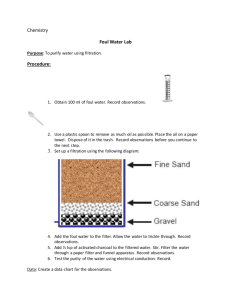
BOILER FEED WATER TREATMENT 60% of water is recovered through this process. We get filtered water of TDS Value 230. (Yahn lambi krna ha k boiler k water ko Q purify krte hain. Contaminations remove krna ye wo. SB yahn bhar dena.) “STEPS INVOLVED IN FEED WATER TREATMENT” The raw water in our case is bore water, which is filtered through series of steps involved which are detailed below. (Bore water is transferred to storage tanks by means of centrifugal pumps). STEP NO. 01 “Stagnant Water in Storage Tanks” Basic Operation: This step is based on Sedimentation process. In this process, small particles are separated and sedimented in water. This process happens naturally when water is still because gravity will pull the heavier sediments down to form a sludge layer. These solid matters settled down could be removed from the bottom either periodically or continuously. Clear water is drained out from the tank surface. Construction: Horizontal flow tanks are the simplest construction. These rectangular tanks allow water to flow horizontally, ensuring that particles are separated from the water during the movement through the tank. The tank is equipped to clean the sediment out periodically in order to allow the process to continue. Impurities: Impurities that are removed through this process includes Iron (Fe), Potassium (K) & Calcium (Ca) impurities. STEP NO. 02 “Sand Filter Multimedia” Basic Operation: Sand filter media is a type of water filter that uses quartz silica sand, not just any regular type of sand as it is a great filtration element in. The quartz silica sand cut into specific shapes and sizes that make them more efficient in catching pool water particles. Construction: Sand filter media uses quartz silica. The sand filter media come in different sizes that vary between (0.45-0.55) mm. Impurities: A sand filter can only filter solid particles from the water, like algae and organic material. Salts that do not dissolve in water, like salts that appear in fertilizers, can be filtered from the water by a sand filter, provided that the particles are large enough This process filters up particles down to 20 microns. (The water is then transferred to next compartment by feed pump of pressure 2 to 3 bars). STEP NO. 03 “Backwashing Filtration” Basic Operation: Backwashing is a process that is used in water and wastewater treatment to pump water backward through filter media, which includes anything placed in a filter that changes the quality of water flowing through it. This process sometimes involves the intermittent use of compressed air and is a form of preventative maintenance so filter media can be reused. Construction: Backwashing water filters are large tank-style filters that get their name from the fact that they clean and renew themselves by backwashing. Backwashing consists of reversing the flow of water so that it enters from the bottom of the filter bed, lifts and rinses the bed, then exits through the top of the filter tank. Impurities: This process removes impurities of size up-to 5 microns. Impurities that are removed through this process includes Iron (Fe) and sand particles. STEP NO. 04 “Cartridge Filtration” Basic Operation: Filtration through cartridge filters is a technique widely used in the elimination of particulates and contaminant compounds contained in the water. The filtration is made by pressure, allowing the passage of clarified water and retaining the particles and the unwanted pollutants, until the filter is saturated and it is necessary to carry out its substitution by new ones. Construction: This constitutes of cartridge filters of length between 40 to 30 inches. A cartridge is encased within a housing or a casing. The cartridge is exposed to water, liquid or solvent that needs filtration, as it flows inside the housing and passes through the filter element. Impurities: Filter cartridges can remove such harmful mineral deposits and chemical additives as arsenic and fluoride from feed water. (The water is then transferred to next vessel by High Pressure pump of pressure 12 to 13 bars). STEP NO. 05 “Vessel/ Membrane Filtration” Basic Operation: Membrane Filtration uses membranes to remove particles from water. The process is similar to conventional sand or media filters in that suspended solids are removed, but generally dissolved solids are not removed. Membrane filtration processes can operate under pressure or vacuum. Construction: The vessel consists of four membranes of different sizes to trap impurities. Filtration membranes are essentially microporous barriers of polymeric, ceramic or metallic materials. Impurities: This process is used to separate dissolved materials (solutes), colloids, or fine particulate from solutions.