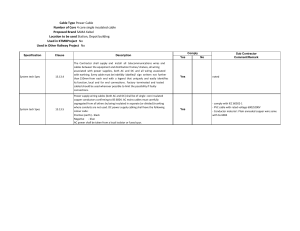
QCS 2010 Section 21 Part 1 General Provisions for Electrical Installation Page 1 GENERAL PROVISIONS FOR ELECTRICAL INSTALLATION .................... 2 1.1.1 1.1.2 1.1.3 1.1.4 1.1.5 1.1.6 1.1.7 1.1.8 1.1.9 1.1.10 1.1.11 1.1.12 1.1.13 1.1.14 1.1.15 1.1.16 1.1.17 1.1.18 1.1.19 1.1.20 1.1.21 1.1.22 1.1.23 1.1.24 1.1.25 1.1.26 1.1.27 Scope Regulations Existing Services Contract Drawings Shop Drawings Progress Drawings As built drawings Builders Work Programme Equipment and Materials Approval Fire and Safety Precautions Protection Quality of Staff/Personnel Climatic Conditions Samples Quality of Materials Equipment Duties and Ratings Workmanship Labels/Circuit Lists/Cable Identification Segregation of Services Electricity Supply Polarity Safety Interlocks Spare Parts Protection of Excavation Supply of materials Special Requirements QCS 2010 2 2 3 3 3 5 5 5 5 6 6 7 7 8 8 9 9 9 10 11 12 12 13 13 14 14 15 Qatar Project Management 1. QCS 2010 Section 21 Part 1 General Provisions for Electrical Installation Page 2 1. GENERAL PROVISIONS FOR ELECTRICAL INSTALLATION 1.1.1 Scope 1 The Electrical Installation Contractor, herein referred to as the 'Contractor' within this part and all other Section 21 parts of this specifications shall carry out all electrical works complete in accordance with the requirements of the Project Documentation. 2 The scope of work shall include but not be limited to: (a) (c) (d) (e) (f) (g) (h) 1.1.2 Regulations 1 All supplies and services offered in response to this specification shall conform to the latest standards. 2 The design, equipment and installation requirements shall comply with the standards and recommendations laid down by the following : (a) (b) (c) (d) (e) (f) (g) 3 Regulations for Electrical Installations as issued by the Qatar General Electricity and Water Corporation (QGEWC) Qatar Regulations for Electrical Installations as issued by the Institution of Electrical Engineers (I.E.E.), London (for points not included in QGEWC Regulations) Recommendations for Lighting Installations as issued by QGEWC and the Chartered Institute of Building Services, London Standards relating to Electrical Installations and equipment as issued by International Electrotechnical Commission (I.E.C.) and British Standards Institute (BSI) Regulations for telephone system installation as issued by Q-TEL National Electrical Code issued by National Fire Protection Association (NFPA), Boston, U.S.A Rules of the Qatar Civil Defence Department for Fire Alarm Installations. Where two or more applicable standards and/or the Specifications are in conflict, the most stringent shall apply. QCS 2010 Qatar Project Management (b) the supply and installation of all services, equipment, components, accessories and fittings required for the operation of the facility to the extent specified and detailed on the Drawings and Specifications including 400 days maintenance or as stipulated in the contract specification and all extended warranties after provisional handover builder's work in connection with the Electrical Installations, including supply, necessary inserts sleeves and making good. any work which can be reasonably inferred as necessary for the safe, satisfactory operation of each system, whether such work is specified or shown on drawings or not the supply and installation of cables, conduits, boxes and termination points, for the motors, starters, controls and the like for the Process Equipment, Heating, Ventilation and Air-conditioning and Plumbing services arranging for installation of permanent Electrical supply by the Qatar General Electricity and Water Corporation (QGEWC), including submission of all necessary documents to the QGEWC, and carrying all necessary approvals and obtaining consumption meters Moreover, the contractor shall allow in his tender and be responsible for the payment of all charges by way of examination, certification, depositing or connection fee to any Statutory Authority. (I.e. Electricity, Water, Drainage, Telephone, Fire, etc). attending upon the Supply Authority installing mains power supply and carrying out primary and secondary injection tests arranging and carrying out all necessary approvals with Q-TEL for the Telephone System arranging and carrying out all necessary approvals with the Qatar Civil Defence Department for the Fire Alarm System, extinguishing and protection systems. QCS 2010 Section 21 Part 1 General Provisions for Electrical Installation Page 3 Existing Services 1 The contractor is deemed to have visited and inspected the site to familiarise himself with the existing site conditions and services at tender stage. 2 The contractor shall obtain the existing services record drawings from QGEWC and various utility services departments (i.e. Q-TEL, CDD etc). 3 Co-ordination between shop drawings, work on site and existing services shall be carried out by the Contractor. 4 The Contractor shall be fully responsible for any damages to the existing services including repairs, and penalties imposed by the concerned parties etc and for removing any site obstacles such as underground cables, pipes, civil works etc. which is obstructing his work on site. 5 The Contractor shall also be responsible for liaison with QGEWC, Q-TEL and all other government utility departments to disconnect or divert the existing services supply to the existing site prior to demolishing. 1.1.4 Contract Drawings 1 The indication and/or description in any of the Contracts documents, unless otherwise specifically stated, implies an instruction to supply and fix such items. 2 Notes on Drawings referring to individual items of work take precedence over the Specification. 3 Drawings show the general run of cables, raceways, etc. and the approximate location of equipment and utilities; symbols and schematic diagrams are of no dimensional significance. Obtain from the Engineer dimensions not shown on, or which cannot be determined from Drawings. Do not scale drawings to obtain locations. 4 Notify the Engineer of conflicting requirements. Where departures from the drawings are deemed necessary, details of such departure and reasons thereupon shall be submitted to the Engineer for approval. 5 No such departure shall be made without prior written approval of the Engineer. 1.1.5 Shop Drawings 1 The term 'shop drawings' includes fabrication, erection, layout and setting out drawings; manufacturer's standard drawings, schedules; descriptive literature, illustrations, catalogues and brochures; performance and test data; wiring and control diagrams and other drawings and descriptive data pertaining to materials, equipment, raceway systems, control systems and methods of construction as required to show that materials, equipment and systems and position thereof, conform to the Contract Documents. The term 'manufactured' applies to standard units usually mass produced. The term 'fabricated' means items specifically assembled or made out of selected materials to meet individual design requirements. 2 Shop drawings shall establish actual detail of all manufactured or fabricated items, indicate proper relation to adjoining work, amplify design details of electrical equipment in proper relation to physical spaces in the structure, and incorporate minor changes of design or construction to suit actual conditions. 3 The Contractor shall submit for approval, and obtain in due time to conform to the Contract Program, all shop and installation drawings based on the design drawings approved by the QGEWC and all other relevant Municipality and Government Authorities. QCS 2010 Qatar Project Management 1.1.3 QCS 2010 Section 21 Part 1 General Provisions for Electrical Installation Page 4 4 The Contractor, immediately after being awarded the said Contract, shall prepare and submit shop drawings. Shop drawings shall be submitted with such promptness as to cause no delay in his own work nor to any other Contractor. No extensions of time will be granted because of failure to have shop drawings submitted in ample time to allow for processing, in accordance with the submittals schedule outlined in Section 9, Part 1, Clause 1.1.4. 5 Provide shop drawings, to a scale not smaller than the corresponding layout drawings, showing the following and obtain approval before commencing work: (a) (b) (c) (e) (f) (g) (h) (i) (j) (k) 6 Drawings shall be ISO standard size A1. Lettering shall be stencilled. Shop drawings and samples shall be properly identified with the name of the Project, the Contractor, the SubContractor and the date, and signed by Contractors Authorised Engineers. 7 Final co-ordination of electrical works with mechanical, structural and architectural work shall be carried out from complete shop drawings and sufficient time shall be allowed for coordination and checking of shop drawings and calculations after shop drawings are submitted. 8 Individual shop drawings shall be submitted following the distribution of the co-ordination drawings and shall bear a stamp indicating that the work has been co-ordinated with other trades. 9 The Engineer's review and approval of shop drawings submitted by and approved by the Contractor is for general conformance with the design concept and information given in the Contract Documents and shall not relieve the Contractor from responsibility for any deviations from the requirements of the Contract Documents. The Engineer's review and approval shall not be construed as a complete check nor shall it relieve the Contractor from responsibility for error of any sort in shop drawings or schedules, or from the necessity of furnishing any work required by the Contract Documents which may have been omitted on the shop drawings. The Engineer's review and approval of a component item shall not indicate review and approval of the complete assembly in which it functions. 10 The Engineer or the supervising consultant shall forward electrical drawings and specifications which are to be submitted for approval to QGEWC, when appropriate. However, it shall be the Contractors responsibility to obtain written approval from QGEWC for all such drawings and specifications appertaining to the work carried out under the contract. QCS 2010 Qatar Project Management (d) exact runs and sizes of conduits, ducts, cables, cable trays and trunking layout drawings for each separate electrical installation showing the actual locations of points, suitably identified, the locations of switchgears, switchboards, motor control centres and distribution boards, details and types of fittings plans showing the equipment assembly, space requirements, clearances and locations for cable entrances and anchor bolts elevations showing all parts, devices, components and nameplates, positions and arrangements of the equipment. Show as many elevations as necessary to clearly depict component and device arrangements schedules of points, indicating how the various outlets are connected to the distribution boards, size of circuit wiring, the rating of the protective device and the type and size of appliance of fitting schematic diagram of connections of distribution boards, and equipment to main switchboards showing sizes of feeders, etc schematic and elementary wiring diagrams, of each unit of each equipment, showing numbered terminal points, numbered wires and numbered interconnections to other equipment and remote devices connection wiring diagrams, of each unit of each equipment, showing numbered terminal points, numbered wires and numbered interconnections to other equipment and remote devices complete catalogue information of all parts and components of electrical equipment all cable routings and layouts for the different electrical services, feeders and branch circuits showing routes, sizes and types of cables any other data necessary for the proper maintenance of the installations. QCS 2010 Section 21 Part 1 General Provisions for Electrical Installation Page 5 QGEWC approvals may take a considerable time to obtain and the contractor should make allowance for this and be available for liaising with and pursuing approvals with QGEWC. Progress Drawings 1 Provide and keep on the job at all times, one complete and separate set of blackline prints of the electrical work on which shall be clearly, neatly and accurately noted, promptly as the work progresses, all architectural and electrical changes, revisions and additions to the work. Whatever work is installed otherwise than as shown on the Contract Drawings, such changes shall be noted. 2 Indicate daily progress on these prints by colouring in the various conduit, ducts, trunking, cable trays, fixtures, apparatus and associated installation works erected. 1.1.7 As built drawings 1 The contractor shall provide the as built drawings, as approved by the engineers, in DXF format or AutoCAD DWG format, either in floppy diskettes or in CD-ROM, as per the Project Documentation requirement. The drawings shall be submitted not later than 2 months after completion of the Project, or putting into operation, whichever is earlier. An addition, 3 sets of hard copy of all relevant drawings, which will be required for operation and maintenance, shall be supplied in bound book forms immediately after the commissioning of the Project. The quality of these drawings shall be consistent with the standard of QGEWC. Diary sheets for Work completed shall not be authorised until such records have been presented to the Engineer and accepted. 2 The contractor shall supply, 3 sets of all operation and maintenance manuals in original, from the manufacturer in bound book forms, at least 2 weeks prior to commissioning of the equipment. These shall also be supplied, in computer diskettes, based on popular Microsoft window based publishing software programmes, along with the as built drawings as mentioned above, as specified in the Project Documentation or as directed by the Engineer. 1.1.8 Builders Work 1 Lay electrical works in advance of pouring concrete slabs and construction of walls. Obtain Engineer's approval before commencing builder's work in connection with electrical installation. Related co-ordinated shop-drawings shall be submitted for approval as per the related clause 1.1.5 of this section. Materials approval shall be obtained as per procedure detailed in clause 1.1.9 below. The contractor shall make it certain that drawings properly coordinated with other works are submitted immediately after signing of the contract and approval of drawings and the materials are obtained at least one month prior to the commencement date of the construction. 2 Check with other trades to ensure equipment and material can be installed in space provided. 3 Provide other trades with information necessary for them to execute their work. 4 Details on drawings which are specific regarding dimensions and locations, are for information purposes. Co-ordinate with other trades to ensure work can be installed as indicated. 1.1.9 Programme 1 The Contractor shall produce a work programme based on CPM or Bar-chart form or as directed by the Engineer indicating the time required for various operations to complete the Project in time. The following points shall be highlighted in the programme: (a) (b) (c) mobilisation drawings/submittals approvals QCS 2010 Qatar Project Management 1.1.6 QCS 2010 (d) (e) (f) (g) (h) (i) (j) (k) Section 21 Part 1 General Provisions for Electrical Installation Page 6 equipment deliveries including delivery periods from supply sources external to the State of Qatar first fix cabling main/sub-main distribution equipment second fix fixing of light fittings testing commissioning and handing over. The Contractor is responsible for all liaison with QGEWC in respect of programming the installation and commissioning of complete electrical system. The Contractor shall ensure that QGEWC are at all times kept informed of the current progress of the electrical works on site and that his approved electricity supply subcontractor programs the cable laying works in the specified sequence in accordance with the approved programme. 1.1.10 Equipment and Materials Approval 1 Approval of materials and equipment shall be based on latest manufacturer's published data. 2 Complete and detailed information of all materials and equipment to be incorporated in the work shall be submitted. Submit detailed description and specifications, catalogues cuts, installation data, diagrams, dimensions, controls and any other data required to demonstrate compliance with the Contract Documents. Each item submitted shall be referenced to the applicable paragraph in the Specification. 3 At the request of the Engineer, submit a sample of any equipment or material for further study before approval. Where samples are required by the Engineer, the period required to obtain the sample will be taken into account when scheduling approvals. 4 Only approved materials shall be employed at the site. All materials installed which are not approved shall be removed and reinstated by approved ones. 5 Time periods for equipment and materials approvals shall be as outlined in Section 9, Part 1, Clause 1.1.4. 1.1.11 Fire and Safety Precautions 1 Establish from Architectural Drawings where fire and smoke barriers exist, and make adequate provision of fire and smoke barriers in and around trunking, conduits, cables, etc., where they pass through floors and fire rated walls, and where protection systems are installed pack space between wiring and sleeve full with Fire Retardant Material and seal with caulking. 2 The Contractor shall ensure that this work is carried out such that the integrity of any such fire barrier is properly maintained where pierced by electrical services. 3 For each switchboard the Contractor shall supply the following equipment: (a) (b) (c) 4 1 no. electrical grade rubber mat to BS 921 1000 mm wide extending the full length of the switchboard 1 no. pair of electrical grade rubber gloves to BS 697. The hand glove should have the date of test stamped on it. 1 no. notice in English and Arabic advising treatment for a person suffering from electrical shock. The contractor shall put the notice for electrical shock treatment in details with sketches and instructions as per standard procedures. The notice shall comply with the requirement of the QGEWC in content and format. However, this should include the following as a minimum, QCS 2010 Qatar Project Management 2 QCS 2010 Section 21 Part 1 General Provisions for Electrical Installation Page 7 ACT IMMEDIATELY (i) Safeguard Yourself (ii) Switch off current or break electric circuit (iii) Use or stand on some dry non-conducting material to remove the CASUALTY from cable or source of electricity. (iv) Start artificial respiration and call for Medical Aid TREATMENT FOR ELECTRIC SHOCK ARTIFICIAL RESPIRATION (KISS OF LIFE, MOUTH TO MOUTH METHOD) Lay the casualty on back and if possible on a table (vi) Kneel or stand near to the casualty’s head (vii) Remove any obstruction from the mouth (viii) Support the nape of the neck and press top of the head so that it is tilted backwards (ix) Open your mouth and take a deep breath, pinch the casualty’s nostrils with your fingers. Seal your lips round his mouth and blow into his lungs until the chest rises. (x) Remove your mouth and watch the chest falls (xi) Repeat and continue inflation at your natural rate of breathing. Continue to give artificial respiration until natural breathing is restored or until the medical aid arrives (xii) When the casualty is breathing, place in recovery position, lying and resting on the side. Remain with and watch casualty closely. 1.1.12 Protection 1 The Contractor shall be responsible for his work and equipment until finally inspected, tested, accepted and handed over. Materials and equipment which are not immediately installed after delivery to site shall be stored carefully. Close open ends of work with temporary covers or plugs during construction to prevent entry of obstructing material. 2 Protect work and material of other trades from damage that might be caused by his work or workmen and make good damage thus caused. 3 Protect exposed live equipment during construction for personnel safety. 4 Shield and mark live parts "LIVE 240 VOLTS" or with appropriate voltage in English and Arabic. 5 Arrange for installation of temporary doors for room containing electrical distribution equipment. Keep these doors locked except when under direct supervision of an electrician. 1.1.13 Quality of Staff/Personnel 1 The electrical services installation shall be carried out in a professional manner by experienced and qualified personnel. 2 Electrical contractor shall be to the classifications required by QGEWC and shall carry a valid licence. 3 Prior to the commencement of works the Contractor shall notify the Engineer of his intended site staffing levels. QCS 2010 Qatar Project Management (v) QCS 2010 Section 21 Part 1 General Provisions for Electrical Installation Page 8 The Contractor shall appoint one graduate Electrical Engineer full time with 5 years experience in similar works and qualified staff/personnel for the supervision of the Electrical Installation Works. 5 The name, qualifications and experience of the nominated engineers shall be submitted to the engineer for approval within 15 days of the receipt of the order to commence the works. 6 An Electrical Foreman of 10 years experience in similar projects should be full time available on site for direct follow up and implementation of the electrical works. 7 Qualified and Experienced Electricians shall be available on site to carry out the works in accordance with the programme. 8 The Engineer reserves the right to require the Contractor to provide information and documentation as may be necessary to establish the validity of any individual persons proficiency and effect their removal from site should they prove to be unsatisfactory. 1.1.14 Climatic Conditions 1 The climate in Qatar in the summer months is hot and humid and a humidity of 100 % at 30 °C has been recorded. (a) (b) violent sand and dust storms of several hours duration occur and even on comparatively still days, fine dust is carried in suspension in the atmosphere. all apparatus and equipment shall, therefore, be so designed and constructed that they operate satisfactorily and without any deleterious effect for prolonged and continuous periods in the conditions stated above and at the following ambient temperature conditions: (i) maximum sun radiation temperature in summer 84 °C (ii) maximum ambient temperature in summer 52 °C (iii) average max. ambient temperature in summer 45 °C (iv) minimum ambient temperature in winter 0 °C (v) the altitude of Qatar may be taken as sea level. 2 The temperatures quoted above make no allowance for heat generated from equipment itself or from any other equipment in the vicinity 3 The capacity and ratings of all electrical equipment and materials given are, unless otherwise indicated, for Qatar climatic conditions. Provide the basis of the derating factors applied in each case 4 Where specific sizes are indicated e.g. cable sizes, due allowances have been made in the design for the climatic conditions of Qatar and derating has been applied 5 Where no ratings or sizes are indicated for components and other accessories, supply equipment which will give trouble free service in the ambient conditions stated above. 1.1.15 Samples 1 The term „samples’ includes natural materials, fabricated items, equipment, devices, appliances, or parts thereof as specified and other samples as may be required to determine whether kind, quality, construction, workmanship, finish, colour and other characteristics of materials conform to requirements of the Contract Documents. 2 Samples shall establish kind, quality and other required characteristics of various parts of the work. Indicate details of construction, dimensions, capacities, weights and electrical performance characteristic of equipment or material. 3 Samples and sample board should be prepared and identified by the manufacturer and stamped/engraved with make, type, Cat No. and size marking should be indelible and legible. QCS 2010 Qatar Project Management 4 QCS 2010 Section 21 Part 1 General Provisions for Electrical Installation Page 9 Quality of Materials 1 Manufacturers shall provide their standard guarantees for products furnished under this Contract. However, such guarantees shall be in addition to and not in lieu of all other liabilities which manufacturers and the Contractor may have by law or by other provisions of the Contract Documents. 2 All materials, items of equipment and workmanship furnished under this Contract shall carry standard warranty against all defects in materials and workmanship. Any faults due to defective or improper material, equipment, workmanship or Contractor's design which develop shall be made good, forthwith, by and at the expense of the Contractor, including all other damage done to areas, materials and other systems resulting from this failure. 3 Guarantee that all elements of the systems are of sufficient capacity to meet the specified performance requirements as set forth herein or as indicated. 4 Upon receipt of notice from the Engineer, of failure of any part of system or equipment during the period of maintenance, the affected parts shall be replaced. 1.1.17 Equipment Duties and Ratings 1 Power ratings shown for the proposed equipment are in accordance with the best information available to the Engineer and are to be considered as minimum ratings. In the event equipment items proposed by the Contractor should require motors with different power rating than shown, it shall be the Contractor’s responsibility to furnish circuit breaker, starting equipment, feeder and branch circuits, conduits, and accessories etc. as required to comply with the electrical code and prevent excessive voltage drop without added cost to the Client. 2 Where equipment to be furnished is installed in an existing enclosure or adjacent to existing equipment, the Contractor shall field check the dimensions of existing equipment, location of conduits, etc., and shall familiarise himself with all existing conditions and difficulties to be encountered in performing such work. 3 Degree of protection for all electrical equipment shall be as follows: IP 54, for indoor equipment IP 55, for outdoor equipment IP 68, for submersible equipment 4 All external equipment to be of metallic construction. 5 The equipment shall be located generally as indicated on the drawings and the contractor shall ensure that the equipment is suitably constructed to permit installation as shown. The equipment shall where necessary be constructed in modular form to permit access into the buildings and facilitate ease of erection at site. 6 The equipment arrangements and single line diagram are for guidance only and show a practical arrangement that would be acceptable. The contractor may propose an alternative arrangement which meets the requirements of the specification. 7 All equipment performing similar duties shall be of a single type and make and be fully interchangeable in order to limit the stock of spare parts required. This is to apply particularly to such items as motors, switchgear, instruments, controls, relays, etc. 1.1.18 Workmanship 1 The entire work provided in this specification shall be constructed and finished in every respect in a workmanlike and substantial manner. The Contractor shall provide the system in accordance with the best trade practice and to the satisfaction of the Engineer. QCS 2010 Qatar Project Management 1.1.16 QCS 2010 Section 21 Part 1 General Provisions for Electrical Installation Page 10 Keep others fully informed as to the shape, size and position of all openings required for apparatus and give full information sufficiently in advance of the work so that all openings may be built in advance. Provide and install all sleeves, supports, etc., hereinafter specified or required. 3 Obtain detailed information from the manufacturers of apparatus as to the proper method of installing and connecting same. Obtain all information from others which may be necessary to facilitate work and the completion of the whole Project. 4 Provide the services of an experienced foreman, who shall be continuously in charge of the erection of the electrical work, together with all necessary skilled workmen, helpers and labourers, required to properly unload, transfer, erect and connect up, adjust, start, operate and test the system. 5 Before installing any work, verify that it does not interfere with clearance required for other work. Notice of adverse conditions shall be forwarded in writing to the Engineer before any work in question is installed. If notification is not made, and work installed causes interference with the contemplated design, make such changes in his work as directed by the Engineer to permit the installation of all work of the Project, at no additional cost to the Client. 6 Raceways shall be run as straight and direct as possible in general forming right angles with or parallel with walls or piping and neatly spaced, with risers erected plumb and true, maintain a clearance of at least 25 mm between finished coverings and adjoining work. Approved ceiling height shall be obtained from Architectural Drawings. 7 All equipment and accessories shall operate without objectionable noise or vibration. Should operation of any of the equipment or systems produce noise or vibration which is, in the opinion of the Engineer objectionable, make change in equipment and do all work necessary to eliminate the objectionable noise or vibration at no additional cost to the Client. 8 Wherever possible services shall not cross expansion joints. Where this is unavoidable the services shall accommodate the design movement without damage, by use of approved expansion couplings/flexible conduit arrangement. 9 All MV, HV and EHV works shall be carried out by a contractor or sub-contractor pre-qualified and approved by QGEWC. Proof of such approval shall be required in writing prior to the works commencing on site and the name of any sub–contractor to be used shall be entered in the relevant form of tender when the tender is submitted. All cable jointers to be used on the Contract shall be required to undertake and pass a trade test conducted by QGEWC at the Contractor’s expense. 1.1.19 Labels/Circuit Lists/Cable Identification 1 For substations, switchgears, switchboards, motor control centres and panel boards: (a) 2 For Distribution Boards and Circuit Breakers: (a) (b) 3 engraved lamacoid name plates, black with minimum 6 mm high white lettering. where individually enclosed or in substations, switchgears, switchboards, motor control centres and panel boards without doors : engraved lamacoid nameplates, black with 3 mm high white lettering. in panel boards with doors : directories mounted inside transparent plastic covers in metal frames. Wiring Identification: (a) (b) (c) identify wiring with permanent indelible, identifying markings, either numbered or coloured, heat shrinkable tube or ferrules, on both ends of phase conductors of feeders and branch circuit wiring. maintain phase sequence and colour coding throughout colour code to standards above as specified elsewhere QCS 2010 Qatar Project Management 2 QCS 2010 (d) 4 (c) (d) colour code conduits and metallic sheathed cables code with plastic sleeve or paint end points where conduit or cable enters wall, ceiling or floor and also at 15 m intervals along its length. colours to be 25 mm wide prime colour and 20 mm wide auxiliary colour to standards above number code, per Circuit Schedule, all feeder and branch circuit cables at both connection points and in manholes, handholes, pull-boxes and junction boxes with fibre or non-ferrous metal tags, fastened with non-ferrous wire. for Device Plates of local toggle switches, toggle switch type motor starters, pilot lights and the like, whose junction is not readily apparent : plates to be engraved with 3 mm high letters describing equipment controlled or indicated. phase identification letters shall be stamped into the metal of the busbars of each phase of the main buses in each substation, switchgear, switchboards, motor control centre and panel board in addition to colour identification Letters shall be visible without disassembling current carrying supporting elements. busbars shall be sleeved for phase identification by using high temperature grade heat shrinkable coloured PVC sleeving throughout its length. In no circumstances will any kind of wrapping tape be accepted on busbars. For Doors: (a) where switchboard rooms, cable chambers, metal screened spaces and the like contain electric power cables, bus bars or equipment operating at voltages exceeding 600 V : enamelled sheet metal, red on white, reading "Danger - High Voltage". For Rooms: (a) 9 use colour coded wires in communication cables, matched throughout system. to switchboard rooms, electric closets, metal screened spaces assigned to electrical equipment, and the like : enamelled sheet metal, red on white, reading "Electrical Equipment Room - No Storage Permitted". Languages: (a) nameplates with directional, operational or warning labels shall be in Arabic and English. 1.1.20 Segregation of Services 1 Electrical services shall be segregated as specified throughout the installation to obviate the following; (a) (b) (c) (d) (e) (f) electrical interference from one circuit to another a fault on one circuit affecting another unnecessary fire damage difficulties in circuit identification voltage limits for general safety difficulties in removal and/or maintenance. 2 All raceways shall be kept clear of other services except where intentionally earthed or bonded. Generally, raceways shall be kept 150 mm away from and above hot water and 75 mm away from other services. 3 Unless specifically indicated otherwise, normal, emergency, low voltage cables and wiring shall be segregated throughout the installation generally in the following manner: QCS 2010 Qatar Project Management (b) (c) 8 Page 11 For Busbars: (a) 7 General Provisions for Electrical Installation Device Plates: (a) 6 Part 1 Conduit and Cable Identification: (a) (b) 5 Section 21 QCS 2010 (a) (b) 4 Section 21 Part 1 General Provisions for Electrical Installation Page 12 armoured and sheathed cables: Where more than one tray has been specified or is necessary to accommodate the number of cables on a run, where practical, segregation shall be achieved by dedicating each tray to either normal or emergency services. Where normal and emergency cables have to run together in trays, ducts or trenches, they shall be formed in two groups, one normal and one emergency insulated conductors: Insulated conductor circuits shall, where possible, be segregated throughout by enclosing in separate conduits, trunking or trunking compartments. Fire Alarms: (a) fire alarm cables shall be segregated from other services throughout and be either armoured and sheathed cable, or insulated conductors enclosed in conduit or trunking, as indicated on the drawings. Electricity Supply 1 The Supply Authority will make available, at the incoming terminals of each Main Switchboard (Medium Voltage Panel) a 3 phase + Neutral, 4 wire, 415 V, 50 Hz supply of adequate capacity and having the following tolerances: (a) (b) voltage frequency 6% ± 0.1 Hz (short term ± 0.15 Hz for a duration of only a few seconds) 2 Phase rotation of supply to BS 158. 3 Neutral: Solidly earthed at transformer location 4 Earthing system: TNS 5 Obtain fault level and fault duration time from the Supply Authority (QGEWC). 6 Obtain confirmation from the Supply Authority of the size and number of cables they will provide to Main Switchboards. Allow for adequate and appropriate cable glands, lugs and boxes. 7 After inspection and approval of the contractor’s installation, QGEWC will permit energisation of the feeder cables to the installation. 8 QGEWC will only inspect the contractor's installation and permit energisation of the power supply after receiving a written request to do so from the contractor. 9 The contractor will be responsible for any delay caused by omission to make the request in good time. 10 The contractor shall provide a generator of adequate capacity to carry out all precommissioning tests. Per-commissioning tests may be carried out using mains electricity if this is available. 1.1.22 Polarity 1 The polarity of all apparatus used for the Works specified shall be arranged as follows when apparatus is viewed from the front: (a) (b) for two pole apparatus the phase or “live” pole at the top (or left hand side) and the '“neutral or earthed” pole at the bottom (or right hand side). On plug and socket outlets the polarity shall conform to BS 196, BS 546, or BS 1363 as appropriate for three or four pole apparatus the phases in order red, yellow, blue and neutral reading from top to bottom or left to right in the case of vertical and horizontal layouts respectively. QCS 2010 Qatar Project Management 1.1.21 QCS 2010 Section 21 Part 1 General Provisions for Electrical Installation Page 13 2 All cables shall be so connected between main switchboards, distribution boards, plant and accessories so that the correct sequence of phase colours is preserved throughout the system. 3 All cable cores shall be identified with phase colours. Where more than one phase is incorporated on a common system in one room then the live cores shall be red, yellow, blue, as appropriate, and fittings and switch accessories shall be permanently labelled and segregated in accordance with I.E.E. Regulations. 1.1.23 Safety Interlocks 1 A complete system of interlocks and safety devices shall be provided as necessary for the safe and continuous operation of the plant in order to provide for the following: safety of personnel engaged on operation and maintenance of the plant correct sequence of operation of the plant during start up and shut down safety of the plant when operating under normal or emergency conditions. 2 Interlocks shall be preventive and not corrective 3 The Contractor shall be responsible for the preparation of interlocking schemes for the approval of the Engineer. 4 Locks for interlocking purposes shall be of the figure lock type. 5 No spare or master key shall be provided, unless specified. 6 Device items are to be arranged to ensure that there is no danger of interchange with existing locks on other units. 1.1.24 Spare Parts 1 General: (a) (b) (c) 2 Main Low Tension Boards: (a) (b) (c) (d) 3 2 % spare moulded case circuit breakers of all different frame sizes, but in any case not less than 2 nos. circuit breaker of each size 5 % spare indicating lamps for each indicating lamp in the switchgear one set of tools required for switchgear maintenance provide complete spare parts as recommended by the manufacturer for different sizes of ACB. Switchboards, Motor Control Centres and Distribution Boards: (a) (b) (c) (d) (e) 4 provide sufficient spare parts for all the electrical items included within the scope of works. Submit to the Engineer a list of all spare parts to be required for a further two years operation from the date of issue of the Maintenance Certificate spare parts required include but not necessarily limited to those listed below, provided specified in the Project Documentation or where quantities for each item or equipment is recommended by the manufacturer spare parts to be delivered to central stores. 5 % spare combination magnetic motor starters 5 % spare circuit breakers for each rating of each MCCB 5 % spare HRC fuses for each rating 5 % spare of load break switch (isolators) of each size 5 % spare of current operated ELCB of each size Disconnecting Switches: (a) 5 % spare switch of each size. QCS 2010 Qatar Project Management (a) (b) (c) QCS 2010 5 (b) (c) (d) General Provisions for Electrical Installation Page 14 plug fuses - furnish ten percent (10%) of the number of each size and type of fuses installed, but in any case not less than six fuses of each sizes wall switches - provide five percent (5%) of the number of each size and type of wall switch installed socket outlets - provide five percent (5%) of the number of each size and type installed lamps - provide five percent (5%) lamps of each size and type for indicating panels and pilot lights installed for different systems. Lighting Fixtures: (a) for lighting fixtures provide the following spare parts: (i) 2 % of the total quantity of each type of lighting fixture. This quantity shall not be less than one fixture of each type (ii) additional diffusers for 5 % of the total quantity of each type of lighting fixture provided with acrylic, plastic or glass enclosures. Diffusers shall be identical to those of the installed fixtures. This quantity shall not be less than two diffusers of each type (iii) 10 % spare lamps of each wattage of different type (iv) 5 % of the total quantity of controlgear (ballast) of each type and size but in no case less than (6) ballast of each size and type. Emergency Generating Sets: (a) complete itemised list of different spares to be included and priced by the tenderers. For emergency generator, furnish by the generator supplier to maintain it for two years. 8 The tenderer shall submit with his offer detail prices of the spare parts he is required to provide under the Contract indicating the quantity and the unit rate of each item. 1.1.25 Protection of Excavation 1 The Contractor shall comply with all requirements of the Police Department for marking, lighting and protecting excavations. It is the responsibility of the Contractor to ascertain the requirements of Police Department and to comply fully with these requirements. No additional payments will be authorised under any circumstances for marking, lighting or protecting excavations. 2 Where carriageway works and road crossings are performed the Contractor shall provide steel plates of sufficient size and quality to permit the safe passage of traffic and the plate shall be so placed (if necessary fixed) to permit reasonable traffic flow. 3 All doorways, gates and entrances shall be kept clear with full access. Where excavations impede pedestrian access, crossings boards shall be provided. Crossing boards shall be 1250mm wide with a hand rail on both sides 1 metre high and guard rails on both sides at vehicular access to premises etc. Ducts will not be installed at entrances to premises unless instructed by the Engineer. 4 Materials excavated shall be placed so as to prevent nuisance or damage. Where this is not possible, the material shall be removed from site and returned for backfilling on completion of cable laying at the Contractor’s expense. In cases where the excavated material is not to be used for backfilling trenches it must be removed from site on the same day as it is excavated. Surplus material shall only be disposed of at Government approved sites. At the time of Contract award the Contractor shall contact the Ministry of Municipal Affairs and Agriculture to ascertain the approved sites and route. 1.1.26 Supply of materials 1 Where materials are to be supplied by the Contractor, the following shall apply: (a) Materials shall be ordered in accordance with the Specifications issued by QGEWC. QCS 2010 Qatar Project Management 7 Part 1 Circuit Accessories: (a) 6 Section 21 QCS 2010 (b) (c) Section 21 Part 1 General Provisions for Electrical Installation Page 15 Specifications and details of the proposed supplier shall be submitted to QGEWC before a firm order being placed. On delivery of materials from outside of Qatar, QGEWC inspectors shall be given the opportunity to inspect the materials prior to their use. Special Requirements 1 The Contractor shall consult the public utility authorities not less than one month before it is proposed to commence work to ascertain whether any underground installations will be affected by the proposed work, in which event the Contractor shall make all necessary arrangements with the public utility authorities to safeguard the installation. 2 The Contractor shall give at least one week’s notice in writing to the public utility authorities of the dates upon which it is intended to operate plant or equipment or carry out any work for which permission has been given in writing by the public utility authorities: such operations of work shall only be carried out in the presence of the public utility authorities unless notice has been obtained in writing from the public utility authorities that they do not require to be present. 3 The public utility authorities may require work to be executed on their installation during the period of the Contract: the Contractor shall afford all facilities to the public utility authorities’ contractors or workmen until their diversion work is complete. The Contractor shall co ordinate the work of the public utility authorities and his own activities and when necessary shall amend his programme of working to suit all requirements of the department in connection with their diversion work and shall keep the Engineer informed of all arrangements made. 4 The Contractor shall locate and mark with suitable posts all the public utility authorities underground installations that are within the area of the Works and shall ensure that such markers are maintained in their correct positions at all times; the Contractor shall advise the public utility authorities of any installation not found where shown on the Drawings, or found but not shown or found damaged or subsequently damaged. END OF PART QCS 2010 Qatar Project Management 1.1.27 QCS 2010 Section 21 Part 2 MV Factory Built Assemblies (FBA’s) Page 1 2. MV FACTORY BUILT ASSEMBLIES (FBA’S)................................................2 2.1 GENERAL .......................................................................................................2 2.1.1 2.1.2 2.1.3 2.1.4 2.1.5 Scope General Reference References Submissions Quality Assurance 2.2 PRODUCTS ....................................................................................................4 2.2.1 2.2.2 2.2.3 2.2.4 Cubicle Switchboards Motor Control Centres MCCB Panel Boards Distribution Boards 2.3 INSTALLATION ............................................................................................21 2.3.1 2.3.2 General Earth Bonding 4 17 19 20 21 21 Qatar Project Management QCS 2010 2 2 2 3 3 QCS 2010 Section 21 Part 2 MV Factory Built Assemblies (FBA’s) Page 2 2. MV FACTORY BUILT ASSEMBLIES (FBA’S) 2.1 GENERAL 2.1.1 Scope 1 This Part shall include all labour, materials and accessories for the complete performance of all MV Cubicle Switchboards, Main Switchboards, Submain Switchboards, Motor Control Centres, MCCB panel boards, distribution boards in accordance with the Specifications and Drawings. 2 Related Parts and Sections are as follows: General Provisions for Electrical Installation Cables and Small Wiring Conduits Trunking Cable Trays Power factor correction capacitors 3 Factory built assemblies of switchgear and control gear (MCCs) shall be suitable for operation under the ambient and service conditions specified. They shall comply with all local regulations and requirements. The contractor shall be responsible for making himself aware of any special conditions which apply to the installation. 4 The Contractor shall be responsible for ensuring that all details relating to the construction and protection systems are fully compliant with the latest requirements of QGEWC and construction shall not commence until QGEWC approval has been obtained. The Contractor shall provided all protection relays, interlocks and devices deemed necessary by QGEWC. 2.1.2 General Reference 1 The work of this Part is integral with the whole of the Project Documentation and is not intended to be interpreted outside that context. 2 Co-ordinate the work with all other services affecting the work of this Part. 2.1.3 References 1 The following standards are referred to in this Section: BS 37 Pt. 1 .............................................. Electricity meters general BS 89, IEC 51 .......................................... Direct acting indicating electrical measuring instruments BS 142 ..................................................... Electrical protective relays BS 4794, Pt. 2 IEC 337-2 ........................ Control devices BS 5685, IEC 521 .................................... Electric meters BS 6231 ................................................... PVC insulated cables for switchgear BS 7626, IEC 185 .................................... Current transformers BS EN 60073 ............................................ Basic and safety principles for man-machine interface, marking and identification coding principles for indicators and actuators BS 88, BS EN 60127 ............................... Cartridge fuses BS 159, BS EN 60439-2 .......................... Busbar and connection BS EN 60439, IEC 439 ............................ Factory built assemblies LV BS EN 60947-4 IEC-1 & 1A ..................... Contactors BS EN 60529, IEC 529 ............................ Degree of protection of enclosures BS EN 60947-3, IEC 408 ......................... Air break switches BS 4752, IEC 157-1, BS EN 60439 ......... Switchgear and control-gear QCS 2010 Qatar Project Management This Section Part 1 Part 6 Part 7 Part 8 Part 9 Part 16 QCS 2010 Section 21 Part 2 MV Factory Built Assemblies (FBA’s) Page 3 BS 5472, BS EN 60439 ........................... Low voltage switchgear and control-gear BS 7354, BS EN 60439, BS EN 6094 ...... Electrical power switchgear 2.1.4 Submissions 1 Shop Drawings: All submittals in accordance with Part 1: (a) Product Data: (a) (b) (c) full specifications of the enclosures and the components of the switchgear, switchboards and motor control centres, with relevant sheets of manufacturer’s catalogues type test certificates of all components fully type tested and whole assembled MCCs from an internationally recognised testing authority or from independent testing lab in accordance with IEC 439 confirmation that the switchgears, switchboards and motor control centres comply with the relevant specification as mentioned in this Section. 2.1.5 Quality Assurance 1 The switchgear manufacturer must have a previous record of satisfactory service in Qatar for at least 3 years. 2 All new and refurbished Motor Control Centres shall be subject to routine tests to detect faults and workmanship in accordance with BSEN 60439-1 clause 8.3.1. Standard assemblies and/or products used within the assembly shall also be subject to tests at the manufacture’s works who supplied the products. Routine tests shall include: (a) (b) (c) (d) (e) the effectiveness of mechanical actuating elements, interlock, locks etc. shall be checked. The conductors and cables shall be checked for proper laying and the devices for proper mounting. A visual inspection is also necessary to ensure that the prescribed degree of protection, creepage and clearances are maintained. all termination types and connections especially screwed connections shall be checked for adequate contact. factory built assemblies such as motor control centres for pumping stations and treatment plants, unit mounted stand alone control panels etc. shall be inspected thoroughly and tested at the manufacturer's works to verify the electrical operation in accordance with the control philosophy by simulating the site conditions. the manufacturer shall submit the process flow diagram together with cause and effects for the assemblies involving complex control schemes and complicated interlock, sequence controls, etc. the tests so conducted on the assembly at manufacturer's works shall be repeated as integrated tests on site with all field devices and interfaces present. QCS 2010 Qatar Project Management 2 submit dimensional drawings of all the switchgears, switchboards and motor control centres, including sections and elevations, showing the following: (i) arrangement of all components, instruments, indication and dimensions of all busbars (ii) positions and method of fixing cables and boxes (iii) location of terminal blocks (iv) single line diagram of the circuits showing the rating of all components, the type and size of the incoming and outgoing feeders (v) schematic and elementary wiring diagrams, for each control unit, showing numbered terminal points, numbered wires and numbered interconnections to other equipment and remote devices (vi) connection wiring diagrams, for each control unit, showing numbered terminal points, numbered wires and numbered interconnections to other equipment and remote devices (vii) complete catalogue information for all components (viii) a complete list of parts, with prices, that would be necessary to maintain and/or modify the equipment (ix) other relevant data. QCS 2010 Section 21 (f) (g) (h) (i) (j) PRODUCTS 2.2.1 Cubicle Switchboards 1 General: (b) (c) (d) (e) (f) (g) (h) (i) Page 4 the manufacturer shall submit in advance, the testing procedure to the Engineer for approval prior to conducting the tests. Motor Control Centres shall be subjected to dielectric tests as described in BSEN 60439-1 clause 8.3.2. All electrical components of the assembly shall be connected for the test, excluding those designed for lower test voltage and currents e.g. measuring instruments. anti-interference capacitors installed between the live and exposed conductive parts shall be capable of withstanding the test voltage without being disconnected from the circuit. the protective measures with regard to protection against direct and indirect contact shall be checked as per BSEN 60439-1 clause 8.3.3 Motor Control Centres shall be Totally Type Tested to BSEN 60439-1 clause 8.2. ASTA/KEMA type test certificate together with test report including reports/terms under (k) shall be submitted to the Engineer for approval. following is a list of verifications and tests to be performed on a Totally Type Tested Assembly according to Table 7 clause 8.2 of BSEN 60439-1. A test report shall be submitted to the Engineer (i) temperature rise limits (ii) dielectric properties (iii) short circuit withstand strength (iv) effectiveness of protective circuit effective connection between the exposed conductive parts of the assembly and the protective circuits. short circuit withstand strength of the protective circuit (v) clearances and creepage distances (vi) mechanical operation (vii) degree of protection 2.2 (a) MV Factory Built Assemblies (FBA’s) M.V. cubicle switchboards shall be of indoor construction, purpose made, floor standing, totally enclosed, cellular cubicle type, dust protected, vermin proof and of clean and modern appearance containing the main components shown on the Drawings and/or specified the switchboards shall be fabricated, assembled, wired, checked, tested and co-ordinated at the factory by one manufacturer using the same make for all internal switchgear components and shall be constructed in accordance with BS EN 60439 or IEC 439 the switchboard shall be equipped with Air Circuit Breakers, moulded case circuit breakers, relays, instruments, transformers, ancillary devices necessary for operation protection or measurement purposes and Auto Transfer Switch with Manual by pass arrangement as indicated on the Drawings the normal components, fittings and accessories required for safe and proper operation of switchgear shall be provided, whether specifically mentioned herein or not to withstand thermal and mechanical stresses set up by short circuit conditions in accordance with the fault through current of the feeding transformer. In general fault breaking capacities for main switchboards shall be as stipulated in QGEWC regulations minimum 44KA for 3 Seconds. spare ways indicated on the Single Line Diagram shall be fully equipped all FBA’s should have a manufacturers name plate indicating busbar rating, fault current, year of manufacture, serial no., etc. the MCCs shall be designed, manufactured and tested to IP54 in compliance with the requirements of IEC 60529. equipment such as Variable Frequency Drives (VFD), UPS and others with large watt loss, if specifically mentioned in the particular requirements to be included in the MCC, that require forced ventilation by employing external fan and louvers as recommended QCS 2010 Qatar Project Management (k) Part 2 QCS 2010 Section 21 (j) (k) (n) (o) (p) (q) (r) (s) (t) (u) (v) (w) (x) MV Factory Built Assemblies (FBA’s) Page 5 by the manufacturer, the degree of protection (IP rating) shall be reduced to IP43 from IP54. the MCCs shall be designed and type tested to withstand a fault current of 44 kA for 3 seconds symmetrical. Additionally the MCCs shall be type tested for safe containment of an internal arcing fault, which will check the capability of the steel structure to withstand the forces associated with the arc, and ensure safety and integrity of the assembly for continuous use. This is to establish that the enclosure of MCCs together with internal partitions and/or barriers withstands the pressure and temperature arising from internal arcing with short circuit current and thus provides protection for persons in front of or within the close proximity of the MCCs in the event of internal arcing. the test certificate must show that the neutral bar has been tested with the full fault current and for the full time specified. separate test certificates for incoming sections will be acceptable. the MCCs shall be designed and equipped with properly sized circuit breakers and/or fused disconnect switches, having a minimum factor of safety of capacity 1.5 taking into account the connected load and its diversity, with provision for selective shortcircuit co-ordination so that faults are cleared without disturbing other circuits. the MCCs shall be designed for indoor installation except where specified for outdoor installation. the MCCs shall be designed to operate satisfactorily in an ambient air temperature of +50° C and RH exceeding 90%. unless otherwise specified temperature up to +70° C and RH up to 100% shall apply during transport, storage and installation. Equipment subjected to these extreme service conditions without being operated shall not suffer irreversible damage when operated under normal specified conditions. the altitude of the site installation shall not exceed 100 meters. the MCCs shall normally be located indoors in service conditions as specified above. However some parts of the MCCs such as sensors, field instruments and pilot devices may require installation in highly corrosive gaseous environments. Gases such as hydrogen sulfide and methane may adversely affect the functions of the components and devices. In such application environments, special measure shall be adopted to prevent corrosion and the subsequent rise in resistance leading to temporary or permanent interruption in control or power circuits. the temperature rise in MCCs shall not be allowed to damage the components, connectors, wires, terminals etc. With the equipment in normal service condition, no live part shall become subjected to high temperature causing overheating that increases the risk of internal arcing accidents. extreme care shall be taken while designing the MCCs to ensure external surface temperature is maintained within the specified limits. the clearances and creepage distances in the MCCs shall be based on rated impulse withstand voltage in accordance with BS EN 60439-1 to ensure that the equipment designed is capable of withstanding the specified voltage without failure under specified test conditions. the equipped MCC must confirm to the clearance and creepage distances and withstand voltages explicitly by taking into account the specified service conditions. the maximum height of assemblies shall be 2400 mm above the finished floor level. site consideration including safety and maintenance shall be taken into account in the design of assemblies. These considerations shall include: (i) clear floor space of at least 900 mm shall be provided in front of the MCC from the free edge of the doors in the open position. Clear floor space of 900mm shall be provided behind the MCC when the doors are in the open position if the MCC is less than 4000mm long. If the MCC is 4000mm or longer the space provided shall be 1200mm. The clear floor space behind the MCC is not required when a true front access assembly is provided. (ii) in order to provide an unobstructed exit route a clear path of not less than 900 mm shall be provided at each end of the MCC. (iii) provision of sufficient space to allow for doors to open fully without fouling other items of equipment or other open doors. (iv) limiting the size and weight of assembly sections to those imposed by transportation, site access and permitted levels of site floor loading. QCS 2010 Qatar Project Management (l) (m) Part 2 QCS 2010 Section 21 (v) 2 Part 2 MV Factory Built Assemblies (FBA’s) Page 6 clear floor space of at least 1000 mm shall be provided from the sides of all MCCs in order to allow possible future extension. Construction: (a) (b) (c) (e) (f) (g) (h) (i) (j) (k) (l) (m) (n) (o) QCS 2010 Qatar Project Management (d) unless specified otherwise in the Project Documentation, main switchboards for general purpose indoor uses shall be constructed to comply with the requirements of BS EN 60439-1 (IEC 439) Form 4 Type 3 or Type 7 and conform with GAMBICA. switchboard shall be factory built, totally enclosed, and have provision for rear access. Size, rating arrangements shall be as indicated on the Drawings the switchboard shall consist of standard cubicles assembled together on continuous base channels to form a rigid in line flush fronted free standing continuous switchboard assembly. For small installations where particularly specified, true front access MCCs must be provided. For all other cases front and rear access MCCs must be provided. MCCs shall be constructed such that doors and covers are flush with one another and aligned to a common vertical plane; manufactured out of mild steel coated with Alu Zinc having the following thickness: Plinth/bed frame - 3.00 mm Frames - 2.00 mm Covers and Doors - 2.00 mm Mounting plate - 3.00 mm Gland Plate - 3.00 mm a separate cubicle section shall be provided for the main incoming circuit