timeline & Financial Constraint • Currently where they are Where they want to be in future what is bridge here and how many stages Storage / Over capacity / Stock out cases • Input – Output = Storage Profit – Loss = Revenue Income – Expenditure = Revenue Core Problem Peripheral Problem Short Run Solution 1 …. 2 …. 1 …. 2 …. Long Run Solution 1 …. 2 …. 1 …. 2 …. Govt. Related Cases FIR Matrix • Think from PESTEL point of view SOS solution to Cases • Past – Present – Future Problem, Solution • Current situation – Capacity constraint (HR, Capital, Time) • 5W & 1H – Who, What, Where, When, Why, How • 3V – Variety, Volume, Value (14/30 A.A Case) , Revenue = Variety x Volume x Value • Funnel approach (filter based on parameter) – e.g. Booz report, Govt. disinvestment case • 5 Why to come to an reason ---- Aircraft incidents (10/30 A.A Case) High Low High 1 …. 2 …. 1 …. 2 …. Low 1 …. 2 …. 1 …. 2 …. Do following assessment after Solution • FIR 2*2 Matrix Feasibility – Impact – Risk -------- see FIR matrix through lens of PESTEL (9/30 A.A Case) • PESTEL Analysis (P= Politico-Admin, S=Socio-Cultural) FIR Feasibility CCapability IInvestment TTime EEffort Unconventional Case Case Framework Breakdown Must ask questions • Objective = Why, what benefit • Time • Since when it is occurring • By what time it has to be solved • Money = Any constraint • Quantum of damage • Geography = location of plants, operations • Competitor = facing challenges ? • Industry = vide issues ? • Economy • Regulatory Constraints • Company = Line of business, m share • Value Chain = know current process completely Barriers to Entry Suppliers Need Capital Requirement Govt. Regulations HR & Legal Cost Patents / Proprietary Items Economies of Scale Access to Distribution Channel Switching Cost Brand Loyalty Awareness Accessibility Availability Affordability Post Sales Experience Product Differentiation During Sales experience Market Entry 3 type of situations First of its kind product Product exist but new to given geography Objective of Market Entry Similar product exist in this geography Step 1 Step 2 Step 3 • Check Market Attractiveness • Market Size • Market Share • Market Growth • Check Financial Feasibility • Cost, Pricing & Profit • Check Barriers to Entry • Regulatory Barrier • Macro- Environment (PESTEL) • Industry Analysis • Porter’s 5 • Know Competitor • Know Customer • Define Customer Persona • Know Product feature gap • Define MVP • 6-P Step 4 Step 5 Step 6 • Operational / Value Chain Feasibility • Raw Materials • Logistics (I/B, O/B) • Production • Distribution • Marketing • Again check Financial viability based on Step 3 & • Re-Calculate Market Share • If we enter Market • Scratch Start • JV • M&A Financial Non Financial Profit Branding Break even Sale of complementary goods Market Size Calculation (A.A 13/24 video, time: 0:30) Look at 3 parameters: 1. Availability – supply chain side 2. Accessibility – regulations side 3. Affordability – willingness to pay and capability to buy Who are consumers: 1. New Customers 2. Repeat purchasers – using life of the product Market Share Calculation (A.A 13/24 video, time: 4:30) Monopolistic Market Share: Little difficult to calculate Fragmented market share: 50 players with 2% Market Share 1. Unlikely to have more than 2% Market Share in 1st year 2. Go for acquisition Consolidated market share: 5 players with 20% M. Share 1. Look at history of last player. 4 were already there and 5th was entering. What 5th player got Market Share in 1st 2nd 3rd year of operations. Compare product with them, value chain, competitive adv. Vis-àvis 5th player and also with other 4 players and calculate your Market Share 2. Say if they have 10% in 3 years then may be we may also have same Market Share 3. Also look at market growth rate If nothing comes to mind then 5% market share and take approval of interviewer and then move ahead Growth Strategy High Growth Low M. Share High Growth High M. Share Growth Strategy Current Revenue stream from Low Growth Low M. Share Low Growth High M. Share Inorganic Growth Organic Current Market Company Old Product Inc. Volume Product More Usage New Product New Market Product Extension VAS Old Product JV New Product Product Extension Positioning People M&A New Geography Inc. Margin Increase Customer Reduce Cost Increase Price Competitor Customer Product Price Place Promotion Packaging Process Growth Strategy – model 2 Growth Strategy Inorganic Growth Organic Current Market Same Channel New Channel Same Product Bundle Product New Customer More Usage JV Product Extension Old Product New Product Same Customer Frequency New Product New Market Price New Variation Marketing Product Extension Diversified Product M&A Synergies during M&A – Part 1 Synergy Revenue Synergy Increased Volume Increased Product Price Cost Synergy Increased Marketing Channel Shared R&D HR Layoffs of duplicate roles Shared Operations Low FC & VC Tax Saving Production Inc. Debt Capacity Cross- Selling Logistics Inc. in cost of capital Reduction of Competition Sales & Distribution Improvement in Working Cap. Access to New Markets Infrastructure Inc. in Profitability Reduced Cost High production & Low cost Finance Synergy Revenue addition by Inc. in Market Share Cost efficiency by Economies of Scale Financial Value Generation Due Diligence during M&A – Part 2 Due Diligence – look into following aspects Vision & Mission Support Services Finance HR IT System Value Chain Legal Operations Strategic Cultural Integration during M&A– Part 4 Marketing Strategy Systems Pain points during M&A– Part 3 Financial HR Integration Structure Shared Culture or Values Due Diligence Style Skill Staff Root Cause Analysis - Product Manager or otherwise External Factors • Any campaign by competitor – higher discount or big campaign • Any regulation by govt • Economic factor – pandemic, demonetization Internal Factors • • • • • • • • Any new campaign visibility lost for particular product Demographic pattern (change of behaviour based on age, gender, location etc.) Product Pattern (any change in specific pattern e.g. quality, stockout) Any other data pattern Any particular time of issue Customer Journey (which touchpoint is having the issue) Technical – App Updates, android or ios, mobile model, any bugs Any visual / process simplification – learning curve If stuck during case in between Critical Comparison / Trend Analysis vis-à-vis competitor, past data Ask / Revisit – Primary & Secondary Objective Segment and Process Mapping Mini Synthesis 4P & 5C Ask for Help Healthcare Sector Comprises of • Healthcare services (hospitals, clinics, diagnostic centres) • Medical devices and equipment (scanner, machines, OTG devices) • IT technologies (bio science, apps, SAAS) • Medicines / Pharmaceuticals • Insurance Growth drivers • Lifestyle diseases • Medical Tourism • FDI investments • Awareness and easy approachability through m-apps • Government’s agenda • Rural healthcare • R&D = Pandemics




