ENERGY
Makes things happen.
Definition
• Energy is the ability to do work
• Energy makes things to happen.
The unit of energy
The unit of energy is the Joule whose symbol is J
1 joule is the amount of work done by a force of 1 Newton when it
moves a distance of 1 metre.
1 Joule = 1Nm
* All energy is measured in Joule
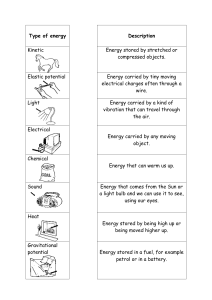
Types of Energy
The main types of energy are:
1 Kinetic energy
2 Potential energy
3 Light energy
4 Sound energy
5 Electrical energy
6 Heat energy/thermal energy
7 Nuclear energy
Kinetic energy (K.e)
• this is the energy of movement/motion.
• Bodies that are moving like
• A flying aeroplane
• A moving car
• A girl running
• The kinetic energy of a body depends on:
(i)The mass of the body
(ii)The speed/velocity of the body
Calculating Kinetic energy
• K.e = ½ mv2
•
v2 = v x v
m= mass of the body in kg
• Calculate the kinetic energy of a body of mass 24kg that moves with a
speed of 2.4m/s
• K.e = ½ mv2
m= 24kg
• =1/2x24x 2.4x2.4
v=2.4m/s
• =
Potential energy
• this is energy that is stored up in a body
• It is a result of the position of the body above the ground or its state
Forms of potential energy
potential energy
Chemical p.e
elastic p.e
gravitational p.e
Chemical potential energy
• This is energy stored in chemical bonds
• It is released during chemical reactions
• Sources of chemical potential energy include
• (I) all food e.g a birthday cake, sweets, rice, sweet potatoes.
• (ii) fuels e.g petrol, paraffin, cooking gas.
• (iii) batteries and cells are chemical energy stores.
Elastic Potential energy
This is energy stored in stretched and compressed bodies.
For example, a stretched catapult:
a stretched bow and arrow.
a compressed spring.
a stretched rubber band.
Gravitational potential energy (g.p.e)
• This is energy in bodies that are raised above the ground.
• For example
• A rock on top of a mountain
• Water in a raised dam
• A boy on top of the roof
• A girl standing on the balcony
• A book on top of the table
• A bird resting on top of a tree
Factors that affect the g.p.e
• The g.p.e of a body depends on two factors which are:
• the mass of the body
• the height above the ground
Calculating the g.p.e
g.p.e = mgh
m= mass of the body in kgs
g = acceleration due to gravity in m/s2 = 10m/s2
h= height above the ground in metres
Example of calculating g.p.e
• Calculate the g.p.e of a body of mass 65 kg, that is 5.6m above the
ground. {g=10m/s2}
Solution
g.p.e =mgh
=65 x 10 x 5.6
=
m=65kg
g= 10m/s2
h=6.5m