breaker and cable glands shall be provided for the incoming cables in accordance with the QGEWC regulations. each cubicle shall be divided into segregated busbar section and circuit section. The circuit section shall be further divided into segregated compartments for housing main and emergency circuit breakers and other devices. Access to internal components of any compartment must be feasible by isolating its particular switch. The hinged door shall be mechanically interlocked with the switch in such a manner that the door can be opened only in the „OFF’ position the switchboards shall be totally enclosed, all hinged doors, covers shall be gasketed to provide protection against dust cabinet shall have adequate means of lifting and shall be capable of being rolled or moved into the installation position and bolted directly to the floor the switchboards shall be provided with suitable cable glands to suit the type, size and number of cables as indicated on the Drawings. The cable glands or bracket where required shall be adequately mounted inside the switchboard. The switchboards shall be provided with the proper cable fixing clamps and terminal lugs for incoming and outgoing cables as well as earth bonding connections after fabrication, steel work shall be cleaned, zinc sprayed and stove enamelled with one prime coat, two under-coats and one finishing coat, the surface being rubbed down after each coat the finish of all parts shall be entirely suitable for the climatic conditions on site. the equipment shall be finished with at least two coats of undercoat and two coats of high grade acrylic stove enamel or approved equivalent. Cubicle interiors shall be completely painted white, however this is not essential for the rear of the door. The height of the switch board shall be limited to 2200mm unless specifically required to meet the site constraints and approved in writing by the Engineer. any damage caused to the finish during transportation and erection shall be returned to the manufacturer for repair if it cannot be perfectly repaired on site. The structure shall be protected from rust and oxidization. The paint shall be applied to rust and grease free surface of metal. The steel shall be electro – zinc plated (ZINTEC) and must have a minimum of priming coat, undercoat and finishing coat. The undercoat and finishing coat shall be stove enamelled. The exterior shall be green to BS 4800, shade 14E53. The switchboard degree of protection shall be IP 42 to BS EN 60529. all plastic parts used within the assembly shall be of flame-retardant, self extinguishing type and halogen free. MCCs shall have internal separation by means of metallic or non-metallic partitions or barriers. QCS 2010 Section 21 (p) (q) (r) (s) (t) (v) (w) (x) (y) (z) (aa) (bb) (cc) (dd) (ee) (ff) (gg) (hh) (ii) MV Factory Built Assemblies (FBA’s) Page 7 all internal components within the compartment /cubicle shall be provided with the degree of protections to IP 2X as minimum whereas the degree of Protection to IP4X shall be provided to adjacent functional units preventing contact with live parts. electrical continuity between the exposed conductive parts of MCCs and protective circuits of the installation shall be ensured to provide protection against indirect contact by using protective circuits. the protective circuits throughout the installation shall be so designed that it is impossible to break the protective path with the removal of any component from the MCC. all outgoing circuit’s protective conductors shall have a separate terminal of adequate size duly identified in accordance with the Identification Section explained elsewhere in QCS. MCCs must be designed by giving highest importance to accessibility especially when in service/fully powered, allowing easy viewing for inspection and operation, replacement of fuses and extension of additional functional units etc. floor mounted assembles shall either be provided with an integral plinth or a separate rolled mild steel channel bed frame, at least 50 mm high. Fixing shall be by not less than four holding down bolts per assembly section, located around the periphery of the section. The fixing shall not be visible from outside the section, but shall be readily accessible from within. fixings for wall and pole mounted enclosures shall be provided outside the enclosure. The back of the enclosure shall not be drilled to accept fixings. the type of cubicle construction shall be multi-compartment type unless specified otherwise. compartments containing switchfuses, starters, control sections, distribution boards, busbars, downdroppers and similar equipment shall be fully segregated. There shall be no aperture large enough to admit a 1mm diameter wire between any two adjacent compartments. Each cubicle/compartment shall have its own door. interconnecting cables between adjacent compartments shall not proceed directly from one to the other but shall pass through a vertical wall into a cabling compartment before re-entering. Holes for interconnecting cables shall be of the minimum size necessary. All such holes shall be filled with insulating grommets. all cubicles shall be provided with a means of ensuring that equipment can be adequately isolated for maintenance purposes without interrupting essential loads which may continue to operate whilst maintenance is being undertaken. distribution sections shall be fully insulated to allow safe operation by non-engineering personnel. doors shall be adequately sized to accommodate readily and neatly all mounted equipment, open at least 120 degrees, be rigidly constructed, suitably braced and provided with at least two substantial hinges which shall be captive when the door is closed. Doors shall be provided with stays to prevent over opening. each door shall be provided with non-rusting metalic „T’ type handles at least one of, which shall be lockable. the doors shall be fixed to the frame by substantial single knuckle non-rusting type, or internal concealed type hinges. Hinges shall be on the left hand side of the door. Hinges shall not be welded to either the door or frame. Substantial continuous stainless steel type hinges over the whole height of the door may be considered if the manufacturer can provide evidence of long continuous service of this type of hinge on his product. locking combinations shall be provided as specified. Three keys for each key type shall be provided on individual key rings having a nametag showing identify details. where the need of padlocking facilities is identified by the engineer/employer, the padlocks shall be supplied and fitted. equipment shall not be mounted on covers. Covers shall not weigh more than 30 kg, and any cover over 7.5 kg shall be provided with a means of supporting the lower edge when its securing bolts are being inserted or removed. removable back covers shall be provided. each door shall be provided with an internal welded earthing stud, and shall be bonded to the assembly main earth bar. QCS 2010 Qatar Project Management (u) Part 2 QCS 2010 Section 21 (jj) (kk) (ll) (mm) (oo) (pp) (qq) (rr) (ss) (tt) (uu) (vv) (ww) (xx) (yy) (zz) (aaa) (bbb) (ccc) (ddd) (eee) (fff) MV Factory Built Assemblies (FBA’s) Page 8 every incomer, starter, feeder, etc. shall have an individual terminal/gland box. Control compartments and small power and lighting distribution boards must also have independent gland boxes but these may be common to more than one circuit. terminal/gland boxes may be externally mounted on the rear of the MCC or internal. Terminal/gland boxes shall not inhibit access to or maintenance of any part of the MCC. outgoing main and control cables shall be glanded at the compartment so as to ensure a full earth screen to each compartment and shall also be glanded at plinth level to make the complete MCC vermin-proof. Compartment gland plates shall be a minimum of 300mm above the plinth level gland plate. gasket material used for sealing panel doors and covers and for door mounted instruments shall be of highest quality and should not be subject to deterioration by temperature, UV, hydrogen sulphide and methane. doors and covers giving access to potentially live conductors shall be provided with prominent warning labels, in English and Arabic. doors on outdoor assemblies shall be retained in the open position by the provision of adequately fixed stays. each cubicle/compartment shall be provided with a removable steel components mounting plate located clear of the cubicle rear panel. all components, other than door mounted, shall be located on the component mounting plate by bolting into tapped holes or by using self-tapping screws. Nuts used for securing components shall be captive. rail type fixings may be used where appropriate. Components shall not be mounted on any other surface. no components shall be located within the assembly at a height greater than 2000 mm or less than 500 mm above finished floor level. it shall be possible to replace and maintain any component without first removing other components. bolts and nuts for cover fixing shall be captive and provided with protective washers to prevent damage to paintwork. unless specified otherwise control supplies shall be 110V a.c. derived from a transformer within the control compartment or in a separate compartment, fused on its primary circuit. Neutral shall be earthed with a removable link. Individual compartments shall be fed through a fused tapping next to the main 110v bus adjacent to the transformer. Proper fuse coordination to be achieved to avoid one section fault from affecting the other section. Transformer shall be rated for at least 150% of the maximum loading for long service life. auxiliary supplies such as 24 V AC/DC, 240 V AC etc. are specified in the relevant individual component’s specifications. each compartment shall be provided with a separately fixed compartment heater rated 110 Volts AC. Apart from those in motor starter compartments the heaters shall be controlled by means of individual “OFF/AUTO” switches. Auto operation shall be by means of adjustable panel mounted humidistat covering the range of humidity envisaged. MCCs shall be designed for ready extension at each end. all terminals for outgoing connections shall be located at a low level in the compartment adjacent to the cable gland trays. Adequate space shall be provided the installation and dressing of site cables. It should be noted that site cables are frequently oversized to allow for high ambient temperatures and long cable routes. Direct termination on equipment such as Distribution Board Fuses or Miniature Circuit Breakers (MCB’s) shall not be permitted. all main switches shall be arranged such that a minimum distance of 700mm exists between the glandplate and the bottom of the circuit breaker or terminals, whichever is the less. all live terminals shall be fully shrouded by using high-grade high temperature material. all cable entries shall be affected using brass cable glands to IP rating as specified. all cable glands shall be provided with earth tags. cables shall enter assemblies through detachable steel or aluminum/brass (for single core cables); gland plates fitted at least 200 mm above finished floor level. gland plates shall be rust proofed and provided with a welded and bonded earthing stud, and adequately sized to accommodate present and known future cabling QCS 2010 Qatar Project Management (nn) Part 2 QCS 2010 Section 21 Part 2 MV Factory Built Assemblies (FBA’s) Page 9 3 Labels: (a) (b) (c) (d) (e) (f) provide identification on all equipment e.g. control panels, MCC, controllers, raceways, boxes and conductors, devices etc in accordance with BS 61346, BS 61666, BS 61175 and BS 60445 standards or latest edition of other applicable standards to the approval of the Engineer. all labels shall be permanent, and be machine generated. NO HANDWRITTEN OR NON-PERMANENT LABELS SHALL BE ALLOWED. prior to making any label or nameplate for the purpose of identification, submit a detailed schedule indicating nameplate size, lettering size, color, material and actual nameplate information for the Engineer's review and approval. all external labels, nameplates, operational and warning signs shall be provided in English. material used in making the engraved labels shall be of highest quality suitable for the environmental and climatic conditions as specified in the relevant section. critical devices such as disconnect switches; service feeders and branch circuit protective feeders shall be legibly labeled to indicate its purpose and point of origin. The legibility distance shall not be less than 2.0 meters. QCS 2010 Qatar Project Management requirements. Access to both sides of each gland plate when it is in position shall be possible from within the assembly. Cables shall enter at the top or bottom of assemblies as specified and/or as shown on the relevant drawings where applicable. (ggg) cableways shall be provided to ensure that apart from inter-connections no cable routed to one cubicle shall pass through any other cubicle. 2 (hhh) for cable sizes 300mm and above insulated glands shall be fitted. (iii) provision for accommodation of rising armored cables shall be provided with adequate cable supports and a form of cable entry via approved cable glands secured to a steel glanding plate. (jjj) space shall be provided to accommodate cable glands of appropriate size for incoming and outgoing circuits. All gland plates and trays shall be adequately earthed. (kkk) cable disconnecting links shall be provided where specified and shall be used for maintenance purposes only. The links shall be fitted to the bus bar risers immediately before the cable terminations and shall be easily accessible. The links shall be labeled „ISOLATING LINK’ and the circuit or cable reference shall be quoted. (lll) within each assembly, all metal parts of equipment supplied, other than those forming part of an electric circuit, shall be bonded to the earth bar. Metalwork may be used for this purpose provided that earth continuity conductors are fitted at all joints and other discontinuities and those connections to metal work are made using a welded or bolted stud. (mmm) the following metal parts must be provided with equipotential bonding connected to an earth busbar system by using yellow/green earth cable of at least 6.0 mm square. (i) gland plates (ii) gland covers (iii) side sheets (iv) top barriers (v) intermediate barriers (vi) top covers (vii) end covers (viii) rear Covers (ix) front covers (x) cable Boxes (xi) doors and bolted front covers (xii) horizontal busbar barriers. (nnn) each compartment shall be provided with a smoke detector. In addition to this a heat sensitive cable shall be run throughout the MCC passing through each compartment. Both shall be connected to the fire alarm panel and shall additionally be arranged to open the main supply circuit breaker and inhibit the start up of the standby generator. (mmm) The height of the switch board shall be limited to 2200mm unless specifically required to meet the site constraints.Proposal shall be approved in writing by the Engineer. QCS 2010 Section 21 (g) (h) (i) (j) MV Factory Built Assemblies (FBA’s) Page 10 identification nameplates shall be provided in addition to the manufacturer's equipment nameplates as required by NEMA, BS, IEC or UL. warning signs and instruction labels wherever needed shall be provided in accordance with all applicable local regulations. the contractor shall clearly show locations and fixing arrangements of nameplates and labels on layout drawings. the contractor shall comply with the following requirements for labels: (i) provide equipment identification labels for all electrical equipment including, but not limited to switchgear, control panels, switchboards, transfer switches, disconnect switches, transformers, generators, power factor capacitors, fixed equipment, motor starters, MCCs etc. (ii) provided sub-classification label for all emergency power system, junction boxes and pull boxes. (iii) external labels: Clear Perspex back engraved, in black letters on white backgorund in English with chamfered edges fixed with stainless steel screws with nuts and flat & lock washers. The letters should be filled in white and the rear surface painted black. (iv) internal labels: Multi-layered plastic to an approved design engraved in English, and fixed with stainless steel screws. Alternatively special purpose made DIN rail may be used for fixing labels as approved by the engineer. (v) all labels shall be screw or rivet fixed and adhesive labels shall not be permitted under any circumstances. (vi) internal components labels shall have circuit designations correlated with the drawings. (vii) labels shall not be attached to trunking covers or other readily removable items. (viii) electrical equipment enclosures, vaults, doors and fences shall be provided with "DANGER KEEP OUT" warning sign, showing proper voltage. (ix) disconnect switches and emergency devices shall have "CAUTION" warning signs as directed by the Engineer. (x) fuse and MCB distribution boards shall be provided with internal, screw fixed, engraved circuit labels. Ink on paper, ink on plastic, printed paper, printed plastic, plastic film or any kind of adhesive labels shall not be permitted. (xi) provide a main Title Label all for electrical distribution and all other control equipment, panels etc. (xii) provide a Function Label for door mounted components. (xiii) every internal component - Identification Label. (xiv) provide a Identification Label for Protective devices - ( e.g. fuse/mcb type, rating). (xv) provide a Title Label for Communication equipment. (xvi) compartments with doors and covers not electrically interlocked to an isolator, external label - “ DANGER, LIVE TERMINALS ” with flash and voltage in red letters on white background in Arabic and English. (xvii) provide a function description Label for group of terminal blocks. (xviii) letter size shall be to the approval of the Engineer Switchboard Wiring: (a) (b) (c) (d) wiring shall generally be of the multi-stranded high temperature to minimum 105° C flexible PVC insulated, 600/1000V single core stranded copper type cable to BS EN 6231. Where it is proposed to use alternative high temperature, double insulated or other special cable or insulated flexible laminated bus bar this should be brought to the attention of the Engineer for his approval. wiring shall be supported in insulated cleats or cable trunking. Adhesive type cleats or mounts shall not be used unless augmented by screw fixings. busbar chambers shall not be used as trunking for small wiring. wiring shall be neatly laid and run in limited compression insulated cleats, insulated straps or, where more than ten wires follow the same route, in plastic slotted-sided trunking with clip-on covers. Where trunking is used, the effective overall crosssectional area of cables shall not be greater than 70% of the trunking cross sectional area. QCS 2010 Qatar Project Management 4 Part 2 QCS 2010 Section 21 (e) (f) (g) (h) (j) (k) (l) (m) MV Factory Built Assemblies (FBA’s) Page 11 wiring to items of equipment mounted on hinged doors or subject to movement shall run in plastic sleeving or flexible conduit, being securely anchored at both ends; leaving ample slack to prevent wiring strain, arranged so that they are subject to torsion rather than bending. holes in steelwork through which cables pass shall be protected using grommets or bushes, suitable for the size of hole. cables used for control, extra low voltage and instrument signal transmission, likely to be affected by interference, shall be screened and/or spaced from each other and from heavy current power cables. The separation distance shall ensure that the resultant electrical noise is insufficient to cause any form of malfunction of associated equipment or give false readings. a sufficient number of terminal connections including 15 % spare terminals shall be provided for all control and instrument wiring. all wiring shall be identified at each end by means of glossy plastic ferrules showing the wire number as on the schematic diagrams. Ferrules shall be color coded, „Z’ type and indelibly marked. where single core cable is to be accommodated, a non-magnetic gland plate shall be provided. For cable size 300 mm Sq. and above insulated glands shall be fitted. undrilled gland plates shall be provided for the reception of conduits and threaded glands. Boxes and glands shall be within the cubicles except where otherwise approved. single strand wire shall not be used. The minimum cross sectional area of the wire 2 2 used shall be 1.0 mm (multi strand flexible) for control circuit and 2.5 mm for power circuit. Both ends of every wire shall be fitted with a white cable marker as described above. Clip on type cable markers shall not be used. Color-coding shall be: Red - Red phase Yellow - Yellow phase Blue - Blue phase Black - Neutral Green and Yellow - Earth/Protective conductors Grey - 110V a.c White - 60 D.C Purple - <50V a.c Brown - Current Transformers Identification of conductors and auxiliary circuit shall be in accordance with BS EN 60445 and BS EN 60446 Terminations shall be as follows:(i) all wiring shall have crimped terminations, only one wire being held by any one crimp. Crimped lugs shall be of the insulated type without conductor exposure between the crimp and wire insulation. (ii) the type of crimp used shall be appropriate for the type of terminal to which it connects. The crimping shall be tubular when the tightening screw sits directly above it, or fork type if the tightening screw passes through the lug. (iii) terminations shall be neatly arranged leaving adequate length for one termination. (iv) all terminal blocks for the connection of small wiring shall comprise shrouded anti-tracking molding of melamine phenolic or comparable material with provision for securing conductors either by high tensile screws and clamps or alternatively in the case of small telephone type conductors by solder tag connection. (v) terminal blocks shall be arranged to facilitate easy access to both terminals and wiring ends. Connections for outgoing circuits to auxiliary pilot cables shall be provided with test links. (vi) removable rail terminals shall be provided for all wiring, mounted at an angle to provide ease of access. Centre-disconnecting link type terminals shall be provided for analogue signal circuits, external control devices and all alarm/telemetry signals. Sufficient, suitably sized earth terminals and end stops shall also be provided. QCS 2010 Qatar Project Management (i) Part 2 QCS 2010 Section 21 Part 2 MV Factory Built Assemblies (FBA’s) Page 12 (vii) 5 Safety Measures. (a) (b) (c) (d) 6 circuit breakers shall be provided with suitable means to prevent unauthorised and accidental operations. Interlocks to prevent dangerous operations shall be provided wherever necessary. High voltage parts shall be protected to prevent accidental human contact. Warning signs of durable type fixed on visible place shall be provided on high voltage parts. Earthing of metal parts shall be provided. mechanical interlocking shall be provided where required. All electrical interlocking shall be of the double interlocked type having separate permissive and prohibitive interlocks. Thus to allow a device to operate there must be an absence of prohibitive signals and a presence of permissive signals from the remaining devices in the interlocked system i.e. fail safe. suitable equipment shall be provided mechanically to prevent a device being manually operated when a prohibitive signal from another part of the interlocked system is present. when the MCC includes a standby generator incomer in addition to the QGEWC incomer, mechanical and electrical interlocks shall be provided in accordance with QGEWC regulations. Pilot Devices: (a) (b) pilot devices shall confirm to BS EN 60947-5.1. These shall be circular, 22 mm dia suitable for mounting on the cubicle door. The pilot devices shall have two main parts the operator and the Snap-On contact block. The mounting between the cubicle door and the operator shall be done through Snap-On flange. Pilot devices shall be designed to provide IP65 as a minimum protection when installed in the enclosures. Terminals shall be protected to IP2X. push buttons shall comply with the following specifications unless specified otherwise in particular requirements: (i) standard design (ii) mushroom/stayput/lockable type where specified QCS 2010 Qatar Project Management (n) the gap between gland plates and associated terminals shall be such that conductors can be safely manipulated and connected without damage. Terminals shall face the door of a cubicle for ease of connection. (viii) barriers shall be provided on all terminal banks, to group terminals into logical divisions. Power terminals of different phases shall be barriered from each other and separated from control terminals. (ix) in all cases care shall be taken to ensure that terminals are easily accessible after all wiring and plant cabling has been installed and terminated. All connections shall be made on the front of terminal blocks. (x) no more than one conductor shall be connected to one side of a terminal. Where several conductors are to be connected, shorting bars shall be provided across multiple terminals. Outgoing cables shall be wired so that all assembly wiring is connected to one side only. (xi) the terminal numbers, voltage grouping and terminal block layout shall correspond precisely with wiring diagrams so that quick and accurate identification of wiring can be made. (xii) all terminals shall show the circuit wire number reference. (xiii) a separate dedicated telemetry/RTU section shall be provided in the MCC cubicle equipped with all terminals duly wired and located in the side or on the top of the compartment interior leaving maximum room for free issued fully wired and tagged RTU complete with all associated hardware’s on a mounting plate. When a PLC control system is provided the PLC should be suitable for telemetry communication and shall be configured to communicate with the SCADA master station. (xiv) the MCC vendor shall co-ordinate with the RTU vendor through the contractor to confirm the size of free issued duly wired RTU on a backplate. The MCC vendor shall install and complete interconnection wiring between the RTU and the MCC accordingly. The contractor shall submit for the Engineer's approval, samples of wires, numbered ferules, and terminal pins or lugs which he proposes to use. QCS 2010 Section 21 Part 2 MV Factory Built Assemblies (FBA’s) Page 13 (iii) (iv) (v) (vi) (vii) (viii) (ix) (x) (xi) (c) (e) (f) 7 Busbars: (a) (b) (c) (d) the busbars shall be electro-tinned hard drawn, high conductivity 99.9 % purity, suitably sleeved for phase identification to BS 158 all busbars shall extend through the length of the board with same cross section throughout unless indicated otherwise 2 a copper Earth Busbar sized at least 50 % of the phase busbars or 300 mm , whichever is greater, shall be provided along the full length of the board busbars shall be adequately supported by porcelain or moulded insulators spaced on suitable centres so that the complete assembly can withstand the maximum mechanical stresses to which it may be subjected to under fault conditions QCS 2010 Qatar Project Management (d) non illuminated anodized Aluminum Bezel 1NO+1NC configuration minimum RED button for STOP function GREEN button for START function [Recessed type] mushroom RED for Emergency STOP function BLACK button for manual RESET WHITE button for lamp test push buttons for other functions where applicable shall be subjected to the approval of engineer. selector switches shall comply with the following specifications unless specified otherwise in particular requirements: (i) standard design (ii) lever type cam operated (iii) Twist Release/Push-Pull/KEY type where specified and/or approved by engineer. (iv) non illuminated (v) anodized aluminum bezel (vi) No. of positions as per logic diagram (vii) BLACK color (viii) 1NO+1NC configuration minimum indicators shall comply with the following specifications unless specified otherwise in particular requirements: (i) low voltage transformer latch type 110V/50Hz primary (ii) bulbs shall be long life neon types rated at least 10% higher than the operating voltage. (iii) GREEN colour for RUN/ON indication (iv) WHITE/Grey colour for STOP/OFF indication (v) AMBER colour for TRIP/FAULT indications (vi) BLUE colour for equipment selected „On-Auto’ indication (vii) WHITE color for SUPPLY AVAILABLE / ENERGISED (viii) RED colour for DANGER (in operation) indication (ix) indicators for other conditions where applicable shall be subjected to the approval of the Engineer. (x) the pilot light operator shall be designed to facilitate removal of bulb from the front of the unit without requiring any tool. (xi) LEDs shall not be permitted unless forming built-in feature of stand-alone product/controller to indicate operation status. LEDs shall be allowed only when forming built-in feature of stand-alone product/controller to indicate operation status. emergency and safety switches where specified shall confirm to BS EN 60947-3, Utilization Category AC23 and comply with the following specifications: (i) IP65 metal/thermoplastic enclosure suitable for installation in non-safe areas involving Methane and H2S gases. (ii) visible operating handle with marking OFF/ON position (iii) lockable in Off position by using padlocks (iv) suitable for base/wall mounting (v) the breaking capacity shall be more than the largest circuit it breaks (vi) the emergency switch shall have red handle on a yellow background QCS 2010 Section 21 (e) (f) (g) (h) (i) (j) (m) (n) (o) (p) (q) (r) 8 MV Factory Built Assemblies (FBA’s) Page 14 unless otherwise stipulated in the particular specification or drawings busbars shall be housed in separate adequately ventilated compartment which shall not contain any wiring or apparatus other than that required for connections for busbars rating : As indicated on the drawings. the mechanical and dielectric strength of bus bars and supports shall be capable of withstanding the worst conditions of electrical surge, which can occur in the installation bus bars shall be sleeved for phase identification by using high temperature grade heat shrinkable colored PVC sleeving throughout its length. In no circumstances will any kind of wrapping tape be accepted on busbars. all three phases and the neutral busbar shall be of same size enclosed in a common separate chamber. the mains horizontal busbars shall be housed in a separate chamber located on the top of the assembly. Busbars located elsewhere not on the Top shall be accepted at the discretion of the Engineer after verifying the certification, site location, available space and considering other factors necessary for ease in operation and maintenance of the assemblies. Insulation barriers shall be provided at each cubicle division. vertical busbars shall be fully enclosed in a separate chamber. bus bars connections shall be identified by phase color marking and adequately supported by suitable supports designed to withstand the full fault capacity as specified herein. connections from the main bus bars to MCCB’s controlling main motor starters and outgoing distribution feeder shall be via solid copper bus bars. Connections to busbars shall take the form of rigid bolted copper strips. Caliper sliding connections or similar movable contacts shall not operate directly onto the busbars or down-droppers. The utilization of “Fault Free Zones” will be permitted for the connection between the busbar risers and functional units rated 32 amps or below. These may be of copper conductors of solid rigid manufacture or insulated flexible conductors provided that they are securely fastened, provided in both cases that under normal operating condition an internal short circuit is only a remote possibility. For all functional units the connections between the busbar and the functional units should be sized to the frame rating of the short circuit protection device in the functional unit and an ASTA/KEMA 2 certificate for their short circuit let though (I T) capability shall be provided. bolted copper bus bar links shall be provided where specified and shall be used for maintenance purposes only. The link section shall be easily accessible from the front or top of the board and shall have a lockable cover. Provision for storing the links nuts and bolts shall be made in the switchboard. the temperature rise of busbars shall be limited to that which will not cause damage to the insulating material when carrying their rated current at the site ambient temperature and shall in any case not exceed 60°c reduced by the amount the site ambient temperature exceeds 40°c. The neutral shall be solidly earthed at the MCC. The neutral-earth link shall be adjacent to the incomer, externally labeled and be easily accessible. Instruments: (a) the Measuring Instruments shall include ammeters, voltmeters, kWh meters, selector switches and associated accessories as indicated on the Drawings and described herein as follows: (i) Ammeter, Voltmeter and Power Factor Meter: the measuring instruments shall be moving iron vane type, flush pattern with dust and moisture proof enclosure. Anti-glare glass front, anti-parallax scales and white faces with black numerals and marking shall be used. All instruments shall be of long scale 240 degree with full load indicating approximately at 180° 2 the dial size shall be 10 x 10 cm . accuracy shall be one percent of full scale values moving elements shall be provided with zero adjustments located at face of dial. the ammeter shall be capable of withstanding twice of rated current for 10 QCS 2010 Qatar Project Management (k) (l) Part 2 QCS 2010 Section 21 (b) MV Factory Built Assemblies (FBA’s) Page 15 minutes and overload sustained under fault conditions without damage or loss of accuracy. voltmeter shall have a measuring range from 0 to 500 V and shall withstand twice the rated full scale voltage for 1.0 minute without damage three ammeters or a single ammeter with selector switch shall be provided to read the current of each phase, as indicated on the Drawings the voltmeter selector switch shall be of the rotary type with cam operated contactor and shall have (7) positions off, R-Y, Y-B, R-B, R-N, Y-N, B-N single and poly phase power factor meters with associated current and potential transformers shall be provided as required and specified herein ammeters shall have maximum demand pointers. Current Transformers: (i) current transformers shall be of the bar primary type, air cooled and suitably insulated. The current transformers shall be of Class X accuracy for restricted earth fault protection and Class 1 accuracy for metering purposes, as stipulated in the QGEWC Regulations (ii) current transformers shall be rated not less than 5 VA and shall have thermal and mechanical rating at least equal to those of the main circuit breakers. (iii) following are the approved ratings of the current transformers (CTs) as approved by QGEWC. 100/5 200/5 500/5 800/5 1200/5 1600/5 2000/5 2500/5 (iv) removable links shall be located on the main busbars of each phase and neutral to enable easy maintenance and replacement. (v) current transformers shall comply with BS 3938 and should be suitably rated and designed to carry out the appropriate function as indicated. (vi) The rated burden of the current transformers shall be 30% in excess of the sum of burdens of all relays, instruments and related loads. (vii) the short time rating shall not be less than 44kVA for 3 seconds. (viii) identification labels giving type, ratio’s, rating output, manufacturer and serial numbers shall be fitted. Duplicate rating labels are to be fitted on the exterior of the mounting chambers suitably located to enable reading without removal of Any cover. Labels shall be supplied for multi ratio current transformers indicating the connection required for alternative ratios. (ix) bar type current transformers shall be provided in preference to those with wound primaries. Short time current factors shall relate to the full fault level for three seconds. For overcurrent protection the product of VA rated burden and rated accuracy limit factor shall be 150 unless otherwise agreed with the Engineer. (x) one secondary terminal of each current transformer shall be earthed through a removable link. kWh Meters: (i) the kWh meters shall be suitable for operation on 415/240 Volt, 3 phase, 4 wire, 50 Hz supply and shall conform to BS 37 Part 1 and BS 5685 (ii) the meters shall be dust-proof and vermin proof, protected from corrosion due to high humidity and compensated against the effect of temperature up to 55 °C (iii) the meters shall maintain their accuracy over many years service under Qatar climatic conditions. The counter shall be of the cycle meter type with six figures, the lowest figure being unit. Pointer type counters are not acceptable (iv) the meter cover and cases shall be of metal (v) meters shall not have less than 5 mm diameter terminal holes and shall be operated through three current transformers and the counter of the meter should be calibrated to read the primary kWh. The current transformers shall be selected from the standard sizes stipulated in QGEWC Regulations QCS 2010 Qatar Project Management (c) Part 2 QCS 2010 Section 21 Part 2 MV Factory Built Assemblies (FBA’s) Page 16 (vi) (d) Restricted Earth Fault Protection. (a) Restricted earth fault protection shall be provided for main switchboards in accordance with the QGEWC Regulations. (b) 30 DC supply is required for tripping of the LV ACBs through D.C. shunt trip for restricted earth fault relay. Contractor to provide for this unit a trickle charger and long life nickel cadmium batteries. The unit shall be designed to operate on 240 volts, 1 phase & 50 Hz A.C. Supply and for continuous duty at an ambient temperature of 50 ºC and 98% relative humidity. The capacity of the unit is to be determined by the manufacturer and based on number of trip unit , all to the approval of the Engineer and KAHRAMAA. 10 Anti-Condensation Heaters. QCS 2010 Qatar Project Management 9 all meters shall be handed over to the Qatar General Electricity & Water Corporation for calibration prior to final installation and connection. power monitor (PM): (i) power monitor (PM) shall be a true RMS digital instrument, with LCD display, capable of controlling and measurement highly non-linear loads accurately and able to detect voltage based disturbances. (ii) the LCD unit combined with function keys, minimum IP54, shall be mounted locally on the Incomer cubicle door. (iii) PM shall be CE marked and confirm to BS EN 61010-1 (iv) the Power Monitor shall register all measured values and log current and previous measured values for reporting and printing purposes. (v) the Power Monitor shall be supplied with software, user manual and associated interconnecting cables. (vi) PM shall be provided with user friendly software minimum windows 2000 based communication (fully supported by Latest Edition of Windows Based Operating System) program allowing easy access to all features with pull down menus (vii) true RMS measurement of current and voltage (viii) control and measurement of highly nonlinear loads (ix) capable to detect voltage based disturbances (x) interface capability with PLC/RTU/Circuit breaker (xi) provide load shedding capabilities (xii) provide interface with Power Factor Correction Control equipment (xiii) RS-485 port (xiv) modbus communication protocol (xv) DNP3.0 Communication protocol (xvi) web enabled Ethernet capability (xvii) measurement of Harmonics (xviii) monitoring of disturbances in the power supply network (xix) continuous sampling at 128 times per cycle (xx) trending analysis for historical data collection (xxi) sequence of events (xxii) RMS current of each phase (xxiii) RMS voltage L1-L2-L3-N (xxiv) average system voltage (Vav) (xxv) average system current (Iav) (xxvi) real power (KW) (xxvii) reactive power (KVAr) (xxviii) apparent power (KVA) (xxix) power factor (cos phi) (xxx) peak demand (xxxi) frequency (HZ) (xxxii) temperature (T) (xxxiii) THD current (%Ithd) (xxxiv) THD Voltage (%Vthd) (xxxv) K-factor100 QCS 2010 Section 21 (a) (b) Part 2 anti-condensation heaters shall be provided inside each compartment in strategic positions. These shall be controlled by an internally mounted humidistat and an external overriding ON/AUTO switch heaters shall be of sufficient size to maintain the air temperature inside compartment o at least 10 C above the outside ambient. 2.2.2 Motor Control Centres 1 General: (a) (b) (e) 2 provide the metal enclosed motor control centres as indicated, specified and required the motor control centres shall be switchboard type construction as described for M.V. cubicle switchboards except as modified herein the motor control centres shall be front access only shipment shall be made in sections to facilitate field handling, and the shipped sections shall be joined together to form a complete back-to-wall or back-to-back unit assembly as indicated the motor control centres shall be free-standing or wall-mounted, as indicated in the Project Drawings. Construction (a) (b) (c) (d) (e) (f) (g) (h) (i) (j) (k) (l) (m) (n) (o) (p) vertical sections shall contain adequate space for connecting the incoming power supply circuits, outgoing branch circuits, motor circuits and control circuits to terminals, horizontal and vertical power bus bars, horizontal earth bus, circuit breakers, magnetic starters, contactors, control stations, pilot lights, timers, terminals, transformers, panels, relays, ammeters, voltmeters, meter switches, earth leakage protection, space heaters, thermostats, fans, vents, screens, filters and switches the vertical sections shall be fabricated from heavy gauge steel (minimum thickness of 1.5 mm), with uniform surfaces unless otherwise indicated, the standard section shall be 800 mm wide (600 mm for equipment and components, 200 mm for vertical wire way) by 600 mm deep holes shall be provided in the structural base of each section for anchor bolts sections shall contain wireways, brackets, supports, plates, trims, barriers, gaskets, doors, base channels, lifting angles and hardware horizontal wireways (top and bottom) shall extend through the width of each section wire way openings shall be provided between sections with closing plates on the end sections each vertical section shall contain its own individual full height vertical wire way separated from the vertical bus by a metal barrier, and also separated from the individual control units by the side pan of the control unit. wire ties shall be furnished in the vertical wireways to group and securely hold the conductors in place a separate cover shall be provided on the vertical wire way control units shall be isolated from one another by horizontal steel barriers front to rear bracing shall not interfere with the cable entrance areas hinged doors shall be equipped with screwdriver operated quarter-turn latches that catch automatically when the door is pushed closed. Large doors shall be equipped with additional latches provision shall be included to add a vertical section on either end of the line up in the future the power supply compartment shall be sized to accommodate the incoming power conductors. The compartment shall be located at the top or bottom of the vertical section as shown on the Drawings. The power compartment shall be covered by a hinged door and shall be held closed with quarter-turn pawl type latches busbars shall be provided for the power and earth systems. When shown on the Drawings, provide full length full capacity and insulated neutral bus and cable connectors. Bus joints shall be connected with bolts, nuts and spring washers. The main horizontal power bus shall be located in the centre or near the top of each section, joined together to form a continuous bus for the full length of the motor control centre. The horizontal power bus shall be copper and the current rating shall be as shown on the Drawings. The vertical power buses shall be copper full height QCS 2010 Qatar Project Management (c) (d) MV Factory Built Assemblies (FBA’s) Page 17 QCS 2010 Section 21 (q) (s) (t) (u) (v) (w) (x) (y) (z) (aa) (bb) MV Factory Built Assemblies (FBA’s) Page 18 and rated for the section total load. The minimum current rating for the vertical power buses shall be 300 amperes or as specified in the Project Documentation. Small openings in the vertical barriers shall permit the plug-on control unit contacts to pass through and engage with the vertical bus bars. Unused plug-on openings in the vertical barriers shall be equipped with plastic snap-in closing plugs. each Incomer Section shall consist of: (i) 4 Pole ACB/MCCB (For Generator Incomer) (ii) 3 Pole ACB/MCCB with solid neutral link (For Mains Incomer) (iii) 1X Voltmeter 96X96, 240 degree scale for mains bus voltage live indication (For Mains Incomer) (iv) 3X Voltmeter 96X96, 240 degree scale for generator bus voltage live indication (For Generator Incomer) (v) 1X Voltmeter Selector Switch 7 Position (For Mains Incomer) (vi) 1X Ammeter 96X96, 240 degree scale (For Mains Incomer) (vii) 3X Ammeter 96X96, 240 degree scale (For Generator Incomer) (viii) 6X Maximum Demand Indicator 96X96 (May be included with ammeter) (ix) 1X Ammeter selector switch 5 position (For Mains Incomer) (x) Power Monitor (xi) phase failure/phase sequence relay for sensing the main incomer, generator incomer and busbar voltage. (xii) 2X IDMTL overload relay (may be included in the circuit breaker) (xiii) 2X IDMTL earth fault relay (may be included in the circuit breaker) (xiv) 2X IDMTL restricted earth fault relay (xv) 1X Frequency meter (45-55)Hz (xvi) 1X Supply on indicator lamp (xvii) auto/manual changeover for MCC with two or more Incomers (See Metering Section below) (xviii) trip circuit healthy test facility in case of a circuit breaker designed to trip on fault through externally mounted protection devices e.g. IDMT (Inverse Definite Minimum Time relay), UV relay etc. (xix) control fuses (xx) open/close/trip indicating lamps (xxi) terminals etc. the changeover function shall be fully automatic mains Generator on failure of power and vice versa. a separate metering section shall be included in order to accommodate analogue meters, Power Monitor, control relays, timers, PLC, selector switches, push buttons, indicating lamps etc. as necessary for interlocking scheme for the incomers. an auto/manual changeover scheme shall be included unless specified otherwise, as a definite requirement for two or more incomers, fully wired and factory tested. detailed drawings shall be prepared during the design stage and the same to be submitted to the Engineer for approval prior to the manufacturing. installations requiring a mobile generator shall be provided with an appliance inlet socket outlet or junction box. the appliance inlet shall be used for generators up to 125 A and be housed in a weather proof box fixed and located outside the MCC Room as shown on plant and equipment drawing. The junction box shall have detachable gland plate at the bottom facilitating easy connection and disconnection of the generator cable. For higher capacity generator ratings above 125 A, a weatherproof junction box shall be provided with solid copper links and ample space for terminating cables. a separate section shall be provided to house the QGEWC kWh meter. The kWh meter compartment shall be provided with a 300mm X 300mm X 12mm thick plywood mounting board and a ten way terminal block in accordance with QGEWC regulations. the kWh meter shall be CT operated for loads exceeding 100A. each outgoing starter, feeder or other functional unit shall be enclosed within its own section providing Form 4 segregation. one spare equipped feeder section (MCCB only) per MCC shall be provided as minimum. The rating shall be subject to the approval of the engineer. the Common Control section shall consist of the following controls and instruments as minimum for guidance purpose only subject to the approval of the engineer: (i) non door interlock MCCB QCS 2010 Qatar Project Management (r) Part 2 QCS 2010 Section 21 Part 2 MV Factory Built Assemblies (FBA’s) Page 19 (ii) (iii) (iv) (v) (vi) 2.2.3 MCCB Panel Boards 1 General. (a) (b) (c) (d) 2 MCCB panel boards shall be manufactured to BS EN 60439-1, factory assembled and certified by an authorising testing body the panel board shall be suitable for operating on a 3 phase, 4 wire, 415 V supply the symmetrical through fault rating shall be 25 kA for a duration of 3 seconds if necessary, the panel board shall include a suitable hardwood backboard to accommodate the QGEWC metering equipment. Construction. (a) (b) (c) (d) (e) (f) (g) the panel board shall be of robust construction, fabricated from heavy gauge folded steel angles strengthened by horizontal and vertical folded channels the frame work shall be enclosed in self-supporting, screw -on front, rear and top covers of sheet steel with gaskets the doors shall be lockable and have concealed hinges provided with gaskets thickness of the steel sheet shall be not less than 1.5 mm the panel shall be suitable for wall mounting. the structure shall be protected from rust and oxidisation before being given a coat of primer and finishing coats the finished paint colour shall be to Engineer’s approval selected from BS 381. QCS 2010 Qatar Project Management (cc) 24 V DC regulated power supply 24 V DC Ni Cd battery 24 V DC Ni Cd battery charger power distribution MCBs for field instruments programmable Logic Controller (PLC) – Refer to Instrumentation & Control Section for specifications (vii) Video Display Unit where specified - Refer to Instrumentation & Control Section for specifications (viii) pressure & level indicators - Refer to Instrumentation & Control Section for specifications (ix) sounder complete with auto cut-off time and mute pushbutton as specified in the particular requirements. (x) flashing Beacon Light (mounted outside building) as specified in the particular requirements. (xi) local/remote selector switch (xii) float/level selector switch (xiii) pumps Duty-Standby selector switch (xiv) push buttons for lamp test, fault-reset etc. (xv) status Indicating Lamps (xvi) control relays, timers and control fuses as required according to the logic + 20% as spares wired to the terminals. (xvii) zener barriers (xviii) hygrostatically controlled Anti-condensation heater (xix) standard and special terminals to suit the applications requirement (xx) terminal kiosk (A separate partitioned terminals arrangement clearly labelled identifying IN/OUT). [All wires to field devices and telemetry section must be routed through terminal kiosk]. (xxi) 240V, 13 amp AC single phase 3 pin (flat) standard socket the telemetry section shall consist of the following controls as minimum for guidance purpose only subject to the approval of the engineer: (i) Non door interlock MCCB (ii) 24 V DC Ni Cd battery (iii) 24 V DC Ni Cd battery charger (iv) Remote Terminal Unit (RTU) – Refer to Instrumentation & Control Section for specifications (v) Interposing relays (vi) Hygrostatically controlled Anti-condensation heater (vii) Terminals, control fuses and surge protection etc. QCS 2010 Section 21 3 MV Factory Built Assemblies (FBA’s) Page 20 Busbars (a) (b) 4 Part 2 the bus bars shall be of high conductivity, rectangular section, hard drawn copper, electrolytically tined suitably marked and colour coded in accordance with BS 158/159 the short circuit ratings of the bus bars shall be as stated above Components (a) 2.2.4 Distribution Boards 1 Distribution boards shall be provided to serve lighting, fans, socket outlets, and other appliances. Board shall be arranged in banks of ways as indicated on the schedule of points. 2 The Distribution Board shall be a part of the MCC cubicle assembly unless otherwise indicated in the project Documentation 3 Where there is Distribution Board stand alone, then: (i) (ii) (iii) (iv) Distribution Boards shall be flush mounted type, or surface mounted type and shall be mounted separately from motor control centres or switchboards. The boards shall be totally enclosed, dust protected, vermin proof type. Distribution boards installed in all plant rooms and other process areas shall be corrosion resistant. Enclosure shall be fabricated from robust galvanised sheet steel fully rust-proofed, stove enamelled, of minimum thickness of 1.5mm and shall be protected to IP 32 for internal use with neoprene gaskets for the doors. The distribution boards shall be provided with fixed cover and a hinged door with padlock which can be opened without any obstruction about 120 degrees and conduit knockouts from the top and bottom. The hinged door with a lock and key shall be integral part of the fixed cover. The cabinet shall be constructed so that it is necessary to open the door to operate Miniature Circuit Breakers or ELCB. Access to interior components and internal wiring shall be gained by removing a separate barrier within the enclosure. 4 All distribution boards shall be controlled by an adequately rated on-load main isolator or circuit breaker to interrupt the supply to the entire distribution board. This main isolator or circuit breaker shall be double pole for single phase DBs and triple pole for three phase DBs.Moreover,it shall be connected to the busbar directly without links whatsoever. 5 A circuit label shall be provided to indicate the area served by each MCB. 6 Busbars shall: (a) (b) (c) be of appropriate current carrying capacity at least equal to the rating of the main incoming isolator or circuit breaker. be of high electrical conductivity copper. Where the main isolator or circuit breaker is connected to bus bars then these bus bars shall be shrouded. QCS 2010 Qatar Project Management the switch boards shall comprise of the following components: (i) incoming: suitably rated isolator/MCCB as indicated on the tender drawings and to comply with relevant Clauses of this specifications (ii) outgoing: Moulded Case Circuit Breakers of 25 kA fault level with ratings as per the tender drawings and de rated for 50 ºC ambient temperature.. All MCCB of rating 100 Amps and above shall have adjustable thermal and magnetic facilities (iii) meters: 3 ammeters with dead pointer to indicate the maximum reading and 1 No. 0-500 Volt voltmeter with Off/ph-ph/ph-N selector switch, for incoming supply. QCS 2010 Section 21 Part 2 MV Factory Built Assemblies (FBA’s) Page 21 Each DB shall have separate earth and neutral bars having the same number of connection as there are for phase connections. A cable connection shall be made from earth bar to the incoming cable gland earth tag. All phase and neutral bars shall be sized to carry the full load current of the controlling breaker which shall be of flat tinned copper rigidly mounted, supported on shock-resisting, non-hygroscopic, high grade insulators with high resistance to tracking, not subject to mould growth or termite attack with adequate spacing and clearance. 8 Connection from the bus bars to the breakers shall be made by using solid circular insulated conductors or insulated and tinned copper strip neatly set and formed. Each connection to or from a phase or neutral bar shall have its own brass fixing screws, washers, butts and locknuts. 9 Each distribution board shall be fitted with an identification label on its front cover. The label shall be suitably inscribed stating the distribution boards reference number/letter, rating in volts & amperes and the number of ways in English and Arabic. In addition to the above a reference card shall be fitted inside the distribution board giving details of each circuit, MCB size, cable size and location. The reference card shall be affixed to the inside of the distribution board’s door via a transparent envelope. 10 Distribution Boards (DB) located remote from the main switch boards shall be mounted at a height of not less than 1200mm from finished floor level to bottom of the DB and maximum height of this DB shall be 2200mm from finished floor level to top of DB. 11 All live terminals of parts and bus bars shall shrouded with insulating materials to ensure that it is impossible for any live metal to be touched while withdrawing or replacing MCBs. 12 The correct rating of breakers shall be fitted in each way to conform to the size of the final circuit conductor and its connected load in conformity with KAHRAMAA. 13 All breakers and DBs shall be of one make throughout the whole of the works. 2.3 INSTALLATION 2.3.1 General 1 The M.V. cubicle switchboards shall be supplied and installed in the building or in a separate services building or in substations as indicated on the Drawings. 2 The Contractor shall submit details of proposed equipment and method of installation to the Engineer and QGEWC for approval prior to commencement of installation work. 3 Provide all the motor control equipment installations, wiring installations and tests, including connections and interconnections for the electrical controls as indicated, specified and required. Assure proper fits for all equipment and materials in the spaces shown on the Drawings. 4 Equipment shall be installed level and securely attached to the concrete foundations and walls with expansion anchors. The sections shall be joined together with bolts, nuts and washers to form a complete unit assembly. Floor standing equipment shall be installed on concrete plinths as shown on the Drawings. 2.3.2 Earth Bonding 1 Each panel section shall be individually bonded to main earth bar located in the electrical rooms. 2 Each panel section shall be cross bonded to adjacent panel section earthing terminal. QCS 2010 Qatar Project Management 7 QCS 2010 Section 21 Part 2 MV Factory Built Assemblies (FBA’s) Page 22 END OF PART Qatar Project Management QCS 2010 QCS 2010 Section 21 Part 3 Protective Devices Page 1 3. PROTECTIVE DEVICES ............................................................................... 2 3.1 GENERAL ...................................................................................................... 2 3.1.1 3.1.2 3.1.3 3.1.4 3.1.5 3.1.6 3.1.7 Scope General Reference Ratings Standards Overcurrent Protective Device Co-ordination Quality Assurance Manufacturers 3.2 PRODUCTS ................................................................................................... 3 3.2.1 3.2.2 3.2.3 3.2.4 3.2.5 3.2.6 3.2.7 3.2.8 3.2.9 3.2.10 3.2.11 3.2.12 3.2.13 3.2.14 3.2.15 3.2.16 3.2.17 3.2.18 Air Circuit Breakers Moulded Case Circuit Breakers Miniature Circuit Breakers MCB/ELCB Earth Leakage Circuit Breakers (ELCB) Overload Relays Fuses Fuse Switches Isolating Switches Stop Lock-off Push Buttons Control Relays/Auxiliary Relays/Interposing Relays Protection Relays Alarm System Padlocks Hours Run Meters Thermistor relay Moisture and mechanical seal leakage protection Timers 3 5 6 6 6 7 8 9 10 10 10 11 11 12 12 12 13 13 Qatar Project Management QCS 2010 2 2 2 2 2 3 3 QCS 2010 Section 21 Part 3 Protective Devices Page 2 PROTECTIVE DEVICES 3.1 GENERAL 3.1.1 Scope 1 This Part shall specify the requirements for protective devices. 3.1.2 General Reference 1 The work of this Part is integral with the whole of the Project Documentation and is not intended to be interpreted outside that context. 2 Co-ordinate the work with all other services affecting the work of this Section. 3.1.3 Ratings 1 The ratings of the various overcurrent protective devices shall be, in general, as indicated on the Project Drawings. However, the protective device ratings shall be confirmed based on the equipment and items being provided by the Contractor. Contractor shall provide calculation and justification for proposing any change in the rating. 3.1.4 Standards 1 The following standards shall be followed: BS88 BS EN 60255-6, IEC 255 BS EN 60269, IEC 269 BS EN 61008-1 BS EN 60898, IEC 157-1A BS EN 61810-1 BS EN 60947, IEC 947-2 Cartridge fuses Electrical relays Cartridge fuses for voltages up to and including 1000VAC and 1500 V AC Earth Leakage circuit breakers Miniature and Moulded Case Circuit Breakers Electrical Relays Low Voltage circuit breakers 3.1.5 Overcurrent Protective Device Co-ordination 1 The Contractor shall carry out and provide an overcurrent protective device. Co-ordination study as part of his material submission, as outlined below: 2 Properly co-ordinated automatically operated overcurrent protective devices shall be provided for this Project. The overcurrent protective devices shown on the Drawings shall be coordinated for adequate continuous current and interrupting capacity to assure proper overcurrent protective devices operation under normal and fault conditions in the system. 3 All overcurrent protective devices on this Project and the first upstream device of the existing electrical system shall be co-ordinated so that they will perform as follows. When two or more overcurrent protective devices (including the first upstream protective device of the existing system) in series with each other experience current flow greater than their rated current, the device with the lowest rated current shall trip and/or open the circuit first and thereby prevent the higher rated devices from operating. 4 The Supplier of the overcurrent protective devices shall prepare a co-ordination study to verify the above stated performance requirements. The study shall be documented by the Supplier and the documents shall include but not be limited to the following: (a) a composite drawing or drawings (on full size, reproducible, log-log paper) showing the entire new electrical system (including the first upstream protective device of the existing system) showing all protective device curves (including motor overloads), short circuit duties, motor starting curves and damage curves for motors, equipment QCS 2010 Qatar Project Management 3. QCS 2010 (b) (c) (d) Section 21 Part 3 Protective Devices Page 3 5 This documented co-ordination study shall be submitted for review before the overcurrent devices are supplied for the Project. 3.1.6 Quality Assurance 1 The suppliers manufacturing facility shall be certified to the ISO - 9001 series of standards from the International Standards Organisation. 3.1.7 Manufacturers 1 Preference will be given to one manufacturer of ACB, MCCB and MCB to ensure proper coordination in accordance with Clause 3.1 above. 3.2 PRODUCTS 3.2.1 Air Circuit Breakers 1 To IEC 947-2 or BS EN 60947-2, suitable for triple pole service and shall have breaking capacity of 50 kA symmetrical for 3 seconds at 415 Volts. ACBs shall be of the horizontal withdraw able, load making and breaking type with the contacts being of the double break pattern with arcing chutes, shutters etc. The main arcing contacts shall be of the high pressure butt type with wipe and roll action on opening and closing. The main contacts shall be of silver alloy. Removable arc chutes shall be fitted together with an air circuit breaker. ACB shall be complete with a mechanical ON/OFF position indicator, pad-lockable. ACB shall conform to B.S. En 60947-2 (EN 60947-2, IEC 947-2) and B.S. En 60664-1. Each circuit breaker shall be enclosed in sheet steel and provided with three phase manual and automatic isolating devices suitably interlocked so as to prevent isolation except when the circuit breaker is in open position. It shall be arranged in such a manner that it will not be possible to withdraw the breaker or remove the front cover unless the ACB is in the isolated position. Provision shall be made for locking the ACB in this position (isolated position). Shutters shall be provided to protect the live terminals against accidental touch when the ACBs are in a fully withdraw able position. The ACB shall have solid sate overload and short circuit protection devices along with earth fault trip mechanism. The solid state circuit shall be provided with proper LED indication to indicate the trip status of the ACB. The ACBs shall be equipped with shunt trip of 30V DC trip mechanism for tripping the breaker with restrictive earth fault relay to be provided separately with suitable size of CTs. QCS 2010 Qatar Project Management and conductors. This drawing or drawings shall show that all protective devices are properly co-ordinated to perform as stated above manufacturer’s overcurrent operating curves (on full size, reproducible, log-log paper) for each overcurrent device. In the case of fuses, both minimum melt and maximum clearing time curves shall be included reproducible copies of all Project single line diagrams so marked to show short circuit duties at all switchboards and motor control centres, and which operating curve applies to each overcurrent device on the diagram (the operating curves shall also be correspondingly marked) a tabulation of the short circuit duties at all switchboards and motor control centres, sizes and ratings of all overcurrent protective devices and the required settings of all of the adjustable overcurrent protective devices so that the performance requirements are met. Protective devices which have earth fault protection features are specifically required to meet this performance requirement. QCS 2010 Section 21 Part 3 Protective Devices Page 4 2 The Air Circuit Breakers (the conventional type and not moulded case circuit breaker) shall be 500 V, 50 Hz, triple pole with neutral link for incoming and outgoing ACB or four poles for bus tie ACB only with ratings as shown on the Drawings. They shall be air break, trip free, draw-out type with mechanical and electrical ON/OFF indicators. 3 Where air circuit breakers are to be electrically operated by automatic motor wound spring mechanism, a standby manual operating handle shall be provided for operating the circuit breaker in case of power or motor failure. 4 The air circuit breaker shall be provided with built-in overcurrent, short circuit and Earth fault protection having the following characteristics:- 5 The circuit breaker shall have three position on the draw-out mechanism, namely service position where all main and auxiliary contacts are made, test position where main contacts are open but auxiliary contacts are closed and isolated position where all contacts are open. An indicator shall clearly show these positions and provisions shall be made for locking the breakers in any position. ON/OFF indicator shall be provided. 6 Mechanical Interlocks shall be provided to prevent withdrawing or inserting of the breaker when it is „ON’. Any attempt to do so shall trip the breaker automatically. 7 The withdrawable part of the circuit breaker shall be effectively connected to earth through scraping contacts that shall make before and break after the main and auxiliary contacts. 8 The moving contacts comprising the main and arcing contacts shall be of the spring loaded, self aligning type. The arc contacts shall be arranged to make before and break after the main contacts. 9 The air circuit breaker shall include but not limited to the following as minimum:(a) (b) (c) (d) (e) (f) (g) (h) (i) (j) 8NO/8NC auxiliary contacts arc chutes folding extension rail charging handle open and close push buttons trip indicator spring charge motor spring charge indicator breaker position indicator mechanically and electrically. micro-processor based protection and management unit that provides the following control and monitoring features:(i) overcurrent protection (ii) short circuit protection (iii) earth fault protection (iv) neutral protection (v) thermal memory (vi) alarm logging (vii) field selectable Manual or Auto reset (viii) microprocessor malfunction watch dog (ix) programmable input/outputs (x) load monitoring (xi) operation counter QCS 2010 Qatar Project Management a. adjustable long time delay current setting between 50 – 200% with variable tripping time characteristics. b. adjustable short time delay current setting 200 – 800% with variable tripping time characteristics. c. instantaneous tripping for heavier over current applications adjustable from 400 – 1600% of the base current. d. adjustable earth fault trip current setting 20 – 80% with variable tripping time characteristics. QCS 2010 (k) (l) Section 21 Part 3 Protective Devices Page 5 (xii) serial communication. carriage/Lifting Truck for ACB exceeding 25 Kg in weight [One carriage for each site/project regardless of number of breakers provided shunt trip and under voltage release 10 The Main Incoming Circuit Breakers shall be provided with cable terminal boxes to suit the incoming cables from the transformer/source supply. The gland plate for the incoming cables shall be non-ferrous material brass compression type glands, earthing tags and shrouds. In case single core PILCA/PVC cables are used, the clamping arrangement is to supplied as per the sketch nos. 9 & 10 shown on pages 144/145 of KAHRAMAA regulations. 11 Circuit breakers shall be tropicalised to operate continuously in an ambient temperature of 55 °C and high relative humidity. 13 The ACB shall have adjustable settings and the following facility: Long time current setting and tripping delay. Overload signal. Short time pick up and tripping delay. Instantaneous pick-up. Earth leakage test button. Long time rating plug screw. Test connector Lamp test, reset and battery test. Indication of tripping cause. Digital display. Three phase bar graph and power display. Setting / programmable buttons. 14 The ultimate breaking capacity (ICU) shall be minimum of 44KA. The rated service breaking capacity (ICS) and rated short time withstand current (ICW) shall be equal to or greater than ICU. 15 The ACB section of the switch board shall be in separate cubicle separated from other parts of the switch board. This section shall not have any outgoing feeders. 3.2.2 Moulded Case Circuit Breakers 1 Shall have a combination of thermal and magnetic tripping giving an inverse time delay protection against sustained overloads and instantaneous tripping under heavy overloads and short circuits. Unless otherwise stated in the particular specification or drawings, MCCB shall have a minimum short circuit rating of 25 kA. 2 Breakers shall have a quick make, quick break over-centre switching mechanism that is mechanically trip free from the handle so that contacts cannot be held closed against short circuits and abnormal current. 3 Tripping due to overload or short circuits shall be clearly indicated by the handle assuming a position mid-way between the manual ON and OFF position. 4 Latch surfaces shall be polished. 5 Poles shall be constructed to open, close and trip simultaneously. 6 Ampere ratings shall be clearly visible. QCS 2010 Qatar Project Management 12 Type test certificate for each size of circuit breakers and MCCB from an internationally recognised testing authority acceptable to the Engineer shall be provided. QCS 2010 Section 21 Part 3 Protective Devices Page 6 Breakers shall be completely enclosed in a moulded case to IEC No. 157 - 1A, suitable for installation inside switchboards. 8 Non-interchangeable trip breakers shall have the trip unit sealed. 9 Breakers with earth leakage relay protection shall be provided with shunt trips. 10 Frame sizes shall be as per manufacturer’s standard size and as approved by the Engineer. 11 The magnetic trip shall be adjustable type for rating 200 Amp. and above, with 8 settings from 1.5 to 10 times the rated current of the circuit breaker. 12 Each MCCB shall be housed in a separate Compartment with the operating handle door interlocked when used as an Incomer, feeder or motor starter isolator, so that access can only be gained to the Compartment with the MCCB in the OFF position. Padlocking shall be provided in the OFF position only. When the MCCB is used for control transformers, distribution or ICA compartments the handle shall be internally mounted with appropriate shrouding and warning labels. 13 Each MCCB shall be complete with 2 N/O and 2 N/C spare auxiliary contacts (10A, 240v rating) in addition to those required for the Contract. 14 Each MCCB used as an Incomer or feeder shall have facilities for electrical as well as mechanical interlock. 15 All incoming circuit breakers shall be provided with electrical & mechanical interlocking scheme to ensure that only one incoming supply can be energized at any one time where more than one supply is available. 3.2.3 Miniature Circuit Breakers 1 These shall be type C for general purpose uses, suitable for the load they feed, and shall have short circuit rating of 9 kA, unless specified otherwise in the Project Documentation. 2 They shall be fault rated so that fuse backup protection is not required. 3 They shall be rated in accordance with BS EN 60898, IEC 898. 4 They shall include the following minimum features: (a) (b) (c) magnetic and thermal trip elements trip-free mechanisms locking of facilities with detachable proprietary brackets and clearly marked ratings. 5 RCBO shall comply with BS EN 61008-1 & BS EN 61009-1 3.2.4 MCB/ELCB 1 Combined MCB/ELCB units shall be provided for final circuits supplying socket outlets, water heaters and water pumps. 2 The units shall have a trip sensitivity of 30 mA. 3.2.5 Earth Leakage Circuit Breakers (ELCB) 1 Current operated earth leakage circuit breakers shall provide accident protection by interrupting dangerous contact with voltage which may be present in faulty electrical equipment as a result of frame faults, insufficient insulation or misuse. QCS 2010 Qatar Project Management 7 QCS 2010 Section 21 Part 3 Protective Devices Page 7 The ELCB shall also provide high degree of protection against earth leakage, fire and electric shock. It shall withstand at least 10 kA or as specified in the project documents. The breakers shall comply with BS EN 61008-1 and the recommended specification CEE 227 of the IEC on rules of approval of electrical equipment. 3 The breaker shall consist of a core balance transformer, a tripping coil with contact assembly, main supply contacts, ON/OFF switch, a test button and a trip free mechanism all enclosed in a robust body of all insulated material. 4 Degree of Protection against earth leakage throughout the electrical installation shall be as indicated on the Drawings. Unless otherwise indicated, ELCB shall have 30 mA trip settings. 5 The breaker protecting lighting and or power circuits shall be mounted in the panel board enclosure. 3.2.6 Overload Relays 1 Thermal Overload Relay (a) (b) (c) (d) (e) (f) (g) (h) (i) 2 thermal overload relay where specified shall be of Bi-metallic inverse time-lag type, which shall be used with a contactor in the starter circuit enabling switching device to open both control and power circuit (fully isolating the power to the motor terminal box) when the current in the relay exceeds a predetermined value. the thermal overload relay shall fully comply with the requirement of BS EN 60255-8 the thermal overload relay shall be simple and robust suitable for direct contactor mounting or if to be mounted separately shall be used with manufacturer supplied links and associated attachment. the thermal overload relay shall be designed to include ambient temperature compensation feature from – 20 Deg C to + 65 Deg C eliminating the need of any calibration in the field during operation. the thermal overload relay shall provide the following protections:(i) over-current/Overload (ii) single phasing/Phase failure the thermal overload relay shall have MAN/AUTO field convertible Reset button located on top of the relay for resetting of the relay after trip. Additionally a facility shall be provided on the door of starter compartment to reset the relay if so required/specified. the thermal overload relay shall have two characteristics, the one when the relay bimetals are in cold state that will break the contacts of the relay within 8-10 seconds and the other when in hot state the contacts breaking shall be reduced to approximately one third of the tripping time as indicated for the cold characteristics. The tripping time may be allowed to vary depending upon the starting of the motor such as normal/heavy-duty. the thermal overload relay shall have been type tested and ASTA certified to achieve Type 2 co-ordination in accordance with BS EN 60947. thermal overload relays shall be used for motors rating up to and including 11 kW. Electronic Motor Protection Relay (a) General (i) the Motor Protection shall be an intelligent electronic device that is user friendly and user configurable, capable of controlling the motor manually or automatic. (ii) EMPR shall be CE marked and confirm to BSEN 60947-1 (iii) EMPR with LCD display shall be provided in the MCC for each sewage pump motor starter regardless of the rating of the pump and non-sewage pump drives above 11.0 KW. The LCD unit combined with function keys, minimum IP54, shall be mounted on the cubicle door (iv) non sewage pump drives upto 11.0 KW inclusive may be provided with ambient compensated bi-metal type thermal overload relay. (v) EMPR shall have built-in RS485 communication port utilizing Modbus RTU protocol for serial communication with other devices on the network. QCS 2010 Qatar Project Management 2 QCS 2010 Section 21 Part 3 Protective Devices Page 8 (vi) (vii) (b) (d) (e) 3.2.7 Fuses 1 These shall be selected according to the application and be suitable for the type of load they feed, for example motor starting, cable protection, protection for the semi conductor devices, control transformer protection etc. QCS 2010 Qatar Project Management (c) EMPR shall be supplied with software, user manual and interconnecting cables. EMPR shall be provided with user friendly software minimum windows 2000 based communication (fully supported by Latest Edition of Windows Based Operating System) program allowing easy access to all features with pull down menus. the protection features shall include the following as minimum:(i) over load protection (ii) over current protection (iii) over voltage protection (iv) under voltage protection (v) under current protection (vi) phase sequence (vii) phase imbalance (viii) phase loss (ix) earth leakage (x) earth fault (xi) thermistor broken (xii) open contactor (xiii) locked rotor motor current sensing shall be through external 5 A or 1 A current transformer. The following measured values shall be displayed on the LCD mounted on the starter compartment door. (i) RMS current of each phase (ii) RMS voltage (iii) earth leakage current (iv) continuous monitoring of thermal capacity of the motor (v) thermal capacity used (vi) power factor of the motor (vii) motor kW (viii) phase unbalance (ix) parameter settings (x) percentage of FLC of the motor (xi) adjustable delayed start/stop (xii) maintenance Log EMPR shall be capable of registering all trip commands and log trip and pre-trip metering values for reporting and printing purposes. Programmable Ranges (i) overload – shall be based on the calculation of accumulated I²t value and selected thermal capacity curve. The tripping time shall be 0-10 Sec. Adjustable. (ii) locked rotor – To trip the motor within 1 to 5 Sec. when the running current exceeds the stalled rotor trip level of 1.5 to 5.0 x FLC. (iii) phase unbalance – Should there be a phase current unbalance of greater than 15% lasting for 5 seconds an alarm shall be generated. If the condition prolonged for 10 seconds or more a trip shall occurs. (iv) earth fault – The earth fault shall be measured as a percentage of primary range of current transformer. The setting range for the ground current shall be 0.1 to 1.0 x ground fault CT primary current. An adjustable delay time of 0-30 seconds shall allow preventing nuisance alarm from momentary surges. It should be possible to make the alarm setting below the trip level to indicate early warning insulation breakdown. (v) thermistor/over temperature – EMPR shall be capable of accepting PTC and NTC sensors. Thermistor level shall be selectable for both alarm and trip conditions with an adjustable time delay of 0-5 seconds. (vi) under current – 10 – 100% of motor FLC with a time delay of 0-30 seconds. QCS 2010 Section 21 Part 3 Protective Devices Page 9 Fuses shall be sized according to the condition under which they will operate such as normal, small sustained overload, heavy overload etc. in order to consider the operating characteristics accordingly. 3 The fuse shall either include a suitable fuse carrier or it shall be capable of isolation. If the fuse carrier is included it shall be such that when it is being withdrawn normally or when it is completely withdrawn the operator is completely protected from accidental contact with any live metal of its fuse link, fuse contacts and fixed contacts. 4 Fuse/links shall be fixed inside cubicles with sufficient spacing to facilitate easy fuse/link withdrawal. 5 If the fuse is capable of isolation it shall be so interlocked with the switch that isolation is complete before the fuse enclosure can be opened further. The switch shall be prevented from closing while the fuse-cover is open. 6 All fuses shall be of HBC/HRC cartridge type to BS 88/BS EN 60269. 7 Fuse holders and fittings shall be made of molded plastic insulating material of an approved make. Ceramic materials will not be accepted. Fuse fittings shall be fully shrouded and it shall be possible to change the fuses without danger of contact with live metal. Fuse holder terminals shall be of the clamp type where the screw does not directly tighten onto the conductor. 8 Fuse fittings shall have basic sizes of 16, 32, 63, 100 and 200A and the fuse holders shall be able to accept fuse links of that rating on any BS rating down to the next basic size. 9 A mechanical indication device shall be built into the fuse to indicate operation/fail status. 10 All small wiring for voltmeters etc. from the busbars shall be via busbar mounted fuse holders containing 20 amp fuse links. The fuse holders shall be solidly bolted to the busbars. 3.2.8 Fuse Switches 1 Fuse switches where specified shall comprise flush/surface mounted heavy duty composite air break switches and fuse units complying with BS EN 60947-3 and fitted with fuses to BS EN 60269 and shall be rated and equipped as detailed. Composite units shall be contained within an enclosure of metal and shall be fitted with an earthing terminal or equivalent to enable the enclosures to be earthed irrespective of any means of connection such as is provided for attaching armoring or other metallic covering of the cable supplying the composite unit. 2 Fuse switch shall be capable of making, carrying and breaking current under normal circuit condition, which may include specified operating overload conditions and also carrying for specified time currents under specified circuit conditions such as those of short circuit. 3 The switch breaking capacity shall be related to AC 23 utilization category or other approved equivalent standard for 415 V 3 phase 50 Hz 4 wire operation for use on specified fault level and for service and site climatic conditions as described in section 16480 Factory Built Assembly (FBA). 4 BS EN 60269 complied HRC fuses shall be provided as a mean of overcurrent/overload protective device to protect the switch. The maximum rated current of the fuse with regard to the prospective short circuit current in the actual circuit shall be mentioned. 5 The fuse shall be connected after the switch so that a short circuit will not occur in the fusecombination, thus for an expected fault to take place after the combination fuse switch unit QCS 2010 Qatar Project Management 2 QCS 2010 Section 21 Part 3 Protective Devices Page 10 In the event of a fault this combination shall provide protection, permitting switching without, for example contact welding and preventing separation of main contacts in case of fault occurring during running. 7 The combination fuse switch unit shall be housed in an enclosure so constructed that the cover cannot be opened until the switch is fully opened and the construction shall be such that when the cover is opened a competent examiner can override the interlock and operate the switch. After such operation the cover shall be prevented from closing with the switch position indicator in a false position. 8 Switches shall be provided with mechanical ON/OFF indicators and operating handles. 9 Means shall be provided for locking the switch in the OFF position only. 10 The combination fuse switch unit shall be fitted with 2NO + 2 NC auxiliary contacts wired to the terminals. 3.2.9 Isolating Switches 1 The switch when used alone as explained above as an Isolator shall confirm to the utilization category AC23 and shall fully comply with the requirement specified for isolating functions specially the isolating distance in accordance with the applicable standard. 2 An Isolator shall be capable of opening and closing the circuit ON-LOAD with full voltage applied across the terminals. 3 The Isolator shall be capable of carrying currents under normal circuit conditions and carrying for specified time currents under abnormal conditions such as those of short-circuit. 4 All other features of the Isolator shall be same as specified above for combination fuse switch unit. 3.2.10 Stop Lock-off Push Buttons 1 Stop lock-off push buttons for motors shall be the mushroom headed red stay-put type with automatic latching, the units having to be key operated to be released. 2 Push buttons shall be housed in a surface mounting weatherproof enclosure to IP 65. 3 Push buttons shall be UV stabilised. 3.2.11 Control Relays/Auxiliary Relays/Interposing Relays 1 All auxiliary relays shall mainly comply with BS EN 116000 and BS EN 116205-7. 2 Where similar relays have different operating voltages and/or different contact configurations, they shall be non-interchangeable. 3 Voltage at nominal operating temperature and shall not „drop-out’ at greater than 60 % of the nominal coil voltage. 4 Relays shall be continuously rated and capable of sustaining a voltage 10 % in excess of the nominal coil voltage. 5 Relays shall be fully encapsulated and be of the plug-in type, with terminals protected to a minimum of IP2X. 6 Plug-in relays shall be fitted with transparent dust-proof covers. External connections shall be screw clamp terminals, which are easily accessible with the relay in position. QCS 2010 Qatar Project Management 6 QCS 2010 Section 21 Part 3 Protective Devices Page 11 Relays shall include the provision for manual operation. 8 The pin configuration of the relay shall be printed on the casing and on the bases in order to ensure correct pin alignment. 9 Relays shall be suitable for operation at plus 10% and minus 20% of their nominal rated voltage. 10 The contacts configuration shall be either normally open/normally closed or changeover contact combinations. 11 The contact material used in the Relay for general logic design shall be AgCdO. Specific applications requiring extra low switching current shall have GOLD Flash contacts for minimal voltage drop across the contacts. 12 It will not be permitted to use mixed voltages on the different contacts of a particular relay. If necessary additional relays shall be used by employing good engineering practices such as operation of add-on relay through auxiliary contact of main relay. 13 Relays Coil shall be vacuum impregnated ensuring satisfactorily operation for the adverse climatic conditions as specified. 14 The relays shall be mounted on DIN Rail. 15 Relays shall be secured to their bases by retaining bar or clip to prevent malfunction due to the relay being loosened in its base. 16 Care shall be taken to ensure that relay contacts and associated wiring are suitably fused protected. 17 All type of relays shall have a means of visual indication e.g. light emitting diode (LED) or neon bulb mounted within their clear covers connected directly across the relay coil to indicate when the relay is energized. These indicators shall be easily seen when the relay compartment door is opened. 18 A permanent means of identification shall be affixed to both relay and base in line with the circuit diagram reference. 19 Where remote supply voltages are used, a warning label engraved in English and Arabic shall be fitted, clearly identifying the source of supply. 20 The relay shall be designed for minimum 1 Million mechanical operation and 200,000+ electrical operations at rated load. 3.2.12 Protection Relays 1 Protection relays shall comply with BS EN 60225-6, BS EN 61810-1, IEC 255. 2 Secondary injection shall be easily possible by means of purpose-made voltage and/or current plug-in type test terminal blocks which automatically open circuit or short circuit the integral voltage transformers or current transformers respectively and provide termination’s for the test supply. Disconnection of any permanent wiring will not be acceptable. 3.2.13 Alarm System 1 Auxiliary relays and auxiliary contacts and circuit breakers shall be provided as necessary and if indicated to transmit alarm signals to remote control buildings. 2 Alarms shall be as indicated on the Contract Drawings and shall be selected from: QCS 2010 Qatar Project Management 7 QCS 2010 (a) (b) (c) Section 21 Part 3 Protective Devices Page 12 circuit breaker tripped power failure standby generator failed-to-start. Padlocks 1 Padlocks shall be provided for all handle operated circuit breakers, fuse-switches, isolators and the like. 2 Padlocks and keys shall be housed inside a safety key box located in the relevant electrical switch rooms, including padlocks and keys for lockable field equipment supplied from the switch-room. 3 Safety key boxes shall also be lockable using a master key. 3.2.15 Hours Run Meters 1 There shall be two counters provided for each motor. The one counter shall be nonresettable hour run meter, rotating disc type for measuring total operating period (accumulative) of a motor. The minimum size shall be 48 x 48 mm. The counting capacity shall be 99,999.99 hours. The color of the decimal digits shall be red while the color of other digits shall be white. 2 The second counter shall be provided for counting total (accumulative) number of start of motors 75kW and above. This shall be non-resettable, electronic type with permanent memory retention arrangement and LCD display to indicate Number of start of a motor. 3.2.16 Thermistor relay 1 All motors where recommended by the manufacturer or 30 kW and above shall be protected against excessive temperature, poor cooling, high ambient temperature, high starting frequency etc. by providing thermistors unless otherwise specified. 2 Thermistors shall be of PTC (Positive Temperature Coefficient) type made of platinum wire Pt100 having resistance of 100 ohms at 0 degree C. These shall be embedded in the stator winding/slot and the leads of the elements shall be brought out to a separate terminal block located within the junction box of the motor. 3 Thermistors shall have a tamper proof pre-set point and fast response time. 4 Thermistors shall be designed to include the following features:(a) (b) (c) (d) (e) (f) (g) (h) 5 tamperproof rapid responding UL/CSA recognized component eliminates nuisance trips field-proven Klixon design requiring no field adjustment allows full use of motor rating directly senses winding over-heating Thermistors shall protect the motor against the following conditions:(a) (b) (c) (d) (e) (f) locked rotor running overload single phasing voltage unbalance high motor ambient temperature blocked ventilation QCS 2010 Qatar Project Management 3.2.14 QCS 2010 Section 21 Part 3 Protective Devices Page 13 Thermistors have to be connected to a separate control unit that enables tripping of the motor through the starter contactor upon change of resistance of elements in the thermistor circuit beyond pre-determined value. 7 The wiring of the relay module shall be so done, that inhibit the starting of the pumps automatically even after the temperature limit sensors have cooled and reclosed the circuit. The facility shall be provided in the motor control centre to reset the control circuit manually, ensuring that a proper cause of overheating has been determined and corrected prior to the restart of the pumps in auto mode. 8 Additional to the sensing of winding temperature by the thermistor, means shall be provided to monitor the bearing temperature wherever possible and as recommended by the motor manufacturer. 3.2.17 Moisture and mechanical seal leakage protection 1 All submersible sewage pump motors shall be provided with a dedicated moisture and mechanical seal leakage protection relay. 2 The moisture sensing probes extended into the oil chamber located between the lower (outer) and upper (inner) seals to detect the presence of moisture in case of failure of outer seal. 3 The probes shall also detects water in the motor chamber and provide a warning prior to the water reaching the bearing or wound stator assemblies. The sensor leads must be connected to a moisture relay equipped with alarm contacts for indication. 4 The moisture detection relay shall be supplied by the pump motor manufacturer and to be free issued by the contractor to the Motor Control Centre Vendor together with detailed schematic diagrams and work instructions pertaining to the mounting and location of the relay. 5 The Motor Control Centre vendor shall strictly adhere to the wiring practices and works instructions as provided by the manufacturer. 3.2.18 Timers 1 Timers shall be plug-in or surface-mounting types; solid state microprocessor based employing CMOS IC technology. 2 Timers shall be suitable for operation on a nominal 240 V AC, 110V AC, 24 V AC/DC or other voltage as specified or deemed necessary for the safe operation. 3 Timers shall have linearly calibrated scales, in units of time, each scale division being a maximum of 5% of full scale. Repeat accuracy shall be within 0.5% of full scale. 4 Timers shall be provided with “energized” and “timed out” indicators. 5 Plug-in timers shall be fitted with transparent dust-proof covers. External connections shall be screw clamp terminals which are easily accessible with the timer in position 6 Timers shall be secured to their bases by retaining bar or clip to prevent malfunction due to the relay being loosened in its base. 7 The pin configuration shall be printed on the casing of the timer and on its associated bases in order to ensure correct pin alignment. 8 Timer shall be provided with 10 Amps. Rated output relay with DPDT contacts. QCS 2010 Qatar Project Management 6 QCS 2010 Section 21 Part 3 Protective Devices Page 14 9 Unless specified otherwise, timers shall be provided for circuits that require delay on operate, delay on release, and star-delta starting of a 3-phase induction motor. 10 Multifunction timing relay programmable where specified shall be provided to the satisfaction of the engineer. 11 The use of pneumatic timers, motor driven timers and other special timers shall be avoided unless specifically mentioned in the particular requirements and the same shall be subjected to the review and approval by the engineer. END OF PART Qatar Project Management QCS 2010 QCS 2010 Section 21 Part 4 Motor Starters Page 1 4. MOTOR STARTERS ..................................................................................... 2 4.1 GENERAL ...................................................................................................... 2 4.1.1 4.1.2 Scope References 4.2 PRODUCTS ................................................................................................... 2 4.2.1 4.2.2 4.2.3 4.2.4 4.2.5 4.2.6 Starters DOL Starters Star Delta Starters Auto Transformer Starting Slip Ring Rotor Resistance Starters Reduced Voltage “Soft Starters” 4.3 INSTALLATION ............................................................................................. 6 4.3.1 Earth Bonding 2 3 3 4 4 5 6 Qatar Project Management QCS 2010 2 2 QCS 2010 Section 21 Part 4 Motor Starters Page 2 4. MOTOR STARTERS 4.1 GENERAL 4.1.1 Scope 1 This Part includes the supply and installation of motor starters and associated equipment. 4.1.2 References 1 The following standards shall be followed BS EN 60439, IEC 439 BS EN 60947-4 BS EN 60947-1, IEC 947 Coding of indicating devices and actuators by colour and supplementary means Specification for low-voltage switchgear and control gear assembly Contactors and motor Starters Low Voltage switchgear and control gear 4.2 PRODUCTS 4.2.1 Starters 1 Motor starters shall be rated to carry the full load current of its rated duty at its most severe load conditions. All starters shall be capable of a minimum of 10 starts per hour at 100% full load torque unless otherwise specified. 2 Motor starters shall be rated to carry the full load current of its rated duty at its most severe load conditions. All starters shall be capable of at least 20 starts per hour at 100 % full load torque. 3 In accordance with the current QGEWC regulations, motors up to and including 11 kW shall be started direct on line. Motors above 11 kW shall incorporate assisted starting. 4 Motor starters shall be housed in a separate cubicle compartment of the relevant motor control centre and each starter cubicle shall contain the following components, or as otherwise indicated on the Project Drawings or Project Documentation. (a) (b) (c) (d) (e) (f) (g) (h) (i) (j) 1 no. triple pole ACB or MCCB or fuse switch, as indicated on the Project Documents, externally operated and interlocked with the cubicle door. There shall be provision for padlocking in the OFF position. 1 no. starter, comprising one of the following types, as indicated on the Project Drawings: (i) direct on line (ii) star/delta (iii) close transition star/delta (iv) reduced voltage “soft start” (v) rotor resistance (vi) auto - transformer 1 no. motor protection relay, as specified in Part 3 1 no. set of auxiliary relays and timers required to provide the necessary indication and control sequence 1 no. set of main motor terminals and auxiliary terminals for remote controls and indications. 1 no. set of terminals for remote lock-off stop push buttons 1 no. control circuit transformer, where applicable 1 no. anti-condensation heater 1 no. set of power factor correction capacitors with separate fuses for all drives above 11 kW, to give a power factor of not less than 0.85. Thermistor relays where applicable QCS 2010 Qatar Project Management BS EN 60073 QCS 2010 Section 21 Part 4 Motor Starters Page 3 5 The components of the starter shall be type tested and ASTA certified to achieve Type 2 coordination in accordance with IEC 947. 6 The following equipment shall be mounted on the door of the starter cubicle, or as otherwise indicated in the Project Drawings or Project Documentation. (a) (j) (k) 7 All starters shall contain a totally enclosed dust proof timer, or the operation will be controlled by a timer in the automatic section, which shall prevent pump(s) starting after a power failure until after a pre-set time has elapsed. The timer(s) or contacts shall be adjustable in the range 50 to 200 percent of the anticipated maximum delay which shall be taken as twice the total time required for all pumps to start and run steadily having been started consecutively. The timer(s) or contacts shall be set to give individual sequential start after a power failure with no drive starting until its predecessor has reached full steady running. 4.2.2 DOL Starters 1 DOL starters shall consist of a TP contactor for switching direct on line in accordance with BS EN 60947-4-1 and fitted with auxiliary contacts. 2 Contactors shall be selected for category AC-3 duty. 4.2.3 Star Delta Starters 1 Star-delta starters shall be provided with contactors as for DOL starters, arranged in such a manner to ensure the star contactor opens before the delta contactor closes. 2 The period of running in star and the transition time shall be controlled by adjustable solid state type timers. 3 For closed transition type star-delta starters, further requirements shall be wire wound or pressed sheet resistor banks of sufficient thermal rating to allow three (3) consecutive starts of 30 seconds period followed by a 15 minutes rest and another 30 seconds starting period. They shall also be of sufficient thermal rating to allow 10 starts per hour in line with the pump and starter specification unless otherwise specified. Resistance values shall be chosen to give a high starting current with low transient current. A thermal cut out shall be provided for transient resistance banks. Starter cubicles incorporating resistor banks shall be well ventilated and vermin proof with ventilation louvres. QCS 2010 Qatar Project Management (b) (c) (d) (e) (f) (g) (h) (i) 1 no. ammeter, 96 X 96, with 240° scale fitted with suppressed scale to read motor running and starting current, with an adjustable red pointer to indicate full load current. The scale range shall be such that normal full load current gives approximately 60% full scale deflection. 2 no. pilot lamps to indicate “SUPPLY ON” (Green) and “MOTOR RUNNING” (Red). 1 no. pilot lamp to indicate “MOTOR FAILED” (Amber) pilot lamps (a separate lamp for each motor fault conditions) 1 no. “Hand/OFF/AUTO” Selector switch 1 set “Start/Stop” push button 1 no. externally operated overload reset push button 1 no. motor and cubicle heater “OFF/AUTO” control switch, where applicable 1 no. electronic hour counter reading to 99999 hours with analogue display, memory and battery backup with reset button lamp test push button 1 duty label. QCS 2010 Section 21 Part 4 Motor Starters Page 4 Auto Transformer Starting 1 For auto-transformer starting there shall be provided magnetically operated starting, accelerating and running contactors operating under adjustable electronic timing devices. The auto-transformers shall limit the starting current to 4 times full load current (FLC) with 60%, 70% and 80% tappings. The auto-transformer starting system shall be capable of 10 starts per hour, each of 15 seconds operation time and a reset time of 2 hours at the end. The auto-transformer shall also be capable of starting the duty motor 10 times in an hour under actual operating conditions. 4.2.5 Slip Ring Rotor Resistance Starters 1 Where slip ring rotor resistance motor starters are employed the rotor resistance shall be of the metal grid type and shall limit the starting current to that specified for the size of drive. 2 For slip ring rotor resistance starting there shall be provided magnetically operated starting, accelerating and running contactors, operating under mechanical or electronic timing devices. 3 Rotor resistance shall be mounted in floor standing units, panel top units or integral panel units, complying with the following requirements: (a) floor standing units: (i) the rotor resistance may be mounted within floor standing cubicle constructed of 2 mm (minimum ) thick sheet steel of welded construction (ii) the cubicles shall be provided with adequate ventilation louvers and access to the resistance units shall be by means of a lockable, hinged front door (iii) the cubicle shall be arranged for cabling from below (iv) both the exterior and interior of the cubicle shall be stove enamelled to BS 4800 shade 14 E 53 and the exterior shall be provided with warning notices to indicate electrical hazard within (v) each cubicle shall be equipped with a heater which shall be continuously “on” while the associated resistance bank is de-energised (b) Panel Top Units: (i) the rotor resistance may be mounted within separate cubicles mounted on top of the control panel. These cubicles shall be identical in construction to the control panel and dummy cubicles shall be provided as necessary to ensure uniform height of the entire control panel (ii) the cubicles shall be provided with adequate ventilation louvers and access to the resistance units shall be by means of a lockable, hinged front door (iii) cable connections to the main control panel shall be via suitable cable glands to maintain the integrity of the control panel enclosure (iv) each cubicle shall be equipped with a heater which shall be continuously “on” while the associated resistance bank is de-energised. (c) Integral Panel Units: (i) the rotor resistance may be mounted within a cubicle with the control panel itself provided that: the resistance cubicle is adequately ventilated font and rear the resistance cubicle is provided with suitable cable gland entries to maintain the integrity of the control panel enclosure the resistance cubicle is located so that no electrical components are mounted above it the motor starter equipment is located in a separate, totally enclosed cubicle within the control panel 1 no. TP wound magnetic overload relay fully adjustable but set at the actual current setting required to trip under a stalled motor condition with the maximum time that the motor characteristic permits this condition to exist. QCS 2010 Qatar Project Management 4.2.4 QCS 2010 Section 21 Part 4 Motor Starters Page 5 Reduced Voltage “Soft Starters” 1 Solid-state reduced voltage motor starters shall be closed transition, shunt duty type with isolation contactor and bypass contactor. When the motor reaches full speed, the bypass contactor bypasses the soft starter power section. The solid-state power section shall consist of six silicon controlled rectifiers (two per phase connected back to back, in reverse parallel configuration) to provide soft start. The starters shall conform to the latest IEC Standards. 2 The starters shall use the current limit method of starting with the current adjustable between 150 percent and 425 percent of full load current of the motor. At turn-on, the control ramps up to the current limit in approximately 1 second and maintains that current until the motor comes up to full speed. If a problem exists and the motor fails to reach rated speed within a predetermined period of time, the control will shutdown. The starter shall provide a smooth, stepless acceleration and deceleration of the load from start to full speed and from full speed to stop. The starter shall be equipped with metal oxide varistor type surge suppressers across the SCR to protect against voltage transients and resistor/capacitor scrubber networks to protect against false firing of the SCR. Each SCR heat sink shall have a temperature sensor that shall shut the starter down in the event of an over temperature condition. When a starter failure occurs, the actual problem shall be indicated by an LED on the control panel front. 3 There shall be a overcurrent protective device, which shall provide over current protection and main disconnect function for the control unit. The position of the operating handle shall indicate “ON” or “OFF” position of the protective device and include provision for padlocking in the “OFF” position. This protective device shall be equipped with a shunt trip and shall trip when there is a SCR or plant power failure. Motor space heaters shall be energised when the motor is not running. 4 The reduced voltage starters shall be equipped with micro-processor controlled motor protection relays to control, monitor and protect the motors. The relay shall monitor three phase current and voltage and make trip and alarm decisions based on pre-programmed motor current and voltage conditions. Control functions shall include start detection, starter transition, incomplete sequence and number of starts per hour. The relay shall monitor and display load current of each phase, percent of full load current of each phase and running time. The relay shall protect the motor against time overcurrent, instantaneous overcurrent, underload, phase unbalance, earth fault, phase loss and phase reversal. 5 The manufacturer shall supply certified test results to confirm that the controller has been tested to substantiate designs according to applicable standards. The tests shall verify not only the performance of the unit and integrated assembly, but also the suitability of the enclosure venting, rigidity and bus bracing. In addition, the unit shall be factory tested in accordance with applicable standards. 6 Manufacturer shall be prepared to show proper evidence of having tested for noise immunity on both input and output power connections. 7 The softstarter shall be supplied factory configured ready to commission, without requiring any parametering or reconfiguration at site. 8 The softstarter shall have the following protective feature as minimum:(a) (b) (c) (d) (e) (f) (g) 9 over temperature overload jam stall phase Loss phase reversal shorted SCR The softstarter shall have the following control feature as minimum:(a) kick start 0-85% locked rotor torque – 0 to 2 seconds QCS 2010 Qatar Project Management 4.2.6 QCS 2010 (b) (c) (d) Section 21 Part 4 Motor Starters Page 6 ramp start 0-85% locked rotor torque – 1 to 60 seconds current limit start 0-85% locked rotor current – 1 to 60 S soft stop 0 to 60 seconds The softstarter shall be provided with high speed fuses as recommended. 4.3 INSTALLATION 1 The Contractor shall submit details of proposed equipment and method of installation to the Engineer and QGEWC for approval prior to commencement of installation work. 2 Provide all the motor control equipment installations, wiring installations and tests, including connections and interconnections for the electrical controls as indicated, specified and required. Assure proper fits for all equipment and materials in the spaces shown on the Drawings. The starter can be installed in a separate cubicle for MCC or can be an item in the Distribution Board, as per the Project Documentation. The installation procedures as applicable for MCC and DB shall also in general applicable for motor starter items. 3 Equipment shall be installed level and securely attached to the cubicle frames. The sections shall be joined together with bolts, nuts and washers to form a complete unit assembly. Floor standing equipment shall be installed on concrete plinths as shown on the Drawings. 4.3.1 Earth Bonding 1 Each panel board shall be individually bonded to main earth bar located in the electrical rooms. 2 Each panel section shall be cross bonded to adjacent panel section earthing terminal. END OF PART QCS 2010 Qatar Project Management 10 QCS 2010 Section 21 Part 5 Variable Speed Controllers Page 1 5. VARIABLE SPEED CONTROLLERS ............................................................ 2 5.1 GENERAL ...................................................................................................... 2 5.1.1 5.1.2 5.1.3 5.1.4 Description Standards Quality Assurance Warranty 5.2 PRODUCTS ................................................................................................... 4 5.2.1 5.2.2 5.2.3 5.2.4 5.2.5 5.2.6 5.2.7 5.2.8 5.2.9 Ratings Design Characteristics Control System Controller Keypad Communications Interface Fault Detection Protection Features Emergency Stop Control Drive Enclosures 5.3 INSTALLATION ............................................................................................. 7 5.3.1 5.3.2 5.3.3 Documentation Commissioning Training 4 5 5 6 6 6 6 7 7 7 8 8 Qatar Project Management QCS 2010 2 3 3 3 QCS 2010 Section 21 Part 5 Variable Speed Controllers Page 2 VARIABLE SPEED CONTROLLERS 5.1 GENERAL 5.1.1 Description 1 Variable Frequency Drives (VFD) shall be of the solid state, static, voltage source type, using minimum 32 bits microprocessor or the latest available, digital sine wave approximation Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) type. VFD’s shall be suitable for the particular application, controlling mainly pumps with variable torque characteristics. 2 The VFD and associated control equipment shall be housed within a cubicle forming part of the relevant Factory Built Assembly. A stand-alone control panel may however be provided depending on the design, if the application requires special ventilation arrangements, or due to space constrains within the FBA cubicles. Detailed technical proposals shall be submitted for the Engineer’s review and approval. 3 The VFD shall be of a proven design that provides high pump efficiency, high availability, minimum maintenance, substantial energy reduction and longer bearing and seal life at reduced speeds. 4 The VFD shall control the speed by employing advanced torque control techniques and auto tuning that measure and set all constant and critical parameters of the motor automatically. 5 The VFD cubicle to be considered as a starter with the only addition of VFD with display unit and keypad and therefore shall comply with the requirements as described for starters and FBA’s in QCS. 6 The contractor shall provide a properly matched pump - motor - drive system for the specific duty operating in conjunction with VFD considering load - torque characteristics, KW rating, efficiency, thermal capacity, power factor improvement etc. 7 The driving motor speed shall be variable between maximum speed at full load and at any intermediate speed down to a tenth of full load speed by means of a variable frequency from the VFD. The VFD shall provide a constant torque availability at any speed with a starting torque of 1.5 times full load torque at maximum speed. The VFD shall be capable of supplying the motor continuously at any frequency. 8 The VFD shall utilize a full wave bridge design incorporating diode rectifiers or semicontrolled bridge consisting of diodes-thyristors combination or 6-pulse/12-pulse converter (whichever satisfy regulations pertaining to reduced harmonics distortion) or the latest available technology. 9 A DC link choke-smoothing reactor shall be included to limit fault throughput. 10 The thyristors shall be chosen to have a rating of 2.5 times the normal peak working voltage. Voltage peak transients for every thyristor shall be suppressed by a capacitor/resistance network and excessively high rates of change of voltage (dv/dt) shall be limited by a "snubber" network. Voltage spikes, which may be detrimental to any solid state component or relay, shall be suppressed by suitable networks. 11 The thyristors shall be capable of maintaining continuously 10 per cent in excess of the current imposed by the maximum load conditions. Thyristors shall be protected against current overloads caused by malfunction of components or circuitry within the inverter or external loads. Overcurrent protection and rate of current rise (di/dt) in the thyristors shall be controlled by electronic current limiting devices, which shall cause trip current circuits to operate. QCS 2010 Qatar Project Management 5. QCS 2010 Section 21 Part 5 Variable Speed Controllers Page 3 Thyristor heat sinks shall be provided with thermostats, which shall effect tripping in the event of excessive temperatures occurring. 13 The printed circuit boards shall confirm to BS 4584 or other approved equivalent standard and connections by multi-way sockets suitably treated to avoid high resistances being formed between the plug and socket. 14 Anti-condensation heaters shall be provided complete with a hygrostat type switch with reasonable setting range (50-100%), which operates when the preset value of %RH is exceeded above dew point and have OFF/AUTO control on the cubicle front door. The heater shall not be in operation when the VFD is functioning. 15 It will be necessary to conduct field tests to measure the harmonics with all VFDs regardless of whether filters, reactors, chokes etc. are installed or not, running at 100 percent and 50 percent loads for the duration of at least 3 hours under each load condition. If drives don’t meet the specified performance, the contractor shall provide an acceptable solution at no extra cost. 16 The VFD shall be selected based on the following as the main advantages:(a) (b) (c) (d) (e) User friendly allowing the operator to configure the VFD at site with ease. Uniform motor running at all speeds. Power factor close to unity regardless of the speed of the motor. High overall system efficiency No increase of noise in the motor. 17 The VFD shall be arranged to prevent nuisance tripping due to failure of supply for a short duration (transient disturbances). 5.1.2 Standards 1 The drive shall conform to the requirements of IEC 146. 2 The drive shall comply with EMC requirements such as EC directive 89/336/EEC. 3 The drive shall conform to the guidelines outlined in the Electricity Association, London, Engineering Recommendation G.5/3 regarding harmonic distortion. The level of harmonic distortion shall not exceed 5 %. 4 The contractor shall carry out a harmonic assessment for the project and provide whatever corrective measures are necessary to ensure that the installations harmonic distortion does not cause deviations of the voltage characteristics other than those allowed by European Standard EN 5016 – Voltage characteristics of electricity supplied by public distribution systems. The contractor shall obtain QGEWC approval of the assessment and the corrective measures proposed. The contractor shall also provide cross-referenced confirmations from the machine/motor suppliers and the control gear/soft starter or VSD manufacturers that the equipment they are supplying is totally mutually compatible. 5 Total Harmonic distortion (THD) shall be limited to lowest level under 5% as per G5/4 in order not to create stresses and resultant problems for the plant’s distribution systems. It may therefore be necessary to provide active type a harmonic filter to achieve the required limits as set by QGEWC and/or IEEE519. 5.1.3 Quality Assurance 1 The suppliers manufacturing facility shall be certified to the ISO - 9001 series of standards from the International Standards Organisation. 5.1.4 Warranty 1 The drive shall be warranted for a minimum of three years by the manufacturer. QCS 2010 Qatar Project Management 12 QCS 2010 Section 21 Part 5 Variable Speed Controllers Page 4 PRODUCTS 5.2.1 Ratings 1 The VFD shall convert 415 V - 3 Phase - 50 Hz, power to an adjustable voltage and frequency for controlling the speed of the pump. The output voltage shall vary proportionally with the output frequency to maintain a constant volts/hertz value up to a nominal frequency. Above nominal frequency, the output voltage shall remain constant. 2 The incoming line power factor shall range between 1.0 and 0.95, lagging, over the entire operating speed range. 3 The drive shall be capable of being stored at a temperature between -0 °C and 70 °C. 4 The drive shall be capable of operating in ambient temperature between 0 °C and 50 °C with a relative humidity of up to 95 % (non-condensing). 5 The drive shall be capable of operating at altitudes up to 200 metres above sea level. 6 The drive shall be capable of operating at a minimum efficiency of 95% at full load and full speed. 7 The rating of the drive unit must be sufficient for the continuous maximum rating of the motor and not its running load. 8 The modulating control scheme shall closely approximate actual sine wave current throughout the speed range of the drive. 9 The frequency resolution of the VFD shall be 0.01Hz. 10 The VFD shall not be sensitive to line notching from other VFD operating nearby. 11 The VFD shall be capable of passing through a momentary power outage of 3 cycles without causing the drive to trip. 12 The VFD shall have an adjustable IR compensation (voltage boost) control capable of providing 100% starting torque from the motor. The control shall be adjustable and provide the additional voltage only at the frequency range required starting the motor. 13 Upon restoration of power following a power loss, if the VFD status is healthy, the VFD shall be capable of re-starting upon receiving a start signal from the main processor. 14 The VFD shall continuously monitor its output current and frequency. Should the drive be operating in current limit or below 10 Hz for 10 seconds (stall condition), the VFD will shut down. The VFD shall allow site configuration of the parameters to match the application requirements. 15 The VFD shall have the capability to avoid up to five critical operating ranges. The critical operating ranges (skip frequencies) shall have selectable bandwidth, configurable via the operator interface. 16 The VFD shall be capable of operating with the output open circuited. 17 The VFD shall be capable of regenerating power from the motor to the DC bus for controlled deceleration. The maximum deceleration rate shall be determined by the losses in the drive system. The deceleration rate shall be constant and independent of motor speed. QCS 2010 Qatar Project Management 5.2 QCS 2010 Section 21 Part 5 Variable Speed Controllers Page 5 Design Characteristics 1 The VSD shall have a fixed and alternatively variable V/f curve characteristic suitable for the required application. 2 The VSD shall be capable of varying the motor speed from a maximum speed at full load and at any intermediate speed down to 10% full load speed. 3 The drive shall be designed to be selectable for variable or constant torque. When selected for constant torque, the drive shall supply 150% of rated current for up to one minute. When selected for variable torque the drive shall supply 115% of rated current for up to one minute. 4 The VSD shall employ a pulse width modulated (PWM) inverter system with insulated gate bipolar transistors (IGBT) to minimise audible motor noise and increase overall performance. 5 The drive shall be designed to have an adjustable PWM carrier frequency with a minimum range from 2k Hz to 8k Hz to minimise audible motor noise. 6 The drive shall be optimised for 4k Hz switching frequency at 44 kW (60 HP) or less and 2 K Hz at 55 kW (75 HP) and larger. 7 The drive must be capable of switching on to a motor already rotating in either direction. 8 The starting arrangement must include a ramp speed control, to achieve starting currents not exceeding normal full load current. 5.2.3 Control System 1 The VFD shall have self-diagnostic features on power-up to validate memory, analogue reference, communication link, dynamic breaking if any, and control power etc. 2 The VFD design shall include SCR heatsink construction for heat transfer 3 The VFD shall include semiconductor metal oxide varistors (MOVs) or other approved equivalent method to the approval of the Engineer for protection against voltage surges. 4 Other built-in features of the VFD shall be PID, auto start, multiple pump control, reverse run protection and restart after instantaneous power failure. 5 The VFD shall self configure to the main operating voltage and frequency. 6 Upon power up, the VFD shall first check availability of connected motor and then update its memory by storing the new data, compare the data, auto tune by optimizing the operating characteristics and run the motor. 7 The VFD shall be factory configured and preset requiring minimal site adjustment during commissioning. 8 The VFD output frequency shall be controllable between 0 – 120 Hz. 9 An AC pre-settable fault current limiting facility shall be provided to ensure that when a setting is exceeded voltage and frequency are automatically controlled. 10 The VFD shall facilitate field adjustment of the following parameters as minimum:(a) (b) (c) (d) (e) The motor acceleration 0-600 seconds The motor deceleration 0-600 seconds The voltage to frequency ratio boost in proportion to load torque Compensation for motor slip from 0-5 per cent with varying load torque Minimum frequency set control QCS 2010 Qatar Project Management 5.2.2 QCS 2010 (f) (g) Section 21 Part 5 Variable Speed Controllers Page 6 Maximum frequency set control Presentable current limit facility The VFD memory shall retain and record, run and fault status with a minimum of 8 last fault conditions. 12 The contractor shall furnish details of specific installation and cable lengths to the manufacturer of the VFD and obtain in writing, the recommended size, type and specification of power and control cables used between the VFD and the motor. 13 The VFD cubicle shall be provided with additional control and accessories if any are deemed necessary to meet the operating logic as described in the particular requirement. 14 The VFD shall include any additional protective features not detailed in the specification but recommended by the manufacturer in order to avoid damage to the VFD or Motor. 5.2.4 Controller Keypad 1 The VFD shall be provided with a unit mounted but detachable LCD display unit, provided with a three metre length of cable, suitable for mounting on the cubicle door. The VFD shall allow the program stored in one drive to be copied to another drive by using the display unit and supplied software. Interconnecting cables and associated accessories together with a user manual must accompany the VFD. 2 All parameters shall be password protected to prevent tampering and unauthorised changes. 5.2.5 Communications Interface 1 The drive shall incorporate an RS 485 serial communications interface to allow full drive control, programming, monitoring and diagnostics, including access to history record. 2 The VFD shall be provided with communication interface and facility to integrate the operation of the system. The facility employing communication protocols e.g. profibus, modbus etc. shall be compatible with other system equipments such as the PLC, RTU etc. 3 The contractor shall provide a suitably sized programming device (laptop) complete with all necessary connection cables, software and licences for configuration and maintenance of the VFD’s. 5.2.6 Fault Detection 1 The drive shall keep a record of the last ten trips, plus a 100 sample history record of up to ten pre-defined parameters to enable fast diagnosis and minimum down time. Automatic printout of history record to a serial printer shall be an available feature. 2 The VFD shall have a programmable fold back function that will sense a controller/motor overload condition and fold back the frequency to avoid a fault condition. 3 A dedicated microprocessor based electronic motor protection system to be provided for the protection of the motor. 4 The VFD shall have UL listed solid state I²t protection and class 10 or equivalent overload protection as per BSEN 60947 meeting Type 2 co-ordination. Semiconductor fuses providing the required protection may be permitted to use as approved by the engineer 5 The VFD shall be protected against short circuit between output phases and ground, analog outputs and logic circuit. 5.2.7 Protection Features 1 The drive shall incorporate the following protective functions: QCS 2010 Qatar Project Management 11 QCS 2010 (a) (b) (c) (d) (e) (f) (g) (h) (i) Section 21 Part 5 Variable Speed Controllers Page 7 active limiting of fundamental current by frequency fold back on acceleration loads and frequency hold on decelerating loads overcurrent protection short circuit protection fast acting supply fuses DC intermediate bus undervoltage DC intermediate bus overvoltage power section overtemperature earth fault protection without damage power section faults. The drive shall be protected against supply-phase loss and mains discontinuity. 3 The drive shall have a selectable auto-restart after trip. 4 The drive shall be designed to shut down with no component failure in the event of any of the above fault conditions arising. 5.2.8 Emergency Stop Control 1 The drive shall incorporate facilities to allow the connection of an Emergency Stop Pushbutton to ensure effective direct stopping of the drive if dangerous situations arise. The means provided should include direct connection to an air-break device e.g. a contactor, arranged such that its opening on-load: (a) (b) (c) does not inhibit any in-built deceleration provided by the variable speed controller does not produce additional safety hazards does not cause damage to the controller. 2 Such contactors shall be to BS EN 60947-1 with utilisation category AC-3. 5.2.9 Drive Enclosures 1 Drive enclosures shall generally be fabricated in accordance with the requirements for motor control centres specified in Part 2. 2 The drive enclosure shall have a protection rating of IP 31 minimum to BS EN 60947-1. 3 Where necessary, forced cooling shall be provided incorporating a visual indication on the front of the cubicle door in the event of a cooling system failure. 4 Ventilation grills shall be fitted with sand trap filters. 5 Anti-condensation heaters shall be provided with a thermostat and have OFF/AUTO control on the cubicle front door. The heater shall not be in operation when the inverter is functioning. 5.3 INSTALLATION 5.3.1 Documentation 1 The following documentation shall be provided: (a) (b) (c) (d) (e) (f) (g) (h) load de-rating (with tender) harmonic distortion (with tender) circuit diagrams maintenance instructions fault diagnosis parts list with part numbers commissioning instructions general arrangements drawings QCS 2010 Qatar Project Management 2 QCS 2010 Section 21 Part 5 Variable Speed Controllers Page 8 A recommended spares list for two years continuous operation shall be submitted at the time of tender. Where multiple, identical units are being supplied a rationalised list, i.e. not a summation of individual drives, requirements, should be produced. 5.3.2 Commissioning 1 The manufacturer of the drive system shall have a factory trained service representative residing in the Qatar for commissioning, programming and to provide training and after sales service. 2 The representative shall be trained in the installation, maintenance and trouble-shooting of the equipment specified and shall assist the Contractor to set-up and commission the variable speed motor drives and controls. 3 System validation tests shall be performed on all VSD’s. 4 The integrated site test on the VFD, motor and all other associated devices shall be conducted to verify the input and output current, voltage, frequency, power factor, acceleration and deceleration rate etc. in accordance with the operating characteristics as approved by the Engineer. 5 Test VFD at different operating conditions by adjusting parameters (25, 50, 75 and 100%). Record the performance and verify. 6 The power system shall be tested for harmonics, line notching and for RFI/EMI in cable circuits and in the air. 7 Tests shall be performed during normal plant operation and during operation with the emergency generator. 8 The test results so obtained shall be used to calculate the Total Harmonic Distortion (%THD) and compare the same with IEEE 519 and QGEWC regulation. 9 The manufacturer's engineer or their trained and qualified engineer working full time with the local supplier shall conduct all tests on site. 10 Upon completion of site tests a duly signed report listing all tests and checks, together with all supporting documents and drawings where applicable, shall be submitted to the Engineer for review. The Owner’s representative shall be invited to witness the tests. 11 Submit all test reports, drawings and supporting documents to the Engineer and QGEWC and obtain written approval from both prior to the system being accepted by the Owner. 5.3.3 Training 1 The AC drive manufacturer shall provide an on site training program for the operating personnel. This program shall provide operating and instruction manuals, training in equipment operation, and troubleshooting of the AC drive. The training program shall include, but not be limited to: (a) (b) (c) (d) (e) (f) Instruction on the basic theory of pulse width modulation control Instruction on the layout of the variable frequency controller indicating the location and purpose of each component instruction on troubleshooting problems related to controller installation and removal of printed circuit boards actions to take under failure of controller necessary cleaning of component parts. END OF PART QCS 2010 Qatar Project Management 2 QCS 2010 Section 21 Part 6 Cables and Small Wiring Page 1 6. CABLES AND SMALL WIRING ..................................................................... 2 6.1 GENERAL ...................................................................................................... 2 6.1.1 6.1.2 6.1.3 6.1.4 6.1.5 Scope References Quality Assurance Submissions Products Delivery, Storage and Handling 6.2 PRODUCTS ................................................................................................... 4 6.2.1 6.2.2 6.2.3 6.2.4 Performance Requirements for Environmental Conditions Cables Sundries Jointing 11 kV, L.V. and Pilot Cables 6.3 INSTALLATION ........................................................................................... 10 6.3.1 6.3.2 6.3.3 6.3.4 6.3.5 6.3.6 6.3.7 6.3.8 General Cable Trays Spacing Between Cables Trench Depth Cable tiles Removal of Existing Cables Ducts Quarry Scalping 4 4 7 9 10 14 15 15 15 15 16 16 Qatar Project Management QCS 2010 2 2 3 3 3 QCS 2010 Section 21 Part 6 Cables and Small Wiring Page 2 6. CABLES AND SMALL WIRING 6.1 GENERAL 6.1.1 Scope 1 This Part specifies the general requirements for power cables and small wiring systems. It shall be read in conjunction with other parts of the Project Documentation. 2 Related Parts and Sections are as follows: General Provisions for Electrical Installations Conduits Trunking Cable Trays Wiring Accessories and General Power Testing 6.1.2 References 1 Cables and wires shall comply with the following standards as appropriate: BS 1442 ........... Galvanized mild steel wire for armouring cables BS 2484 ........... Straight concrete clay ware covers BS 2897 ........... Aluminium strip armour for cables BS 3506 ........... Unplasticised PVC pipe for industrial purposes BS 4066 ........... (IEC 332) Tests on electric cables under fire conditions BS 4660 ........... Unplasticised polyvinyl chloride (PVC-u) pipes and plastic fittings of nominal .............. sizes 110 and 160 for below ground gravity drainage and sewerage BS 5308 ........... Instrumentation cables. BS 5467 (IEC 502) Cables with thermosetting Insulation for electricity supply for voltages of up to and including 600/1000 V and 19000/30000 V BS 6004 ........... (IEC 227) PVC insulated cables (non-armoured) for electrical power BS 6007 ........... Rubber insulated cables for electric power and lighting BS 6207 ........... (IEC 245) Mineral insulated cables. BS 6234 ........... Polythene insulation and sheath for cables. BS 6346 ........... PVC insulated cables for electrical supply. BS 6360 ........... (IEC 228) Copper conductors for cables. BS 6500 ........... (IEC 227) Insulated flexible cords. BS 6622 (IEC 502) Cables with extruded cross linked polyethylene Insulation, for rated voltage 3800/6000 V up to 19000/30000 V BS 6746 ........... PVC Insulation and sheath of electric cables BS 6746C ........ Colour chart for insulation and sheath of electric cables BS 6899 ........... Rubber insulation and sheath of electric cables BS 7671 ........... Requirements for electrical installations BS EN 29453 ... Soft solder alloys-chemical composition and forms ISO 9000 ......... Quality management and assurance standards 2 Cable terminations shall comply with the following specifications: BS 1858 ........... Bitumen based compounds for electrical purposes BS 4579 Performance of mechanical and compression Joints in electric cable and wire connectors BS 6121 ........... Mechanical cable glands for elastomer and plastic Insulated cables BS 6910 Cold pour resin compound and heat shrink cable joints in the voltage range up to 1000 V AC and 1500 V DC QCS 2010 Qatar Project Management This Section Part 1 Part 7 Part 8 Part 9 Part 10 Part 23 QCS 2010 Section 21 Part 6 Cables and Small Wiring Page 3 6.1.3 Quality Assurance 1 The Contractor shall determine the correct size of cables to be used for the equipment selected, based on current rating and voltage drop, as relevant, after taking into consideration: (a) (b) (c) (d) (e) (f) (g) type of cable and wire ambient conditions method of installation the disposition of each cable relative to other cables fault power level protective device ratings motor circuit voltage drop during starting. Voltage drop and current ratings shall be calculated according to QGEWC Regulations or BS 7671 and IEE regulation, whichever is more stringent. 3 All cables and wires shall be suitable for installation and continuous service in the ambient conditions described in Part 1, and shall be manufactured to ISO 9000 or equivalent. 4 Approximate cable route lengths and equipment power ratings indicated on the Project Drawings shall be for calculating cable sizes for tendering purposes. The Contractor shall determine exact cable lengths from site measurements and calculate cable size from the power ratings of the actual equipment being proposed. The Contractor shall be responsible for any increase in costs or design work associated with proposed equipment which has different electrical characteristics than the equipment on which the design was based. 5 Cables from manufacturer whose product have been in satisfactory use in similar services in the state of Qatar for not less than 5 years shall be used only. Certificate of origin shall be submitted with the offer. 6.1.4 Submissions 1 Shop Drawings and Product Data: (a) (b) (c) submit full technical details including cable sizing calculations and catalogue information of each type of cable or wire proposed for the Engineer’s approval before ordering submit copy of test certificates from the manufacturer or an independent testing authority confirming that cables comply with the Specifications submit exact route of the cable runs and relevant Sections in the shop drawings, including fixing details, termination details etc. 6.1.5 Products Delivery, Storage and Handling 1 Reference Part 1. 2 Each drum length of cable shall be allotted a distinct and separate reference number. This number shall appear on the test certificates covering the respective length of cable and shall also be clearly marked on the cable drum. 3 The Contractor shall advise the Engineer upon delivery to site of each drum length, quoting the reference number. The test certificates shall be handed to the Engineer for examination and approval. 4 All cables shall be delivered to site with the manufacturer’s seals, labels or other proof of origin intact. These labels and seals shall not be removed until the cable is required for use and shall be retained for inspection by the Engineer. 5 The Contractor shall be responsible for the off-loading and handling of the cables on site, and shall ensure that cables are delivered to site on drums and properly protected against QCS 2010 Qatar Project Management 2 QCS 2010 Section 21 Part 6 Cables and Small Wiring Page 4 mechanical damage. Where lengths are cut from cables, the open cable ends shall be sealed. PRODUCTS 6.2.1 Performance Requirements for Environmental Conditions 1 The Contractor shall be aware of the need to supply and install all wire and cables for this Contract which are most suitable for the special environmental conditions prevailing in Qatar. 2 All conductors shall have good fatigue resistance and not be subject to breaks due to nicks or cuts when terminating. 6.2.2 Cables 1 Unless otherwise specified, cables and wires of the following specified voltage ratings shall be used as indicated. (a) (b) (c) (d) (e) (f) 2 General: (a) (b) (c) (d) (e) (f) (g) (h) 3 conductors shall be high conductivity copper, to BS 6360 (IEC 228) unless otherwise indicated copper conductors shall be stranded signal control cables shall have solid conductors flexible cords shall have fine stranded conductors conductor sizes shall be metric. Conductors with cross sectional areas smaller than those specified will not be accepted insulation for each conductor shall be colour coded or otherwise identified as required by the Regulations. Colour coding shall be maintained throughout the installation the current carrying capacity of conductors has been determined in accordance with the specified Regulations, the specified type of insulation and the expected conditions of installation all cables shall be as far as practicable, of one manufacturer only. All cables shall comply with the relevant IEC/BS. 600/1000 V rated PVC Insulated armoured cables. (a) (b) (c) (d) (e) (f) 4 6350/11000 V rated cables : 11kV ring and radial circuit 600/1000 V rated cables : Main and sub-main distribution panels, motor control centres, circuits serving process equipment 450/750 V rated cables : Final sub-circuit supplies for lighting, socket outlets, etc. 300/500 V rated cables : Instrumentation 250 V rated cables : Extra low voltage wiring, communication circuits where the maximum voltage is 50 V. Special screened and : Music/paging systems, Cable and TV system cable twisted pair conductors circuits PVC/SWA/PVC cable: 600/1000 V Grade, to BS 6346 conductor: Annealed high conductivity copper, stranded, shaped and laid in an approved manner armour: Single layer of galvanised steel wires for multicore cables insulation: Colour coded to BS 6746C PVC for sheath and insulation to BS 6746 cables shall be terminated with compression glands as specified below, giving adequate mechanical support by locking on the armour and ensuring a high earth continuity. PVC Insulated PVC Sheathed (PVC/PVC) Cable. (a) to BS 6346, 600/1000V Grade, or to BS 6004, 300/500 V Grade QCS 2010 Qatar Project Management 6.2 QCS 2010 (b) (c) (e) (e) 5 (b) (d) cable shall be to BS 6004, rated 450/750 V, with high conductivity copper conductors and PVC compound insulation. Colour coding shall be in accordance with table 51 A of BS 7671 wires shall be continuous from outlet to outlet and no splice shall be made except within outlet and junction boxes. A separate neutral wire shall be provided for each circuit. Wires shall be left sufficiently long enough (minimum 150 mm) to permit making final connections. to BS EN 60702 : Part 1, rated 600/1000 V cable shall comprise of a pressure packed magnesium oxide insulation contained within a continuous soft ductile copper sheath and copper conductors embedded in the dielectric in standard formation cable termination kit shall comprise of conductor insulation of neoprene sleeving retained by cone shaped beads beneath a fibre sealing disc. Each conductor shall be identified with regard to phase etc., by means of sleeving placed over the neoprene insulation cable seals shall comprise of screw-in-pot type seals, with brass ring glands designed to accommodate the pot seal. 2 for cable up to 6 mm : two screw pinching type 2 for cable over 6 mm : grip lug type cable sockets brass saddles: purpose made, two fixing screw type. Heat Resistant and High Temperature cable: (a) (b) to BS 6500, or BS 6004 300/500 V grade, designated EPR (ethylene polypropylene rubber) insulated HOFR sheathed, 85 °C or EPR insulated OFR sheathed, 60 °C. Conductor(s) shall be flexible class 5 tinned copper to BS 6360. Insulation shall be type GP.1 to BS 6899. Outer sheath shall be HOFR (heat, oil, fume resistant) or OFR (oil and fume resistant) sheath type RS3 to BS 6899 and flame retardant to BS 4066 Part 1, temperature rating 60 ° or 85 °C high temperature cable shall be to BS 6500 or BS 6007, designated 300/500 V grade silicone insulated glass braided, 180 °C. Conductors shall be flexible class 5 tinned copper to BS 6360. Insulation shall be silicone rubber type EI 2 to BS 6899. Outer sheath shall be treated glass fibre braid, temperature rating 180 °C. Flexible Cable: (a) (b) 10 flat twin and three core cable shall be to BS 6004 and incorporate an earth conductor placed between the red and black cores for two core cable and between the yellow and blue cores for three core cable conductor: annealed high conductivity copper, stranded, shaped and laid in an approved manner insulation: Colour coded to BS 6746C PVC for sheath and insulation : to BS 6746 Terminals: (a) (b) (c) 9 Page 5 to BS 6007, or BS 6500, rated in accordance with manufacturer’s tables flexible cables subject to excessive heat shall be insulated as (8) above, (a) or (b) as per the Project Documentation requirement. 600/1000V rated XLPE Insulated Cable (a) (b) (c) to BS 5467, 600/1000V grade, designated XLPE/SWA/PVC for armoured multicore cable, and XPLE/PVC for unarmoured cable conductors : plain annealed copper to BS 6360 cable shall comprise of plain copper, stranded circular conductors insulated with an adequate thickness of extruded cross linked polyethylene (XLPE) QCS 2010 Qatar Project Management (c) 8 Cables and Small Wiring Mineral Insulated Cable: (a) (b) 7 Part 6 Single core PVC Insulated Wires: (a) 6 Section 21 QCS 2010 (d) (e) (f) (g) (h) (i) (i) (b) (c) (d) (e) (f) (e) (f) (g) (h) (h) conductors shall be laid up together and warmed circular with suitable performed fillers and warnings, bound with polythene terephthalate (PTP) tape and covered with an extruded PVC sheath, minimum 1.4 mm thick for multicore cable armoured multicore cable shall have steel wire armouring and extruded sheath of black PVC armoured single core cable shall have aluminium wire armouring and extruded sheath of black PVC outer sheath of single core cables shall be at least 2.5 mm thick conductor screen : non-metallic comprising either semi-conducting tape or a layer of extruded semi-conducting material prevent void formation in insulation by careful control of its passage through temperature graded water baths cable shall be terminated with compression glands as specified below, giving adequate mechanical support by locking on the armour and ensuring high earth continuity. cable shall be armoured type, rated 6350/11000 Volts, and shall comply with BS 6622. Single core cable shall be designated 11 kV XLPE/AWA/PVC. Multi-core cable shall be designated 11 kV XLPE/SWA/PVC conductors shall be stranded copper complying with BS 6360, covered with a semiconducting screen extruded on to the conductors insulation shall be extruded cross linked polyethylene suitable for continuous operation at 90 °C, able to accept a final temperature of 250 °C in the event of a short circuit, and covered with a screen consisting of an extruded semi-conducting layer and a copper tape layer armoured cables shall have a secure bedding, over the core or core assembly, for the armour. For single core cable, the bedding shall consist of a PVC sheath. For multi-core cable, the bedding shall consist of non-hygroscopic fillers single core cable shall have aluminium wire armour. Multi-core cables shall have galvanised steel wire armour. Cable shall be covered with a red coloured PVC sheath electrical design stress at any point in the insulation shall not exceed 3 kV per mm to BS 5308 part 2, type 2,300-500 V single copper conductor 1/0.8 mm polyethylene insulation individual screen of aluminium backed polyester tape with tinned copper stranded drain wire collective screen of aluminium backed polyester tape with tinned copper stranded drain wire extruded PVC bedding galvanised steel wire armour PVC outer sheath, gray core identification as BS 5308 Part 2. Instrumentation Cables - Digital Signals: (a) (b) (c) (d) (e) (f) (g) (h) 14 Page 6 Instrumentation Cables - Analogue Signals: (a) (b) (c) (d) 13 Cables and Small Wiring 6350/11000V Cable (a) 12 Part 6 to BS 5308 part 2, type 2 300-500 V single copper conductor 1/0.8 mm polyethylene insulation collective screen of aluminium backed polyester tape with tinned copper stranded drain wire extruded PVC bedding galvanised steel wire armour PVC outer sheath, Gary Core identification as BS 5308 Part 2. Pilot cables shall comply with following requirements: QCS 2010 Qatar Project Management 11 Section 21 QCS 2010 (a) (b) (c) (d) (e) (f) 15 Cables and Small Wiring Page 7 Pilot cables shall be PVC insulated multi core cables to be used for: (i) Standard pilot wires protection schemes (ii) Telecommunication purpose. Conductors shall be stranded copper, plain annealed and in accordance with BS 6360. Core insulation shall be PVC complying with requirements of BS 6746. It shall be applied by an extrusion process and shall form a compact, homogenous body of uniform thickness. Insulation thickness shall be in compliance with BS 6346. Core identification shall be by one of the following: (i) Number printed on the core insulation (ii) Colour, 4mm cores having colours Red, Blue and Black. Bedding shall be compliance with BS 6346. The cables shall have a single layer of galvanised steel wire armour of diameter 1.6mm in accordance with BS 6346. The oversheath shall be of black PVC in compliance with BS 6746 Type 1 compound. It shall have a minimum thickness of 1.7mm and shall be in general compliance with BS 6346. Source Tests on Cables (a) Provide test certificates against each drum and /or cable length. These shall include:(i) (ii) (iii) (iv) 16 Part 6 high voltage D.C. insulation pressure test, between cores, each core to earth, metallic sheath or armour as applicable. insulation resistance test. core continuity and identification. conductor resistance test. Field Tests on Cables (a) (b) (c) inform the Engineer prior to the testing of the cables and be responsible for liaising with any other contractor to whose equipment the cables may be terminated to ensure that all parties concerned are aware of the impending tests, to guarantee the safety of personnel and that the isolation of any equipment has been completed. Any special isolation or preparation required to be carried out before cable testing can be completed, shall be carried out by the Contractor responsible for that equipment. All tests shall be carried out by the Contractor and supervised by the Engineer. All cables shall be tested in accordance with the latest QGEWC requirements and the relevant BS and IEE regulations for the class of cable. QGEWC shall be given the opportunity to witness the testing of high voltage cables and these shall be tested in accordance with their specific requirements. demonstrate correct phasing of cores in all cables throughout the works and test the insulation of all cables, both between the cores and between the cores and earth, during installation with a 500-volt insulation tester. 6.2.3 Sundries 1 Cable Jointing and Termination: (a) (b) (c) (d) joints in wires and cable shall be avoided wherever possible. Joints in flexible cables and cords are not permitted joints and terminations of all power cables shall be made by skilled cable jointers approved by the Engineer no reduction in the number of strands of a cable core shall be allowed at a cable joint or termination ferrules, compression connectors and bare portions of cable core resulting from a jointing or terminating process shall be insulated with an approved type of insulating tape or heat shrinkable tubing after completion of process. Such insulating tape or heat shrinkable tubing shall have equal or better electrical and mechanical properties than those of the original insulation removed, and shall be adhered to the cores etc. securely and permanently. The final thickness shall be in smooth contour throughout the whole length QCS 2010 Qatar Project Management (g) Section 21 QCS 2010 (e) (f) (g) (h) (i) (j) 2 Page 8 every compression joint shall be of a type which has been the subject of a test certificate as described in BS 4579. When a compression joint is made, the appropriate tools specified by the manufacturer of the joint connectors shall be used. a circuit protective conductor having adequate cross sectional area and of same material as the phase conductors shall be installed and connected to maintain the effectiveness of the earth continuity across every cable joint all cable jointing and termination shall be witnessed by the Engineer sufficient spare cable shall be allowed to remake the joint or termination above ground cable joints and terminations shall be accessible cable cores shall pass through glands or termination boxes directly to equipment terminals, without crosses if practicable. straight through joints for copper conductors: Where permitted by the Engineer, conductors shall be jointed by approved type compression connectors using the appropriate tools and connectors joints shall be made core-to-core. Joints Boxes and Termination Boxes (a) (b) (c) (d) malleable cast iron boxes for joints in all power cables shall be compound filled and of adequate size. The boxes shall be fitted with suitable armouring clamps and glands. The armouring of the cables shall be terminated at the armouring clamps and the inner sheath shall pass through the gland. Self amalgamating tapes shall be applied to give fully screening insulation reinstatement where the insulation is screened the box and compound shall be at the correct temperature before the compound is poured to allow total adhesion between the compound and the box. The compound shall then be allowed to cool and topped up before the box is closed. No air locks shall be formed within the box with the consent of the Engineer, plastic shells fitted with suitably sized armour bond and filled with an approved type of cold pouring encapsulating compound to BS 6910 may be used as an alternative to the compound filled cast iron joint boxes for jointing PVC-insulated power cables. In such cases, the complete jointing kit, including plastic shell, compound, insulating tape etc. shall be from the same proprietary manufacturer who is specialised in manufacturing products for this purpose. The jointing methods and procedures, as laid down by the manufacturer, shall be followed in strict accordance MICC mains cable: joints shall be suitably sized galvanised malleable iron adaptable box with glands and fixed base mechanical clamping connectors of approved design. For external use the jointing box shall be enclosed in a second galvanised box with glands, filled with encapsulating compound Cable Glands (a) (b) (c) (d) (e) (f) 5 Cables and Small Wiring cable glands shall be used for terminating cables to switch gear, switch boards, motor control centres, motors and other equipment they shall be brass compression glands and comply with the relevant part of BS 6121, except for MICC cables, which shall comply with BS 6207 Part 2. glands for armoured or screened cables shall have suitable clamps external compression glands shall have close fitting PVC shrouds earthing for armouring and metallic sheaths: suitable brass or copper clamps, and copper strip conductor in accordance with QGEWC requirements, and not less than 2.5 sq. mm cables forming part of a LAN or structured cable system shall be terminated to floor plates or wall sockets compatible with the media interface connector specified for the particular network being used. Cable Sockets: (a) (b) shall be correct size for type of cable shall be sweating type, or an approved crimping type used with an approved crimping tool QCS 2010 Qatar Project Management (b) 4 Part 6 Joints (a) 3 Section 21 QCS 2010 (c) 6 Section 21 Part 6 Cables and Small Wiring Page 9 sweating sockets for conductors 70 sq. mm. and over shall be machined cast brass. Fire Barriers: (a) (b) shall be purpose made, comprising a rigid fixed frame with adjustable seals and a suitable clamping device in fire compartment separation walls and floors shall be same standard of fire resistance as wall or floor. Cable Covers: shall be to BS 2484 and concrete covers exceeding 300 mm wide shall be reinforced. 8 Pipe Ducts : shall be PVC or as indicated. 9 Solder: an alloy of lead and tin to BS EN 29453 grade F or H, unless otherwise recommended by cable manufacturer. 10 Cable Sealing Compounds: shall be tropical grade to BS 1858 or BS 6910 and approved by cable manufacturer, of an oil-resisting compound where the difference in level between cable ends exceeds 6 m. 11 Cleats: shall be an approved claw type cast aluminium, gunmetal, plastic or brass of approved type, two bolt fixing for cables greater than 50 mm diameter. 12 Cable Markers: (a) (b) (c) 13 shall be precast concrete, minimum size 300 x 300 mm x 100 mm deep the markers shall be engraved “HV CABLE”, “ELECTRIC CABLE”, “ELV CABLE”, “EARTH PIT” or “CABLE JOINT”, as applicable cable marker construction details and engravings shall be approved by QGEWC. Cable Transits (a) (b) (c) (d) (e) cable transits shall have a stainless steel frame which shall be cast into or bolted to the structural concrete. the insert blocks shall be proofed against fire, explosion, water, rodents and gas. the design shall be such that at a later date cables can be added or removed with minimal disturbance to the remaining cables. the whole cable transit assembly shall be of an approved proprietary modular system which shall be certified by a recognised International Testing Authority. full details of proposed cable transits shall be submitted for the approval of the Engineer. 6.2.4 Jointing 11 kV, L.V. and Pilot Cables 1 General (a) (b) 2 All jointing shall be carried out to instructions of QGEWC and the Engineer and only by approved Jointers. All jointing shall be carried out in accordance with the QGEWC Safety Rules. All connections to lead sheaths shall be plumbed. 11 kV Cables (a) (b) (c) Terminations - These shall generally be of the heat shrinkable type using compression connectors although occasionally compound filled terminations shall be required. Generally crossed cores shall be avoided. Straight Joints - Intermediate joints shall be joined in the easiest way avoiding crossed cores. Phasing joints - Phasing shall be in accordance with the instructions of QGEWC and the Engineer to obtain correct phasing. The joints shall be of the bituminous filled type using sweated ferrules. QCS 2010 Qatar Project Management 7 QCS 2010 Section 21 Part 6 Cables and Small Wiring Page 10 3 Pilot Cables - These shall be jointed in accordance with instructions of QGEWC and the Engineer. The joints shall be resin filled type using compression connectors for straight joints and mechanical glands for terminations. 4 600/1000 Volt Cables (a) (b) (c) 6.3 INSTALLATION 6.3.1 General 1 Installing cables: (a) (b) (c) (d) (e) (f) (g) (h) (i) (j) (k) (l) (m) (n) pull cable into position by hand, where possible using an adequate number of operative roller guides suitably positioned along cable length obtain approval of pulling cables by winch or similar appliance when pulling by winch or the like, fit a suitable tension gauge into the haulage line between winch and cable. Pulling tension shall not exceed the limit recommended by the cable manufacturer do not allow cable to twist or rotate about its longitudinal axis lay 3 phase groups of single core cables in trefoil formation. If this is not possible obtain instructions install cables to allow any one cable to be subsequently removed without disturbing the remainder underground cable horizontal separation shall be a minimum of 150 mm damaged cables shall be removed, unless the Engineer agrees to a repair. all cables shall be neatly run in all situations. Where two or more cables are to be installed, cable tray must be provided. where power cables are surface run on the external faces of structures or above ground level they shall be installed on cable tray. They shall be protected from radiation of the sun by means of purpose made sunshades, which shall be of an approved design, securely fixed and fully ventilated. mechanical protection by cable tray covers shall be provided for all cable trays above ground/floor level to a height of 1000mm. when more than one cable is to be terminated at particular items of equipment special care should be taken to ensure that all cables to that equipment are routed from a common direction and each is terminated in an orderly and symmetrical fashion. Each and every cable shall be permanently identified at each end by its cable number as noted within the schedules. The identification label shall be of adequate size and style to a pattern approved by the Engineer and shall be securely fixed to its relative cable. identification labels shall also be fixed on cables at each and every entry and exit point of buried ducts, exits and entry to any structure and in such other positions as are necessary to identify and trace the route of any site cable. The use of punch type adhesive labels (Dymo-tape) will not be permitted. where cables enter or leave structures or panel plinths, the ducts including spare ducts shall be sealed at the points of entry or exit. Caulking shall be carried out with an approved asbestos compound and followed by not less than 40mm of epoxy resin two-mix cold waterproof compound or a weak sand/cement mixture as directed by the Engineer. The Contractor shall be responsible for temporarily sealing all cable ducts into structures during the installation stage to prevent accidental flooding of structures. QCS 2010 Qatar Project Management (d) All jointing shall be on a colour basis such that: Core 1: Red phase Core 2: Yellow phase Core 3: Blue phase Core 4: Neutral For terminations heat shrinkable techniques and compression connectors shall be used. For straight joints heat shrinkable techniques of joints using bituminous compound or resin shall be used at the discretion of QGEWC and the Engineer. For tee or branch joints bituminous compound or resin shall be at the discretion of QGEWC and Engineer. Mechanical or sweated connectors shall be used as decided by QGEWC and the Engineer. QCS 2010 (o) (p) (q) (r) (s) (u) (v) (w) Part 6 Cables and Small Wiring Page 11 during caulking care should be taken to ensure that the serving and/or armouring of any cable is not damaged. Any damaged cables shall be replaced entirely. all cables entering or leaving hazardous areas (e.g. wet well), air conditioned areas or areas protected by a fixed fire fighting installation shall do so via approved proprietary manufactured cable transits. Cables entering or leaving structures or passing between rooms of the same classification may be sealed by alternative means subject to the agreement of the Engineer. cables shall be free from kinks and the whole installation shall present a neat appearance. ties of PVC, nylon, plastic or similar material will not be permitted under any circumstances. protection of cables against possible mechanical damage shall be provided wherever seen to be necessary by the Engineer. All cables are to be run with particular regard to neatness. Multiple runs are to be arranged so that cables entering or leaving the run do so in a logical order. all power cables shall be terminated with palm type compression terminals of the correct type and size. special terminals shall be provided where necessary. Standard terminals which have palms/holes which are oversized for the application will not be acceptable. Standard terminals which are drilled out to a larger size, reducing the area of the palm will not be acceptable. removal of strands or shaving of conductors to enable them to be terminated at terminals which are not designed for the size of cable necessary will not be permitted at any point. pneumatic crimping machines shall be employed with correctly sized dies. Hand crimping shall not be used. 2 Bending Radius: as large as possible and cable shall not to bend to a radius less than that specified in the relevant British Standard, QGEWC regulations or manufacturer’s recommendation, whichever is largest. 3 Underground Cables in PVC-u Ducts: (a) (b) (c) (d) (e) (f) (g) (h) (i) cables shall be installed in ducts where there is hard standing or vehicular passage. Ducts where there is vehicular passage or landscaped area shall be concrete encased cable duct size shall be as specified in the Drawings, to BS 3506 Class B or BS 4660. However the minimum duct wall thickness shall be as per the following: DUCT SIZE DUCT WALL THICKNESS (mm) (mm) 75 3.2 100 3.4 150 3.6 200 4.2 run cables at least 300 mm clear of other services, whether the latter run parallel or transversely to cable trench. use pulling compound, or lubricant to avoid excessive stress on the cable, if required run cables below intersecting piped services, unless the cable would be at a depth exceeding 2 m, in which case seek instructions ducts shall not be filled with cables to more than 60 % of their capacity nylon draw cords shall always be left in ducts cable duct pits shall be provided at each change in direction and in any case at distances not exceeding 30 m ducts shall be suitably sealed with polyurethane foam or proprietary cable sealing arrangements if specified empty ducts shall be plugged with removable plugs QCS 2010 Qatar Project Management (t) Section 21 QCS 2010 (j) 4 (b) (c) (d) Cables and Small Wiring Page 12 ducts shall have a minimum diameter of 100 mm. protection shall be provided where mechanical damage is possible unarmoured cables shall be protected by conduit, ducting or trunking cables shall be protected from direct sunlight cable spacings and layouts shall be as table 4A of BS 7671 cables shall be run at least 150 mm from other services. Underground Cables in trenches (a) (b) (c) in areas of hard standing cables may also be installed in concrete or brick cable trenches with removable covers cables may be laid in a single layer on the trench floor, otherwise they shall be supported on the sides of the trench on cable tray by cleats or ladders cable spacings and layouts in the trenches shall be as table 4A of BS 7671 QCS 2010 Qatar Project Management the excavation and backfilling of cable trench work shall be carried out by the Contractor. excavated spoil shall be removed from the route of the trench. There shall be no loose stones or other debris on either side of the trench for a distance of 1000mm. the contractor shall supply and lay the sand bedding, cables, sand blinding, cable cover tiles and marking tape. He shall also supply and lay cable route marker posts after the backfilling and top soiling has been carried out. the sanding and laying of all cables shall satisfy the following requirements: (i) cable depths shall be measured from the finished ground level unless otherwise directed by the Engineer. (ii) H.V. cables shall be laid at a depth of 1 meter. (iii) L.V. cables shall be laid at a depth of 0.6 meter. (iv) H.V. and L.V. cables may be run in the same trench but should be staggered. however where necessary to pass through ductwork, cables shall be laid vertically on top each other with the H.V. cables at the lowest level with a good sand blinding forming the sand bedding for the L.V. cables. (v) before laying in cables the contractor shall inspect the trench work to ensure that the trench bottom is of a smooth and firm contour and free from any sharp materials or obstructions. (vi) cable bedding within the trenches shall be formed by a 200-mm sand layer. (vii) cables shall be laid with adequate separation and shall be “snaked” to avoid tension during backfilling operations and subsequent settlement. (viii) before sanding and backfilling, all laid cables shall be inspected by the Engineer, and a further inspection following sanding and tiling shall be made by the Engineer before backfilling. (ix) after cables have been laid, they shall be covered by a further 200-mm of sand, which shall be well tamped around the cables. Mechanical punners shall not be used for this work. (x) after sanding cable cover tiles shall be placed in position to overlap the cables by a minimum of 50 mm either side of the cables as per Clause 6.3.5 of this Section. (xi) the contractor shall carry out backfilling and shall ensure that cable cover tiles are undisturbed and that large rocks, stones and the like (more than 20mm diameter) are eliminated from backfill spoil. (xii) after backfilling the contractor shall reinstate to finished ground level. The contractor shall lay in position the necessary cable route markers at a maximum of 10 meters apart and at entries to buildings and any change in direction. (xiii) cables are to be spaced in accordance with QGEWC requirements i.e. M.V./M.V. – 700mm, M.V./H.V. – 1000mm and H.V./H.V. – 1000mm. (xiv) the contractor shall provide cable route markers to the approval of the Engineer and engraved “Electricity Cables”, or other suitable legend, with the appropriate voltage. Cables above Ground: (a) (b) (c) (d) (e) 6 Part 6 Direct Buried Cables: (a) 5 Section 21 QCS 2010 (d) 7 (b) (c) (d) (e) other services shall not be run in cable trenches. cables shall be supported in accordance with the methods described in table 4A of BS 7671. Other methods shall be approved by the Engineer cables shall be supported at regular intervals and at spacings a maximum of 400 mm for cleats for horizontal runs and 550 mm for vertical runs vertical cable runs exceeding 100 m shall incorporate tension releasing sections structured cable management systems or ladders shall be of G.R.P or galvanised steel cable supports shall be provided at 300 mm intervals MICC Cables: (I) run on surface of walls ceilings. Where embedded, run in a PVC trough or conduit (ii) run cables in square symmetrical lines. Where single core cables are run in groups, bend the sheaths at maximum 50 mm centres (iii) fix surface run cables with saddles at maximum 300 mm centres. in areas where a constant ambient temperature exceeding 55C will occur, run all final sub-circuits and distribution circuits in heat resistant cable make conversion from PVC cable to heat resistant cable with a fixed block connector housed and fixed into a conduit box or equal, except where the conversion of cable types emanate from a switch, ceiling rose or similar fixed connector accessory. Flexible Cables: (a) (b) flexible cable shall be kept to a minimum and concealed if possible mechanical retainment shall not depend on electrical connections. Sealing Cables: (a) (b) (c) (d) (e) 11 Page 13 seal both ends of cables immediately after tests seal MICC cables immediately after cutting to prevent hygroscopic action by the dielectric. All cables shall give an infinity test when tested on a 1000 volt Megger immediately, and 48 hours after sealing seal aluminium sheathed cables with a metal cap plumbed to the sheath seal plastic sheathed cables with a plastic cap embracing the wires and outer sheath mark cable ends in accordance with the relevant BS. QGEWC will require to carry out inspections at the following stages: (a) (b) (c) (d) (e) Completion of excavations Completion of bedding of trench prior to cable installation. Cable installation Completion of surround over cables and installation of cable tiles etc. Upon completion of reinstatement. 12 The Contractor must not progress from one stage to the next of the above without the approval of QGEWC and the Engineer. The Contractor shall be responsible for arranging inspections by QGEWC to suit his programme of Works. 13 Cable Segregation (a) (b) (c) (d) Only conductors carrying signals of the same instrumentation signal category shall be contained within any one multi-core cable. In each instrumentation signal category, a further segregation is required to ensure that conductors forming part of an intrinsically safe circuit are contained within multi-core cables reserved solely for such circuits. High integrity signals such as data transmission or critical shut down signals shall be contained in separate cables. ICA/Telemetry cables sharing a cable tray, duct or route with power cables shall be avoided. Power cables are defined as a.c. cables above 50 volts with a 10-amp rating. QCS 2010 Qatar Project Management (b) 10 Cables and Small Wiring Heat Resistant Cables: (a) 9 Part 6 Cable Supports: (a) 8 Section 21 QCS 2010 (e) (f) (g) (h) (i) (k) (l) Part 6 Cables and Small Wiring Page 14 Where this is not practicable, a minimum maintained separation between cables should be provided in accordance with Table 6.1. Where the maximum current exceeds 100 amps or the voltage exceeds 650 volts, the minimum segregation shall be in accordance to Clause 6.3.3 of this Section. Where the length of an enforced parallel run between power and ICA/Telemetry cables is greater than 500 meters, a progressive “pro-rata” increase in the segregation distance shall apply. The segregation distances shall be maintained by positive means and shall apply to both above ground and below ground installations. Where a crossover between power and ICA/Telemetry cables is unavoidable the cable shall be arranged to cross at right angles. The number of crossovers shall be kept to a minimum. Where cable installations are of a restrictive nature such as entries into buildings, panels' etc. relaxation of the minimum segregation distance requirement from a power cable(s) is acceptable. The minimum segregation distance shall then be the distance, determined by the length of the parallelism at the restrictive section of the installation. Where a manufacturer’s installation specification requires greater segregation than detailed in Table 6.1 such as for data highway cables etc. the Contractor shall comply with the manufacturer’s segregation specification. Cables of different categories shall not be installed in the same duct Public Telephone service (QTEL) cables shall be installed in separate ducts Table 6.1 Minimum Segregation Distance for Cables Minimum Segregation Distance Requirement in mm Distance over which parallelism exists between signal and power cables in metres Power cable Instrumentation Signal Classification Category to BS 6739 or equivalent Cat. 2 Cat. 3 Maximum current 10 amps at any phase voltage up to 250 volts a.c. or d.c. 0 - <3 3 - <10 10 - <25 25 - <100 100 - <250 250 - < 500 50 100 100 150 200 250 50 100 150 200 250 300 Maximum current 50 amps at any phase voltage up to 650 volts a.c. 0 - <3 3 - <10 10 - <100 100 - <250 250 - < 500 100 150 200 275 350 150 200 250 350 450 Maximum current 100 amps at any phase voltage up to 650 volts a.c. 0 - <3 3 - <10 10 - <100 100 - <250 250 - < 500 175 200 250 350 500 250 300 450 525 650 6.3.2 Cable Trays 1 Generally: (a) (b) install cables on trays in a single layer, unless otherwise specified use purpose made straps or saddles to maintain cables in a neat regular disposition QCS 2010 Qatar Project Management (j) Section 21 QCS 2010 (c) (d) (e) Section 21 Part 6 Spacing Between Cables 1 High Voltage Cables 11,000 volt cables shall be laid with a horizontal spacing of 750mm between centres and a minimum distance of 150mm from trench wall. Pilot cables shall be laid with a horizontal spacing of 140mm from the associated main cable in case of multiple cables trenches pilot cables shall be laid between the power cables. 2 Low Voltage Cables - 1000 volt main cables shall be laid with a horizontal spacing of 600mm between centres and with a minimum distance of 150m m from trench wall. 3 High Voltage and Low Voltage Cables in same trench - Where 11,000 volt and 1000 volt cables are laid in the same trench the spacing between the 11,000 volt and 1,000 volt shall be 750mm. 4 Reduction of Spacing - Any reduction from above spacing can only be permissible for lengths of 10 m or less. 6.3.4 Trench Depth 1 High Voltage - For 11,000 volt cables the trench shall be 950mm deep. 2 Low Voltage (a) For 1,000 V main cables the trench shall be 850mm deep (b) For 1,000 V service cables the trench shall be 650mm deep. 3 Arrangements for Trenches with High Voltage and Low Voltage Cables - Where 11,000 volt and 1,000 volt cables are to be laid along the same route a stepped trench shall be dug with the 1,000 volt cables laid inside i.e away from the road. 6.3.5 Cable tiles 1 The Contractor shall provide and install: (a) (b) (c) Concrete cable tiles over all 66 kV cables. The cable tiles shall be of the size and form shown on the drawings. Samples must be provided for approval by QGEWC and the Engineer and satisfy a test of impact strength in accordance with BS 2484: 1985. Cable tiles over all 11,000 volt cables manufactured from encycled polyethylene or similar complying with the following requirements: Minimum thickness : 12 mm Length : 1m Width : 24mm 2 Tensile : 8.40 N/mm (B S2782 Method 20C) The tiles shall be marked as specified. The cable tiles must be supplied complete with any pins, pegs or other devices for jointing tiles together. Samples must be supplied to QGEWC and the Engineer for approval prior to use. 6.3.6 Removal of Existing Cables 1 The Contractor shall liaise directly with QGEWC regarding the removal of existing cables and shall not, under any circumstances, commence removal of cables until QGEWC have verified QCS 2010 Qatar Project Management (b) Page 15 secure cables with load bearing cleats securely fixed to the tray, where trays do not directly support the cables space cleats, saddles and straps at maximum centres recommended in QGEWC Regulations, as above, or by cable manufacturer cable trays and installation shall be in accordance with Part 9 of this section, QGEWC regulations and BS 7671. 6.3.3 (a) Cables and Small Wiring QCS 2010 Section 21 Part 6 Cables and Small Wiring Page 16 such apparatus as being redundant. Removal of cables shall only be carried out in the presence of a QGEWC Engineer. 2 The Contractor shall arrange uplift of empty cable drums from QGEWC Stores and shall return all recovered cables neatly coiled on the drums provided. 6.3.7 Ducts 1 Ducts are to be supplied by the Contractor. They shall be of the following type: Material Internal Diameter Minimum wall thickness 2 Samples shall be provided for approval by the Engineer prior to use. 6.3.8 Quarry Scalping 1 Shall comprise of quarried limestone materials having particle sizes varying from 5 mm down to dust with a homogenous mixture of all particle sizes. 2 The materials shall have specific mechanical and thermal resistive qualities as defined below: (a) (b) Thermal Resistivity - The material shall be subject to a 90 % compaction, using an amount of water equal to optimum moisture content. After subsequent drying, such that the water content does not exceed 2% of the weight of the sample, the thermal resistivity of the material shall not exceed 2.0 C M/Watt Mechanical Qualities - The scalping material shall have mechanical qualities that meet the requirements of the QCS Roadworks Section. END OF PART QCS 2010 Qatar Project Management - High impact resistance PVC - 150 mm or 100 mm as specified - 3.6 mm (for 150 mm ducts) or 2.4 mm (for 100 mm ducts) QCS 2010 Section 21 Part 7 Conduits and Conduit Boxes Page 1 7. CONDUITS AND CONDUIT BOXES ............................................................. 2 7.1 GENERAL ...................................................................................................... 2 7.1.1 7.1.2 7.1.3 7.1.4 General Reference References Description Submissions 7.2 PRODUCTS ................................................................................................... 3 7.2.1 7.2.2 7.2.3 Rigid PVC Conduit and Fittings Rigid Steel Conduit and Fittings Flexible Conduit and Connections 7.3 INSTALLATION ............................................................................................. 5 7.3.1 7.3.2 7.3.3 7.3.4 Preparation Installation of Conduit Installation of Flexible Conduit Cleaning 3 4 5 5 5 7 8 Qatar Project Management QCS 2010 2 2 2 2 QCS 2010 Section 21 Part 7 Conduits and Conduit Boxes Page 2 7. CONDUITS AND CONDUIT BOXES 7.1 GENERAL 7.1.1 General Reference 1 The work of this section is integral with the whole of the Project Documentation and is not intended to be interpreted outside that context. 2 Co-ordinate the work with all other services affecting the work of this section. 3 Related Parts and Sections are as follows: General Provisions for Electrical Installation Cables and Small Wiring 7.1.2 References 1 The following references are referred to in this Part: BS 731 BS 2782 BS 4568 BS 4607 BS EN 60423 Flexible steel conduits and adapters for the protection of electric cable. Method of testing plastics Steel conduits and fittings, metric units Non-metallic conduits and fittings for electrical installations rigid PVC conduits and conduit fittings, metric units IEC 423-A, Conduit diameters and threads for conduit and fittings. 7.1.3 Description 1 This Section to include the supply, installation and commissioning of all conduit works in accordance with the Project Documentation. 2 General: (a) (b) (c) (d) (e) light and power circuits, fire alarm, telephone, signal and other low current system wiring shall be drawn in conduits unless otherwise indicated conduit system shall generally be concealed and installed as indicated, unless otherwise indicated light and power circuits, fire alarm wiring, telephone wiring, signal wiring and low current system wiring shall each be run in separate conduit and wire way cable insulated for two different categories of circuit shall be segregated irrespective of service, conduit and fitting used shall be: (i) where embedded: heavy gauge rigid PVC complying to BS 4607, BS 6053 and BS 6099 Part 2, section 2.2 (ii) where surface mounted, exposed: galvanised steel conduit as per BS 4568 (iii) where installed above false ceilings and in voids: galvanised steel throughout the circuit (iv) where installed in flame proof and hazardous areas: galvanised steel (v) from terminal box to machine: flexible steel conduit as per BS 731. 7.1.4 Submissions 1 Samples: (a) 2 Product Data: (a) 3 cut-away samples of all sizes of conduits, conduit boxes and fittings of each type shall be fixed to a board and submitted to the Engineer. at the time of submitting samples submit manufacturer’s details, catalogues and copies of test certificates confirming that offered types comply with the Specification. Shop Drawings: QCS 2010 Qatar Project Management This Section Part 1 Part 6 QCS 2010 (a) Section 21 Part 7 PRODUCTS 7.2.1 Rigid PVC Conduit and Fittings 1 Standards: (b) Physical Properties: (a) 3 (c) minimum 20 mm, internal diameter unless otherwise indicated where size is not indicated: select in accordance with the regulations and as proper to the number and size of conductors. The minimum conduit wall thickness shall be as per the following: CONDUIT SIZE CONDUIT WALL THICKNESS (mm) (mm) 20 1.8 25 1.9 32 2.3 38 2.5 50 3.1 Fittings: (a) 5 conduit and fittings shall be: (i) resistant to high temperatures (ii) non-hygroscopic (iii) self-extinguishing (iv) of adequate insulation resistance and electric strength (v) inert to all liquid normally discharged from residential, commercial and industrial premises (vi) suitable for installation, storage and transportation at temperature not normally below -5 ° C. or above 85 ° C. and at these temperatures shall not: soften or suffer any structural degradation show signs of cracking, or deform so that cables cannot be easily drawn in or are likely to be damaged when drawing in, when bent, compressed or exposed to extreme temperature (vii) of adequate mechanical strength and thermal stability (viii) suitably and indelibly marked and identified. Markings shall include nominal size and be easily legible (ix) Smooth inside and outside and free from burrs and sharp edges. Surfaces and corners over which cables may be drawn shall be smooth and well rounded. Sizes of Conduit: (a) (b) 4 conduit and fittings shall comply with BS 4607: Part 1 and CEE Publication 26. In addition, conduit and fittings shall comply with this specification where requirements are more stringent conduit diameters shall comply with QGEWC regulations. conduit entries shall be designed to ensure a watertight joint. Expansion fittings: QCS 2010 Qatar Project Management 2 Page 3 submit drawings of proposed conduit layout and obtain approval before commencing work. 7.2 (a) Conduits and Conduit Boxes QCS 2010 (a) 6 Section 21 Part 7 Page 4 type to be approved. PVC Conduit Boxes: (a) (b) (c) (d) PVC Conduit Boxes can be used through PVC Conduit raceway system and shall comply with BS 4607 metallic conduit boxes as specified elsewhere in this section can be used alternatively if required for PVC conduit raceway system all boxes shall be provided with tapped brass inserts for fixing the screws all boxes for switches, sockets, outlets, etc., shall be rigid PVC or metallic type and their dimensions shall be suitable for fixing the switches, sockets and other accessories. Rigid Steel Conduit and Fittings 1 Rigid Steel Conduit (a) (b) (c) (d) (e) (f) (g) all metallic conduits shall comply with BS 4568 and of Class 4 rigid steel screwed type having an interior and exterior zinc coating of uniform quality and appearance throughout all surfaces conduits shall not be less than 20 mm diameter size, and shall be complete with all necessary threaded fittings, couplings and connecting devices having galvanised equivalent finish conduits and fittings shall be manufactured specially for electric wiring purposes. When manufactured by a continuous weld process, weld heads both inside and outside the tube shall be completely removed prior to galvanising all conduits and fittings shall be free from rust or other defects on delivery to the site and shall be properly stored in covered racking so that it is protected from mechanical damage and damage by weather and water whilst stored on the site all conduits shall be coupled to boxes and trunking wires using brass male bushes. All such bushes shall be hexagon headed, heavy duty long threaded type all conduit expansion couplings used shall be fabricated from material equal or equivalent to that of the conduit with which the coupling is to be used, having factory installed packing ring and pressure ring to prevent entrance of moisture. All coupling shall be equipped with earthing ring or earthing conductor all conduit runs shall be fixed using spacer bar pattern saddles giving not less than 3 mm clearance between the conduit and the surface to which it is fixed. Saddles shall have finish to match the conduit and saddle clips shall be secured to the bar by means of brass screws. Metallic Conduit Boxes: (a) (b) (c) (d) (e) (f) metallic conduit boxes shall be used throughout metallic conduit raceway systems, and shall comply with, or be of demonstrated equivalent quality and performance to BS 4568 requirements. All boxes and covers shall be galvanised, zinc plated or rust-proof finish equivalent to conduit finish circular and/or rectangular boxes shall be used for pull boxes and terminating boxes, according to size and number of conduits connected to box. Boxes shall be either malleable iron or heavy duty steel construction with welded joints and tapped holes to receive metal threaded cover retaining screws. Self tapping screws will not be permitted all boxes, other than those to which a fitting or accessory is to be directly mounted shall be fitted with covers screwed to the box by brass screws. Malleable iron covers shall be used with malleable iron boxes and heavy gauge steel covers shall be used with sheet steel boxes all cover and accessory fixing provisions shall be so positioned that the fixing screws lie completely clear of cable entering the box. All fixing screws shall be of brass all boxes installed in exterior locations, plant rooms, ducts, etc., shall be fitted with approved type gaskets to provide a waterproof seal between box and cover or other items fitted to the box all boxes provided as junction boxes where cable joints are specified or permitted, shall be provided with fixed terminal blocks. Such boxes shall be of suitable size to contain the terminal block and sufficient cable to allow neat connections to be made. The terminal blocks shall be fixed to the box by brass screws and shall comprise QCS 2010 Qatar Project Management 7.2.2 2 Conduits and Conduit Boxes QCS 2010 Section 21 Part 7 Conduits and Conduit Boxes Page 5 brass conductor connectors, with brass clamping screws enclosed in porcelain or other heat resisting insulation material which will not distort or otherwise have its properties damaged by temperatures below the highest temperature at which the insulation of any cable connected to it is destroyed. 7.2.3 Flexible Conduit and Connections 1 Flexible Conduit: (a) (b) (c) 2 Flexible Connections: (a) where connections to electrical machines are to be by multicore glands, the final termination shall be by ring type universal glands and locknuts, and adequate slack cable in the form of a loop or spiral being left to allow for the movement of motors necessitated by belt retensioning, vibration, etc. 7.3 INSTALLATION 7.3.1 Preparation 1 Sets and Bends: (a) (b) conduits up to 32 mm diameter; form on site with an approved bending machine using proper formers, guides, springs, etc., taking care not to deform conduit conduits over 32 mm diameter : use coupling fittings. 7.3.2 Installation of Conduit 1 General (a) (b) (c) (d) (e) (f) (g) (h) (i) (j) (k) (l) run conduit in square, symmetrical lines, parallel to or at right angles to walls and in accordance with the accepted practice conduit system shall be mechanically continuous and watertight after installation. All conduit system shall be arranged wherever possible to be self draining conduit runs between draw-in positions shall conform to QGEWC Regulations regarding no. of bends and lengths of straight run installation shall permit easy drawing in of cables keep conduits at least 100 mm from pipes and other non-electrical services where conduit runs are to be concealed in the structure or are to pass through floor slabs, the Contractor shall be responsible for marking the accurate positions of all chases and holes on site. The Contractor shall arrange the conduit routing to make maximum use of any preformed conduit holes and slots provided in structural beams. Conduit installation on shear walls shall be kept to a minimum. All routings necessary on shear walls shall be agreed with the Engineer before work is put in hand install conduits so as not to interfere with ceiling inserts, lights or ventilation outlets. install conduit in accordance with NECA "Standard of Installation." or other national standards or Codes of Practice to the approval of QGEWC. install nonmetallic conduit in accordance with manufacturer's instructions. arrange supports to prevent misalignment during wiring installation. support conduit using coated steel or malleable iron straps, lay-in adjustable hangers, clevis hangers, and split hangers. group related conduits; support using conduit rack. Construct rack using steel channel ; provide space on each for 25 percent additional conduits. QCS 2010 Qatar Project Management (d) to BS 731, Part 1, watertight, PVC sheathed, spiralled metal type. The conduit shall be terminated at boxes and equipment by means of approved compression glands to be of the unpacked type for normal atmospheric conditions and non-asbestos packaged for damp situations. Adapters shall be of the solid type flexible conduit shall be used for the final connection of rigid conduit to the terminal boxes of machines fitted with a means of drive adjustment and/or where vibrations is likely to occur. flexible conduit for use outdoors shall be weatherproof and certified to be resistant to UV radiation. QCS 2010 Section 21 Part 7 Conduits and Conduit Boxes Page 6 (m) QCS 2010 Qatar Project Management fasten conduit supports to building structure and surfaces under provisions of Section "Supporting Devices" (n) do not support conduit with wire or perforated pipe straps. Remove wire used for temporary supports (o) do not attach conduit to ceiling support wires. (p) arrange conduit to maintain headroom and present neat appearance. (q) route conduit parallel and perpendicular to walls. (r) route conduit installed above accessible ceilings parallel and perpendicular to walls. (s) route conduit in and under slab from point-to-point. (t) maintain adequate clearance between conduit and piping. (u) cut conduit square using saw or pipecutter; de-burr cut ends. (v) bring conduit to shoulder of fittings; fasten securely. (w) join nonmetallic conduit using cement as recommended by manufacturer. Wipe nonmetallic conduit dry and clean before joining. Apply full even coat of cement to entire area inserted in fitting. Allow joint to cure for 20 minutes, minimum. (x) use conduit hubs or sealing locknuts to fasten conduit to boxes and fittings. (y) install no more than equivalent of two 90-degree bends between boxes. Use conduit bodies to make sharp changes in direction, as around beams. Use hydraulic one-shot bender to fabricate and factory elbows for bends in metal conduit larger than 2-inch (50-mm) size. (z) avoid moisture traps; provide junction box with drain fitting at low points in conduit system. (aa) provide suitable fittings to accommodate expansion and deflection where conduit crosses seismic , control and expansion joints. (bb) provide suitable pull string in each empty conduit except sleeves and nipples. (cc) use suitable caps to protect installed conduit against entrance of dirt and moisture. (dd) provide supports for fittings independently of any false ceiling for sunk and concealed conduit systems. (ee) size conduits, draw-in boxes and junction boxes in accordance with regulations. (ff) swab whole of the conduit system to remove any loose matter or dirt before cables are pulled in. (gg) where conduits connect to switch boxes draw-in boxes and the like the conduits must have a machined faced socket screwed on to the end which when tightened is flush with the outside of the box. The conduit is then to be secured to the apparatus by means of a hexagon smooth bore brass bush screwed from the inside of the apparatus into the conduit socket in order to make a sound and tight mechanical joint. (hh) all horizontal runs shall be supported at no more than 900 mm. Vertical runs shall be supported at no more than 1200 mm. Where directional changes occur support shall be provided at no more than 150 mm either side of the bend. (ii) hot bending shall be carried out on all non-metallic conduits. A bending spring of the correct size shall be used in all cases. The heat source shall be provided by a hot air torch. When the conduit is in a pliable state it shall be bent around a suitable former and held in position until the conduit has set. No other method will be approved. (jj) couplers, slip type bends and spouted fittings shall be made using semi permanent mastic sealing compounds. Expansion couplers shall be used in surface installations where straight runs exceed 8 meters. (kk) standard junction or adaptable boxes shall be provided at all junctions and at sharp changes of direction in addition to any special positions where they are required on Site. Inspection couplers may be used in long runs to facilitate drawing in cables. (ll) particular care must be taken to ensure that no water is allowed to enter conduit at any time and all conduits shall be arranged with adequate ventilation and drainage where necessary as directed by the Engineer. Inaccessible junction boxes will not be allowed. (mm) only continuous lengths of buried conduit shall be installed between boxes, no joint boxes being allowed in the floor screeds. Conduits crossing expansion joints shall be fitted with couplings of approved manufacture. (nn) the ends of conduits laid or set in formwork prior to concreting shall be temporarily sealed off with a coupler and a plug. (oo) fixing to surfaces of walls shall be by means of spacer bar saddles securely fixed by screws. Where conduits are concealed or laid in structural floors they shall be held in position with substantial fixings of make and pattern to be approved by the Engineer. QCS 2010 (pp) (qq) (rr) (ss) (tt) (uu) 2 (d) adaptable boxes shall be manufactured from PVC as previously detailed for conduit boxes and sized to provide sufficient space factor. weatherproof boxes and accessories shall be used outdoors where agreed on Site by the Engineer or where indicated in this Specification or on the Drawings. conduit shall be installed such as to permit complete rewiring without the need to remove false ceiling or carry out builders work. no single conduit serving phase socket outlets lighting points and switches shall contain more than one phase. wiring shall be carried out on the looping-in system and no joints other than at looping-in points will be allowed. where the conduit system terminates at any equipment requiring a non-rigid connection a flexible conduit shall be installed of the PVC or PVC sheathed metallic type fully watertight with purpose made connection adapters. each flexible connection shall include not less than 400mm length of flexible conduit and a separate earth conductor shall be run within the conduit connected to the earth terminals in the equipment and the fixed conduit run. The flexible conduit shall not be used as an earth continuity conductor. obtain approval for placing PVC conduits before pouring concrete run conduits in concrete slabs parallel to main reinforcing steel additional openings in finished slabs, where approved, shall be made by drilling, not by breaking conduit boxes shall not be nailed to shuttering boards. to be avoided in partitions and side walls. Surface Mounted Conduit (including conduit installed above false ceiling): (a) 5 fix with distance spacing saddles to allow conduits to be taken directly into accessories without bends or sets. Concealed Conduit: (a) (b) fix securely to prevent movement before casting of concrete and screeds, application of plaster and the like spacing of clips shall be not greater than as follows: (i) (ii) (iii) (c) 6 Spacing 600 mm 900 mm 1000 mm Supports for exposed conduit shall be fixed at each side of bends. fix in conduit wherever it crosses as expansion joint in the structure to which it is fixed. Terminations: (a) 8 conduit size up to 25 mm 32-38 mm 50 mm Expansion Fittings: (a) 7 Page 7 Horizontal or Cross Runs: (a) 4 Conduits and Conduit Boxes Runs in Reinforced Concrete: (a) (b) (c) 3 Part 7 make with a flanged coupling, lead washer and hexagonal male brass bush, where conduit runs terminate in cable trunking, distribution boards or any sheet metal structure. Conduit Boxes: (a) fix at all outlet points. 7.3.3 Installation of Flexible Conduit 1 All conduits must be secured to outlet boxes, junction boxes or cabinets by placing locknuts on outside of box and locknuts and bushings on the inside of box. QCS 2010 Qatar Project Management (vv) Section 21 QCS 2010 Section 21 Part 7 Conduits and Conduit Boxes Page 8 2 Conduits connecting recessed fixtures and their adjacent junction boxes must be flexible metallic conduit 20 mm minimum size and shall be of sufficient length to permit dropping of the fixture below the ceiling and to gain access to the junction box. 3 Conduit to motors shall be terminated in the conduit fittings on the motors, the final connection being made with liquid tight flexible conduit and suitable liquid tight connectors. 4 A green insulated 4 mm (minimum) tinned copper earth connection shall be made between the solid conduit or cable sheath and the equipment, the copper cable being run inside the flexible conduit. Couplings fitted to removable covers or non-metallic equipment etc., shall be bonded to the earthing terminal of the equipment etc. Where changes to flexible conduits occur, a watertight outlet box with threaded entries shall be inserted and the earth connection made to an internal terminal. The cover screws shall not be used for earthing connections. 7.3.4 Cleaning 1 The conduit outlets when installed and before wiring shall be temporarily closed by means of well fitting wooden plugs, and immediately before cables are drawn in, conduit systems shall be thoroughly swabbed out until they are dry and clean 2 QCS 2010 Qatar Project Management END OF PART QCS 2010 Section 21 Part 8 Trunking Page 1 8. TRUNKING .................................................................................................... 2 8.1 GENERAL ...................................................................................................... 2 8.1.1 8.1.2 8.1.3 8.1.4 General Reference References System Description Submissions 8.2 PRODUCTS ................................................................................................... 2 8.2.1 Trunking 8.3 INSTALLATION ............................................................................................. 4 8.3.1 8.3.2 Installation Cleaning and Adjustment 2 4 5 Qatar Project Management QCS 2010 2 2 2 2 QCS 2010 Section 21 Part 8 Trunking Page 2 8. TRUNKING 8.1 GENERAL 8.1.1 General Reference 1 The work of this section is integral with the whole of the Project Documentation and is not intended to be interpreted outside that context. 2 Co-ordinate the work with all other services affecting the work of this Section. 3 Related Parts and Sections are as follows: General Provisions for Installation Cables and Small Wiring Conduits and Conduit Boxes Cable Trays 8.1.2 References 1 The following standards are referred to in this Section: BS 729 BS 3382 BS 4607 BS 4678 BS 4678 Hot dip galvanised coatings on iron and steel articles Zinc on steel components Fittings and components of insulating materials Steel surface trunking Cable trunking of insulating materials BS EN 10142 Hot dip zinc coated sheet steel 8.1.3 System Description 1 The Contractor shall supply and install the complete trunking system as indicated on the Drawings and specified in this Section. 8.1.4 Submissions 1 Samples: submit samples of trunking and accessories. 2 Product Data: at the time of submitting samples submit manufacturer’s details, catalogues etc. 3 Shop Drawings: submit drawings showing route of trunking system and obtain approval before commencing work. 8.2 PRODUCTS 8.2.1 Trunking 1 General: (a) (b) (c) trunking, associated parts and accessories shall be fabricated from hot dipped galvanised sheet steel not less than 16 SWG trunking shall be supplied in 3 m lengths or bigger, each length complete with lid, coupler and coupler screws and shall provide adequate earth continuity throughout the whole trunking run shall be complete with necessary fittings and accessories. All accessories and fixing materials shall also be of galvanised sheet steel of not less than 1 mm thickness QCS 2010 Qatar Project Management This Section Part 1 Part 6 Part 7 Part 9 QCS 2010 (d) (e) (f) 2 (c) (d) (e) (f) (g) (c) lids shall be clipped and fixed at regular intervals not exceeding 2 m on straight runs, by quick release cam type fasteners. In PVC trunking installations the lids can be slide-in type of proper lengths partitions shall be at least 1 mm thick, finished to same standard as trunking. The means of fixing partitions shall prevent them being misplaced and shall not cause corrosion or electrolytic action connectors shall span the complete internal surface of the trunking. Trunking sections shall have butt joints accessories for bends and tee-off shall be supplied from the same manufacturer and provided with lids as necessary. Reduction type tee-offs shall be provided where smaller size branch trunking is required. shall satisfy continuity conditions of BS 4678 shall not cause corrosion 2 separate protective conductor of size not less than 4 mm shall run in the PVC trunking system. shall be 15 x 2 mm minimum having a resistance from fixing to fixing equal to or less than the links used in standard trunking joints. shall have a zinc coating finish to BS 729 or BS 3382 : Part 2, or equivalent fixings used for securing or fitting shall not cause corrosion or electrolytic action. Black screws are not acceptable brackets, mild steel angle or channel finished to same standard as trunking. Vertical Trunking: (a) shall have cable support units with insulated pins at centres not exceeding 3 meters. Horizontal Trunking: (a) 8 shall be to BS 4678: Part 1, but thickness of metal for body and cover material may not be less than those in Table 1. The PVC trunking system shall satisfy the requirement in Part 4 of BS 4678 providing smooth internal and external finishes metal thickness for trunking and connectors exceeding 150 x 150 mm external dimensions shall be to approval and shall not be less than that specified in BS 4678 Part 1 for the largest trunking detailed finish for steel trunking: (i) for internal use: Class 3 heavy protection internally and externally (e.g. galvanised steel to BS EN 10142; protection to BS 4678 : Part 1) (ii) for external use: Class 3 protection Steel Screws and Fasteners: (a) (b) 7 if specified in the Project Documentation, trunking, associated parts and accessories shall be fabricated from high impact PVC-u material, having thickness not less than 1.5 mm and shall be complete with necessary fittings and accessories made from the similar material as for the trunking trunking shall not be smaller than the minimum size stated on the Drawings or specified later and shall be so sized, if not specified, that a space factor of 35 % is not exceeded. The Contractor shall check the minimum size of trunking specified is large enough for his requirements without exceeding this space factor trunking and accessories installed in hazardous and extremely corrosive environments shall be heavy duty GRP or 316 S31 grade stainless steel. Braided Copper Tape: (a) 6 Page 3 Bonding links and fastenings: (a) (b) (c) 5 Trunking Sizes exceeding 100 x 50 mm shall have cable separators with insulated pins at maximum centres not exceeding 2 m. Surface Metal Raceway (a) the surface metal raceway assembly shall comprise of a metal base and cover to form a raceway intended for surface mounting, except in very small sizes. The cover shall QCS 2010 Qatar Project Management (b) 4 Part 8 Trunking and Connectors: (a) 3 Section 21 QCS 2010 (b) (c) (d) (e) 9 Trunking Page 4 be removable to allow wire installation after the raceway has been installed as a complete system. the surface metal raceway shall be constructed of sheet metal channel with fitted cover. the minimum size of the surface metal raceway shall be 50 mm x 50 mm or as specified on the layout drawings. fittings, Boxes, and Extension Rings as practical as possible shall be chosen from the manufacturer's standard range of accessories. all accessories shall be complete with removable covers. (c) (d) (e) the surface nonmetal raceway assembly shall comprise of a molded or extruded nonmetallic base and cover to form a raceway intended for surface mounting. the surface nonmetal raceway shall be constructed of heavy-duty rigid unplasticised PVC channel with fitted cover. The material shall be self-extinguishing and shall be unaffected by sunlight and/or water. The material shall be suitable for continuous 0 ambient temperatures of 65 C. the minimum size of the surface metal raceway shall be 50 mm x 50 mm or as specified on the layout drawings. fittings, Boxes, and Extension Rings as practical as possible shall be chosen from the manufacturer's standard range of accessories. all accessories shall be complete with removable covers. Multioutlet Assembly (a) (b) (c) (d) (e) (f) (g) the multoutlet assembly shall comprise of surface metal raceway with receptacles. Receptacle devices may be pre-wired in which case they are regularly spaced. the multoutlet assembly shall be constructed of sheet metal channel with fitted cover and/or with pre-wired receptacles where specified. the sizes of the multoutlet assembly shall be as indicated on the layout drawings. provide covers and accessories to accept convenience receptacles in conjunction with the wiring devices. the spacing between the receptacle shall be 150, 300 or 450 mm or as specified/indicated on the Drawings. the Colour of receptacle shall be subject to the approval of the Engineer. couplings, elbows, outlet and device boxes, and connectors as practical as possible shall be chosen from the manufacturer's standard range of accessories. Wireway (a) (b) (c) (d) (e) (f) the wireway shall be Narrow sheet metal enclosure, rectangular in cross section with hinged or removable covers for housing and protecting electric wires and cable and in which conductors are laid in place after the wireway has been installed as a complete system. the wireway shall be general purpose, oiltight and dust-tight or rain-tight type as specified and/or indicated on the drawings. knockouts shall be as per manufacturer standard. the sizes of the wireways shall be as indicated on the drawings. the wireways shall be provided with Screw cover and full gasketing. the fittings shall be lay-in type with removable top, bottom, and side and be provided with captive screws. Include drip shield where specified. 8.3 INSTALLATION 8.3.1 Installation 1 Fixing Trunking: (a) (b) trunking shall be properly aligned, and securely fixed at maximum 2 meters centres on straight runs. At bends, angles and offsets fix with additional fixings at centres not exceeding 150 mm on each side of the fitting only manufacturers bends, T-offsets and accessories shall be used. Site fabrication shall not be permitted. QCS 2010 Qatar Project Management (b) 11 Part 8 Surface Nonmetal Raceway (a) 10 Section 21 QCS 2010 2 (c) make a trunking joint where trunking crosses such joints make connection through slotted holes allowing a 10 mm movement horizontally and vertically earth continuity link across joints shall be braided copper tape which is long enough to allow for the maximum movement of trunking. Fold braid ends. where specified, install non-combustible, non-metallic fire barriers (i) where trunking passes through walls, floors and ceilings (ii) at each floor level when trunking is installed in riser ducts. fix at not exceeding 1m centres. Raceway and Wireway (a) (b) (c) (d) (e) (f) (g) install products in accordance with manufacturer's instructions. use flat-head screws, clips, and straps to fasten raceway channel to surfaces. Mount plumb and level. use suitable insulating bushings and inserts at connections to outlets and corner fittings. provide steel channel for supporting the wireways. close ends of wireway and unused conduit openings. earth and bond raceway and wireway as described under the "Earthing and Bonding" Part of QCS. provide circuit cable clamps at no greater than 500 mm intervals for raceways installed in vertical runs. 8.3.2 Cleaning and Adjustment 1 Making Good: (a) (b) (c) make good cutting and damages of the steel trunking systems, remove burrs and rough edges and corrosion and treat with a rust proofing agent, followed by an application of zinc epoxy provide a coat of paint to match adjacent surface for PVC system provide the paint after application of the zinc epoxy for steel trunking system. END OF PART QCS 2010 Qatar Project Management make connections to conduits, multiple boxes, switchgears, switchboards, motor control centres and distribution boards with flanged units. Cable Retaining Straps: (a) 6 Page 5 Connections: (a) 5 Trunking Fire Barriers: (a) 4 Part 8 Settlement and Expansion Joints: (a) (b) 3 Section 21 QCS 2010 Section 21 Part 9 Cable Trays Page 1 9. CABLE TRAYS .............................................................................................. 2 9.1 GENERAL ...................................................................................................... 2 9.1.1 9.1.2 9.1.3 9.1.4 9.1.5 9.1.6 9.1.7 General Reference References Description Quality Assurance Submissions Delivery, Storage and Handling Co-ordination 9.2 PRODUCTS ................................................................................................... 2 9.2.1 9.2.2 General Materials 9.3 INSTALLATION ............................................................................................. 6 9.3.1 9.3.2 9.3.3 Installation Erection Earthing 2 3 6 7 7 Qatar Project Management QCS 2010 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 QCS 2010 Section 21 Part 9 Cable Trays Page 2 9. CABLE TRAYS 9.1 GENERAL 9.1.1 General Reference 1 The work of this section is integral with the whole of the Project Documentation and is not intended to be interpreted outside that context. 2 Co-ordinate the work with all other services affecting the work of this section. 3 Related Parts and Sections are as follows: General Provisions for Electrical Installations Cables and Small Wiring Conduits and Conduit Boxes 9.1.2 References 1 The following standards are referred to in this Part: BS 729 Hot dip galvanized coating on iron and steel articles 9.1.3 Description 1 Provide all labour, materials, equipment, services and accessories necessary to furnish and install the work of this Section, complete and functional, as indicated in the Project Documentation and as specified herein. 9.1.4 Quality Assurance 1 Reference standards as detailed under Part 1 and this Part Clause 9.1.4. 9.1.5 Submissions 1 Reference Part 1 9.1.6 Delivery, Storage and Handling 1 Deliver, store and handle materials and products in a manner to prevent damage. 2 Reference Part 1 9.1.7 Co-ordination 1 The work of this Section shall be completely co-ordinated with the work of other services. 9.2 PRODUCTS 9.2.1 General 1 The cable tray system shall be of one manufacturer and shall include factory-made trays, tray fittings, connectors and necessary accessories and supports to form a complete cable support system. 2 The cable tray system shall include the following factory-made tray elements: (a) straight cable trays and ladders QCS 2010 Qatar Project Management This Section Part 1 Part 6 Part 7 QCS 2010 (b) (c) (d) Section 21 Part 9 Cable Trays Page 3 fittings as horizontal and vertical bends of various angles, crosses, tees, wyes, reducers, vertical riser elements connectors all necessary fixing accessories. Manufacturer’s standard accessories shall be used and site fabrication shall not be permitted. 4 Horizontal run of cables laid on cable tray and exposed to direct sunlight shall be provided with covering at higher level to allow for ventilation. Cable tray shall be raised 15 cm from finished floor level. 5 Cable trays shall confirm to requirements as specified in BS 7671, NFPA 70 - National Electrical Code, U.S.A or other equivalent standard as applicable. 6 Cable trays specification and installation shall be in accordance with QGEWC regulations and IEE latest edition as applicable. 7 The product selected and proposed shall include manufacturer's Instructions that Indicate application conditions and limitations of use stipulated by product testing agency specified under regulatory requirements. 8 The contractor shall select the product only from manufacturer’s specializing in manufacturing products specified in this Section, with a minimum five years documented experience of the products being satisfactorily in use in a similar service and climatic conditions. 9 The contractor shall ensure proper co-ordination with related civil activities prior to the selection of the equipment. 10 The contractor shall clearly show locations of trays, service fittings, junction boxes, and branch circuiting arrangements on the drawings. 9.2.2 Materials 1 The whole of the tray work, trays, fittings, supports shall be of mild steel hot dipped galvanized after manufacture to BS 729. The thickness of the protective sheath on any element shall not be less than 55 microns. 2 Cable trays shall be constructed from mild steel hot dip galvanized and of minimum thickness of 1.5 mm. 3 Insert elements, bolts, screws, pins, etc., shall be mild steel cadmium plated. 4 Tray work shall have oval perforations. Ladder type trays shall be used for vertical runs as approved by the Engineer. 5 All trays (straight and fittings) shall be welded construction and be a heavy duty returned flanged, perforated type, unless specified otherwise. The minimum thickness of heavy duty returned flanged cable trays shall be 1.5 mm. 6 Tray components shall be accurately rolled or formed to close tolerances and all edges rounded. Flanges shall have full round smooth edges. 7 Ladder racks shall be of similar construction. The rungs shall be spaced at maximum 300 mm. The system shall allow for installing additional rungs and for replacement of rungs. 8 For all trays, flanges shall be a minimum of 50 mm deep, unless otherwise specified. 9 Cable tray width and radius of curved sections shall be selected to suit the number of cables as shown on drawings and to the approval of the Engineer. QCS 2010 Qatar Project Management 3 QCS 2010 Section 21 Part 9 Cable Trays Page 4 10 Cable trays and accessories installed in hazardous and extremely corrosive environments shall be heavy duty GRP or 316 S31 grade stainless steel. 11 Ladder Type Cable Tray (a) (b) (c) (d) (j) (k) 12 Trough Type cable Tray (a) (b) (c) (d) (e) (f) (g) (h) (i) 13 bond trays carrying LV cables to earth with 16 Sq. mm. PVC insulated copper single core cable, 25x3 mm copper tape if carrying HV cables. definition: Two longitudinal side rails connected by closely-spaced rungs or ventilated bottoms. description: NEMA VE 1, specified Class or other approved standard, trough type tray. material: Steel, aluminium or heavy duty unplasticised PVC as specified. finish: ASTM A 123 or other approved standard, hot dipped galvanised after fabrication for steel trays. Painted with specified colour epoxy or PVC coated as specified. The material shall be self extinguishing and non-inflammable and shall be unaffected by sunlight or water. It shall be suitable for continuous ambient temperature of 65 degrees C. inside Width: 150, 300, 450, 600, 750 or 900 mm as specified or indicated. inside Depth: 75, 100, 125, or 150 mm as specified or indicated. inside Radius of Fittings: 300, 600 or 900 mm as specified or indicated. provide manufacturer's standard clamps, hangers, brackets, splice plates, reducer plates, blind ends, barrier strips, connectors, and earthing straps. covers: Flanged or Non-flanged as specified, solid or ventilated and flush or raised cover as specified. Solid Bottom Type Cable Tray (a) (b) (c) (d) (e) (f) (g) (h) (i) definition: Two longitudinal side rails connected by corrugated or reinforced solid bottom. description: NEMA VE 1, specified Class or other approved standard, solid bottom cable tray. material: Steel, aluminium or heavy duty unplasticised PVC as specified. finish: ASTM A 123 or other approved standard, hot dipped galvanised after fabrication for steel trays. Painted with specified colour epoxy or PVC coated as specified. The material shall be self extinguishing and non-inflammable and shall be unaffected by sunlight or water. It shall be suitable for continuous ambient temperature of 65 degrees C. inside Width: 150, 300, 450, 600, 750 or 900 mm as specified or indicated. inside Depth: 75, 100, 125, or 150 mm as specified or indicated. inside Radius of Fittings: 300, 600 or 900 mm as specified or indicated. provide manufacturer's standard clamps, hangers, brackets, splice plates, reducer plates, blind ends, barrier strips, connectors, and earthing straps. covers: Flanged or Non-flanged as specified, solid or ventilated and flush or raised cover as specified. QCS 2010 Qatar Project Management (e) (f) (g) (h) (i) definition: Two longitudinal side rails connected by individual cross members (rungs). description: NEMA VE 1, specified Class or other approved standard, ladder type tray. material: Steel or aluminium as specified. finish: ASTM A 123 or other approved standard, hot dipped galvanised after fabrication for steel trays. Painted with specified colour epoxy or PVC coated as specified. The material shall be self extinguishing and non-inflammable and shall be unaffected by sunlight or water. It shall be suitable for continuous ambient temperature of 65° C. inside Width: 150, 300, 450, 600, 750 or 900 mm as specified or indicated. inside Depth: 75, 100, 125, or 150 mm as specified or indicated. straight Section Rung Spacing: 150, 225, 300 or 450 mm as specified or indicated. inside Radius of Fittings: 300, 600 or 900 mm as specified or indicated. provide manufacturer's standard clamps, hangers, brackets, splice plates, reducer plates, blind ends, barrier strips, connectors, and grounding straps. covers: Flanged or Non-flanged as specified, solid or ventilated and flush or raised cover as specified. QCS 2010 14 (b) (c) (d) (i) (h) definition: Single piece formed into channel. Bottom may be solid or with ventilation openings. description: NEMA VE 1, specified Class or other approved standard, solid bottom or ventilated bottom type cable tray as specified. material: Steel, aluminum or heavy duty unplasticised PVC as specified. finish: ASTM A 123 or other approved standard, hot dipped galvanised after fabrication for steel trays. Painted with specified colour epoxy or PVC coated as specified. The material shall be self extinguishing and non-inflammable and shall be unaffected by sunlight or water. It shall be suitable for continuous ambient temperature of 65 degrees C. inside Width: 75 or 100 mm as specified or indicated. outside Depth: As specified or indicated. inside Radius of Fittings: 300, 600 or 900 mm as specified or indicated. provide manufacturer's standard clamps, hangers, brackets, splice plates, reducer plates, blind ends, barrier strips, connectors, and earthing straps. covers: Flanged, solid or ventilated cover as specified. description: NEMA FG 1, specified Class or other approved standard, ladder type tray. material: Fiberglass. inside Width: 150, 300, 450, 600, 750 or 900 mm as specified or indicated. inside Depth: 75, 100, 125, or 150 mm as specified or indicated. straight Section Rung Spacing: 150, 225, 300 or 450 mm as specified or indicated. inside Radius of Fittings: 300, 600 or 900 mm as specified or indicated. provide manufacturer's standard clamps, hangers, brackets, splice plates, reducer plates, blind ends, barrier strips, and connectors. covers: Flanged or Non-flanged as specified, solid or ventilated and flush or raised cover as specified. Fiberglass Trough Type Cable Tray (a) (b) (c) (d) (e) (f) (g) description: NEMA FG 1, specified Class or other approved standard, trough type tray. material: Fiberglass. inside Width: 150, 300, 450, 600, 750 or 900 mm as specified or indicated. inside Depth: 75, 100, 125 or 150 mm as specified or indicated. inside Radius of Fittings: 300, 600 or 900 mm as specified or indicated. provide manufacturer's standard clamps, hangers, brackets, splice plates, reducer plates, blind ends, barrier strips, connectors, and earthing straps. covers: Flanged or Non-flanged as specified, solid or ventilated and flush or raised cover as specified. Fibreglass Solid Bottom Type Cable Tray (a) (b) (c) (d) (e) (f) (g) 18 Page 5 Fiberglass Ladder Type Cable Tray (a) (b) (c) (d) (e) (f) (g) 17 Cable Trays description: NEMA FG 1, specified Class or other approved standard, solid bottom cable tray. material: Fiberglass. inside Width: 150, 300, 450, 600, 750 or 900 mm as specified or indicated. inside Depth: 75, 100, 125 or 150 mm as specified or indicated. inside Radius of Fittings: 300, 600 or 900 mm as specified or indicated. provide manufacturer's standard clamps, hangers, brackets, splice plates, reducer plates, blind ends, barrier strips and connectors. covers: Flanged or Non-flanged as specified, solid or ventilated and flush or raised cover as specified. Fibreglass Channel Type Cable Tray (a) (b) (c) (d) (e) description: NEMA FG 1, specified Class or other approved standard, solid bottom or ventilated as specified, channel type cable tray. material: Fiberglass. inside Width: 75 or 100 mm as specified or indicated. outside Depth: As specified or indicated. inside Radius of Fittings: 300, 600 or 900 mm as specified or indicated. QCS 2010 Qatar Project Management (e) (f) (g) (h) 16 Part 9 Channel Type Cable Tray (a) 15 Section 21 QCS 2010 (f) (g) 19 Section 21 Part 9 Cable Trays Page 6 provide manufacturer's standard clamps, hangers, brackets, splice plates, reducer plates, blind ends, barrier strips, and connectors. covers: Flanged, solid or ventilated cover as specified. Warning Signs (a) engraved nameplates shall be provided and installed along the route of the cable tray: 13-mm black letters on yellow laminated plastic nameplate, engraved with the following wording:- “WARNING! DO NOT USE CABLE TRAY AS WALKWAY, LADDER, OR SUPPORT. USE ONLY AS MECHANICAL SUPPORT FOR CABLES AND TUBING!” INSTALLATION 9.3.1 Installation 1 Drilling, machining or cutting shall not be carried out after application of protective coat, unless previously agreed by the Engineer. If cutting or drilling is necessary, edges shall be cleaned up and painted with zinc based paint before erection. 2 Installation of vertical runs of tray along the line of vertical expansion joints in structure of the facility shall not be allowed. 3 Cables shall be fixed to the trays by means of PVC covered saddles or straps secured with brass or cadmium plated bolts, nuts and washers. 4 20 % spare capacity shall be maintained once all cables have been installed on trays. Double banking of cables shall not be permitted. space between adjacent cables shall be not less than the radius of the bigger cable. 5 Trays shall not be smaller than the minimum size stated on the Drawings or specified later and shall be so sized; if not specified, the Contractor shall calculate the size of the tray and submit to the Engineer for approval. The Contractor shall check the minimum size as specified is large enough for his requirements and provide 20% spare capacity for future use. 6 Install metallic cable tray in accordance with NEMA VE 1 or other approved standard and local regulations as approved by the Engineer. 7 Install fibreglass cable tray in accordance with NEMA FG 1 or other approved standard and local regulations as approved by the Engineer. 8 Support trays in conjunction with supporting devices as described under Section "Supporting Devices". Provide supports at each connection point, at the end of each run, and at other points to maintain spacing between supports of 1200 mm maximum. 9 Use expansion connectors where required. 10 Provide firestopping under provisions of relevant Section to sustain ratings when passing cable tray through fire-rated elements. 11 Ground and bond cable tray under provisions of the Earthing and Bonding Part of QCS. (a) (b) (c) (d) 12 provide continuity between tray components. use anti-oxidant compound to prepare aluminium contact surfaces before assembly. provide specified cross section copper equipment grounding conductor through entire length of tray; bond to each component. connections to tray may be made using mechanical or exothermic connectors. Where specified, install warning signs at 1500 mm centres along cable tray, located to be visible. QCS 2010 Qatar Project Management 9.3 QCS 2010 Section 21 Part 9 Cable Trays Page 7 Where specified, install warning signs at 1500 mm centres along cable tray, located to be visible. 14 Plastic tie-wraps of any description shall not be used for fixing cables to cable tray. 15 Saddle and cleat cables in position as they are installed along the route. Cables should be neatly dressed and crossing of cables should be avoided by good detailed design of cable routing. 16 All cable tray changes in direction or level shall be made via sets and adequately sized angles to provide a support to the cables. 17 Single core cables of the same circuit shall be laid and mounted in purpose made trefoil cleats. 9.3.2 Erection 1 Cable trays arranged one above the other shall have spacing in relation to their width not exceeding a ratio of 1:2 with a minimum distance of 150 mm. 2 Supports Install fixings and supports: (a) at 2 meter centres or as specified in project docutmentation (b) 150 mm from bends, tees, intersections and risers (c) as close as practicable to joints (d) each side of expansion joints. 3 Supports shall be selected from the following types, to suit the site conditions: (a) (b) (c) (d) M12 steel threaded drop rods fixed to ceilings complete with GI channels or brackets wall support brackets cantilever arms steel channels. 4 The cable trays shall be fixed in accordance with site conditions and manufacturer’s recommendations. 5 Join cable tray and accessories with hardware per manufacturer’s recommendations. 6 Avoid mid-span joints. 7 The Contractor shall submit, as required, all calculations relating to tray work and tray supports demonstrating acceptable mechanical stresses and sag. 8 Cable trays installed on roofs shall be supported using GI brackets or concrete blocks. Removable cable tray cover shall be fitted. 9 Access shall be available at all times to remove or replace cables with a minimum of 400 mm between trays and physical obstructions, A/C ductwork etc. 9.3.3 Earthing 1 Cable trays and accessories shall be electrically and mechanically continuous throughout their length. 2 The entire cable tray system shall be bonded and 12 mm x 2.5 mm tinned copper links shall be bolted across each joint in the system by means of bronze nut and bolts, complete with flat and spring washers. QCS 2010 Qatar Project Management 13 QCS 2010 3 Section 21 Part 9 Cable Trays Page 8 All cable trays shall be provided with earth continuity copper tape along the whole route of cable trays which shall be bonded to the main earthing system of the facility. The earth continuity copper tape shall be fixed on cable tray by means of PVC covered saddles or by other means approved by the Engineer. END OF PART Qatar Project Management QCS 2010 QCS 2010 Section 21 Part 10 Wiring Accessories and General Power Page 1 10. WIRING ACCESSORIES AND GENERAL POWER ..................................... 2 10.1 GENERAL ...................................................................................................... 2 10.1.1 10.1.2 10.1.3 10.1.4 General Reference References Description of Work Submittals 10.2 PRODUCTS ................................................................................................... 2 2 3 3 4 4 5 5 5 6 6 6 6 10.3 INSTALLATION ............................................................................................. 7 10.3.1 10.3.2 10.3.3 10.3.4 10.3.5 Mounting Heights Installation of Outlet Boxes Installation of Switches Installation of Junction, Pull and Terminal Boxes Testing QCS 2010 7 7 7 7 8 Qatar Project Management 10.2.1 General 10.2.2 Outlet Boxes 10.2.3 Switches 10.2.4 Ceiling Roses 10.2.5 Socket Outlets 10.2.6 Shaver Socket Outlets 10.2.7 Cooker Control Units 10.2.8 Disconnect Switches and Switch Fuses 10.2.9 Fused Connection Units 10.2.10 Junction, Pull and Terminal Boxes 10.2.11 Timer 10.2.12 Time clocks 2 2 2 2 QCS 2010 Section 21 Part 10 Wiring Accessories and General Power Page 2 WIRING ACCESSORIES AND GENERAL POWER 10.1 GENERAL 10.1.1 General Reference 1 The work of this Section is integral with the whole of the Project Documentation and is not intended to be interpreted outside that context. 2 Co-ordinate the work with all other services affecting the work of this Section. 3 Related Parts and Sections are as follows: This Section Part 1 Part 6 Part 7 Part 8 General Provisions for Electrical Installation Cables and Small wiring Conduits and Conduits Boxes Trunking 10.1.2 References 1 The following standards are referred to in this Part: BS 88 ------------ HRC Fuses BS 546 ---------- Specification Two pole and earthing-pin plugs, socket-outlets and socketoutlet adapters BS 800 ---------- Specification for radio interference limits and measurements for household appliances, portable tools and other electrical equipment causing similar types of interference BS 1363--------- 13A Plugs, Switched and Un-switched Socket Outlets and connection units BS 3456--------- Specifications for safety of household and similar electrical appliances BS 3676--------- Part 1 Switches for household and similar fixed electrical installations BS 4177--------- Cooker Control Units rated 30 Amp. and 45 Amp. 250 volts single phase supply BS 4343--------- Industrial Plugs, Socket Outlets and Couplers BS 4662--------- Boxes for enclosure of electrical Accessories BS 5419--------- Fuse Switches and Switch Fuses BS 5733--------- General requirements for electrical accessories BS 6972--------- General requirements for luminaire supporting couplers 10.1.3 Description of Work 1 This Section shall include all labour, materials, equipment, appliances and accessories necessary for the complete performance of all switches, socket outlets etc. In accordance with the Specifications and Drawings. 10.1.4 Submittals 1 Submit shop drawings, equipment list, relevant samples etc. as mentioned under Section Part 1. 10.2 PRODUCTS 10.2.1 General 1 All individual items of materials shall be of the same make throughout the Project unless specifically approved by the Engineer. QCS 2010 Qatar Project Management 10. QCS 2010 Section 21 10.2.2 Outlet Boxes 1 Outlet Boxes: (a) (b) Part 10 Wiring Accessories and General Power Page 3 galvanized one piece pressed steel, sizes and designs shall suit devices to be fitted with a minimum wall thickness of 1.0 mm. In all hazardous areas specified and/or shown on drawings: explosion proof. Outlet boxes mounted externally or in damp locations shall be totally sealed to ensure water tightness. 10.2.3 Switches 1 Lighting Switches (a) (b) (c) (d) (e) (f) (g) (h) 2 Waterproof Switches: (a) (b) (c) (d) 3 (b) (c) the double pole switches shall be with neon indication lamps and shall be rated 20, 30 or 45 Amps. as indicated on the drawings the face plate shall be of matt chrome, unless specified otherwise in the Project Documentation and shall be engraved „WATER HEATER’, „WATER COOLER’ etc. as required. switches shall be certified for AC-23A duty. Push switches for lighting contactor control: (a) (b) (c) (d) (e) 6 where two or more switches are grouped together and connected to the same phase, multi-gang devices and common plates shall be used. Double Pole Switches: (a) 5 to be watertight IP 56 or as indicated in the Project Documentation to be made of poly-carbonate for indoor application in damp and wet areas. to be metallic suitable for AC-23A duty and have sunshades fitted where exposed to direct sunlight. to be provided with rear entry for outdoor use to avoid the exposure of conduit/cables to the harmful effects of the sun. Switch Plates (a) 4 to BS 3676 to be rated 10, 15 or 20 amps depending on connected load, as stipulated in the QGEWC regulations recessed with concealed conduit, surface pattern elsewhere quick make and break type single pole, double pole, one way, two way or intermediate as indicated surface mounted switches to be either poly-carbonate, or metallic and as indicated in the Project Documentation flush mounted switches to be of the grid fixing type with finish as noted in the Project document. switches shall be certified for AC-23A duty push to make momentary contact switch suitable for inductive load surface mounted type shall be either poly-carbonate, metallic, protected to IP 56 or as indicated in the Project Documentation where two or more switches occur in one position they shall be contained in one case and each shall be appropriately labelled to indicate its function switches shall be certified for AC-23A duty and contactors shall be certified for AC-3 duty. Dimming Switches: QCS 2010 Qatar Project Management 2 QCS 2010 (a) (b) (c) (d) Section 21 Part 10 Wiring Accessories and General Power Page 4 where indicated on the Project Drawings, dimming switches shall be provided, complying with BS5518 dimming switches shall be interference suppressed to conform with BS800 all dimmer units shall be sized to give a 40% margin above the connected load. switches shall be certified for AC-23A duty Ceiling Roses 1 Ceiling roses shall be of the all insulated type conforming to BS67 with a white finish. 2 Ceiling roses shall be provided with insulated terminals for the switched live, neutral and protective conductors; loop-in facilities shall be provided. 3 Plug-in ceiling roses shall be used in large buildings, with extensive false ceiling systems, as detailed in the particular specification. 10.2.5 Socket Outlets 1 General purpose Socket Outlets: (a) (b) (c) 2 15A Socket Outlet: (a) (b) (c) 3 (f) 13A Sockets: to BS 1363 3 rectangular pins, Un-switched type to be complete with weather proof plugs plugs: 13 Amps sockets: fused type with single pole cartridge fuse link of same rating as plug sockets and plugs: (i) to have minimum IP 55 grade protection (ii) housing parts: brass or pressure die-cast finished in grey hammered stove enamel (iii) plugs: cable grips shall have rubber compression rings there shall be rubber gasket between plug and socket to ensure weather tightness. sockets shall have screw on caps that close tight on socket when plugs are not inserted. Socket Outlet Plates: (a) 5 to BS 546 3 round pin (2 P + E) shuttered switched pattern complete with plugs. Neon indicator lamp, unless specified otherwise in the Project Documentation. Weather proof Sockets: (a) (b) (c) (d) (e) 4 to BS 1363 3 rectangular pin (2P+E) shuttered, with combined switch, rated 13A, 250 V to be supplied with plug complete with fuse socket outlet face plates shall be finished as indicated in the Project Documentation. Industrial Sockets: (a) Combined Socket (i) to be a combined unit comprising two sockets, rated 16A, 240V, 1 phase and 32A, 415V, 3 phase (ii) to be equipped with 16A SP and 32A TP MCBs, or as indicted in the Project Documentation (iii) three phase socket to be 5 pin type, single phase socket to be 3 pin type (iv) plugs of the same manufacturer to be provided (v) sockets and plugs to conform to BS 4343 (vi) to have minimum IP 55 ingress protection. (b) plugs and sockets for hazardous area: QCS 2010 Qatar Project Management 10.2.4 QCS 2010 Section 21 (i) (ii) (iii) (iv) Part 10 Wiring Accessories and General Power Page 5 to be suitable for zone 0, zone 1 or zone 2 applications, as relevant, and indicated on the Project Drawings and/or Project Documentation to conform to IEC 309-3 to be corrosion resistant ingress protection to IP 66. Shaver Socket Outlets 1 All shaver socket outlet units shall comply with BS 3456 and IEC 335. 2 Shaver units shall be flush pattern with white moulded insert in matt chrome plate engraved „Shaver Only’ and be suitable for installation in bathrooms, incorporating a double wound isolating transformer to provide an earth free supply. 3 Units shall incorporate primary winding circuit protection in the form of a self-resetting thermal overload device. 4 Units shall incorporate an „ON/OFF’ switch with red neon indicator together with a selector switch for 20 VA load capacity at 240 Volts and 115 Volts 5 Units shall incorporate two pin shuttered outlet configuration and have terminals to accept 2.5 2 mm conductors. 6 Unit outlet boxes shall be a minimum of 45 mm deep, rustproof by galvanising of equal finish and complete with a brass earthing stud secured to the back of the box. 10.2.7 Cooker Control Units 1 Cooker control units shall incorporate a 32 Amp. double pole switch and 13A, 3 pin switched socket outlet and neon indicator lights for both cooker and socket 2 The cooker control unit shall be flush mounted. 10.2.8 Disconnect Switches and Switch Fuses 1 Generally (a) (b) (c) 2 Fuse switch and switch fuses (a) (b) (c) (d) 3 to BS 5419 fuses: to BS 88 bolted type, class Q1, certified for 415V and AC 80 Duty, rated as indicated fused switch carriages: withdrawable type fuse switches: ASTA certified to 50 KA. Disconnect switches (a) (b) (c) 4 to be metal clad with front operated handles interlocked with switch fuse case to prevent opening switch in the “ON” position switch shall have “ON/OFF” indication and provision for locking in “OFF” position utilisation category AC 23A same design as switch-fuses, with solid copper links in place of fuses single pole and neutral, or triple pole and neutral ratings, as indicated. Outdoor Equipment (a) equipment intended for outdoor use shall be certified by the manufacturer as being weatherproof and suitable for use outside in the prevailing conditions and shall be in compliance with the requirements of Part 28, clause 28.2.6 of this Section. QCS 2010 Qatar Project Management 10.2.6 QCS 2010 Section 21 Part 10 Wiring Accessories and General Power Page 6 Fused Connection Units 1 240 V fused connection units shall be switched, shall comply with BS5733 and shall be fitted with a fuse complying with BS1362 with a rating as specified. 2 All fused connection unit shall be fitted with a neon indicator. 3 Live contacts shall not be exposed under normal operating conditions when replacing a fuse. 4 240 V fuse connection units in plant areas, workshops etc., shall be surface mounted, metalclad and shall comply with BS1363 . 5 The type of fused connection unit, particularly relating to the flex outlet, shall be authorised by the Engineer prior to the ordering of accessories. 10.2.10 Junction, Pull and Terminal Boxes 1 The Junction Box shall be completed with a terminal block suitable for connecting up to 10 2 mm copper conductor (phase, neutral and earth) and an all insulated moulded white cover plate with removal covers. 2 The cover plate shall be raised for connecting outgoing cable. 10.2.11 Timer 1 Timers shall be electronic type, unless specified otherwise in the Project Documentation. 2 Timers shall be suitable for operation from supply voltage of 240V, 1-phase, 50Hz system. 3 Timer output contacts shall be suitable for both a.c. and d.c. control circuits. The contacts shall be suitable for duty of AC-2 or DC-3 utilisation category. The rating of output contacts shall be co-ordinated with the application requirements. 4 Timers shall be provided with 2 independent timing scales with sets of change-over output contacts: (a) (b) 10 ................... 200 seconds 0.10 ................ 20 seconds 5 ON/OFF indicator shall be provided to monitor the circuit status. 6 Timers shall be either: (a) delay on energisation or (b) delay on de-energisation type, as per the application requirements Upon supply of rated voltage to the input terminals, the timer shall start, the output relay remains in rest position. After the set time, the output relay pulls in. The relay resets after the input supply has been cut-off. 7 Timers shall be suitable for minimum 10 million operations. 8 The timer shall require a pozi-drive screw driver for changing of the settings. 9 Degree of protection shall be minimum IP 20. 10.2.12 Time clocks 1 Time clocks to control circuits depended on time and hours of the day, may be either (a) (b) Synchronous motor operated, or Quartz controlled motor operated, as per Project Documentation. QCS 2010 Qatar Project Management 10.2.9 QCS 2010 Section 21 Part 10 Wiring Accessories and General Power Page 7 Time clocks shall be suitable for operation from supply voltage of 240V, 1-phase, 50Hz system. 3 Output contacts shall be suitable for both AC and DC control circuits. The contacts shall be suitable for duty of AC-2 or DC-3 utilisation category. The rating of output contacts shall be co-ordinated with the application requirements. 4 The no. of output contacts and the duration of contact closing shall be decided as per the application requirements. 5 Time clocks shall be provided with a time dial setting for 24 hours and 7 days program. 6 Each time clock shall be provided with a minimum running reserve energy for 1 day. 7 Accuracy of clocks shall be better than 1 second per day. 10.3 INSTALLATION 10.3.1 Mounting Heights 1 The mounting heights of wiring accessories shall be as stipulated in the QGEWC Regulations, or as otherwise approved by the Engineer. 10.3.2 Installation of Outlet Boxes 1 Location of Boxes: (a) (b) 2 determine exact location of boxes on site and obtain the Engineer’s approval before commencing installation make allowance for overhead pipes, ducts, variations in arrangement, thickness of finish, window trim, panelling and other construction when locating boxes. Fixing: (a) (b) fix outlet boxes securely fix exposed outlet boxes to permanent inserts or lead anchors with machine screws. 10.3.3 Installation of Switches 1 Lighting Switches: (a) (b) (c) (d) located at the strike side of the door, approximately 150 mm from the edge of door frame plates shall be installed with all four edges in continuous contact with finished wall plates shall be installed with an alignment tolerance of 1.5 mm all switch assembly louvered plates shall have their earthing terminal connected to 2 the earth terminal attached to the switch box by an insulated 2.5 mm protective conductor. 10.3.4 Installation of Junction, Pull and Terminal Boxes 1 Generally: (a) (b) 2 fix junction, pull and terminal boxes where indicated and where required to facilities pulling of wires and cables and connection of future appliances locate boxes as inconspicuously as possible, but accessible after work is completed. Pull Boxes: (a) fix at maximum 10m spacing and to limit the number of bends in conduit to not more than two 90° bends. QCS 2010 Qatar Project Management 2 QCS 2010 Section 21 Part 10 Wiring Accessories and General Power Page 8 10.3.5 Testing 1 Test all switches, socket outlets etc. for correct polarity and continuity of conductors in the presence of and to the entire satisfaction of the Engineer. 2 Carry out live phase to earth loop impedance tests at all switches and socket outlets with an approved earth loop impedance tester to the entire satisfaction of the Engineer. Ensure that all device plates have satisfactory earth continuity to the protective conductor system. 3 Test all socket outlets for instantaneous tripping of associated distribution board current operated earth leakage circuit breaker using testing equipment, approved by the Engineer. QCS 2010 Qatar Project Management END OF PART QCS 2010 Section 21 Part 11 Light Fittings Page 1 11. LIGHT FITTINGS ........................................................................................... 2 11.1 GENERAL ...................................................................................................... 2 11.1.1 11.1.2 11.1.3 11.1.4 General Quality Assurance References Submittals 11.2 PRODUCTS ................................................................................................... 3 11.2.1 11.2.2 11.2.3 11.2.4 11.2.5 11.2.6 Lamps Luminaires Termination/Earthing Ceiling System Noise and Interference External Lighting 11.3 INSTALLATION ............................................................................................. 6 QCS 2010 3 4 5 5 5 5 6 6 Qatar Project Management 11.3.1 Lighting Installation 11.3.2 Installation of Lamps 2 2 2 2 QCS 2010 Section 21 Part 11 Light Fittings Page 2 11. LIGHT FITTINGS 11.1 GENERAL 11.1.1 General 1 This section includes the supply and installation of lighting fittings as shown on the drawings, and as specified. 11.1.2 Quality Assurance 1 Design Criteria: (b) (c) (d) (e) (f) (g) lighting fittings shall be of first class quality, made by approved manufacturers and shall be suitable for trouble free operation on the system voltage at the site lighting fittings shall be complete with internal wiring between lamp holder and termination point. Wiring shall be in silicone rubber insulated heat resistant flexible cables the Contractor shall be responsible for co-ordinating the light fitting installation with any other components of the ceiling systems all lighting fittings shall be complete with accessories and fixing hardware necessary for installation whether so detailed under fixture description or not outdoor lighting fittings shall be installed at mounting heights as specified or instructed on site by the Engineer all outdoor lighting fittings shall be suitably constructed and protected to withstand the corrosive atmosphere and high ambient temperatures of the site, whether indicated under the fittings description or not lighting fittings shall have power factor not less than 0.9. 11.1.3 References 1 The following standards are referred to in this Part: BS 800 BS 3677 BS 4533 BS 5225 BS 60400 BS EN 60081 BS EN 60238 BS EN 60529 BS EN 60662 BS EN 60947-1 BS EN 61167 11.1.4 Submittals 1 Products Data: (a) Limits and methods of measurement of radio interference characteristics of household electrical appliances, portable tools and similar electrical apparatus High pressure mercury vapour lamps Luminaires Photometric data for luminaires Lamp holders for tubular fluorescent lamps and starter holders Tubular fluorescent lamps for general lighting service Edison screw lamp holders Degrees of protection provided by enclosures (IEC 662), High pressure sodium vapour lamps General rules for low voltage switch gear and control gear Metal halide lamps Fluorescent fittings and other electrical discharge lamp fittings, submit: (i) full technical details of the fittings, including the control gear, indicating the type and size of materials used in construction (ii) relevant sheets of manufacturer’s catalogues and dimensional drawings of the fittings, clearly showing the location of the component (iii) wiring diagram of internal connections indicating colour, size and type of wiring (iv) confirmation that control gear is suitable for prolonged and continuous service in the ambient conditions described in Part 1 (v) the power factor under operating conditions and illumination data sheets. (vi) type and quality of any plastic materials used in the fittings. QCS 2010 Qatar Project Management (a) QCS 2010 1 Section 21 Part 11 Light Fittings Page 3 Other lighting fittings, submit: (a) (b) (c) full technical details of the fittings, with relevant manufacturer’s catalogues and illumination data sheets type and quality of all metal finishes size and quality of all glassware. At least one piece of each of the lighting fixtures originally specified and quoted shall be submitted and displayed at the site office, including the alternative items for comparison in the event an alternate make is offered. 11.2 PRODUCTS 11.2.1 Lamps 1 General: (a) (b) (c) (d) (e) 2 Fluorescent Lamps: (a) (b) (c) 3 (c) wattage as indicated in the schedule of luminaires lamps with a high colour rendering index of 80 shall be used as indicated, suitable for indoor applications lumen output of lamps shall be in accordance with BS EN 60662. Metal Halide Lamps (a) (b) 6 wattage as indicated in the Project Documentation colour: deluxe white lumen output of lamps shall be in accordance with BS 3677 burning position: universal. High Pressure Sodium Lamps (a) (b) 5 tubular fluorescent lamp, to BS EN 60081. Lengths/diameters as indicated in the Project Documentation tube colour: cool white, unless otherwise indicated fittings shall comply with BS 800, for suppressing radio frequency interference. High Pressure Mercury Vapour Lamps: (a) (b) (c) (d) 4 lamps shall be furnished and installed in all luminaires covered under the Contract lamps used for temporary lighting services shall not be utilised in the final use in fixture units lamps for permanent installation shall not be placed in the fixtures until so directed by the Engineer, and this shall be accomplished directly before the building areas are ready for occupancy by the Employer lumen output of lamps shall be in accordance with BS EN 5225 generally, high output, low consumption, tri-phosphorus lamps shall be used, unless otherwise indicated. wattage as indicated in the schedule of luminaires lumen output of lamps shall be in accordance with BS EN 61167 Control Gear For Fluorescent Lamps: (a) (b) (c) (d) high frequency electronic ballast not less than 25 kHz to IEC 928, unless specified otherwise when specified, conventional type low loss ballast with electronic starters shall be used and shall provide flicker free operation, as indicated in the Project Documentation glow starters shall not be used capacitors shall be supplied with discharge resistors and shall be housed in aluminium canister. QCS 2010 Qatar Project Management 2 QCS 2010 7 Section 21 Part 11 Light Fittings Page 4 Lamp Holders: (a) (b) (c) SBC, BC GES, Bi-pin, etc. as necessitated by the lamp cap Edison screw lamp holders, to BS EN 60238, to be designed so that the lamp cap only makes electrical contact when fully screwed home, and to have means to prevent the unscrewing of the lamp due to vibration or similar cause Lamp holders for fluorescent lamps, shall be the spring loaded rotary type, to BS 6702. Luminaires 1 Luminaires shall be manufactured to BS 4533 with an appropriate IP classification to BS EN 60529. 2 All lighting fittings shall be supplied complete with appropriate control gear where necessary, lamps, mounting and fixing accessories etc. whether explicitly mentioned in the description of each light fitting or not. All the fittings shall have the same appearance, material, technical details and approximate dimensions. 3 Luminaires shall be connected to the main circuit wiring with heat resistant flexible cables of a 2 minimum conductor size of 1.5 mm insulated with silicon rubber. 4 Break joint rings shall be used in conjunction with batten holders, ceiling roses or back plates mounted onto a flush installation. 5 Standard fluorescent luminaires shall have two suspension or fixing points. The thickness of the luminaries body shall not be less than 0.6 mm. 6 All lamp-holders for flexible pendants shall be of the all insulated skirted pattern with code grips and for batten or wall mounting shall be of similar pattern. All lamp holders shall be of the bayonet cap pattern. 7 The point box suspensions and other parts of the lighting fittings shall be provided to be erected at festival time to suit the building programme for decoration as per the requirements of the Project Documentation. 8 The glassware diffusers, shades and lamps shall not be fitted until all building work is complete. 9 All fittings shall be easy to clean inside and outside, when mounted. 10 All fluorescent fittings shall be suitable for instant start irrespective of any catalogue or list numbers quoted. 11 Diffusers on fluorescent luminaires shall be poly-carbonate unless otherwise specified in the Project Documentation. 12 All fittings that are mounted in areas accessible to the public shall be provided with vandal proof high strength diffusers and shall be additionally provided with a galvanised steel mesh security guard. 13 All luminaires shall be certified by the manufacturer for use in an ambient temperature of 50°C. 14 All luminaires intended for use in hazardous areas shall be certified to be zone 1 or 2 as required at 50°C ambient temperature. 15 Wet well luminaries, fixtures and cabling shall conform to ingress protection IP67,shall be PTFE coated and shall be provided with tungsten halogen lamps i.e. no run up or re-strike time for safety reasons. 16 All wet well luminaries, fixtures and cabling shall conform to ingress protection IP67. QCS 2010 Qatar Project Management 11.2.2 QCS 2010 Section 21 Part 11 Light Fittings Page 5 Termination/Earthing 1 Fused terminal blocks shall be fitted and be of sufficient capacity for the wiring involved. 2 Each terminal shall be capable of accommodating two 2.5 mm conductors. 2 Connector strip terminals shall have a current rating not less than the rating of the circuit protective device and shall be encapsulated in self-extinguishing grade polyethylene. 3 Where connector strips are provided in boxes behind heat producing appliances, porcelain connectors shall be used where temperatures in excess of 70 °C are likely. 4 Conductors shall be clamped between metal surfaces such that no screws make direct contact with the conductor. The metal used in construction of the connector shall be at least 85 °C copper alloy such that good conductivity and electrolytic compatibility are maintained at all times. 5 All light fittings shall be provided with an earthing terminal which shall be connected to the earth continuity lead of the final sub-circuit. 6 The earthing of all pendant or semi-pendant fittings shall be by a separate core in the connecting flex or cable securely bonding the earth terminal on the fitting to the glanded joint of interconnecting cables. In no case shall pendant chains or conduit support tubes be used as a means of earthing. 11.2.4 Ceiling System 1 In false ceilings, luminaires whether surface or recessed mounted shall not be supported by the false ceiling construction. Separate independent supporting systems shall be provided for each luminaire, comprising drop rods, chains or similar. 2 Luminaires installed in false ceilings shall be connected to the lighting circuit using mechanically coupled plug-in ceiling roses. 3 Luminaires shall be positioned to provide ease of access for maintenance, cleaning etc., while not impairing the distribution of light. 4 The Contractor shall ensure that the luminaire manufacturer has the correct details of the ceiling system, including suspension, tiles, etc. He shall ensure that the luminaires are supplied with the correct trim, suspension system and are fully compatible with the ceiling system. 11.2.5 Noise and Interference 1 The noise level from control gear, obtained from the average of sound pressure levels each measured at 2000 mm from the control gear in at least five positions (on each side and below), shall not exceed 30 dB Scale “A” (Noise Rating Number). 11.2.6 External Lighting 1 General: (a) (b) external lighting system shall consist of supply and installation of lighting columns, foundation and fixing of the columns, underground cabling, high pressure sodium vapour lamps or as specified, and control equipment as required contactor units, where specified incorporating a controlling photo-cell and time switch, shall be provided within the external lighting distribution board for the control of external lighting QCS 2010 Qatar Project Management 11.2.3 QCS 2010 (c) 2 Section 21 Part 11 Light Fittings Page 6 underground lighting cabling shall be XLPE or PVC/SWA/PVC or as detailed in in the Project Documentation. Lighting Columns (a) (b) (c) (e) (f) 3 All external lighting fittings shall be adequately earthed. 4 Control gear shall form an integral part of the lighting fittings except where specified, or where this is not possible, it shall be totally enclosed in a housing to suit the installation location. 5 All external fittings shall be dust-tight and waterproof to IP 65. 6 The particular requirements for road lighting and high mast floodlighting are specified in Section 6, Part 12. 11.3 INSTALLATION 11.3.1 Lighting Installation 1 Terminations: (a) (b) general fluorescent fittings mounted direct to conduit outlet boxes shall have the circuit wiring run direct to the fittings terminal position. Flexible conduit pigtail shall be provided for all fixtures to J-boxes terminations for recessed, or semi-recessed pattern fittings fitted in false ceilings, shall have the circuit wiring terminal above the ceiling in a ceiling rose Outlets shall be mounted adjacent to the fitting. 11.3.2 Installation of Lamps 1 Generally install new lamps in all luminaires at substantial completion of work. END OF PART QCS 2010 Qatar Project Management (d) columns shall be hot-dip galvanized steel of either tapered or tubular construction complete with luminaire fixing arms or brackets, as per design. all columns shall be externally painted with 2 coats of aluminium paints, internal surface including the studs inside the cable connecting box with red lead anticorrosive paints, the finishing shall be micaceous iron oxide paint pigmented with aluminium the column shall be equipped with auxiliary control gear and a 15 amp. single pole and neutral cut-out (with a three phase and neutral terminal block), two cable glands and two entry slots in the base of the pole for incoming and outgoing cables a two core and earth 2.5 mm sq. butyl rubber insulated heat resistant flexible cable shall connect the lantern to the cut-out columns shall be provided with base plates having fixing holes and anchor bolts for foundations unless specified otherwise, the column length shall be 5m including buried part or 4m when plinth mounted. The diameter at the bottom shall not be less than 120 mm. QCS 2010 Section 21 Part 12 Emergency Lighting Page 1 12. EMERGENCY LIGHTING .............................................................................. 2 12.1.1 12.1.2 12.1.3 12.1.4 Scope Reference Standards Quality Assurance Warranty 12.2 PRODUCTS ................................................................................................... 2 12.2.1 12.2.2 12.2.3 12.2.4 12.2.5 General Central Battery Units Self Contained Emergency Battery Packs Luminaries and Lamps Obstruction / Beacon lights 12.3 INSTALLATION ............................................................................................. 5 QCS 2010 2 3 4 4 5 5 5 6 Qatar Project Management 12.3.1 Wiring 12.3.2 Installation of Batteries 12.3.3 Luminaries and Lamps 2 2 2 2 QCS 2010 Section 21 Part 12 Emergency Lighting Page 2 12. EMERGENCY LIGHTING 12.1.1 Scope 1 This Part specifies the general requirements for emergency lighting and accessories both maintained and non-maintained. It shall be read in conjunction with other parts of the Specifications and the Project Drawings. 2 Related Parts and Sections are as follows: General Provisions for Electrical Installations Wiring Accessories and General Power Light Fittings Testing 12.1.2 Reference Standards 1 The following standards and documents of other organisations are referred to in this Part, and shall be complied with: BS 4533 .......... General requirements and tests BS 4533 ........... Luminaires for emergency lighting BS 5225 Method of photometric measurement of battery operated emergency lighting luminaires BS 5266 ........... Emergency lighting BS 7671 .......... Requirements for electrical Installations BS EN 60529 ... Degrees of protection provided by enclosures (IP code) ISO 9000 ......... Quality management and assurance standards QGEWC .......... Qatar General Electricity & Water Corporation Regulations. 12.1.3 Quality Assurance 1 The supplier’s manufacturing facility shall be certified to ISO 9000 or equivalent. 12.1.4 Warranty 1 Battery units, luminaires and accessories shall be warranted for a minimum of 5 years by the manufacturer. The battery shall have minimum 10 years useful life. 12.2 PRODUCTS 12.2.1 General 1 Emergency lighting installations shall be complete with emergency batteries, chargers, luminaires and wiring, all as described in Specifications and as indicated on the Project Drawings, complying with BS 5266 Part 1.All emergency lighting shall be Non-maintained type except for the EXIT lights where it shall be maintained unless otherwise explicitly specified in the project documentation. 2 Non-maintained luminaires shall be supplied directly from the battery system. Maintained exit luminaires etc., shall be supplied from a separate supply via an independent transformer and shall only operate from batteries during mains failure. QCS 2010 Qatar Project Management This Section Part 1 Part 10 Part 11 Part 24 QCS 2010 Section 21 Part 12 Emergency Lighting Page 3 3 The operation of the system shall be such that on loss of one or all phases of the main electricity supply, a set of central batteries or individual battery packs shall provide power for 3 hours to illuminate emergency luminaires throughout the building. On restoration of the mains supply the batteries shall be charged by an integral charger such that the system supplies not less than 85 % of its rated voltage after a period of 12 hours. 12.2.2 Central Battery Units 1 Battery chargers: (a) (c) (d) (e) (f) (g) (h) 2 units shall be provided with composite output distribution boards of the sizes and types indicated on the Project Drawings units shall be installed complete with all necessary fixings, maintenance equipment and instructions. Batteries: (a) (b) (c) (d) batteries shall be suitable for the discharge duty they will be required to perform. Batteries shall be of the lead acid, sealed re-combination type or Nickel Cadmium depending on the duty requirements and as indicated on the Project Drawings. The contractor shall submit calculation to justify the Ampere-Hour capacity of the batteries for approval to the Engineer battery system shall be provided with a suitably rated switch disconnector Batteries shall be mounted on suitable tiered galvanized steel shelving with moulded plastic trays to contain any leakage from the battery cells and, to allow safe easy access for maintenance battery terminals shall be coated with the battery manufacturer’s approved grease, and shrouded if not enclosed. QCS 2010 Qatar Project Management (b) battery chargers shall be installed in purpose-made metallic enclosures with an index of protection IP 31 in accordance with BS EN 60529 suitable for wall or floor mounting, depending on size battery charger enclosures may house the system batteries providing the design of the enclosure ensures safe operation with the batteries specified. This arrangement should normally be restricted to smaller systems e.g. for circuit breaker tripping supplies for power supply to emergency lighting system, central battery units shall be wall or floor mounted as required, conforming to BS 4533 Section 102.22, and be of robust, high quality construction. Enclosures shall be metal, with hinged lockable doors and with suitable ventilation provided battery charger shall operate from a 415 V, three phase or 240 V, 50 Hz single phase supply, unless otherwise specified battery charger shall be rated to supply trickle charge and any standing loading plus any additional recharging load that may be imposed battery charger shall use an uncontrolled bridge as the input stage to minimise harmonic generation on the supply system. The characteristics of each charger shall match the requirements of the specific batteries selected and the duty cycle battery charger shall be suitable for fully automatic charging of the appropriate battery and shall be provided with: (i) Mains „ON’ lamp (ii) Main ON/OFF switch (iii) Charge Ammeter Discharge Ammeter (iv) Battery voltmeter (v) Test switch facilities (vi) Contactor/relays to BS 5266 Part 3 (vii) fault protection (viii) output current limitation (ix) lamp indication for appropriate faults e.g. charger fail, low volts etc., with lamp colours in accordance with BS EN 60073 (x) common fault contact for use with a central alarm system or BMS. QCS 2010 Section 21 Part 12 Emergency Lighting Page 4 Self Contained Emergency Battery Packs 1 Where a central emergency battery unit is not installed, individual emergency luminaries shall consist of individual power packs installed within or remote to the luminaries. 2 Battery pack units shall consist of converter/inverter devices, with nickel-cadmium batteries to provide 3 hours operation under mains failure, unless the main supply is restored prior to this. 3 Luminaries with self contained battery packs shall be connected to the „live side’ of the local lighting circuit and lamps shall operate automatically under mains failure conditions. 4 Units shall have the capability of sustaining high temperature so that they can be accommodated in fittings with high internal temperatures. However, if the internal temperature of the fittings exceeds 50 °C, the battery unit shall be mounted remote to the luminaries. In the case of remote mounting, a purpose made remote mounting box shall be provided. 5 Key operated switches shall be provided, at the locations indicated on the Project Drawings, for all self contained emergency pack unit luminaries, to control the operation of the luminaries manually for testing purposes. Test key switches shall be clearly labelled “Emergency Lighting”. 12.2.4 Luminaries and Lamps 1 Clauses of Part II relating to luminaries and lamps shall also apply to emergency luminaries and lamps. 2 Slave luminaries shall comply with BS 4533 Section 102.22 and BS5225 Part 3 and be as specified. 3 Exit sign luminaries lettering shall be both in Arabic and English. The Arabic text shall be above the English text. Maximum viewing distance for minimum legend height shall be guided as follows: H > L/200 H = Height of Legend L = Distance of viewer from the sign 4 Self contained emergency luminaries shall have a red light emitting diode installed on the luminaries so that the red light is visible. 5 With the central battery unit system, emergency luminaries shall be installed with an engraved label fixed to the outer case of the luminaries, so that it is readily identified. The label shall detail the lamp wattage and rated voltage. 6 Generally, marking of emergency luminaries shall comply with BS5266 Part 1. 7 The following illumination level shall be considered for designing the number of luminaries for emergency lighting: (refer to BS 5266, Part 1) Space to Height Ratio for luminaries shall be 4:1 5 lux for vital positions: QCS 2010 first aid and safety equipment exit doors fire alarm call points fire fighting equipment exit and safety signs changes of direction corridor intersection adjacent areas of final exit points Qatar Project Management 12.2.3 QCS 2010 Section 21 Part 12 1 lux for normal working spaces: 8 Emergency Lighting Page 5 on the centreline of escape route toilets lift cars and moving ways plant rooms covered car parks Fluorescent lamps shall be provided for both slave and self contained type luminaire installations. The lamp wattage ratings shall be chosen from the following table: Slave Self contained : 4 watts or 8 watts : 8 watts, 18 watts, 36 watts or 58 watts 12.2.5 Obstruction / Beacon lights 1 2 This regulation is mandatory by International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO). Where a building height is 45m or more, then the contractor shall install permanent obstruction lights as required by ICAO. The contractor shall obtain local navigation authorities requirements and approval for this type of installation.. 3 12.3 INSTALLATION 12.3.1 Wiring 1 Where the emergency lighting system installation is via a central battery unit, the wiring to emergency luminaries shall be carried out in MICC, PVC sheathed cables, unless specified otherwise. 2 Where the emergency lighting scheme is self-contained emergency packs, the wiring system shall either be in MICC Cables as above or in PVC insulated single core wires in conduits. 3 Generally, cables shall be 2.5 mm cross-sectional area unless specified otherwise. 4 The Contractor shall pay careful attention to cable routings so as to keep cable runs to the shortest possible length and ensure the overall volt drop on any circuit is within the tolerances of the luminaries connected and within the limits specified in the QGEWC regulations. 12.3.2 Installation of Batteries 1 The manufacturer’s recommendation/instructions shall always be followed. 2 Insulated tools shall be used. 3 Personnel erecting battery banks shall remove metallic objects from their person i.e. watches, rings etc. 4 Eye and hand protection shall be provided. 5 Batteries shall not be left on site for prolonged periods without being trickle charged to maintain their condition i.e. if delivery is some weeks before commissioning of the charger. 6 Due care shall be observed when handling acidic substances. 2 QCS 2010 Qatar Project Management Total quantity of luminaries shall be calculated based on the illumination level requirement as per item 7 above, the type of luminaries and lamp lumens. QCS 2010 Section 21 Part 12 Emergency Lighting Page 6 12.3.3 Luminaries and Lamps 1 Luminaries and lamp installation shall comply with the requirements stipulated in Part 11 for general light fittings. END OF PART Qatar Project Management QCS 2010 QCS 2010 Section 21 Part 13 Telephone Installations Page 1 13. TELEPHONE INSTALLATIONS .................................................................... 2 13.1 GENERAL ...................................................................................................... 2 13.1.1 Scope 13.1.2 Reference Standards 13.2 2 2 PRODUCTS ................................................................................................... 2 13.2.1 General 13.2.2 Telephone Outlets 2 2 INSTALLATION ............................................................................................. 3 13.3.1 13.3.2 13.3.3 13.3.4 Incoming Line/Site Services Conduits and Trunking Telephone Outlets Special Requirements QCS 2010 3 3 3 3 Qatar Project Management 13.3 QCS 2010 Section 21 Part 13 Telephone Installations Page 2 13. TELEPHONE INSTALLATIONS 13.1 GENERAL 13.1.1 Scope 1 This Part specifies the general requirements for telephone installations carried out as part of a contract for other works. It shall be read in conjunction with the other Parts of the Specifications and the Project Drawings. 2 Related Parts and Sections are as follows: General Provisions for Electrical Installations Cables and Small Wiring Conduits and Conduit Boxes Trunking Cable Trays Wiring Accessories and General Power Structured Cabling Systems Testing 13.1.2 Reference Standards 1 The following standards and documents of other organisations are referred to in this Part, and shall be complied with. BS 13631 Q-TEL 3A plugs, socket outlets, adapters and connection units Regulations 13.2 PRODUCTS 13.2.1 General 1 Telephone cabling and equipment supply and installation shall be carried out by an approved Q-TEL contractor specialising in telephone installations. 2 All telephone related installations carried out by the Contractor shall conform to the Q-TEL standard specifications and regulations together with this specification and the Project Drawings. 3 The Contractor shall supply and install cable ways, empty conduits with draw wires and/or trunking, telephone points and outlets, PVC ducts, telephone junction boxes, and manholes as required and shown on the Project Drawings unless otherwise Specified. 13.2.2 Telephone Outlets 1 The Contractor shall supply and install telephone points and the associated mains power outlets which shall conform to BS1363 . 2 The telephone outlets shall be jack type and from the same manufacturer, and finish as for the lighting and general power outlets, unless specified otherwise. 3 Telephone outlets shall be of the type approved by Q-TEL. QCS 2010 Qatar Project Management This Section Part 1 Part 6 Part 7 Part 8 Part 9 Part 10 Part 14 Part 23 QCS 2010 Section 21 Part 13 Telephone Installations Page 3 INSTALLATION 13.3.1 Incoming Line/Site Services 1 The Contractor shall supply and install the incoming line underground through Q-TEL approved PVC-u pipe ducts with draw wires, together with the manholes/draw pits as indicated on the drawings. 2 The works shall be carried out in co-operation with Q-TEL Engineers. 3 Standard Q-TEL type manhole and manhole covers shall be utilised, appropriate to the manhole location. 4 External ducts shall be installed in a 775 mm deep trench, on 75 mm of dune sand, covered with 75 mm of dune sand, and completed with selected filling materials. 5 Trenches for Q-Tel ducts through rockfill shall be lined with Terram Grade 1000 filter fabric material as specified in Section 6 Clause 14.9.5. 6 Contractor shall arrange with Q-TEL for inspection of the installation during execution stage and on completion, all costs are deemed to be included in his price. 13.3.2 Conduits and Trunking 1 The Contractor shall if required by the Project Specification or on the Project Drawings, allow for the supply and installation of an empty conduit system complete with draw wires and/or a trunking system between the outlet points and the telephone equipment area. 2 Conduit installations shall be concealed within the building fabric and/or concealed in suspended ceiling voids. 3 Conduit and trunking installations shall conform to the requirements of the Specifications and Q-TEL requirements. 4 Unless otherwise specified, the minimum size of the conduit installed shall be 25 mm diameter and telephone underground duct 50 mm diameter as subscriber duct. 5 The Contractor shall be responsible for liaison with the specialist telephone installer and/or QTEL engineers to ensure that: (a) (b) the proposed conduits and trunking are adequate to accommodate cables the specialist installer is provided with the programme requirements and that his work is carried out in accordance with the Contractor’s main programme. 13.3.3 Telephone Outlets 1 Outlets shall be installed at locations indicated on the drawings and at the same heights as the general power socket outlets, unless otherwise specified in the Project Documentation. 13.3.4 Special Requirements 1 The Contractor shall consult the Q-TEL not less than one month before it is proposed to commence work to ascertain whether any underground installations will be affected by the proposed works, in which event the Contractor shall make all necessary arrangements with Q-TEL to safeguard the installation. 2 The Contractor shall give at least one week’s notice in writing to Q-TEL of the dates upon which it is intended to operate plant or equipment or carry out work for which permission has been given in writing by Q-TEL; such operations of work shall only be carried out in the QCS 2010 Qatar Project Management 13.3 QCS 2010 Section 21 Part 13 Telephone Installations Page 4 presence of Q-TEL unless notice shall be obtained in writing from Q-TEL that they do not require to be present. 3 Q-TEL may require work to be executed on their installations during the period of the Contract; the Contractor shall afford all facilities to Q-TEL’s contractors or workmen until their diversion work is complete. The Contractor shall co-ordinate the work of Q-TEL and his own activities and when necessary shall amend his programme of work to suit all requirements of Q-TEL in connection with their diversion work and keep the Engineer informed in writing of all arrangements made. END OF PART Qatar Project Management QCS 2010 QCS 2010 Section 21 Part 14 Structured Cabling Systems Page 1 14. STRUCTURED CABLING SYSTEMS ...................................................................2 14.1 GENERAL ...................................................................................................................2 14.1.1 Scope 14.1.2 Reference Standards 2 2 PRODUCTS ...............................................................................................................2 14.2.1 14.2.2 14.2.3 14.2.4 14.2.5 14.2.6 General Copper Cables Optical Fibre Cables Patch Panels Patch Cords/Line Cords Outlets 14.3 INSTALLATION .........................................................................................................4 2 2 3 3 3 4 14.3.1 Containment Systems 14.3.2 Testing and Commissioning QCS 2010 4 5 Qatar Project Management 14.2 QCS 2010 Section 21 Part 14 Structured Cabling Systems Page 2 14. STRUCTURED CABLING SYSTEMS 14.1 GENERAL 14.1.1 Scope 1 This Part specifies the general requirements for structural cabling system used in data transmission applications for buildings or sub-systems thereof. 2 Related Parts and Sections are as follows: General Provisions for Electrical Installations Cables and Small Wiring Conduits and Conduit Boxes Trunking Cable Trays Uninterruptible Power Supply Systems Testing 14.1.2 Reference Standards 1 The following standards and documents of other organisations are referred to in this Part, and shall be complied with: BS EN 60950 Safety of information technology equipment, including electrical business equipment EN 50173 Information Technologies: Generic Cabling Systems ISO/IEC 11801 Generic Cabling for Customer Premise Cabling EIA/TIA SP-2840 ANSI/EIA/TIA 455-30,46,51,53,61 ANSI/EIA/TIA 568A ANSI/EIA/TIA 592-AAAA ANSI/ICEA S-83-569 (Ref. B.1.40) Bellcore TR-TSY-000020 14.2 PRODUCTS 14.2.1 General 1 The Contractor shall provide structured cabling installations for telephone and computer networks, including distribution frames, patch panels, racking systems (cabinets), patch cords, outlets, adaptors, conduits, PVC ducts and junction boxes, in accordance with the Project Specification and Drawings. 2 Wiring for cabling systems shall be carried out by a Specialist Contractor approved by the Engineer and Q-TEL, who has 5 years experience in Qatar. 14.2.2 Copper Cables 1 Copper cables shall be 24 AWG, 4 pair 0.170 mm diameter, polymer alloy jacket, category 5, unshielded twisted pair (UTP), suitable for extended multi-media transmission distance over frequency range up to 100 MHz, with extremely low noise characteristics. 2 Cables shall conform to ANSI/EIA/TIA 568A, Category 5 and EIA/TIA SP-2840 horizontal UTP. 3 Cables shall conform to the following performance data: NEXT (dB) worst pair at 100 MHz QCS 2010 : 38 dB Qatar Project Management This Section Part 1 Part 6 Part 7 Part 8 Part 9 Part 18 Part 23 QCS 2010 Section 21 Part 14 Attenuation (dB/100 m) Impedance ±7 % (Typical) Structured Cabling Systems : : Page 3 22.0 dB/100 m 100 ohms ±7 % Optical Fibre Cables 1 Optical fibres, cables shall be multi-mode, graded index optical fibres with nominal 62.5/125 µm core/cladding diameter. 2 Fibres shall comply with ANSI/EIA/TIA 592-AAAA (Ref. B1.18) and also with ANSI/EIA/TIA 568A Paragraph 12.5.1 on mechanical terminations. 3 Outdoor optical fibres shall be used to connect buildings to the main distribution frame. 4 Outdoor optical fibres shall comply with the same specifications, however cables shall also be steel jacketed, jelly filled, rodent proof specifically made for outdoor applications, with 12 strands. 5 Optical fibres shall meet the graded-index multi-mode performance specified in Table 14.1. Table 14.1 Graded-Index 62.5/125 µm Multi-mode Cable Characteristics 850 nm 1300 nm Attenuation - dB/km 3.75 1.5 Bandwidth - MHz. km 160 500 6 Attenuation shall be measured in accordance with EIA fibre optic test procedure ANSI/EIA/TIA 455-46, 61, or 53 (Ref. B1.39). Information transmission capacity shall be measured in accordance with the ANSI/EIA/TIA 455-51, or 30 (Ref. B1.39) 7 Mechanical and environment specifications for indoor fibre optical cables shall be in accordance with ANSI/ICEA S-83-569 (Ref. B1.40). Outdoor fibre optic cables shall be in accordance with Bellcore TR-TSY-000020 (Ref. B1.36). 14.2.4 Patch Panels 1 Patch panels shall be type RJ45, 16 port, 1U type in rows of three with extension possible of up to six patch panels. 2 Patch panels shall be housed inside racking system (19” preferred) cabinets with hinged doors on either sides and lockable front doors. 3 Ventilation slots shall be provided in both sides. 4 Rack size shall suit patch panels. 14.2.5 Patch Cords/Line Cords 1 Patch cords, shall be 2 metres long with adapters at both ends suitable for connection to RJ45 16 port IU patch panels. 2 Patch cords shall be Category 5 and be flexible enough to bend without loosing any performance. 3 Patch cords shall be the flexible stranded type. QCS 2010 Qatar Project Management 14.2.3 QCS 2010 Section 21 Part 14 Structured Cabling Systems Page 4 4 Line cords shall have the same specifications as patch cords, however these shall be the solid type, used at wall outlets to connect computers or terminals to distribution cabling systems. 5 Cables shall comply with the performance data specified in Table 14.2. Table 14.2 Specifications for Category 5 solid/stranded line cords or patch cords Attenuation Next (MHz) (Max. dB/305 m) (Min Loss dB/305 m) 1.00 6.80 62.0 4.00 14.0 53.0 10.0 22.4 47.0 16.0 28.3 44.0 20.0 31.7 42.0 25.0 35.9 41.0 31.25 40.9 40.0 62.5 59.3 35.0 100.0 76.1 32.0 14.2.6 Outlets 1 These shall be twin outlet type RJ45 to EN 60950 IBS 7008 having white moulded plastic plates with black shutters for computer outlets and white shutters for telephone outlets. 2 Outlets shall conform to the following specifications: (a) (b) (c) (d) Attenuation (dB) Return loss (dB) Bulk resistance (milli-ohm) Voltage rating : : : : <-0.12 <-21.54 21.85 >1050 V DC for 1 minute 14.3 INSTALLATION 14.3.1 Containment Systems 1 90 mm diameter PVC-u ducts and draw-pits shall be provided from external boundary walls to main distribution frame (MDF) positions and from the MDF to other buildings, as indicated on the Project Drawings. 2 Conduits, trunking and cable trays shall be provided for structured cabling installations, complying with Parts 7, 8 and 9 respectively of Section 21. The minimum conduit size shall be 25mm. 3 The computer wiring shall be laid from the user outlets up to the computer room (server) without any joints in between. Moreover the maximum length of a single run shall not exceed 90 meters, otherwise amplification of signal shall be provided. All public offices and buildings shall be equipped with a complete wireless access points through the building. QCS 2010 Qatar Project Management Frequency QCS 2010 Section 21 Part 14 14.3.2 Testing and Commissioning 1 General (a) (b) 2 Page 5 the Specialist Contractor shall test the complete cabling network to ensure that noise is not interfering with systems and contact resistance are kept within acceptable levels certificates shall be supplied by the Specialist Contractor to certify efficient working of the networks. Wire mapping for correct polarity Length for point to point connectivity under 90 metres Near end cross talk (NEXT) Resistance Impedance Capacitance Noise Attenuation Optical fibre cable shall comply with the following: (a) (b) (c) certificates of compliance with EIA/TIA specifications, and manufacturer’s test certificates attached to the reels/drums white light tests shall be performed to confirm end to end connectivity on delivery to site, after installation and prior to field termination after field termination point to point connectivity shall be tested on each cable by a hand held optical time domain reflectometer, (OTDR), or optical power light meter and light source, capable of reading and measuring signal loss by generating wave lengths of 950 mm and 1300 mm. This shall check the field termination loss and that no damage has occurred from macro/micro bending. END OF PART QCS 2010 Qatar Project Management Copper Cable and Connectors: Each RJ-45 Jack connector shall be tested to ensure Category 5 performance. Each RJ-45 Jack shall be tested for Point to Point connectivity, by utilising hand held time domain reflectometers (TDR), capable of generating pulses of 100 MHz, and of testing that the following parameters are in accordance with EIA/TIA 568A: 3 Structured Cabling Systems QCS 2010 Section 21 Part 15 Electric Motors Page 1 15. ELECTRIC MOTORS .................................................................................... 2 15.1 GENERAL ...................................................................................................... 2 15.1.1 Submittals 15.1.2 References 15.2 PRODUCTS ................................................................................................... 2 15.2.1 Motor Enclosures 15.2.2 Induction Motors 15.3 2 2 2 3 INSTALLATION ............................................................................................. 7 QCS 2010 7 7 7 Qatar Project Management 15.3.1 General 15.3.2 Factory Tests 15.3.3 Field Checks QCS 2010 Section 21 Part 15 Electric Motors Page 2 15. ELECTRIC MOTORS 15.1 GENERAL 15.1.1 Submittals 1 Submit for QGEWC/Engineer approval, shop drawings, factory test reports, manufacturer’s certified reports and technical data for motors supplied with driven equipment to the extent required in this Section and the Specification Sections for mechanical equipment. 2 Shop Drawings. In addition to information to be included in the shop drawings as specified in Part 1, shop drawings shall include the following: (d) (e) (f) (g) (h) motor locked rotor and full load currents power factors and efficiencies at full load, three quarters load and half load motor housing material, winding material, ambient temperatures and maximum elevations in which motor is designed to operate continuously, service factor, insulation Class, temperature rise, type of enclosure, voltage, bearing life and dynamic balance; all of which shall comply to the requirements of the specifications nameplate data dimensions, weights and mounting details of motors motor construction details speed torque/current at 100 % volts wiring diagrams, internal and typical external connections. 3 Current Data. Submit eight copies to the Engineer of field recorded current data. The data shall indicate the full load current for each motor, and current rating for the overload relay in each motor starter and controller. 15.1.2 References 1 The following standards are referred to in this Part: BS 2048 BS 4999 BS 5000 Dimensions for fractional horse-power motors Winding terminations Rotating electrical machines of particular types or for particular applications 15.2 PRODUCTS 15.2.1 Motor Enclosures 1 Motor enclosures shall be selected from BS EN 60034-5 as follows:(a) (b) (c) (d) for submersible applications the enclosure shall be IP68 and be capable of being continuously submersed to a depth of at least 2 metres greater than the maximum immersion depth of the application. Where such motors are to be installed in an area designated as potentially explosive then it shall have the appropriate BASEEFA/CENELEC or other similar National Testing Organisation Certification. Copies of the Certificates shall be submitted. Motors to be used in sewage wet wells shall be certified for use in a Zone 2 area and Certificates shall show that the motors o were tested at an ambient temperature of 50 C. They shall be certified in accordance with BS 4683 Parts 1 and 2 classification Ex d IIA T3. motors shall be of the submersible squirrel cage rotor induction type suitable for operating in the specified medium (sewage, effluent etc.). motors shall be suitable for continuous operation when immersed in the specified medium and when the motor is above the specified medium in an ambient temperature o of 50 C. the motors shall be entirely waterproof and provided with adequate cooling facilities which shall be achieved either by the surrounding liquid in the sump or by providing a motor jacket cooling system supplied with liquid from the pump volute. QCS 2010 Qatar Project Management (a) (b) (c) QCS 2010 (e) (f) (g) (h) (i) 2 Part 15 Electric Motors Page 3 terminal boxes shall be watertight and the motor shall be supplied with an adequate length of multi-core heavy duty flexible cable with tough rubber outer sheath. the cable shall pass through a watertight gland on entry into the motor body. the rotor and impeller assembly shall be dynamically balanced at the duty speed. for indoor applications the enclosure shall be to IP54 of BS EN 60034-5. Submersible motors that are to be installed in dry wells shall be to IP 68 of BSEN60034-5. The cooling method shall be exactly the same as if the motor was installed in a submerged condition. Under no circumstances will an external cooling fan be permitted on dry installed submersible motors. for outdoor application the enclosure shall be to IPW55 of BS EN 60034-5. A certificate shall be issued by the manufacturer certifying the motor suitability for the outdoor application, in the service conditions as described under the general section of this specification. for high voltage motors the enclosure shall be protected to IP55 of BS4999 Part 105 Unless stated otherwise, stator frames shall be of cast iron, foot and flange mounted as required by the Contract. Aluminium frames are permitted for 2.2 kW motors and smaller only. Ductile stainless steel frames shall be used, when specified in the particular specification, for aggressive sewage conditions, and shall be of grade 316L minimum. (a) (b) (c) (d) lifting facilities shall be provided on all motors submersible motors shall be protected by a tandem mechanical seal arrangement. Lip seals are not permitted. The Contractor shall provide complete data on the seal materials, seats, faces etc., and ensure suitability for the medium being sealed i.e. oil chamber, oil and supernatant. on pumps greater than 2.2 kW the mechanical seal performance shall be monitored by monitoring equipment to detect the following:(i) moisture within the oil chamber. (ii) moisture/water or oil within the motor casing. (iii) temperature rise of the hydraulic driven end bearing. (iv) loss of oil from the oil chamber. motors installed outdoors shall be protected from direct sunlight. Fan covers and cooling fans shall be metallic. Plastic fan covers and/or fans shall not be permitted on motors installed outdoors. Sunshades on motors/machinery should be sized such that cable entry points and the ends of cable trays are protected from sunlight. Sun/weather protection shades shall be manufactured from welded mild steel, hot dip galvanised after manufacture, or stainless steel. There shall be no sharp edges or dangerous protrusions on any sun/weather protection shades. 15.2.2 Induction Motors 1 General: (a) (b) (c) (d) (e) (f) motors shall be supplied by the manufacturer of the driven equipment as specified in this section, and specifically outlined in the driven equipment specifications all motors shall be suitable for operation on a 415V, 50 Hz 3 phase supply all motors shall be capable of starting 10 times per hour. The stalled motor current shall not exceed 6 times full load current the motors shall be commercially silent in operation and run free from vibration and the rotors shall be perfectly balanced both statically and dynamically and shall be tested and adjusted for dynamic balance in an approved manner the motors shall be fitted with anti-condensation heaters of a size to maintain the temperature of the windings 5 °C above ambient. Each heater shall be provided with a switch and automatic control to disconnect it when its motor is in operation Terminal Boxes (i) terminal boxes shall be cast iron and shall be designed to accept XLPE or PVC armoured cable as detailed in the Contract. On non-submersible motors, terminal boxes shall be mounted on the right hand side when viewed from the driving end of the motor, unless otherwise required by the Contract. (ii) the motor stool base where appropriate shall be drilled at works vertically below the terminal box gland for the passage of the cables and the edges of the hole slightly countersunk or the hole bushed. (iii) terminals shall be stud-type, substantially designed, anchored to a carrier QCS 2010 Qatar Project Management (j) Section 21 QCS 2010 (h) (i) (j) 2 Part 15 Electric Motors Page 4 terminal block and insulated from the motor frame. Terminals shall be identified in accordance with BS 4999 Part 108 or equivalent. A separate earth stud shall be included on each terminal box. Heater terminals shall be shrouded and prominently labelled. (iv) adequate space and glanding arrangements shall be provided, particularly on smaller motors requiring glanding and terminating of steel wire armoured cable for star/delta starting, anti-condensation heating and thermistor winding protection devices. (v) where a common terminal box is used for main, heater and thermistor cable terminations, a permanent warning label shall be fixed to the terminal box cover. In addition, heater and thermistor cable terminations shall be clearly marked to identify their separate functions and operating voltages. (vi) terminal box covers shall be gasketed to provide a degree of protection equivalent to or better than that of the motor. (vii) for Ex 'd' flameproof motors, terminal boxes may employ Type 'e' increased safety protection, utilising indirect cable entry to the flameproof enclosure. However, this must be of the same type used to obtain the potentially explosive hazardous area motor certification. (viii) 3.3kV motor cable termination boxes shall be high fault level type, with segregated phases, pressure relief diaphragm and sealing chamber. arrangements shall be made with the manufacturer so that the Engineer may witness motor tests the motors shall run in ball and/or roller bearings and the weight of the motor shall be carried by thrust bearings incorporated in the motor body bearings shall be grease lubricated using hydraulic type nipples which are freely accessible without any dismantling, or otherwise piped out to a readily accessible location “Sealed for Life” bearings shall not normally be used. However, for small motors the engineer may allow the use of sealed for life bearings. Motor Ratings: (a) the efficiency and power factor of the motors shall be high over a wide range of load conditions. The motors shall be designed, manufactured and tested in accordance with BS 4999 and BS 5000 (or BS 2048 and BS 5000 in the case of small horsepower motors) for continuously rated industrial electric motors and Class “F” insulation but limited to Class „B’ temperature rise. This shall be in addition to any adjustments necessary for high ambient temperatures at site. The maximum continuous rating (MCR) of each motor shall be as set out in Table 15.1 and shall be rated and designed to suit the climatic conditions at site. This reserve power requirement shall be added to the calculated power prior to any other adjustments e.g. high ambient temperatures at site Table 15.1 MCR Ratings (b) Application Up to 75 kW drive Above 75 kW drive All pump motors (excluding positive displacement type) 10% above that required under all conditions of operation 5% above that required under all conditions of operation Positive displacement pumps and compressors 25% above maximum duty requirements 12.5% above maximum duty requirements motor starters shall be selected from the following to satisfy the stipulated performance requirements and comply with QGEWC starting current restrictions:(i) QCS 2010 motors up to 11 kW (15 hp) shall be squirrel cage suitable for DOL starting having a starting current not greater than 6 x full load current (FLC) Qatar Project Management (g) Section 21 QCS 2010 (d) 3 Page 5 (ii) motors between 11 kW (15 hp) and 37.5 kW shall have their starting current restricted to 4 x FLC and shall use one of the following starting methods; as indicated in the Project Drawings or the Project Documentation: Solid State Reduced Voltage (Soft) Start with torque characteristics suitable for the application Korndorffer Auto Transformer Rotor Resistance Star - Delta (iii) motor over 37.5 kW shall have their starting current restricted to 2.5 FLC and shall use one of the following starting methods: Solid State Reduced Voltage (Soft) Start with torque characteristics suitable for the application Korndorffer Auto Transformer Rotor Resistance (iv) submersible pump motors because of inherent design are to generally comply with the foregoing. The starting method is to be restricted to DOL/ Star-delta starting or soft start according to rating. motors shall be suitable and certified for the zone of hazard in which they are to be installed where flywheels are fitted to the main pump set, the motors shall be capable of starting and driving the pumps under these conditions. non-submersible motors shall be air cooled to IC 41 of BS EN 60034-6. cooling of submersible motors shall be an efficient system to the manufacturer's design. Motor Windings (a) (b) (c) 5 Electric Motors Motor Cooling (a) (b) 4 Part 15 motor windings shall be copper and treated to render them impervious to moisture, saline atmospheres, acid/alkaline fumes, oil and grease. They shall be adequately braced to prevent movement of coils during all conditions of service and be insulated throughout to Class F of BS 2757 or equivalent with a temperature rise limit of Class B. This provision shall be in addition to any adjustments necessary for ambient o temperatures at site of 55 C motor operating voltage and connection type shall be clearly stated on the motor nameplate. for high voltage motors, the stator windings shall use a modern synthetic resin insulation system based on mica glass tape continuously wound on the coils to give a void-free homogeneous structure. The end windings shall be securely braced to prevent harmful movement arising from electro-magnetic and mechanical forces. The rotor bars shall be securely keyed into the rotor. The rotor shall be shrunk and keyed onto the shaft. Thermal Protection (a) (b) (c) all motors rated at 11 kW and above shall unless stated otherwise be equipped with thermostatic contact elements in accordance with QGEWC Regulation 801. Six thermostats shall be provided (3 in use, 3 spare) to BS 4999 Part 111 to give Class 1 protection. Thermostats shall be of the normally closed (break on temperature rise) type. o They shall operate at 160 C on rising temperature and shall be complete with leads and terminals. when thermistors are specified six shall be provided (3 in use, 3 spare) to BS 4999 Part 111 to give Class 1 protection. Thermistors shall be PTC type P160 and shall be complete with control units for motor tripping. when embedded resistance thermometers are specified six shall be provided (3 in use, 3 spare) either in the stator slots or end windings. They shall be of the platinum wire type o compensated for 0 C at 100 ohms (Pt. 100). They shall be complete with evaluating unit QCS 2010 Qatar Project Management (c) Section 21 QCS 2010 (d) (e) (f) (g) 6 (b) (c) (d) (e) (b) (c) (d) (e) and remote temperature indicators with set points for over temperature alarms. when motor winding thermocouples are specified six shall be provided (3 in use, 3 spare) either in the stator slots or end windings. They shall be complete with remote temperature indicator with set points for over-temperature alarm. When motor winding RTD’s (Resistance Temperature Detectors) are specified six shall be provided (3 in use, 3 spare) either in the stator slots or end windings. when bearing temperature indicators are specified the sensors shall be Pt. 100 resistance thermometers installed as close as possible to the bearing and complete with remote temperature indications with set points for alarm. when cooling air temperature indicators are specified two shall be provided to monitor both the warmed air and the fresh air. The sensors shall be Pt. 100 resistance thermometers installed in the air passage and complete with remote temperature indications with set points for alarms. where thermostats or thermistors are used in explosion proof designs, the devices must be of the same type used to obtain the potentially explosive hazardous area motor certification. submersible motors shall be complete with lengths of black PTFE covered flexible cable for Power, Signalling and Protection purposes. each cable shall be a minimum of 20 metres long or as otherwise required by the Contract, and shall be rated in accordance with the cable routing details. As a minimum cables shall be continuously rated to carry the motor full load current when laid in a classified area to the approval of QGEWC. The cable shall be factory fitted according to the connection of the motor winding. flexible cables for use in potentially explosive atmospheres shall be identical to those types used to obtain the potentially explosive hazardous area combined motor/cable certification. Where protection cables are part of an intrinsically safe circuit the outer sheath shall be coloured blue. jointing of cables is not acceptable. cables shall be laid such that there is no fouling of the submersible pump whilst lifting or lowering. The extra length of cable shall be relaxed and not coiled. the motors shall run in ball and/or roller bearings and the weight of the motor shall be carried by thrust bearings incorporated in the motor body. maximum life bearings with oil seals shall be fitted to both drive end and non-drive end bearing housings to prevent ingress of solid particles and liquids. Bearings shall be in accordance with BS 292 or equivalent. bearings that are not sealed for life shall be grease lubricated and shall be fitted with a means for replenishing the grease and a relief device for disposal of excess grease. Hydraulic button head grease nipples in accordance with BS 1486 Part 2 or equivalent shall be provided and shall be extended, where necessary, such that they are located at the top of the frame. Re-greasing points shall be located for ease of access. bearing temperature monitoring facilities shall be provided on submersible motors over 100kW and on non-submersible motors over 250kW. where required, large machines shall be provided with insulated bearings to prevent bearing failure due to circulating rotor currents. Noise Levels (a) 9 Page 6 Bearings (a) 8 Electric Motors Submersible motor cables (a) 7 Part 15 unless otherwise required by the Contract, the noise levels (Sound Power Levels dB(A)) of the motors shall be in accordance with BS EN 60034-9. Paint finish (a) the paint finish shall be entirely compatible with the environment to which the motors will be subjected. This shall consist of an anti-corrosion primer/undercoat with a 2 part heavy duty epoxy resin paint or such other paint finish determined by the application, and as detailed in the specification for Corrosion Protection. QCS 2010 Qatar Project Management (h) Section 21 QCS 2010 Section 21 Part 15 Electric Motors Page 7 15.3 INSTALLATION 15.3.1 General 1 Provide all the equipment installations and wiring installations, including connections as indicated, specified and required. Assure proper fits for all equipment and materials in the spaces as shown on the Drawings. 2 Motor: (a) (d) (e) (f) (g) 15.3.2 Factory Tests 1 Factory tests shall be carried out as follows: (a) (b) (c) All motors: No load current High voltage on windings and auxiliary Windings resistance Vibration One motor: Full load heat run and temperature rise Efficiency at 100 %, 75 %, 50 % and 25 % load Power factor at 100%, 75%, 50% and 25% load Noise Momentary overload Type test certificate shall be provided to cover the following: - Locked rotor current Locked rotor torque Saturation curves Percent slip 2 The Contractor shall provide calculations to demonstrate motor power rating and bearing life with derating factors taken into account. 15.3.3 Field Checks 1 Motor Installations shall be complete and correct. 2 Operation tests shall be performed to observe that motors start, run and stop satisfactorily under design load. END OF PART QCS 2010 Qatar Project Management (b) (c) provide power, control, alarm and earthing installations for all motors as indicated and required check the connections to provide correct rotation for all motors record the full load current to each motor, and the overload relay rating in each motor starter for the certified data submittal provide the wiring for heaters in the motor frames and the required controls to deenergise the heater when the motor operates (if applicable) provide the required wiring for all equipment that shall be furnished and installed according to other relevant Sections of the Specifications install the control stations and/or emergency stop units on steel stanchions or building structures near motors, if specified and as shown on the Drawings. Control stations, where required in accordance with the particular specification, shall incorporate a “Local/Remote” switch, “On/Off” switch and the emergency stop unit field damaged factory finish on equipment shall be touched-up with paint that is equal in quality and colour to the original factory finish. QCS 2010 Section 21 Part 16 Power Factor Correction Capacitors Page 1 16. POWER FACTOR CORRECTION CAPACITORS ........................................ 2 16.1 GENERAL ...................................................................................................... 2 16.1.1 16.1.2 16.1.3 16.1.4 16.1.5 16.1.6 16.1.7 General Description References Quality Assurance Submissions Delivery, Storage and Handling Co-ordination 16.2 PRODUCTS ................................................................................................... 3 16.3 INSTALLATION ............................................................................................. 4 16.3.1 Installation 16.4 3 3 3 4 FIELD TESTS ................................................................................................ 4 16.4.1 Field Tests QCS 2010 4 Qatar Project Management 16.2.1 General 16.2.2 Capacitors 16.2.3 Control and Protection 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 QCS 2010 Section 21 Part 16 Power Factor Correction Capacitors Page 2 POWER FACTOR CORRECTION CAPACITORS 16.1 GENERAL 16.1.1 General 1 This specification section covers the supply and installation of power factor correction equipment operating on electrical power systems up to 600 V ac 50 Hz. 2 The work of this part is integral with the whole of the Project Documentation and is not intended to be interpreted outside that context. 3 Co-ordinate the work with all other services affecting the work of this Section. 4 Related Parts and Sections are as follows: This Section Part 1 Part 2 Part 3 Part 6 Part 15 General Provision for Electrical Installation HV & MV Factory Built Assemblies (FBA’s) Protective Devices Cables and Small Wiring Electric Motors 16.1.2 Description 1 Provide all labour, materials, equipment, services and accessories necessary to furnish and install the work of this Part, complete and functional, as indicated in the Project Documentation and as specified herein. 16.1.3 References 1 The following standards are referred to in this Part: BS 88 BS 1650 BS EN 60949 Cartridge fuses for voltage up to 1000 V ac Capacitors for connection to power frequency systems Control gear for voltage up to 1000 V ac 16.1.4 Quality Assurance 1 Reference standards as detailed under Part 1 and this Part Clause 17.1.4. 16.1.5 Submissions 1 Reference Part 1 16.1.6 Delivery, Storage and Handling 1 Deliver, store and handle materials and products in a manner to prevent damage. 2 Reference Part 1 16.1.7 Co-ordination 1 The work of this Section shall be completely co-ordinated with the work of other services. QCS 2010 Qatar Project Management 16. QCS 2010 Section 21 Part 16 Power Factor Correction Capacitors Page 3 PRODUCTS 16.2.1 General 1 Power factor improvement equipment shall be provided in LV (415 V) Main Distribution Board. Correction shall be automatic and be capable of correcting the power factor to within range 0.9 lagging to unity as required by the design. The power factor setting shall be adjustable. 2 Individual power factor capacitors shall be provided for the larger motorised drives, as indicated on the single line diagrams. 3 All capacitors must be arranged so that they are connected in stages. These stages shall be sized to prevent system over-voltage during light loads conditions. 16.2.2 Capacitors 1 Capacitors shall comply with BS 1650 and shall be of a dry metalised film construction, containing no liquid and must have low losses (typically 0.5 Watts/kVA). 2 Each capacitor shall be housed in a sealed container and be fitted with a fail-safe, pressure sensitive disconnect device. 3 Each capacitor shall be equipped with suitable discharge resistors to reduce the voltage to less than 50V in one minute, or less, after supply disconnection. 4 The capacitors shall be housed in a metal enclosure, forming part of the Main Distribution Board. The enclosure size should allow enough space and cabling etc., for at least one additional capacitor unit to be fitted at a later date. 5 Provision shall be made to ensure that a connection point is available for a series connected, de-tuning reactor in case of problems with harmonics. 6 The equipment must comply with BS 800 with respect to electrical interference. 7 The capacitors shall be protected by a fused switch-disconnector or circuit breaker on the LV motor control centre. 8 The capacitor manufacturer must recommend the maximum fuse or circuit breaker that will ensure the protection of each capacitor bank. 9 All power and control cables used within the capacitor bank enclosure must be in accordance with BS 6231 Type BK. 10 Detuned reactor/harmonic filters (a) (b) anti-resonance reactor detunned or filters deemed necessary to reduce the harmonic content. total Harmonic Distortion (THD) of voltage at point of common couplings shall adhere to IEEE Harmonic Standard 519-1992 and ER G5/4. 16.2.3 Control and Protection 1 Power Factor Regulator (a) the minimum number of capacitor switching steps shall be four (4) as far as practically possible for smaller rating capacitor banks and between 6 to 12 steps for others. The capacitors’ KVAr shall be so chosen to provide maximum programming flexibility such as switching sequence 1:2:2:2, 1:1:1:1 etc. in order to maintain the power factor within the set limits for most of the operating time. QCS 2010 Qatar Project Management 16.2 QCS 2010 Section 21 (b) (c) (e) Power Factor Correction Capacitors Page 4 an alphanumerical LCD, micro-processor based automatic power factor correction regulator shall be provided to control steps and display measurement of the following:(i) power factor (ii) no. of steps connected (iii) step connection and disconnection time (iv) actual current (v) reactive current (vi) active power (vii) reactive power (viii) THD voltage (ix) alarm conditions as listed below the regulator shall have built-in alarm relay for remote indication and following alarm conditions locally:(i) low power factor (ii) abnormal power factor (iii) leading power factor (iv) overcurrent (v) overtemperature (vi) overvoltage (vii) THD high (viii) capacitor overload etc. the regulator shall provide facility to manually energize/denergise capacitor steps for the purpose of testing and verification of required/set power factor. switching contactors shall have a minimum duty category AC4 to BS EN 60947 and a minimum current rating of 1.3 x the current consumed by the capacitor bank (see BS 1650). 16.3 INSTALLATION 16.3.1 Installation 1 Documentation shall be provided detailing: (a) type test certificate (b) routine test certificate (c) maintenance requirements (d) fault diagnosis (e) parts list with part numbers and recommended spares (f) commissioning instructions 16.4 FIELD TESTS 16.4.1 Field Tests 1 The PFCC assembly shall be tested at site during commissioning. The results so obtained shall be verified with the actual requirements and QGEWC regulations. Modifications if any shall be carried-out at no extra cost to the Owner. END OF PART QCS 2010 Qatar Project Management (d) Part 16 QCS 2010 Section 21 Part 17 Standby Diesel Generator Set Page 1 17. STANDBY DIESEL GENERATOR SET......................................................... 2 17.1 GENERAL ...................................................................................................... 2 17.1.1 17.1.2 17.1.3 17.1.4 17.1.5 17.1.6 General Reference Description of Work References Quality Assurance Submittals Period of Maintenance 17.2 PRODUCTS ................................................................................................... 4 17.2.1 17.2.2 17.2.3 17.2.4 17.2.5 17.2.6 Diesel Generator Set Control Panel Automatic Transfer Switch (A.T.S.) System Operation and Performance Manual Operation System Responsibility 17.3 INSTALLATION ........................................................................................... 14 17.3.1 17.3.2 17.3.3 17.3.4 17.3.5 17.3.6 Installation Paint Work Site Quality Control Commissioning Training of Operation and Maintenance Personnel Reference Data Sheet 4 11 12 13 13 13 14 14 14 14 15 15 Qatar Project Management QCS 2010 2 2 2 2 3 4 QCS 2010 Section 21 Part 17 Standby Diesel Generator Set Page 2 STANDBY DIESEL GENERATOR SET 17.1 GENERAL 17.1.1 General Reference 1 The work of this Section is integral with the whole of the Project Documentation and is not intended to be interpreted outside that context. 2 Co-ordinate the work with all other services affecting the work of this Section. 17.1.2 Description of Work 1 The Contractor shall supply, install, commission, test and handover in good operable manner including 400 days guarantee and maintenance of 415 V mains failure, standby diesel generator set and 5 years guarantee for electric motors, as per the Project Documentation. The set shall be arranged for either automatic or manual start on mains failure, as indicated on the Project Drawings. The set shall be complete with diesel engine, generator, control panel, batteries, starting motor, built-in air cooled radiator, main fuel storage tank, daily fuel storage tank, fuel transfer pumps and all other accessories as specified and mentioned in the BOQ. 2 Related Parts and Sections are as follows: This Section Part 1 Part 6 Part 7 Part 8 Part 9 Part 22 General Provisions for Electrical Installation Cables and Small Wiring Conduits Trunking Cable Trays Earthing and Bonding 17.1.3 References 1 The following standards are referred to in this Part BS 4999 BS 5514 Alternators Engines 17.1.4 Quality Assurance 1 Manufacturer's Qualification: (a) 2 Installer's Qualification: (a) 3 the generator set shall be the product of a single manufacturer regularly engaged as a manufacturer of such equipment. all the Diesel Generator installation work shall be carried out by a Diesel Generator sub-contractor. Diesel Generator sub-contractor shall be one who is normally an agent representing one or more of the approved makes of D/G sets. Diesel Generator installation shall be supervised, checked and tested by a qualified representative of the manufacturer and handover the works in perfect running order to the satisfaction of the Engineer. Source Quality Control: (a) test the combined engine generator set at the factory and submit the certified test copies of all tests to the Engineer for his approval. QCS 2010 Qatar Project Management 17. QCS 2010 4 Standby Diesel Generator Set Page 3 the manufacturer should have an agent in Qatar who is well experienced in installation and maintenance of diesel generators of the size specified herein. The agent should have been associated with the manufacturer for a minimum period of five years. Design Criteria: (a) (b) all materials and equipment shall comply with relevant IEC and BS specifications as regards quality of materials, performance and proving tests the emergency power supply system and its components shall be such as may be properly maintained and serviced without the necessity of carrying expensive spare part stocks, or being subjected to interrupted service due to the lack of spare parts emergency generator set shall be designed to allow easy replacement of major items subject to wear. 17.1.5 Submittals 1 Shop Drawings: (a) (b) (c) (d) (e) (f) (g) submit shop drawings for approval in accordance to Part 1 shop drawings shall be complete, as to be record drawings, not general outline drawings used for sales and guide layouts submit a complete wiring diagram for the generator set, drawn on a single standard size sheet, showing the following: (i) all components of: engine starting control engine alarm generator control battery battery charger earthing transfer switch control relays (ii) interior wiring, terminals and interconnecting wiring (iii) certified dimensions and weights. submit a composite wiring diagram of the entire emergency transfer system showing all wiring between the engine starting panel, engine generator set and the automatic transfer switches wiring diagrams shall clearly show: (i) main current conductors, in heavy lines (ii) control conductors, with colour and/or number coding (iii) location of relays and apparatus (iv) description of function, type and catalogue, of all components. alternator Control Panel: (i) submit a schematic line diagram showing: Interlocks Protection Instruments submit general arrangement drawings of the generator installation and the generator building layout. Product Data submitted in accordance to Part 1. (a) (b) submit curves showing the actual performance of a similar engine (same model, stroke, etc.) to that proposed, superimposed on the standard published performance curves for continuous, and maximum operation submit the detailed information together with manufacturer's catalogues for the following: (i) generating set manufacturer (ii) name and Address (iii) generating set Model No. QCS 2010 Qatar Project Management (c) 2 Part 17 Local Agent: (a) 5 Section 21 QCS 2010 (c) (d) (e) (f) (g) Section 21 Part 17 Standby Diesel Generator Set Page 4 (iv) diesel Engine (v) radiator (vi) fuel System (vi) alternator (vii) exciter (viii) starting Battery (ix) control Panel (x) service Facilities test certificates list of spare parts certified factory test reports instruction manuals for operation and maintenance parts catalogue with manufacturer address. Period of Maintenance 1 During the maintenance period of 400 days the sub-contractor shall repair and replace directly, at his own expense, any of the plant, material or work performed or furnished under the respective works in the Project which may develop under the conditions provided for by the Project and under proper use in the works or that portion thereof taken over by the Engineer. The guarantee period for all electric motors shall be 5 years. 2 The sub-contractor shall obtain and submit to the Engineer all guarantees or certificates or warranty available from the manufacturers, but only as supplementary to the sub-contractor's own liabilities under the Project and in no way invalidate them. 3 The D/G sub-contractor shall be responsible for the satisfactory operation of the D/G installation during the Maintenance and Guarantee Period. He shall carry out necessary inspection, preventive maintenance and testing to keep the set ready all the time. The set shall function satisfactorily during power failures. The D/G sub-contractor shall carry out routine testing of the installation once in every month throughout the Maintenance and Guarantee Period. The testing shall be carried in presence of Engineer. The sub-contractor shall himself provide all electrical and mechanical spare parts, grease, lubricating oils, touchup paints, etc., required for the maintenance of the D/G installation. The owner shall be responsible only for providing diesel oil as and when required. The D/G sub-contractor shall prepare log-books listed full details of maintenance work and each log-book entry shall be countersigned by the Engineer. 17.2 PRODUCTS 17.2.1 Diesel Generator Set 1 The set shall be of rugged reliable design and built for long trouble free service under the worst specified climatic conditions and made by an approved reputable manufacturer. 2 Rating: (a) 3 the rated output shall be as specified elsewhere or as indicated on the drawings, 240/415 Volts, 3 phase, 4 wire and 50 Hz. The rated output shall mean the net full continuous derated output in Qatar at an ambient temperature up to 50°C at a relative humidity of 95%. The set shall also be capable of 110% load for one hour under these conditions at the rated speed without undue heating of the engine or alternator and without mechanical or electrical troubles. Diesel Engine: (a) The diesel engine shall be of the stationary heavy duty, turbo charged compression/ignition, multi cylinder 4 stroke operation. The steel base frame shall be provided with spring type vibration isolators. The engine shall be able to deliver full load in the shortest possible time after start. The engine speed shall not exceed 1500 r.p.m. The engine construction shall be in such a way as to allow for dismantling of QCS 2010 Qatar Project Management 17.1.6 QCS 2010 (b) (d) Part 17 Standby Diesel Generator Set Page 5 any engine component for inspection or repair without undue complication i.e. without dismantling of other non-defective parts. The crank case shall be provided with inspection windows starting system: The diesel engine shall be equipped with starting system detailed hereunder and as per Engineer's approval. (i) Battery Starting System: batteries for starting shall be of the nickel cadmium type, 24 Volt, heavy duty diesel starting type and of sufficient capacity to allow 6 consecutive start attempts each of 15 seconds with 1 minute intervals. It shall be possible by means of a selector to alter the starting sequence to provide a single start attempt of 1 minute before lockout and alarm. The battery used for starting may also be used to energise the diesel plant control system but shall have enough capacity remaining after 3 engine start attempts to energise the system continuously for 24 hours. The control system shall be suitable to continue operating correctly during the voltage dips occurring on the battery during the engine starts. Cooling System: (i) radiator : built-in type with sufficient capacity to dissipate the total joules per hour rejected by the engine cooling system at 110 % full load (ii) blower fan: to have sufficient pressure to circulate required quantity of air for engine cooling. The fan shall be provided with a suitable guard. D/G room o inside temperature should not exceed 56 C (iii) jacket water heaters: to be provided on engine to facilitate quick starting under low ambient conditions (iv) the cooling system shall be capable of keeping the temperature of cooling water at safe limits at all conditions of load required in the specifications. Maximum temperature of cooling water after 10 hours of continuous running at full load at worst Qatar climatic conditions shall not exceed the maximum temperature limits of the diesel engine (v) the cooling system shall include an engine shaft driven circulating water pump. The water jacket of the engine cylinder shall be so constructed that the water in the jacket can be drained completely (vi) the radiator finned tubes shall have a common inlet and common outlet headers (vii) drain valve and a filling valve shall be provided to the radiator for flushing and quick filling (viii) Cooling water piping, complete with all necessary supports; control valves, flanges and fittings, thermometers, pressure gauges, relays etc., shall be supplied and installed to form a complete engine water cooling line. Piping shall be as of BS 1387 (ix) the water pump discharge valve shall preferably be a globe valve, the other valves shall be (sluice) gate valve. Fuel System (i) The engine shall be suitable for running on diesel oil as described below: Specific gravity at 60F distillation : 0.834 (P.P. 123/40) IBM : 219 C 10% : 250 C 50% : 276 C 90% : 314 C F.E.P. : 342 C Flash Point PME : 189 C Sulphur : 1.1% Calorific value BTU/lb. gross carbon residue. : 19750 0.01/wt diesel index : 62 Viscosity redwood seconds at 100F : 34 (ii) QCS 2010 Daily Fuel Tank: Fuel supply to the engine shall be maintained by a separate day tank Qatar Project Management (c) Section 21 QCS 2010 Section 21 Standby Diesel Generator Set Page 6 located in the room. Daily fuel tank shall be sufficient capacity for continuous run of 8 hours at full load, unless otherwise specified in the Project Documentation. The daily service tank shall be manufactured from mild steel to a rectangular shape in accordance with BS 799 and shall be complete with the following minimum equipment and facilities:Inspection cover vent/breather pipe filler pipe connection overflow connection drain valve and sump drain emergency dump valve operated by the fire alarm system and by a fusible link mounted over the diesel engine dial type contents gauge calibrated in gallons and litres level switches to control fuel transfer pump level switches to operate high and low fuel level alarm circuits in the diesel alternator set control panel lifting lugs. the contractor shall provide and install an external dump sump of sufficient capacity to contain the contents of a full day tank and all pipework necessary to carry the dumped fuel quickly by gravity, to a safe location in the event of a fire being detected in the generator house. The sump shall be constructed to contain the fuel without leakage to the surrounding ground and shall be provided with a lockable cover. Provision to allow emptying of the sump by portable pump shall be provided. (iii) Main Fuel Storage Tank: The Contractor shall supply and install a cylindrical diesel oil storage tank with a capacity to operate the associated diesel generator set continuously on full load for a minimum of 3 days, unless otherwise specified in the Project Documentation. the tank shall be welded mild steel construction suitably protected from corrosion in accordance with BS. 2594 and shall be installed in the location indicated on the drawings. The storage tank shall be complete with pipes, fittings, feed lines, vents. etc. The tank shall be of the approved type located outside the diesel engine room. The tank shall be provided with 600 mm inspection manhole with cover, 50 mm filling pipe with cooped filling terminal, 50 mm air vent pipe with screen outlets, isolating valve, valved drain etc. Electronic fuel indicator with an audio/visual alarm shall be provided for main fuel storage tank Also the storage tank and its accessories must comply with the Qatar. Regulations for generator installations. (iv) Duplex Diesel Oil Pumping Set: Provide packaged type duplex, self priming, fuel oil pumping and straining set with a capacity of four times the total fuel consumption of engine at full load. Pump sets shall be factory assembled, piped, wired and tested. Pumps shall be activated by a switch in the day tank automatically. All pumps installed in the D/G room shall be flame-proof and fire-resistant as per NFPA Regulations Piping shall be complete to suction, discharge and return line connections. Provide gate valves and unions arranged to permit removal of either pump while the system is in operation. Install check valves and relief valves on pump outlet and gate valves prior to pressure gauges Suction strainer shall be flanged connection, duplex type, one-piece, cast-iron body, ASTM A48 Class 30, with 1.2 mm perforation brass baskets Oil pump set shall be factory assembled on a structural steel channel QCS 2010 Qatar Project Management Part 17 QCS 2010 Section 21 Part 17 Standby Diesel Generator Set Page 7 beam base to include pumps, motors, flexible couplings and guards. Pump set shall be suitable for diesel oil Suitable manually operated pump shall be provided. Tank Gauges: Provide as shown on the Drawings. Each gauge is to be provided with an aluminium case and calibrated to indicate level of fuel in the tank. Mounted on gauges shall also be a high/low level alarm switch. The switches and gauges shall be designed for operation from a 24 Volt DC, loop powered system. Locate indicating gauges as shown on the Drawings or required Tank fittings and pressure fittings shall be made of solid bar stock to prevent leak possibilities. (vi) Diesel Oil Piping: Provide all diesel oil piping from storage tank to day tank fill lines, water tight fill boxes, vents, vent caps, tank foot valves, and accessories Provide swing check valves and gate valves at pump inlets. Provide approved anti-siphon valves at high points of suction lines. Provide whatever additional valves that may be required by local regulations All piping shall be provided with ground joint unions at piece of apparatus to facilitate connecting and disconnecting All piping, unless otherwise specified, shall be schedule 40 standard weight black wrought iron pipe Steel vent pipelines shall run from the fuel oil storage tanks, carried to the proper height within building construction and terminating with vent fittings. Fittings shall be "Bronze Ventilating Brick" with thickness of 20 mesh bronze wire gauge in front of louvered opening. (e) Lubricating System (i) The lubricating oil system shall be forced fed type. The details of the system shall be included in the offer. The shaft bearing lubricating shall be directly fed from the lubricating oil pump and not through the main bearings (ii) The lubricating oil shall be of a type readily available internationally (iii) The lubrication system shall be positive displacement type. By-pass arrangement should be provided in case of filter clogging (iv) A heat-exchanger shall be provided for cooling the lubricating oil and this shall be of long-life type i.e. the system shall not require constant cleaning or other maintenance work. A valve for taking oil sample shall be provided. The coolant for the above shall be jacket water of the engine. That is, the cooling system of the engine and the lube-oil heat-exchanger cooling system shall work in parallel or in series. If the lube-oil pressure reaches low value, the engine shall be shut down automatically and also immediately should give audible alarm together with visual indication. The lube-oil system shall be provided with means to monitor pressure at important points at the engine-monitor panel (v) a large capacity oil sump shall be provided and incorporated in the construction of the bed plate (vi) the system of lubrication shall ensure that adequate oil is pumped to all rotating parts (vii) The system shall incorporate a level dipstick, filler cap and tube and crankcase breather pipe or outlet (viii) the capacity of the lubricating oil system shall be sufficient to enable the engine to run continuously for 12 hours at any load without replenishment. (ix) Suitable manual-pumping arrangement for easy draining of the whole quantity of lube-oil into a drum shall be provided. (f) Exhaust System: QCS 2010 Qatar Project Management (v) QCS 2010 Section 21 (i) (ii) (iii) (v) (vi) (vii) (g) Standby Diesel Generator Set Page 8 Exhaust pipes shall be of Schedule 40 black steel and of adequate size to ensure that back pressure does not exceed the value specified by the manufacturer The exhaust pipe shall be connected through airtight flexible coupling to the engine Exhaust pipes shall be adequately lagged with 75 mm thick (minimum) rock wool covered with aluminium sheaths of minimum thickness 1.5 mm so that to 0 take care of exhaust gas temperature in pipes exceeding 500 C. When exhaust pipes pass through walls or roof a suitable weatherproof sleeve or thimble shall be provided to isolate exhaust pipe from the building. A silencer of heavy duty residential type shall be provided in the exhaust system and it shall also be lagged. The operation of casting the sleeves in the concrete, if required, will be carried out by a civil contractor Exhaust pipes and silencers shall be supported from the ceiling by special vibration isolating hangers and the pipe shall be slanted away from the engine and a condensate trap fitted at the lowest points. Approved rain caps shall be installed at the discharge end of the exhaust pipes on the roof. Suitable flexible expansion joints shall be provided along the pipe run to take care of expansion requirements the completed exhaust system shall be capable of limiting the noise level at the external outlet to 65 dB (A) at three metres from the end of the exhaust pipe suitable guards shall be provided with the exhaust pipe to prevent small animals/reptiles from entering. Filters: Cleanable/replaceable elements should be provided. (i) Fuel Oil System The system shall have the following filters fitted before the fuel injection pumps: A primary fuel filter of ample capacity to prevent all particles of 10 microns size or smaller. A secondary filter to prevent all particles down to 3 microns size or smaller. (ii) Lubricating Oil System This system should have full flow filters of sufficient capacity Tenderers shall give full particulars of the filters used. It shall be mentioned in if filter elements are cleanable for replaceable, in which case, the working hours after which the element and the Lubricating oil is to be replaced should be stated. (iii) (h) Intake and Exhaust System Air is inducted to the engine manifold through Precleaner Large capacity air cleaner Both filters are required due to severity of dust storms and dust suspensions in the air The engine exhaust line shall be fitted with flexible fitting efficient silencer to give efficient silencing with minimum back pressure and terminated outside the engine room. Ventilation: (i) The following ventilation works are required for the diesel engine generator room. Aluminium inlet louvres with washable metal filters shall be provided for outside air intake into the engine room. Filters shall be sized to perform their duty with a face velocity not more than 1 metre per second when the engine is running. Filters shall be installed in an appropriate arrangement QCS 2010 Qatar Project Management (iv) Part 17 QCS 2010 Section 21 Part 17 Standby Diesel Generator Set Page 9 on the generator room walls. The total filter area shall consider air for engine intakes and radiator cooling requirements. Filters with handles and easily operated retaining latches shall be provided. The radiator shall be provided with a motorised louvre, interlocked with the generator, so that the generator will shut down in the event of the louvre not opening on start up. The louvre shall be capable of being manually opened in the event of drive motor failure. Gravity louvres shall not be allowed for the radiator exhaust. Governing System: (i) the engine shall run steadily at any load within its rating at its rated speed, and the changes in speed due to change in load shall comply with BS 5514/77 for Class A1 or with ISO 3067 (ii) the governor should be of the electronic type to comply with BS 5514/77 Class A1. (j) Coupling and Common Bed: (i) the engine and the alternator shall be suitably coupled directly without interposing gear arrangement (ii) the common bed shall be provided with spring type anti-vibration mountings devices for fixing to the floor (iii) the engine vibration shall be the minimum possible and shall comply with the relevant BS. The vibratory force induced as the engine passed through resonance revolutions during starting and stopping period shall not cause any damage to the whole system (k) Engine Control Panel: The engine-generator control panel shall be of rigid and robust construction and rust-proof and shall be of the electronic modular type utilising environmentally sealed, solid state, micro-processor based modules for engine control and AC metering. The panel shall be capable of operating under the operating temperature range of 0 degrees to + 70 degrees Celsius. Metering accuracy shall be 0.5% true RMS. The electronic control system shall employ solid-state transducers for constant monitoring of oil pressure and coolant temperature through a Single Sire Serial Data Link. Unless otherwise specified in the Project Documentation, the control panel shall provide the following features: (i) automatic start/stop engine control with programmable safety shutdowns and associated flashing LED indicators for low oil pressure, high coolant temperature, overspeed overcrank and emergency stop (ii) adjustable 1 to 60 second cycle cranking with rest periods (iii) cool-down timer, adjustable between 0 and 30 sec. (iv) LCD digital readout for: engine oil pressure (N/mg) lubricant oil pressure gauge (N/mg) 0 cooling temperature ( C) 0 exhaust gas temperature gauge ( C) exhaust turbo-blower pressure gauge (N/mg) engine RPM system DC Volts engine run hours eight system diagnostic codes generator AC Volts generator AC Amps Generator frequency The system diagnostic codes shall be designed to enhance the system protection and to allow for trouble shooting by untrained personnel. These signals shall be: QCS 2010 Qatar Project Management (i) QCS 2010 Section 21 Part 17 Standby Diesel Generator Set Page 10 -loss of engine speed -invalid engine control switch -internal circuit fault -loss of coolant temperature -loss of data sending unit -unscheduled engine shutdown -invalid programming switch position -loss of failure of programme setting 4 Alternator and Exciter (a) the alternator shall be able to withstand the stresses caused by the sudden application of the loads (i) Type : Self excited, self ventilated, air cooled, splash-proof, synchronous alternator (ii) Output : As per Project Documentation, at Qatar Climatic Condition (iii) Voltage : 415 V (iv) Frequency : 50 Hz (v) No. of poles : 4 (vi) No. of phases : 3, (ungraded neutral to be brought out) (vii) Power factor : 80% lagging (viii) Commercial efficiency not less than 90 % (including excitation and field losses) (ix) Voltage regulation : Automatic and static. (b) Class F insulation shall be provided for the alternator and exciter windings with the temperature rise as Class B and de-rated for the ambient conditions. the alternator shall be suitable for continuous running duty type S1, BS 2613 (latest edition) the alternator unit shall be capable of giving 110% of nominal rated output for one hour under site conditions. The rotor shall be capable of withstanding an over-speed test of 15% for 5 minutes distortion of no-load voltage wave form at alternator terminals shall be within 5 % from the sinusoidal wave form voltage adjustable range of the output voltage by adjusting the exciter shall be not less than 3 % of rated voltage at rated load and not less than ± 5 % of rated voltage under no-load conditions. This adjustment shall be able to be performed from panel mounted handle or knob the voltage of the alternator shall be automatically controlled by electronic static circuits the alternator shall not be switched on the load until terminal voltage has reached at least 90 % of the nominal value. It is essential that the voltage regulation equipment shall have sufficient fast response time so that the alternator is ready to accept load in the shortest possible time the voltage regulator shall be designed to maintain the alternator terminal voltage constant within ± 1 % of the nominal value from no load to full load within normal variations of engine speed with change in load the exciter shall be brushless, self excited, rotor mounted type. The rectifying elements shall be silicon. The silicon diodes of the three phase rectified bridge assembly shall be protected against surges and overloads such that the generator will continue to run with a diode failure. Diodes shall have heat sinks suitable for the ambient conditions described. Means shall be provided to indicate exciter diode failure on the remote control panel (c) (d) (e) (f) (g) (h) (i) (j) QCS 2010 Qatar Project Management These panels shall be provided with the following control switches: -engine control switch -ammeter -voltmeter phase selector -emergency stop -indicator/display test switch -voltage adjust potentiometer QCS 2010 (k) (l) (m) (n) (o) (q) (r) (s) (t) (u) (v) (w) 5 Part 17 Standby Diesel Generator Set Page 11 the unit shall be suitably protected so that when there is a sudden variation of load, the sudden increase of field current in the rotor shall be curtailed and thus the speed build up of the engine and the voltage build up of generator shall vary proportionately alternator protection. The alternator shall be provided with protection against over speed, over voltage, over current, short circuit, reverse power, single phasing earth fault and any other found necessary. The neutral points of alternators shall be solid by connecting to earth terminals with cable end boxes shall be provided respectively for the alternator and exciter the cooling air for alternator and exciter shall be drawn through openings at the nondrive end and exhausted sideways at the driving end the alternator shall be fitted with anti-condensation heater to keep the winding in good, dry and safe condition. The anti-condensation heater shall be automatically cutoff when the machine is running. Necessary on-off switches shall be provided on the control panel and the operation status of the heater shall be indicated temperature Rise: Alternator components shall be sound electrically and mechanically in continuous operation lasting over 24 hours at the rated output insulation Resistance: Insulation resistance of the machine at strategic points shall be provided along with the submission dielectric Strength: The Dielectric strength, the voltage of testing and test procedure at various points of the machine shall be submitted with the shop drawings radio and television interference suppression devices shall be provided in accordance with the requirements of BS. 800. Components used for suppression shall be to BS 613 vibration at the fixed components of the alternator under excited no-load operation shall be as per relevant BS. terminal symbols for the alternator shall be in accordance with BS822 requirements panel Wiring: (i) all wiring of battery charger, exciter and control panel shall be P.V.C tropical grade of adequate current carrying capacity to prevent over-heating under worst climatic conditions (ii) all wiring shall conform to the relevant BS and at least 50 % derated with 2 minimum size of 2.5 mm or its equivalent. terminal Board (I) terminal boards shall have pairs of terminals for Incoming and Outgoing wires and not more than two wires shall be connected to any one terminal (ii) insulating barriers shall be provided between adjacent connectors. Labels for wiring designation marks shall be provided on the fixed portion of the terminal boards as well as wires. No live metal shall be exposed at the back of the terminal boards (iii) terminal boards having pressure type terminal lusts or equivalent shall be used so that no terminal clamp is necessary. 10 % spare terminals shall be provided for each terminal board assembly. Guards (a) Suitable guards with brackets and securing arrangements of substantial construction shall protect all exposed rotating or moving parts. All guards shall be mechanically fixed to the generator set. Special attention shall be given to guarding the flywheelcoupling and the radiator fan drive. 17.2.2 Control Panel 1 Cabinet (a) (b) (c) heavy gauge, 2.5 mm thick, sheet steel construction, totally enclosed, dust and water protected and vermin proof to IP 55 a hinged, lockable door shall give access to control and instruments "live" parts shall be secured to prevent inadvertent contact with them QCS 2010 Qatar Project Management (p) Section 21 QCS 2010 (d) 2 Part 17 Standby Diesel Generator Set Page 12 controls for diesel engine, alternator, exciter, meters and alarm device shall be positioned to give ample space for removing and installing components. Control Panel Equipment and Instrumentation (a) control panel shall include: (unless otherwise specified in the Project Documentation) (I) 3 pole air circuit breaker with over-current, short circuit and earth fault protection as specified in this specification. (unless part of a main switchboard, as indicated on the drawings) (ii) busbar system as specified in this specification (unless part of a main switchboard, as indicated on the drawings) (iii) voltmeter (0-500V) with selector switch to read phase to phase and phase to neutral voltages (iv) ammeters of suitable range 3 Nos. (v) frequency meter of range 45 - 55 Hz (vi) duty selector switch OFF/TEST/MANUAL/AUTO key operated (viii) solid state voltage and frequency sensing relays (ix) microprocessor control unit incorporating, but not limited to the following: 30 sec engine warm-up with override engine minimum run time of 10 minutes engine cool down time of 10 minutes return to mains time delay of 30 sec. 80% stand-by voltage setting before load transfer 80% stand-by frequency setting before load transfer auto exerciser of seven days from initial command that allows operation with or without load transfer controls for remote operation and alarm signalling (x) current transformer for measuring and protection devices (xi) watt meter for unbalanced phases (xii) voltage trimmer (xiii) visual and audible alarm for engine starting, engine running overspeed, high water temperature, low oil pressure, failure to start, engine stalling or shut down, low fuel level in tanks, overvoltage and alternator overload. (xiv) indicator lamps for supply available, battery charger and cooling water heater (xv) manual start, stop, emergency OFF and lamp test push-buttons (xvi) manual and automatic service push-buttons (xvii) control switch for alternator circuit breaker, ON and OFF (xviii) mimic diagram with moving coil indicator for position of air circuit breaker (xix) battery charger, automatic type, nominal current 10 Amps. for charging 24 volts nickel cadmium starter battery and all required instruments (xx) all other accessories, fuses, terminal boards, small wiring, etc. Automatic Transfer Switch (A.T.S.) (a) (b) (c) (d) (e) the A.T.S. shall consist of 4 pole, 3 phase, break before make except for the neutral, rated as shown on the Drawings in accordance with QGEWC regulations with the A.T.S. provide manual change-over switches to by-pass the A.T.S. in case of emergency, maintenance or repair the arrangement, wiring and components shall satisfy the requirements of the Diesel generator Manufacturer. His written approval shall be submitted control voltage of A.T.S. shall be normally fed from the main supply, in case of failure of the main supply it shall be fed automatically from the emergency supply. in addition to transfer switches the A.T.S. arrangement shall be equipped with the following: (i) a selector switch to control the operation of A.T.S. on normal, emergency, automatic and OFF (ii) adjustable - 3 phase voltage sensing relays sense failure in a phase/phases and voltage drop below 70 % of the normal voltage (pick-up and drop-out voltages and adjustable within the range 70 - 100 % of the normal voltage) (iii) visual Mechanical Indicator for transfer switch position (iv) indicator lamps to show transfer switch position normal, emergency and OFF. QCS 2010 Qatar Project Management 17.2.3 Section 21 QCS 2010 Section 21 (v) (vi) (vii) (viii) Part 17 Standby Diesel Generator Set Page 13 an adjustable time delay relay of 1 - 3 seconds for starting signal to the Generator set after cutting of main supply an adjustable time delay relay of 0 - 3 minutes which allows A.T.S. from Normal to Emergency after the voltage build up relay of the generator has sensed 90 % rated voltage when frequency within 90 % rated of rated frequency an adjustable time delay relay of 1 - 10 minutes to allow A.T.S. from Emergency to Normal an adjustable time delay relay of 0.5 - 5 seconds to prevent instantaneous transition from EMERGENCY to NORMAL i.e. the delay allows time sufficient For the residual motor voltage to decay to a safe switching level. System Operation and Performance 1 The normal mode of system operation shall provide for unattended automatic transfer of load for the emergency power system. Emergency power shall be supplied to the system emergency loads within 10 seconds after interruption of the normal service. Upon receiving a signal from the ATS indicating a failure or normal power from transformer, the system control unit will signal engine generator to start. Generator circuit breakers are open at this time and the emergency busbar is dead. The generating set to reach approximately 90% of rated frequency and voltage signals to start sensor. The sensor then inhibits the operation of sensors and initiates a closing signal to circuit breaker, connecting this generating set to the emergency busbar. The priority control then initiates operation of the designated transfer switch, applying load up to the total kW rating of the generating set. 2 If the generating set fails to start after cranking for the suitable cranking period, it shall be locked off the busbar and the overcrank light on its switchboard shall light and the alarm sound. The control prevents critical transfer switch from operating. The generating set may receive troubleshooting signals after placing its engine control function switch in the "OFF" position. When the generating set is operational, it may again be placed into automatic operation by returning its function switch to the "remote" position. 3 If a generating set stalls and shuts down during normal operation, its respective switchboard circuit breaker shall open, removing it from the busbar. The appropriate failure light operates and the alarm sounds. The load shedding contacts in the control close, tripping a breaker in the load circuits, reducing system load to the rating of the remaining available generating capacity. After the generating set is made operable, it can be automatically reconnected to the busbar by resetting the load shed switch and engine control switch. 4 After normal power has been restored and the time delay on stop has expired, it shall be possible to manually shut down the generator and restore the mains power. 5 Under circumstance or condition operation of an emergency stop push button shall immediately shut down the engine. 17.2.5 Manual Operation 1 The manual operation of the Diesel Generator Set shall have the following features: (a) (b) the emergency power system shall have the capacity of being manually operated. The generator may be started by engine control switch located on the engine control unit. Once started and stable, the generator may be manually connected to the emergency busbar through generator circuit breaker the generator control unit shall be equipped with a generator breaker control switch, engine speed adjusting potentiometer and a generator voltage adjust thermostat and facilitate. 17.2.6 System Responsibility 1 The generating set, switchboard and automatic transfer switches shall be interconnected according to building load requirements and to manufacturer's recommendations, to prevent QCS 2010 Qatar Project Management 17.2.4 QCS 2010 Section 21 Part 17 Standby Diesel Generator Set Page 14 the emergency generating system from stalling or faltering due to momentary or temporary overloads beyond system rating, from distribution faults, motor starting loads. 17.3 INSTALLATION 17.3.1 Installation 1 Product Delivery, Storage Handling: (a) (b) (c) 2 Installation: (a) (b) 3 Control Boards: (a) 4 the engine and generator shall be properly aligned and mounted on a common steel base through resilient mountings to prevent vibrations. The whole set shall be fixed on the concrete slabs through suitable number of adjustable spring type vibration isolators. Foundation and other builder's work shall be as recommended by the manufacturer and approved by the Engineer except as may be described in this Section or shown on the drawings carry out installation strictly in accordance with the manufacturer's recommendation. run all outgoing cables from the generator to the control boards in the floor trench as indicated on the Project Drawings. Record Print: (a) fix record print of each generator set, framed behind non-glare plexiglass, on a wall near the generator control room. 17.3.2 Paint Work 1 Paint work of each set shall be of the highest quality to withstand the worst weather conditions specified. All steel works such as tanks, pipes, frames, louvers, ladders, platform, etc. shall be given two undercoats of anti-rust paint and two enamel finishing. 2 The diesel generator set, day tank internal metalworks and control panel shall be finished to BS 4800, shade 14E53. 17.3.3 Site Quality Control 1 Final Testing: (a) (b) testing shall be carried out at full load after completion of installation by the Engine manufacturer's qualified representative in the presence of the Engineer if the above cannot be done then testing shall be done at the manufacturer/supplier's premises at full load in the presence of the Engineer. All arrangements and costs incurred by such a test shall be responsibility of the sub-contractor. 17.3.4 Commissioning 1 Simulated Power Failure Test: (a) engine-generator shall be made ready for automatic operation and started by means of the test transfer switch on the automatic transfer switch. Unit shall run for the QCS 2010 Qatar Project Management (d) (c) lift all generator equipment using eyes, yokes and skids provided by the manufacturer do not store equipment assemblies exposed to weather physically protected all generator equipment against damage from work of other trades cover all generator equipment with suitable material to avoid damage to finish. Contractor shall submit the calculation to prove the adequacy of capacity of the crane he intends to use for installation of the D-G set QCS 2010 Section 21 Part 17 Standby Diesel Generator Set Page 15 duration of all time delays and then automatically shut-down. This test shall be made with unit operating, and twice with unit simulated for a starting failure. 2 Testing of the Set: Engine: (i) the engine shall be tested at site before and after erection to BS 649 and amendments or equivalent including items which are said to be subject to mutual agreement. The test shall include inspection, after testing the following parts (ii) subsequent running test of eight hours shall be carried out of the set (iii) the engine shall be subjected to vigorous performance tests at site to the satisfaction of the Engineer and the main items shall include: Output characteristics Temperature rise Checking of valve clearance, fuel pump setting, governor setting, pipeline connections, exhaust piping and flexible connections Checking the base and set are level in all directions, checking alignment of engine and generator and vibration isolators location and proper installation Checking of proper operation of engine safety devices Checking of fuel pipelines, fuel pumps, tank level gauges and level control switches operation. (b) Alternator and Exciter: (i) the alternator and exciter shall be tested to BS 5000, P.99 amendments thereof (ii) tests at site before erection and after erection prior to handing over shall be carried out to the satisfaction of the Engineer. The main items of tests deemed necessary by the Engineer shall be carried out at the expense of the Contractor. The performance test shall be for 24 hours under the worst climatic conditions prevailing in Qatar (iii) the Contractor shall be fully responsible to provide all the necessary facilities for the test at his own expense. 17.3.5 Training of Operation and Maintenance Personnel 1 The Contractor shall train a number of persons who will be selected by the Engineer for the operation and maintenance of all the works within the Project before these works are handed over to the Engineer. 2 The training has to be carried out by qualified staff of the Contractor for each specified service and shall be provided for a one month period following the certificate of completion. 17.3.6 Reference Data Sheet This Form or similar is to be completed by the Electrical sub-contractor as Well as D/G subcontractor and to be submitted for approval to the Engineer unless otherwise Specified. --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------1. Name and Address of D/G sub-contractor 2. Detail of work in hand now with proposed D/G sub-contractor --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------Name of Government Amount of D/G Project Installation Works --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------a. ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- QCS 2010 Qatar Project Management (a) QCS 2010 Section 21 Part 17 Standby Diesel Generator Set Page 16 b. ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------c. ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------d. ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------e. ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------We confirm that the Statements given above are true, to the best of our knowledge and it is known to us that Engineer reserves the right to refuse to award sub-contract to us if the above Statements are found to be incorrect. Signature Signature Position in company of person signing Position in company of person signing END OF PART QCS 2010 Name of D/G sub-contractor Qatar Project Management Name of Electrical Contractor QCS 2010 Section 21 Part 18 Uninterruptible Power Supply Systems Page 1 18. UNINTERRUPTIBLE POWER SUPPLY SYSTEMS...................................... 2 18.1 GENERAL ...................................................................................................... 2 18.1.1 18.1.2 18.1.3 18.1.4 Scope Description References Submissions 18.2 PRODUCTS ................................................................................................... 2 18.2.1 18.2.2 18.2.3 18.2.4 18.2.5 18.2.6 18.2.7 18.2.8 System Rectifier/Charger Battery Static Switch Monitoring and Control Test Procedures Environment Protective Devices, Controls and Monitors 2 3 3 4 4 5 5 5 Qatar Project Management QCS 2010 2 2 2 2 QCS 2010 Section 21 Part 18 Uninterruptible Power Supply Systems Page 2 18. UNINTERRUPTIBLE POWER SUPPLY SYSTEMS 18.1 GENERAL 18.1.1 Scope 1 This Part specifies the requirements for uninterruptible power supply systems. 2 Related Parts and Sections are as follows: Cables and small wiring Conduits Trunking Cable trays Accessories and General Power 18.1.2 Description 1 A single UPS System shall be provided for the Main Control Room (MCR) Data Communication system (DCS) and peripheral equipment. 18.1.3 References 1 The following Standards are referred to in this Part: IEC 157 IEC 158 Low Voltage Switchgear and Control gear Low Voltage Control gear 18.1.4 Submissions 1 Submit in accordance with Part 1 2 Shop Drawings (a) submit dimensional drawings of the main switchboard, including sections and elevations, showing the following: (i) sizes and positions of components (ii) positions and method of fixing cable and boxes (iii) location of terminal boards (iv)other pertinent data. 3 Project Data (a) Submit: (i) full specifications of the enclosure and the components of the equipment with relevant sheets of manufacturer’s catalogues (ii) confirmation that the equipment complies with the relevant specifications. 18.2 PRODUCTS 18.2.1 System 1 The UPS system shall be comprise of single rectifier, battery charger and inverter modules: (a) the UPS system shall be designed in such a way that any spare part, printed circuit board, sub-assembly or component, can be replaced without any adjustment (b) it shall supply clean, uninterrupted power to the critical loads and meet the specifications (c) transformers shall be manufactured using vacuum pressure impregnated insulation. QCS 2010 Qatar Project Management This Section Part 6 Part 7 Part 8 Part 9 Part 10 QCS 2010 Section 21 Part 18 Uninterruptible Power Supply Systems Page 3 The Contractor shall assess the electrical load capacity of the UPS taking into account derating for non-linear loads and worst case ambient temperature conditions. 3 The UPS cabinet shall be designed such that all components are removable from the front and cable entry by floor mounted gland plates. 4 UPS shall be designed and manufactured “standalone” for automatic operation and as such circuit connections; protection devices and the like shall comply with BS EN 60950, BS EN 50091-3 and BS EN 60439. 5 The UPS shall be designed to supply clean, uninterrupted power to the loads. 6 The design of UPS shall take account of continuous load capacity, de-rating for non-linear loads and ambient temperature conditions. The UPS shall be sized to supply all instrumentation and control equipment including but not limited to control and computer room hardware, mimic, annunciation, telecommunication systems and emergency lighting etc. where applicable. 7 Main Features The UPS shall consist of fully controlled rectifier charger, battery bank, inverter, static bypass and manual bypass capable to providing safe and secure power supply for a minimum period of 8 hours. The UPS shall include the following features as minimum:(a) (b) (c) (d) (e) (f) (g) (h) (i) optimal quality of the output voltage transient over-voltages and spike protection voltage variations and mains failures protection frequency variations protection true single phase regulation low noise low THD (Not to exceed BS G5/4 limits) PC connectivity for parametering as described under particular requirements. serial communication 100100 by employing industry standard modbus, fieldbus, NP etc protocol as described under particular requirements. 18.2.2 Rectifier/Charger 1 The rectifier/charger shall be of solid-state type with fully controlled 6-pulse thyristor bridge and anti-harmonic chokes. It shall have 10 sec walk-in ramp for input current, adjustable battery current and voltage. It shall recharge a fully discharge battery in 24 hours. A boost charge facility shall be provided. A normally open contact rated at 240 Vac, 2A, close on boost charge, shall be provided for remote monitoring. Input voltage ratings are as follows: (a) Mains 1 (input to rectifier/charger) Voltage : 415 volts AC ± 10% Wiring : 3-phase, 4 wire + Earth. Frequency : 45 to 55 Hz. (b) Mains 2 (input to static switch) Voltage : 415 volts AC (± 15%) Wiring : 3-phase, 4 wire + Earth. Frequency : 50 Hz (c) Synchronisation Range: ± 0.75 HZ 18.2.3 Battery 1 Unless otherwise specified in the Project Documentation, the batteries shall be of sealed nickel cadmium maintenance free type and sized for the pre-selected time with the UPS operating at rated load. The battery bank shall be sized to maintain full load for a period of 8 hours QCS 2010 Qatar Project Management 2 QCS 2010 1 Section 21 Part 18 Uninterruptible Power Supply Systems Page 4 The inverter shall be of transistorised PWM type, for the specified UPS rated power at 0.8 p.f. Output rating shall be as follows: Wiring Voltage Transient Voltage Regulation Harmonic distortion Efficiency Audible noise : 3-phase, 4 wire and earth. : 415/240 volts (± 1%), 50 Hz (± 0.25 Hz). : Voltage transients shall not exceed ± 5 % for a 100 % load step change and the return to steady state value shall be in less than 20 milliseconds. : Less than 4% THD : For 100% load 92% & For 50% load 91% : 65 dBA @ 1.5m 2 Overload Capabilities: (a) inverter shall sustain 125 % overload for at least 10 minutes and 150 % overloads for 1 minute. After delay, if overload persists, the load shall be transferred to bypass supply without break if Mains 2 voltage is within tolerance limits. The UPS shall check the load and if the load is below overload threshold, inverter shall restart automatically and load shall be transferred back to inverter. Facility to inhibit automatic re-transfer shall be provided. 3 The automatic retransfer to the inverter shall be blocked if a transfer to the mains was initiated six times within one minute or in case of non-synchronization of the inverter with the mains. 18.2.4 Static Switch 1 The static switch shall have anti-parallel connected thyristor bank for instantaneous load transfer between the inverter and the mains 2 supply. 2 Maintenance manual By Pass: (a) Manual bypass switch system of full UPS shall be integrated into the UPS so that load can be transferred to mains supply WITHOUT break for maintenance of UPS. Procedure for transfer to maintenance bypass and back to UPS shall be controlled by the bypass menu of the UPS, thus eliminating possibility of causing disturbance of load by operator who is unaware of correct procedures. 18.2.5 Monitoring and Control 1 Monitors: (a) (b) (c) the following status information shall be monitored by indicating lights on the front panel of the UPS: (i) rectifier-charger on (ii) load on inverter (iii) load on Mains 2 bypass (iv) alarm (v) inverter shutdown imminent (vi) boost charge an audible alarm shall warn the user of faults or operating problems. The system shall be equipped with an alarm off button. Metering values displayed on an alpha-numeric display. The following measurements shall be available: (i) inverter output voltage (L-L) (ii) inverter output frequency (iii) inverter output currents (iv) voltage across battery terminals QCS 2010 Qatar Project Management Output synchronised in amplitude, phase & frequency to mains 2 when mains 2 is within tolerance limits. Phase difference between inverter output and mains 2 held below 3؛ (electrical) in such condition so that the maximum gap while transfer to UPS from Mains 2 and vice versa occurs shall be less than 167 micro seconds. QCS 2010 Section 21 (v) (vi) (vii) 2 Part 18 Uninterruptible Power Supply Systems Page 5 battery current (charge/discharge) mains 1 (rectifier/charger) input voltages (L-L) rectifier/charger input currents. Remote Control And Monitoring: (a) Remote transmission shall be possible for all controls, monitors and measurement indication on the UPS unit to the site DCS. Test Procedures 1 The UPS manufacturer shall provide proof of a stringent Quality Assurance Program. In particular the main equipment manufacturing stages sanctioned by appropriate tests such as: incoming components inspection, discrete sub-assembly tests and complete functional checks on the final product. Equipment shall undergo on-load burn-in leaving the factory. Final inspection and calibration operations shall be documented in a report drawn up by the supplier’s Quality Inspection department. 18.2.7 Environment Ambient temperature : Maximum relative humidity : 0 0 0 C to + 50 C 95 % 18.2.8 Protective Devices, Controls and Monitors 1 The UPS shall be built on modular basis. 2 Main Protections - The UPS shall include the following protections as minimum:(a) (b) (c) (d) (e) (f) 3 Input over voltage Load short circuit Over temperature Surge protection Noise protection Battery deep discharge protection Controls shall be micro processor based and the following main controls shall be possible: (a) (b) (c) (d) (e) rectifier/charger on/off inverter on/off forced shutdown forced transfer upon forced shutdown of inverter when the (mains 2) is outside tolerances self-test END OF PART QCS 2010 bypass power supply Qatar Project Management 18.2.6 QCS 2010 Section 21 Part 19 Sound and Call Systems Page 1 19. SOUND AND CALL SYSTEMS ..................................................................... 2 19.1 GENERAL ...................................................................................................... 2 19.1.1 19.1.2 19.1.3 19.1.4 Scope Reference Standards Quality Assurance Submittals 19.2 PRODUCTS ................................................................................................... 3 19.2.1 19.2.2 19.2.3 19.2.4 Public Address Systems Farash Call Systems Intercom Systems Auto Class Change Over Systems 19.3 INSTALLATION ............................................................................................. 7 19.3.1 19.3.2 19.3.3 19.3.4 Wiring and Wiring Facilities Testing and Commissioning Maintenance and Guarantees Training 3 6 6 7 7 8 8 8 Qatar Project Management QCS 2010 2 2 2 2 QCS 2010 Section 21 Part 19 Sound and Call Systems Page 2 19. SOUND AND CALL SYSTEMS 19.1 GENERAL 19.1.1 Scope 1 This Part specifies the general requirements for sound and call systems, including amplification and tone selection/control equipment, input stations, loudspeakers, power connections, cables and terminations. 2 Related Parts and Sections are as follows: General Provisions for Electrical Installations Cables and small wiring Conduits and Conduit Boxes Trunking Cable Trays Telephone Installation Structured Cabling Systems Testing 19.1.2 Reference Standards 1 The following standards are referred to in this Part, and shall be complied with: BS 6840 BS 7671 Sound system equipment Requirements for electrical installations ISO 9000 Quality management and assurance standards 19.1.3 Quality Assurance 1 Manufacturer’s qualifications: the equipment and accessories to be furnished for the sound and call systems shall be the products of one internationally reputed manufacturer regularly engaged in producing such systems for a minimum of ten years. Manufacturers shall be certified to ISO 9000 or equivalent. 2 Installer’s qualifications: Installations shall be executed by the manufacturer’s personnel. Installations may be executed under the supervision of the manufacturer’s personnel, with the Engineer’s approval, provided the installer has three years previous experience of such installations and has completed three similar projects within Qatar. 3 Mixing of major components from different manufacturer, to make one system, shall not be permitted. All components shall by supplied from a single source/manufacturer. 19.1.4 Submittals 1 The Contractor shall include a detailed list of all equipment and materials proposed 2 The Contractor shall include a complete set of catalogues, illustrations, diagrams and any other descriptive literature sufficient to present complete information about systems for the Engineer's approval. 3 The Contractor shall include in detail the maintenance programme of equipment and system capacity to accept future expansions. 4 The Contractor shall include a detailed list of recommended spare parts required for 2 years. QCS 2010 Qatar Project Management This Section Part 1 Part 6 Part 7 Part 8 Part 9 Part 13 Part 14 Part 23 QCS 2010 Section 21 19.2 PRODUCTS 19.2.1 Public Address Systems 1 General (a) (b) (c) (e) (f) (g) 2 Page 3 the Contractor shall provide and install complete intercommunication systems with hand-free operation, electronic centralised microprocessor controls and full functionality as specified, to BS 6840 where applicable systems shall include central exchange controllers, disk stations, surface mounted wall stations, privacy hand-sets, wall receptacles, cables, terminals and strips as specified to provide a complete working system equipment shall be reliable, long life, maintenance free and have low power consumption when specified for a large installation having multiple microphone stations, it shall be possible to automatically isolate remaining microphone input stations or other auxiliary input terminals as soon as one is activated. Stations shall be activated by push button action. multiple channel input and zone selector modules shall permit flexible arrangements for selecting the input channels on priority basis. Stations with higher priority shall override announcements activated by others with lower priority order systems shall permit announcement on individual zones, any combination of zones and simultaneous announcements on all zones system layouts shall be according to the Project Drawings. Amplifiers (a) (b) (c) (d) (e) (f) 3 Sound and Call Systems master module amplifiers shall incorporate a master volume control, a sliding control for both treble and bass, a built-in limiter plus and LED indicator and headphone socket to permit input signal monitoring amplifiers shall incorporate a push button ON/OFF switch with indicator lamps to define unit status amplifiers shall incorporate a power supply section, mains transformer, output transformer and printed circuit boards to provide necessary amplification of input signals. Amplifier outputs shall have voltage tappings of 100, 70 and 50 volts amplifiers shall be accommodated in racks (19" rack is preferred) with sliding facilities. for multiple zones, one amplifier shall be assigned to each zone. Systems shall include an additional amplifier to be used as common standby with switching facilities to connect the standby instead of the faulty amplifier technical performance (i) Rated Output Power : refer to Project Documentation (ii) Max. Power Consumption : refer to Project Documentation (iii) Frequency Response : 60 Hz - 16 kHz (iv) Distortion at 1 kHz : < 0.5% THD o o (v) Operating Temp. Range : 0 C to 45 C (vi) Relative Humidity : 95% Channel Input Modules: shall be programmed so that inter-channel priority forms can be achieved via an interconnection block on main printed circuit boards as follows: (a) (b) (c) (d) mixing mode : all input channels shall have the same priority and signals may be mixed together serial/cascade priority mode : Channel 1 has priority over 2, 2 over 3, and so on first served priority mode : The first channel switched on shall block the input for other channels. technical performance (i) Input Level : 500 mV - 8V max. (ii) Frequency Response : 60 Hz - 16 kHz (iii) Distortion : < 0.2 % THD (iv) S/N : > 65 dB (v) Cross-talk Attenuation : > 60 dB QCS 2010 Qatar Project Management (d) Part 19 QCS 2010 Section 21 (vi) (vii) 4 Operating Temp. Range : Relative Humidity : Sound and Call Systems o Page 4 o 0 C to 45 C 95 % Active zone selectors: zone selectors shall have the capability of switching ON and OFF loudspeakers in various zones by means of electronic built-in facilities. Switching shall be based on pre-programmed cascaded order to permit selection of one of the following modes: (a) (b) (c) manual operation : Loudspeakers shall be selected by means of push button switches. Each switch corresponds to one zone zone programming : in conjunction with input modules to provide the facilities for connecting any of the zones with any of the input channels remote control from microphone station : selection of any of the loudspeaker zones shall be achieved by operating the appropriate switches on the microphone control unit. It shall be possible by operating a switch in the microphone control unit to access all the channels at the same time for common announcements When specified in the Project Documentation, facility for switching to alarm mode shall be provided. When an alarm signal is initiated, all loudspeaker zones shall be automatically switched and prepared to receive any common announcement. The alert/alarm signal Input Units shall be coupled to amplifier units to perform the following functions: (a) two tone alert signal : 550 Hz tone followed by 440 Hz tone (b) alarm signal : continuous repetition of the alert signal (c) time signal : 550 Hz tone (d) priority : microphone input channel (e) pre-set control of microphone : independent of master volume control. Various modes of initiating attention signals shall be by pressing a switch on the unit front panel, or remotely by the microphone „ON' switch on the microphone control unit attached to the unit, or any other microphone stations. 6 Central Equipment Assemblies (a) (b) (c) 7 when specified, free standing racked shelf assemblies shall be provided suitable for accommodating all amplifiers, input modules, zone selector modules and alarm units when specified, central equipment shall include AM/FM radio tuners and tape playback set. Units shall be integrated and connected to systems through switching and control units central equipment racks shall be rack type (19” preferred) accessible from back and with removable side panels. Racks shall be provided with mounting facilities to permit sliding in and out of units with facilities to fix units to racks by screws to the front side Loud Speakers : Loud speakers shall comply with IEC 268, Parts 5 and 14 (a) (b) wall speakers: these speakers shall be provided with a resonating board and an aluminium grille for universal application for flush or surface-mounted enclosures. The speaker shall be a high performance type and shall be provided with auto-transformer with taps for 1/4, 1/2 and 1/1 output. The normal rated capacity shall be 4-5 W, if not otherwise specified in the Project Documentation. A volume control shall be incorporated. The sound pressure shall be approximately 100 dB ceiling speakers: these speakers shall be designed, including their accessories, for recess installation in various suspended ceiling types. The grille shall be aluminium. The speaker shall be of the same type as wall speakers QCS 2010 Qatar Project Management 5 Part 19 QCS 2010 (c) (e) (f) (g) 8 Sound and Call Systems Page 5 sound column speakers : these shall be designed for interior installation or in weatherproof design for exterior installation. The enclosure shall be of aluminium and shall be for wall or pole mounting, with suitable accessories. They shall be provided with adjustable cast aluminium fixing arms, which allow sound columns to be adjusted o o through 20 vertically and 75 horizontally and shall include multiple loud speakers of 8 Ohms nominal impedance, symmetrically positioned within sound columns. An autotransformer with taps for 1/4, 1/2 and 1/1 capacity shall be built in. The normal rated capacity shall be 10, 20, 30 or 40 W as indicated in the Project Documentation. The Column boxes shall accommodate multiple speaker systems depending on capacity, which may be as follows (preferably as per manufacturer’s standard design): (i) 10 W - 3 speakers (ii) 20 W - 4 speakers (iii) 30 W - 6 speakers (iv) 50 W - 8 speakers horn speakers : these speakers shall be designed weatherproof for exterior installation. The enclosure shall be of aluminium, impact-resistant and coated with weatherproof paints. They shall be provided with swivel brackets for fixing. An auto-transformer with taps for 1/8, 1/4, 1/2 and 1/1 capacity shall be built in. The normal rated capacity shall be 10, 20, 30 or 40 W as indicated in the Project Documentation the speaker systems may be any of the above or their combinations, according to requirements in the Project Documentation. unless otherwise specified, the paint finishing shall be white when mounted on walls. technical performance (i) Sound pressure level at 1 kHz Octave, 1 m, at 1 W in accordance with IEC : refer to Project Documentation (ii) Power handling capacity : refer to Project Documentation. (iii) Frequency response : 60 Hz to 16 Hz (iv) Input Voltage : 100/70 Volts as per driving amplifier. o o (v) Environment conditions : 0 C to 45 C. Microphone Stations (a) (b) (c) (d) (e) 9 Part 19 microphone input stations shall consist of swan-necked microphones on table stands, incorporating zone selector switches for remotely controlling loudspeaker zones. If specified in the Project Documentation, adjustable height microphone, floor stands with collapsible type boom shall be provided microphones shall be dynamic cardoid type or condenser type with balanced line level output and suitable for use with unscreened cable. table stands shall incorporate the following features : (i) microphone switch and LED indicator (ii) colour-coded switches for switching ON/OFF zones. (iii) one `ALL CALL' switch for switching `ON' all loudspeaker zones for common announcements. (iv) LED indicators shall operate in parallel with indicators on corresponding amplifier input channels. The Contractor shall submit details of the proposed provisions to confirm the normal conditions of the system and the perfect selection of zones and input channels, before the operator executes the feed message of feed in the required signal. technical performance (i) Frequency Range : 60 Hz - 16 kHz (ii) Rated output Impedance : 200 Ohms (iii) Sensitivity : 2 mV/Pa o o (iv) Operating temp. Range : 10 C to +45 C (v) Relative humidity : 95% microphone input stations shall be complete with microphone accessories and 10m length microphone connections. Provisions shall be made for stations to avoid the possibilities of feedback. Cassette decks shall have a sequencer which will accept 2 music cassettes, with audio sensing and auto reverse playback features, to provide truly continuous back-ground music. Cassettes shall auto-eject on power-off or jammed tape. technical performance QCS 2010 Qatar Project Management (d) Section 21 QCS 2010 (i) (ii) (iii) (iv) (v) (vi) 10 Section 21 Part 19 Frequency Distortion at 1kHz Signal to Noise Ratio Wow & Flutter Tape Speed Power Supply Sound and Call Systems : : : : : : Page 6 60 Hz to 16 kHz < 3 % THD < 49 dB 0.35 % WRMS 4.75 cm/sec. 240 volts, 50 Hz FM/AM Tuners shall be 6 channel radios with digital display and a provision of six pre-set stations. : : : (iv) (v) : : Freq. Response Distortion FM/AM tuner section 3 mV for FM channel, 20 mV for AM channel 100 mV at ± 100 mV at 50 % modulation 27.5 kHz deviations To European standard Less than 1 % THD of 1 kHz @ 30 % 1 kHz @ nominal modulation output. 19.2.2 Farash Call Systems 1 Farash call systems shall be provided and installed in the areas indicated on the Project Drawings. Systems shall comprise call control panels with audible and visual indications initiated by call push buttons located in the various areas indicated. Call control panels shall have a resetting facility, for visual (sound ends when finger removed from button), after the call is attended. Systems shall be wired with low voltage wiring independent of other standard wiring systems. 2 Door strike: When specified and as per the Project Drawings, door strike system shall be provided to open, close and latch the entry doors by remote control push-buttons 19.2.3 Intercom Systems 1 System Operation (a) (b) (c) (d) (e) 2 calls shall be placed from any master station to any other station in the system unless specifically blocked. Calling parties shall touch-dial the appropriate digit numbers of desired stations, at which time a „connection tone” shall be heard and an LED illuminated at both stations to signify completion of connections. Voice communications may then begin. Connections may be cancelled by either party by pressing a cancel button master stations shall be equipped with a privacy/open facility to permit any user to place his station in the “privacy” mode. When calling a station that is in “privacy” mode, a unique “privacy tone” shall be heard at both stations for a pre-determined time interval as pre-set at the central exchange upon completion of conversation and cancellation by either party, the “private” station shall be restored to “privacy” without further control manipulation should calls be placed to stations already in use, the interrupted “busy tone” shall be heard by the calling party slide-type volume controls to adjust incoming volumes shall be included on each desk master station. Control settings shall be clearly visible. Stations shall contain continuously adjustable volume controls. Control Exchange Controllers (a) (b) (c) central controllers shall provide all control, switching logic, signalling and operating features listed throughout this specification circuitry and components shall be arranged on slide-in printed circuit boards of the highest quality central controllers shall not require external devices to program system functions and features QCS 2010 Qatar Project Management technical performance (i) Characteristics (ii) Sensitivity (iii) Normal Output QCS 2010 (d) (e) (f) (g) 3 Section 21 Part 19 Sound and Call Systems Page 7 central exchanges shall be equipped with the required number of subscriber boards necessary to accommodate the quantity of stations required expansion to ultimate cabinet capacity shall require addition of the requiredquantity of plug-in type subscriber boards. One plug-in board shall be required to increase exchange capacity station wiring connections to central controllers shall be by means of screw terminals. Soldering, wire wrap and pressure connectors shall not be used. Interwiring between circuit board receptacles shall be by master printed circuit lines central controllers shall be powered by closely regulated power supplies at maximum 24 Volt. Power supply mains transformers shall be mounted within or adjacent to exchange cabinets. Master Stations (c) (d) intercom stations shall be the master type capable of receiving and initiating calls intercom stations shall either be the desk-mounted type as used in commercial offices or a wall-mounted industrial type in workshop and plant areas, as indicated on the Project Drawings stations shall have handsets for confidential conversations. Lifting handsets shall switch off microphones and loudspeakers to provide fully telephonic facilities master stations installed in workshop areas shall comprise of heavy duty waterproof units for use in dusty and/or damp environments. 4 System cabling shall comprise individual twisted pair telephone cables connected to the central controller from each of the stations. 19.2.4 Auto Class Change Over Systems 1 Auto-class change over systems for the automatic ringing of class change bells shall be provided located at different places within school buildings as shown on the Project Drawings. The system shall be microprocessor controlled and programmable. 2 Systems shall include the following salient features: (a) (b) (c) (d) (e) (f) (g) 7 days a week programming override to silence the alarm on week ends i.e. Friday minimum time adjustable to 5 minutes over ride switch to operate the bells in the event of timer failure or wrong time easy system to programme the timing throughout the week and also separate selection through a two way switch for summer/winter schedules DC backup using nickel cadmium batteries for 24 hours spring reserve selector switch to select the operation mode in Manual/Auto/Off positions. 19.3 INSTALLATION 19.3.1 Wiring and Wiring Facilities 1 Wiring shall be executed to provide a complete and satisfactory functional system in all respects. 2 Wiring shall be carried out using multi-core and twisted pair conductors as indicated on the drawings. Wires/cables shall be enclosed in conduits and/or trunking. Vertical cable distribution cabling shall be on cable ladders. Cabling, conducting and trunking shall be in conformity with the relevant Specifications. 3 Cable terminations, components and junction boxes shall have identification tags, indicating polarity and function in a consistent manner throughout the system so that it can be crossreferenced with the as-built drawings and manufacturer's diagrams. 4 Signalling cables shall be electrically and physically separated and isolated from the mains voltage cables. Microphone cables shall be separated from the loudspeaker cables in a separate conduit. QCS 2010 Qatar Project Management (a) (b) QCS 2010 Section 21 Part 19 Sound and Call Systems Page 8 Testing and Commissioning 1 After the installations are completed, the Contractor shall conduct acceptance tests to confirm the compliance of the systems with the Specifications. The Contractor shall present a list of the acceptance test items to be performed for Engineer's approval. 2 The test instruments and personnel to conduct the test shall be provided by the Contractor. 19.3.3 Maintenance and Guarantees 1 The Contractor shall be responsible for the system maintenance and repair of any fault for a period of 400 days starting from the provisional handing over. During this period the Contractor shall replace and/or repair any fault with all spare parts without any cost to the Employer. 2 The Contractor shall guarantee the system for a period of 400 days. During this period the Contractor shall clear any failure due to design problems or poor installation and workmanship. 19.3.4 Training 1 Training of personnel designated by the Engineer shall be carried out to enable to take over, operation and maintenance of the sound and call systems in the shortest time. 2 The Contractor shall submit a detailed training program which shall include theoretical and practical training for 1 month for personnel to be deputed by the Employer, at the end of the guarantee period, in addition to the Employer’s personnel participation in the installation and testing stages as specified earlier, and maintenance during the guarantee period of 400 days. END OF PART QCS 2010 Qatar Project Management 19.3.2 QCS 2010 Section 21 Part 20 Elevators/Escalators Page 1 20. ELEVATORS/ESCALATORS ........................................................................ 2 20.1 GENERAL ...................................................................................................... 2 20.1.1 20.1.2 20.1.3 20.1.4 20.1.5 Scope References Submittals Quality Assurance Warranty 20.2 PRODUCTS ................................................................................................... 3 20.2.1 20.2.2 20.2.3 20.2.4 Description Electric Traction Passenger Lifts Electro-Hydraulic Passenger Lift Escalators 20.3 INSTALLATION ........................................................................................... 11 20.3.1 20.3.2 20.3.3 20.3.4 20.3.5 20.3.6 20.3.7 20.3.8 20.3.9 Site Condition Inspection Preparatory Work Installation Field Quality Control Field Adjustments Acceptance Inspection and Tests Clean Up Manufacturer's Services Maintenance and Guarantees 3 4 7 8 11 12 12 13 13 13 13 14 14 Qatar Project Management QCS 2010 2 2 2 3 3 QCS 2010 Section 21 Part 20 Elevators/Escalators Page 2 20. ELEVATORS/ESCALATORS 20.1 GENERAL 20.1.1 Scope 1 This Part specifics the general requirements for elevators and escalators used only for passengers 2 Related Parts and Sections are as follows: Section 5 Section 16 Section 17 General Provisions for Electrical Installations Motor Starters Cables and Small wiring Conduits and Conduit Boxes Trunking Cable Trays Wiring Accessories and General Power Light fittings Electric Motors Earthing and Bonding Testing Concrete Structural metal work Metal work 20.1.2 References 1 The following standards and documents of other organisations are referred to in this Part, and shall be complied with: BS 476 BS 5655 (EN 81) BS 5656 (EN 115) BS 6977 BS 7255 Fire tests on building materials and structures Lifts and service lifts Safety rules for the construction and installation of escalators and passenger conveyors Insulated flexible cables for lifts and for other flexible connections Code of practice for safe working in lifts BS EN 9000 Quality management and assurance standards Qatar General Electricity & Water Corporation Regulations for passenger and goods lifts. 20.1.3 Submittals 1 Manufacturer’s product data and samples. (a) (b) 2 submit three 75 x 300 or 300 mm length samples of each required finish, excluding those intended for painting after installation, for the Engineer’s approval catalogues shall be provided of signal equipment units to show push buttons, lights, graphics and mounting provisions. Shop Drawings: (a) (b) (c) drawings for all main components including the pit, hoistway, and the machine room general arrangements, foundations and installations, sectional elevations of the hoistway, car and entrance details, and signal details component specifications and preventative maintenance charts electrical schematics and one copy of the approved master electric schematic and approved lubrication chart shall be framed with a clear plastic cover and mounted on the machine room wall QCS 2010 Qatar Project Management This Section Part 1 Part 4 Part 6 Part 7 Part 8 Part 9 Part 10 Part 11 Part 15 Part 22 Part 23 QCS 2010 3 Section 21 Part 20 Elevators/Escalators Page 3 Motor data including: manufacturer minimum guaranteed efficiency power factor under all load conditions locked rotor current motor speed mounting details Certificates of Compliance. 5 Certified Test Reports. 6 Operation and Maintenance Manuals. 7 Training Programme. 20.1.4 Quality Assurance 1 Products shall be from an experienced manufacturer who can demonstrate equal or larger capacity installations using similar equipment, installed and successfully operating for at least 5 years, with names and phone numbers of contacts at installations to verify performance. The manufacturer shall comply with ISO 9000 or equivalent. 20.1.5 Warranty 1 All components shall be free of defects in materials or workmanship. 2 The Contractor shall remain responsible for routine maintenance for 400 days from the date of acceptance of the installation by the Engineer. During this period the Contractor shall promptly replace and/or repair any fault with supply of all spare parts without any cost to the Client. 3 Motors shall have 5 year warranties. 4 Individual warranties by component manufacturers in lieu of single source responsibility by the elevator manufacturer shall not be acceptable. 5 Items which fail during the warranty period, excluding expendable items, shall be replaced without cost to the Employer. 6 Manufacturer’s guarantee and warranty certificates shall be provided prior to equipment startup. 20.2 PRODUCTS 20.2.1 Description 1 Equipment shall be provided by a single manufacturer who shall design, fabricate, and test all components of the elevators as well as supervise, install and commission the units. 2 Elevators shall be complete in all respects and shall include but not necessarily be limited to the following components: (a) (b) (c) (d) (e) (f) (g) machine room equipment hoistway equipment elevator entrance ways door opening and closing devices elevator cars car control stations landing control stations QCS 2010 Qatar Project Management 4 QCS 2010 (h) Section 21 Part 20 Elevators/Escalators Page 4 appurtenances 3 The Contractor shall make all modifications, adjustment, and improvements to the elevator system necessary to meet the performance requirements specified. The elevator shall provide safe, smooth operation, complying with all building and elevator codes required by the authorities. 20.2.2 Electric Traction Passenger Lifts 1 Machine Room Equipment (a) (c) (d) (e) 2 Hoistway Equipment (a) (b) (c) (d) (e) (f) 3 guide rails and brackets: T-section cold drawn (not fabricated) guide rails and brackets suitable for travel, car weight and support locations at structural floors, with backing as EN 81 buffers: energy dissipation type with blocking and supports normal terminal stopping devices: in accordance with EN 81 electricity wiring: copper conductors with 600 volt insulation throughout with individual wires coded, with 10 % spare capacity. All connections shall be identified on studs or terminal blocks, rated 75 °C minimum. Splices or similar connections in wiring are not permitted except at terminal blocks, control cabinets or junction boxes. Flexible heavy-duty service cord to BS 6977 may be used between fixed car wiring and car door switches conduit and duct shall be PVC jacketed or galvanised steel 20 mm minimum diameter. Flexible conduit shall not exceed 450 mm in length and shall be as in Part 7 entrance equipment: (i) door hangers: shall use two-point suspension with upthrust rollers (ii) door tracks: replaceable bar or formed cold drawn steel with smooth hanger contact surface (iii) interlocks: operable without retiring cam, with interlocks that are visible and conspicuous when doors are open, painted matt black (iv) closures: spring or aspirator type (v) pit stop switches to BS EN 81 Hoistway entrances shall be fire rated in accordance with BS 476 Part 8, with frames as follows: (a) (b) (c) floor entrances, jambs and heads shall be fabricated steel with a 304 stainless steel cladding frames shall be hollow metal, bolted to form a one-piece unit jamb and head depth and profiles shall be as indicated on the Project Drawings, fabricated from mild steel not less than 1.2 mm thick, steel pan construction, with side-opening doors, rubber bumpers to cushion closing impact, and finished QCS 2010 Qatar Project Management (b) general: shall be provided with manufacturer’s standard pre-engineered elevator system in accordance with the specification. Manufacturer’s may provide custommanufactured elevator systems that meet specified requirements. Where components are not specified, components shall be provided as for manufacturer’s standard pre-engineered elevator systems, or as necessary to produce a safe and fully operational elevator system motor control: solid-state power converter/inverter with line filters or chokes to prevent peaks or spikes from feeding back into building power systems hoisting machine: variable voltage variable frequency (VVVF) thyristor, traction-type, geared hoisting machine with squirrel cage motors designed specifically for elevators. Unless specified otherwise, variable voltage variable frequency AC drives shall be used. Refer to part 5 of this section for general specification selector: microprocessor solid-state, integrated controller with durable cabinet, lockable doors and adequate ventilation to dissipate heat, wired to identified terminal block studs, with identifying symbols or letters identical to those on wiring diagrams, permanently marked adjacent to each component on the controller The microprocessor based controller shall include the facility to interface with Remote Elevator Monitoring (REM) and Elevator Management Service (EMS) as a part of Building Management System through the data network system. QCS 2010 (d) (e) 4 (b) Elevators/Escalators Page 5 faces as specified. Each door panel shall include gibs. The trailing door gib shall be in the sill groove throughout the length of travel sills: extruded hard aluminium fascia toe guards, dust and fascia width hanger covers: 1.5 mm galvanised steel with door open bumpers on entrances equipped with vertical struts. safety edge devices shall be full height, infra red, non contact, door edge safety devices to detect obstruction in the doorway and reverse nudging action : in the event that the safety edge is operated for a pre-determined time interval (15-20 seconds) after automatic door closing has been initiated, a buzzer shall sound, and the doors shall close with a maximum of 0.35 Kg-meters kinetic energy Microprocessor based Variable Voltage Variable Frequency (VVVF) drive operational control shall be extended for door control as integral with the car movement. Car Equipment (a) (b) (c) (d) (e) (f) (g) (h) (i) (j) (k) car frames: welded or bolted steel channel construction platforms: isolated type, steel, construction fire proofed on the underside guide shoes: nylon sliding type car sills: hard aluminium type sill toe guards: in accordance with EN 81 car door hangers and tracks: as specifications on hoistway entrance hangers and tracks headers: minimum 1.2 mm thick steel shaped to provide stiffening flanges car door electrical contacts shall operate in conjunction with the car doors so that elevators cannot operate unless doors are closed, or within tolerances allowed by EN 81 door operators : shall be microprocessor based a.c./d.c. capable of opening doors at no less than 60 m/min and accomplishing reversal in no more than 65 mm of door movement car finishes front return, side & rear wall, door, handrail, floor, ceiling panels, and light fixtures shall be finished as detailed in the Specifications removable panels shall be provided as specified for side and rear wall panels at elevators with facings glued to plywood, full-height between top of base and ceiling of car. Panel joints shall be flush with panel surfaces in accordance with manufacturer’s standard layouts. Elevator car suspended ceiling panels shall have suitable strong backing in the ceiling frame to prevent sagging, without exposed screws or bolts. Car Control Stations (a) (b) (c) (d) (e) (f) (g) car control stations shall have durable vandal resistant face plates and micro-Touch Buttons located no higher than 1620 mm above the car floor (875 mm for alarm buttons) floor buttons, alarm buttons, door open buttons shall be identified by engraved or painted letters or symbols in accordance with EN 81 car floor buttons shall have 16 mm numbers on the face of buttons corresponding to the floors served for registration of the car stops. Call registration lights, located within or behind the buttons, shall illuminate the floor number corresponding to the call registered alarm buttons at the bottom of stations shall be provided to ring bells located on the car doors. Open and close buttons shall be provided to stop motion of doors and cause them to return automatically to their fully open or closed position respectively. Buttons shall be effective while cars are at landings and until cars start into motion, regardless of any special operational features car top control stations shall be in accordance with EN81, mounted on car tops, accessible from landings work lights and plug receptacles shall be provided top of elevator car with on-off switches and bulb guards car position indicators shall be provided in elevator car operating panels with digital indicators representing floors served and direction of car travel QCS 2010 Qatar Project Management (c) 1 Part 20 Door Opening and Control Devices (a) 1 Section 21 QCS 2010 Section 21 (i) (ii) 1 Elevators/Escalators Page 6 when cars leave or pass a floor, the numeral representing the floor shall be displayed, thereby indicating the position of the car in the hoistway at all times proper direction arrows shall be continuously illuminated to indicate the direction of travel Landing Control Stations (a) micro-touch buttons stations shall be provided adjacent to door jambs of each entrance with the following features: (i) flush-mounted vandal resistant durable faceplates and buttons for each direction of travel, illuminated to indicate call registration (ii) A fire recall station shall be provided at the main access level in addition to the call button signal fixtures shall be provided at each entrance to indicate the intended direction of travel of the elevator to waiting passengers, with the following features: (i) display numerals for car level, arrow and a gong mounted in the box fastened in the wall. Up or down arrows shall be illuminated and a gong sounded (once for up direction travel and twice for down direction travel) prior to the car’s arrival at the floor. The light shall remain illuminated until shortly before the elevator doors start to close (ii) hall lanterns shall be provided, of impact resistant plastic lenses and with satin stainless steel finish. Performance. The elevator shall: (a) (b) (c) speed to within plus or minus 10 % of the specified speed under any loading condition safely lower, stop, and hold up to 125 % of the rated load stop the elevator within plus or minus 10 mm of the design landing elevation under any loading condition. 3 Unless otherwise specified in the Project Documentation, operation shall be "Selective Down Collective Automatic Operation" as defined in EN 81. Doors shall open automatically when a car arrives at the main floor to permit egress of passengers, whether or not the main floor call has been registered in the car. When the car has arrived at the landing it shall have its doors open until the car is dispatched, or on expiration of a timed loading interval with no demand. 4 Emergency Features shall comply with EN 81 for Emergency Firemen’s Service, and the following: (a) (b) (c) (d) emergency operation: the elevator shall be equipped with a control system to operate and recall the car in fire or other emergency condition. terminals shall be provided on the controller for connection of signals from the sensors. Operation shall be similar on all elevators and visual/audible signals shall operate until return is complete or automatic operation restored standby lighting and alarm: during power failure, car lighting and car alarm shall be supplied with standby power via a car-mounted battery unit, including solid state charger, with testing means, installed in common metal container. Batteries shall be rechargeable with 10 year minimum life expectancy. Car mounted units shall operate alarm bell and light only emergency landing device: in the event of normal power failure, an emergency evacuation power supply shall drive the lift to a nearby floor. This controller shall be operated by sealed batteries which will be kept automatically charged for use by the unit: (i) standby power shall be provided by 24/12 V battery units mounted in the machine room, including solid-state chargers with testing means installed in common metal containers (ii) upon arrival at floor landings, elevator doors shall open automatically and remain open until the regular door time has expired. Elevators shall then become inactivated (iii) upon restoration of normal power supply to the building, elevators shall automatically resume normal operation. QCS 2010 Qatar Project Management (b) 2 Part 20 QCS 2010 Section 21 Part 20 Elevators/Escalators Page 7 5 Protection of electrical work: boxes and enclosures shall be provided with gasket covers. Doors and motors shall be totally enclosed. 20.2.3 Electro-Hydraulic Passenger Lift 1 General: materials and equipment associated with electro-hydraulic passenger lifts shall comply generally with the requirements stipulated for electric traction lifts above, with specific requirements stipulated below. 2 Lift Machines (a) (c) (d) (e) (f) 3 Drive Motor. Motors shall be suitable for operation for 415 V 50 Hz 3 Phase (a) (b) (c) (d) (e) 4 motor drive: solid-state power converter/inverter with line filters or chokes to prevent peaks or spikes from feeding back into building power systems pump drive: variable voltage variable frequency(VVVF) thyristor controlled, geared machine with squirrel cage motors designed specifically for elevators. Unless specified otherwise, variable voltage variable frequency a.c. drives shall be used. Refer to part 5 of this section for general specification control: microprocessor solid-state, integrated controller with durable cabinet, lockable doors and adequate ventilation to dissipate heat, wired to identified terminal block studs, with identifying symbols or letters identical to those on wiring diagrams, permanently marked adjacent to each component on the controller The microprocessor based controller shall include the facility to interface with Remote Elevator Monitoring (REM) and Elevator Management Service (EMS) as a part of Building Management System through the data network system shall run with the minimum of noise and vibration, capable of a continuous duty cycle of at least 60 motor starts per hour. Contractors shall submit full test certificates in triplicate for all tests. Refer to part 5 of this section for motor starter general specification and part 15 for electric motor general specification. Anti-creep devices shall be provided which shall automatically limit the car movement within 75 mm of the landing, from any point within the interlock zone, irrespective of handling doors. Devices shall only operate in landing level interlocked zones, and shall operate cars in the „UP’ direction only. Operation may depend on the availability of the electrical power supply provided that: (a) (b) main switches are kept in closed positions at all times except during maintenance, repairs and inspections electrical protective devices shall not cause electrical power to be removed from the anti-creep mechanism, except when such a device operates in consequence of motor failure. 5 Mufflers: High pressure systems shall be suitably muffled. Flexible pipes shall be included to prevent the hydraulic pulse attenuation from being transmitted to cars. 6 Cylinders and rams QCS 2010 Qatar Project Management (b) hydraulic pumps shall of the high efficiency type of either vane or screw type design. Means shall be provided where pumps may be coupled to the driving motors without the effect of eccentric loading on the pump bearings if pumps/motors of monoblock construction are offered, access shall be provided for inspection/replacement of coupling systems, thrust bearings, etc. pump/motor assemblies shall be mounted on rigid mild steel bedplates and suitably insulated, to absorb vibration of pump/motor assemblies direction of rotation of pumps shall be clearly indicated on pumps where they can be readily seen pumps shall be clearly marked to indicate inlets and outlets, related to a specified direction of rotation if external to power systems. Inlet sides to pumps shall be fitted with renewable fine mesh filters data plates with manufacturer’s name, part model and serial number shall be permanently displayed on or adjacent to pump/motor assemblies. QCS 2010 (a) (b) (c) (d) (e) (f) (g) (b) Page 8 Cars shall be directly supported by one side-acting steel ram turned true parallel, fine polished, and of sufficient diameter and strength to raise the Contract load at Contract speed ram attachments to car platforms shall be of sufficient strength to support ram weight with a safety factor of 4 rams shall not be subjected to bending stresses or eccentric loading. Eccentric loading shall be taken by car frames and guide shoes Rams shall be provided with solid metal stops at limits of stroke, or other means to prevent rams travelling beyond limits of cylinders multi stage rams, shall only be used if approved by the Engineer cylinder interconnections shall incorporate flow restriction valves to limit ram descent speed, should supply pressure lines fracture suitable trays shall be fitted to ram heads to collect leakage from ram seals. all necessary pipework and supports shall be provided between cylinder and valve block assemblies. Pipes shall be supported such that undue stresses are eliminated at all joints, bends and fittings, particularly at sections of systems subject to vibration cross-sectional areas of pipework shall be sufficient to prevent cavitation and starvation and not to induce turbulence or rise in temperature of oil. Oil Storage Tank (a) 3 Elevators/Escalators Pipes and Pipe Supports (a) 2 Part 20 oil storage tanks shall be constructed of heavy gauge sheet steel provided with tight fitting covers, oil level gauges and protective vents. Suction inlets shall be provided with filters to prevent ingress of foreign matter to systems. Means of completely draining oil storage tanks shall be provided. Valves (a) (b) (c) (d) (e) (f) (g) check valves shall be provided and shall be installed so that they hold the lift car with the Contract load at any point in the lift well, when the pump stops, or the pressure drops below the minimum operating pressure check, relief and other auxiliary valves shall withstand a static pressure equal to twice the normal operative pressure without damage valve gear/blocks shall be fitted with gradual restriction/release of hydraulic fluid to provide smooth acceleration and slowing of cars main pressure supply restrictions shall be diverted back to oil reservoirs and not to pump outlets relief valves shall be located between pumps and check valves and shall be of such types and so installed in by-pass connections that valves shall pass oil directly to tanks and not to pump suction sides main controlling valves shall be constructed such that they will remain closed to supply when pressure is shut off electrically controlled valves shall remain safe in the event of power supply failure. 20.2.4 Escalators 1 Escalator Trusses (a) (b) (c) (d) (e) (f) escalator trusses shall be of welded construction, fabricated from warm rolled standard ST 52 steel profiles. Sides of trusses shall be of frame work design truss design shall ensure that the maximum deflection is less than D/880 of the 2 distance between end supports with a calculated passenger load of 500 N/m . oil tight welded 5 mm sheet steel bottom plate shall be welded over the full length and width of the bottom of the trusses prior to welding, profiles shall be sand blasted, and after welding shall be protected against corrosion by minimum 40 µm thick primer coat a maintenance room shall be provided at the end of the lower landing to EN 115 truss support angles welded to the truss at the ends of both landings shall be capable of carrying the weight of the escalator and the load transmitted by 2 the passengers (5000 N/m ) QCS 2010 Qatar Project Management 1 Section 21 QCS 2010 (g) (h) 2 (b) (b) (c) (d) (e) closed track systems shall be provided to guide and support step chains and steps as they cycle around trusses track holders shall be welded to the framework of the trusses in order to fasten the individual tracks main drives shall be located in upper landings and shall consist of a rigid solid shaft to eliminate tension with self-aligning spherical roller bearings main drive shaft bearings shall be replaceable without dismantling balustrades main drives shall provide smooth operation and power transfer from drives to moving steps. tension carriages shall be located at lower landings of escalators for tensioning step chains step chains shall be guided laterally by sliding block guides and constantly tensioned by two compression springs reversal tracks shall be fabricated from 3.5 mm sheet steel special openings shall be provided to remove steps for maintenance or replacement correct chain tension shall be monitored by safety switches at each side of the tension carriages. Step Chain (a) (b) (c) (d) step chains shall be made of flat steel links, provided with wheels and interconnected by pins made of hardened ground steel the breaking strength per stand shall be 150 kn. The safety factor shall be 5 for the maximum rise. Step chain pins shall allow a maximum pin pressure of 32.3 2 N/mm at maximum rise both sides of step chains shall be linked by solid axles to optimise performance step chain wheels shall be provided at both ends of step axles between step chain links and shall have sealed bearings and oil resistant rubber tyres. Steps (a) (b) (c) (d) (e) (f) 7 teflon sliding supports shall be used at the lower landing and if an expansion joint of the building is located between upper and lower landings anti vibration rubber pads shall be provided to ensure that escalator support angles are isolated from building structures. Pads shall be used at both landings. Tension carriage (a) 6 Page 9 steps shall be one piece die-cast aluminium design with cleated treads and rises, ensuring maximum safety as each step meshes with the adjacent step step rollers shall have polyurethane tyres step tread pitches shall be 8.47 mm. Riser pitches shall be 16.94 mm steps shall be fastened to step chain by means of spring loaded pins providing a positive fixing to the axle, allowing the steps to be easily removed for maintenance step systems shall be designed such that step removal does not require dismantling of skirting or balustrade parts steps with yellow demonstration lines or yellow plastic inserts may be required, as specified. Handrail drive system (a) (b) (c) (d) handrail drive systems shall be driven directly from step chains via drive sprockets and reinforced toothed belts handrail drive units shall be located on both sides of the escalator in the incline section close to upper landings syncronisity between steps and handrails shall be assured to within EN115 recommendations design and positioning of drive systems shall be such that components can be inspected without need for step removal QCS 2010 Qatar Project Management (b) (c) 5 Elevators/Escalators Main Drive (a) 4 Part 20 Track System (a) 3 Section 21 QCS 2010 (e) (f) (g) (h) 8 Page 10 handrails shall be provided as endless vulcanised loops. Handrails shall have endless inner steel cord members to make handrails free of elongation, eliminating the need for frequent retensioning handrail guides shall be made from extruded aluminium profiles, having special polymer covers throughout the length to reduce friction between guides and handrails to a minimum passenger lines shall have tensioned spring clamps located between aluminium profiles and glass panels return lines shall have aluminium profiles fastened to trusses using screws. balustrade heights above finished floors shall be 1000 mm or 930 mm in upper and lower landing areas inclined sections heights shall be 842 mm at right angles to step nose lines material and finishes for balustrades, decking and skirting profiles shall be as specified Combs, Comb Plates and Floor Plates (a) (b) (c) (d) (e) combs, comb plates and floor plates shall be designed for maximum passenger loads in accordance with EN 115 combs shall be made of die cast aluminium, screwed to comb plates for ease of replacement if necessary. Comb teeth shall have intentional rupture points, allowing them to break easily in the event of objects getting trapped between steps and combs, thereby preventing serious damage comb plates shall be made from extruded aluminium profiles with laterally extending grooves preventing passengers from slipping. Grooves shall be powder coated black and the surfaces finished as stated in the particular specification fixed floor plates shall be made from extruded aluminium profiles with laterally extending grooves to match the comb plate. The grooves shall be powder coated black and surface finished as specified removable floor plates shall be provided, allowing access to both machine rooms and maintenance rooms. Removable floor plates shall be constructed from low weight extruded aluminium profile sections allowing ease of the removal by one service mechanic. Standard removable floor plates shall be recessed by 7 mm, allowing for infill materials as specified. Drive Machinery and Brakes (a) (b) (c) (d) (e) 1 Elevators/Escalators drives, motors and gearboxes shall be designed to ensure quiet and smooth operation of the escalator star delta starting shall be provided for motors > 5 kW motor insulation Class F, protection class IP 55 operational brakes located between motor and gear boxes shall have an AC commercial magnets and shall use asbestos free brake linings. Double acting shoe brakes shall be fail safe and shall operate automatically via springs in the event of power failure or on safety switches tripping a hand winding devices shall be provided with machines in order to move step bands by hand Electronic Controllers (a) (b) (c) (d) protection class controller cabinet shall be IP 54 control voltages shall be < 50 V cabinets shall have an industrial enamel triple corrosion resistant coating with the following layers: phosphate layer primer coating, minimum 25 µm layer thickness final coating, colour RAL 5019 (blue), minimum 35 µm layer thickness, or as otherwise specified controllers shall be equipped with modular electronic boards. Mother boards shall cover all basic functions QCS 2010 Qatar Project Management (b) (c) 10 Part 20 Balustrades, decking and skirting (a) 9 Section 21 QCS 2010 (e) (f) 2 Part 20 Elevators/Escalators Page 11 interface capabilities shall be provided for remote monitoring by volt free contacts controllers shall include the following functions: directional settings supervision of power supply voltage full motor protection against overheating fault indicator by means of display control of safety contacts asymmetric relays Operation Panels (d) (e) (f) operation panels shall be installed at upper landings and at lower landings panels shall be located in steel panels next to handrail entry guards operational panels at the lower landings shall be equipped with key switches and stop buttons only operation panels at upper landings shall be equipped with key switches, key boards, displays and stop buttons displays shall have 8 digits, using 5 x 7 dot matrix for alpha numeric indicators with text shown in plain language after setting of passwords via the key board, displays shall show maintenance and fault finding information, including but not limited to: memory of faults (50 messages deep) e.g. amount of faults within a definite period of time operating hour counter (total and per week) start counter (total and per week) stopping distance and deceleration indicator Electrical Safety Devices (a) the escalator shall be equipped with all safety devices required by EN 115 including, but not limited to: (i) emergency stop buttons and key switches at landings (ii) handrail entry devices (iii) broken step chain devices (iv) comb plate safety devices (v) broken step and chain wheel control contacts (vi) step chain roller monitoring switches (vii) non reversal devices (electronic device, located in the controller) (viii) operational brakes (ix) motor thermal devices (x) sockets for manual inspection (xi) main and secondary circuit breakers (xii) earthing contacts (xiii) asymmetric relays (inside controllers) (xiv) hand lamps 20.3 INSTALLATION 20.3.1 Site Condition Inspection 1 Before the commencement of installation of equipment the hoistway and machine room areas shall be examined to verify that no irregularities exist that would effect the execution of the work, particularly: (a) (b) 2 the hoistway size, plumpness and wellway lengths the support areas for bracket and beams etc. Installation shall not commence until previous work conforms to Project requirements. QCS 2010 Qatar Project Management (a) (b) (c) 3 Section 21 QCS 2010 Section 21 Part 20 Elevators/Escalators 20.3.2 Preparatory Work 1 Legal Hoistways and Pit Enclosures. The following shall be provided: (a) (b) (c) 2 Machine Rooms. The following shall be provided: (a) (b) (c) (d) (e) (f) 3 clear plumb hoistway with variations not exceeding 25 mm at any point bevel cants (15 degrees from vertical) over any rear or side wall ledges or beams that project 50 mm or more into the hoistway provisions for guide rail bracket supports in concrete in place as required, with necessary supports provided by elevator installer as indicated on shop drawings walls and floors cut and patch as necessary blockouts or cutouts for push button stations, hall lanterns and position indicators front hoistway wall, erected after entrances have been installed pit ladders, cars and counterweight buffers, and rail load supports waterproof pits and 600 x 600 x 600 mm deep sump pit barriers at open hoistways and entrances during construction cars, entrances, and special metal finishes protected from damage after installation hoistways vented to outside air. facilities conforming to EN 81 and requirements of authorities having jurisdiction concrete on metal deck machine room floors fire-rated, self-closing, and lockable machine room access doors installed machine room ventilation machine room floor slab, smoke venting grates, dampers, and ducts installed machine room walls, ceiling and floor painted and monocoat beam fireproofing sealed to prevent flaking. Electrical Services. The following shall be provided: (a) (b) (c) (d) (e) pit and machine room lighting and convenience outlets in accordance with EN 81 conduits run from elevator hoistways to ground level control consoles. Sizes and locations as indicated on elevator installation drawings 415 V, 3-phase, 50 Hz main power feeders to terminals of each elevator controller unit, including protected lockable "OFF" disconnect switch (copper conductors to terminals) 240 V a.c., single-phase, 50 Hz, power feeders to each car controller available for lighting and exhaust blowers, including individual 20-amp circuit breakers at locations shown on elevator shop drawings suitable power feeders and branch wiring circuits as required to elevator control panels in machine rooms as designated by elevator installer. 20.3.3 Installation 1 The elevator installer shall supervise and co-ordinate the preparation of all shop drawings, the selection and furnishing of all materials included in the specifications, and the installer shall also install the cars. Installation work shall be to BS 7255. The elevator installer shall also be responsible for the supply and installation of the following: (a) (b) (c) (d) (e) (f) (g) 2 electrical controls and signal fixtures and wires complete conduit and wiring to lighting and ventilating fixtures, with temporary power and lighting as required headers, tracks and thresholds hangers and gibs on car doors and hang doors communications system as specified basic car construction of 1.2 mm steel, with vent slots in accordance with EN 81, and wall panels as specified exhaust blowers, isolated from steel canopies on rubber grommets. Each equipment item shall be installed in accordance with accepted manufacturer's directions, referenced codes and specifications, with clearances complying with the same. QCS 2010 Qatar Project Management (d) (e) (f) (g) (h) (i) (j) (k) Page 12 QCS 2010 Section 21 Part 20 Elevators/Escalators Page 13 3 Items shall be installed so that they may be removed by portable hoists or other means for maintenance and/or repair, and so that access for maintenance is safe and readily available, in accordance with BS 7255. 20.3.4 Field Quality Control 1 Inspection (a) (b) work at job sites will be checked during the course of installations. Full co-operation with inspections is mandatory corrective work required shall be accomplished prior to performing further installations dependent upon, or related to, required corrections. Acceptance. The Engineer’s and Employer’s acceptance inspections shall be performed, before acceptance of the works. Verification will be required that tests have been completed, corrective work accomplished and installation approved for issuance of a permit to operate. 20.3.5 Field Adjustments 1 Guide rails shall be aligned vertically within a tolerance of 1.5 mm in 30 m. Joints shall be secure without gaps and irregularities filed to a smooth surface. 2 Cars shall be balanced to equalise pressure of roller guide shoes on rails 3 Equipment shall be lubricated in accordance with manufacturer's instructions. 4 Motors, controller, levelling switches, stopping switches, door operators, interlocking, and safety devices shall be adjusted to achieve required performance levels. 20.3.6 Acceptance Inspection and Tests 1 Acceptance of installations shall be made only after all field quality control and tests are complete, all submittals and certificates have been received, and the Engineer is satisfied that the following have been satisfactorily completed. The Contractor shall supply, labour, materials and equipment necessary for tests: (a) (b) (c) (d) workmanship and equipment comply with specifications speed, capacity, and floor-to-floor performance comply with specifications performance of the following are satisfactory: (i) starting, accelerating, running (ii) decelerating, stopping accuracy, stopping (iii) door operation and closing pressure (iv) equipment noise levels. in all test conditions, speed and performance times specified shall be met, stopping accuracy shall be maintained without re-levelling, and general ride quality shall be acceptable to the Engineer. Temperature tests may also be required, at the Engineer’s discretion. 2 Should tests detect any defects or poor workmanship, or non-compliance with or variance from the specification requirements, the following work and/or repairs shall be completed at no expense to the Employer: (a) (b) (c) replace all equipment that does not meet specification requirements perform all work and supply all labour, materials, and equipment necessary to complete specified operation and/ or performance perform all retesting required by the authorities and the Engineer to verify specified operation and/ or performance. 20.3.7 Clean Up 1 Areas shall be kept orderly and free from debris during Project progress. QCS 2010 Qatar Project Management 2 QCS 2010 Section 21 Part 20 Elevators/Escalators Page 14 Loose materials and filings resulting from work on hoistway surfaces and truss interiors shall be removed. 3 The machine room equipment and floor shall be cleared of dirt, oil and grease. 4 Hoistways, cars, car enclosures, entrances, operating and signal fixtures, handrails, and trim shall be cleaned of dirt, grease, and finger marks. 20.3.8 Manufacturer's Services 1 The manufacturer's representative shall inspect the final installation and supervise initial operation. Manufacturer’s certificates shall be provided prior to field testing equipment. 2 The manufacturer's representative shall instruct and train plant personnel for at least one 8 hour day on proper operation and maintenance procedures. 20.3.9 Maintenance and Guarantees 1 The Contractor shall be responsible for the system maintenance and repair of any fault for a period of 400 days starting from the provisional handing over. During this period the Contractor shall replace and/or repair any fault with all spare parts without any cost to the Client. 2 The Contractor shall guarantee the system for a period of 400 days. During this period the Contractor shall clear any failure due to design problems or poor installation and workmanship. END OF PART QCS 2010 Qatar Project Management 2 QCS 2010 Section 21 Part 21 Lightning Protection Page 1 21. LIGHTNING PROTECTION ........................................................................... 2 21.1 GENERAL ...................................................................................................... 2 21.1.1 21.1.2 21.1.3 21.1.4 Scope References Quality Assurance Submittals 21.2 PRODUCTS ................................................................................................... 2 21.2.1 Materials 2 INSTALLATION ............................................................................................. 3 21.3.1 Installation 21.3.2 Testing QCS 2010 3 4 Qatar Project Management 21.3 2 2 2 2 QCS 2010 Section 21 Part 21 Lightning Protection 21. LIGHTNING PROTECTION 21.1 GENERAL 21.1.1 Scope 1 This Part specifies the requirements for lightening protection. 2 Related Parts and Section are as follows: General Provisions for Electrical Installation Conduit Cable Trays Cables and Small Wiring Trunking HV and MV Factory Built Assemblies (FBA’s) 21.1.2 References 1 The following standards are referred to in this Part: BS 6651 BS 7430 Code of practice for protection of structures against lightning. Code of practice for earthing 21.1.3 Quality Assurance 1 Design Criteria: (a) the lightning protection system shall be in accordance with QGEWC Rules and Regulations. 21.1.4 Submittals 1 Shop Drawing and product Data per Part 1. (a) (b) submit full technical details and conductor size calculations of each type of cable or wire proposed submit exact route of each cable or wire proposed. 21.2 PRODUCTS 21.2.1 Materials 1 Generally: (a) 2 products used in the lightning protection system shall be copper or an approved copper alloy, unless otherwise specified, and specifically manufactured for the purpose. Air Termination Conductors and Down Conductors: (a) (b) (c) lightning air terminals and down conductors for lightning air terminals shall be provided as indicated on the drawings. Where vertical air terminations are used, they shall be min of 15 mm diameter tinned copper (air termination rod) 0.8 meter long with top spike, unless otherwise specified in the Project Documentation generally, roof conductors and down conductors shall be of PVC sheathed 3 x 20 mm (minimum) copper tape. PVC colour to be approved by the Engineer. However, bare copper tape may be unless indicated otherwise on the Project Drawings or Specification air termination rods shall be securely anchored and welded QCS 2010 Qatar Project Management This Section Part 1 Part 7 Part 9 Part 6 Part 8 Part 2 Page 2 QCS 2010 (d) (e) (f) (g) (h) (i) (c) shall be of the earth rod type earth rod electrodes: 16 mm diameter steel core copper jacketed type, comprising a high strength steel alloy core with a molten welded copper covering, minimum 0.25 mm thick to be not less than 3.6 m long, in 1.2 m sections coupled by strong bronze couplers. shall connection of rod electrodes: bolted type. to comprise a bolted copper link fixed on porcelain insulators and complete with studs, nuts and washers to take the earth tape and a bolted lug adequately sized for the final connection of the earth electrode. Bolts, Washers And Nuts In Bolted Connections: (a) 8 25 x 3 mm tinned copper tape, unless otherwise indicated on the Project Drawings or Specification. Removable Earth Links: (a) 7 down conductors shall be run along the outer surface of the wall or column of the building down conductors shall be as short as possible, protected and directly connected to earthing system through test links (refer to item 7 below) anchoring bolts shall be used to hold roof conductors and down conductors in firm position lightning conductor connectors shall be provided for conductor splice connections and conductor terminal connections the connectors shall be heavy duty, cast metal and shall have hex-head screws in the bodies and holes in the tongues for bolts TV antenna, HVAC equipment, handrails and structures in the vicinity of the lightning protection system, if any, shall be bonded to the system by 3x20 sq. mm (minimum) PVC sheathed copper tape. Earth Connectors: (a) 6 high copper alloy or silicone bronze. Ferrous hardware is not acceptable. Earth Pit Cover (a) (b) (c) shall be of heavy duty construction shall have a recessed lifting hook shall have a brass plate, engraved “Electrical Earth Below”. 21.3 INSTALLATION 21.3.1 Installation 1 Removable Earth Links (a) (b) 2 Page 3 Earth Electrodes: (a) (b) 5 Lightning Protection Main Earth Loops: (a) 4 Part 21 fix in every main earth lead to enable the electrode system to be disconnected for testing install in an accessible position, above ground as close as possible to the earth electrode. Bolted Connections: (a) (b) multiple bolt type where bare copper is bolted in connections contact surfaces shall electroplated. QCS 2010 be silver Qatar Project Management 3 Section 21 QCS 2010 3 Page 4 where earthing terminal connections are to be brazed to equipment, thoroughly clean metal prior to brazing and repaint impaired surfaces to prevent corrosion. protect by: (i) painting with a moisture resistant bituminous paint or compound, or (ii) wrapping with protective tape to exclude moisture. Earth Rod Electrodes: (a) extensible rods of the same diameter shall be installed in holes drilled into the ground. If ground conditions permit, rods may be driven into the ground either manually or mechanically. The earth electrode shall be installed at such a depth that it penetrates the summer water table by a minimum of 2 metres. Under no circumstances shall lightning protection electrodes be connected to any QGEWC earthing electrode. A minimum distance of 7 metres shall be provided between any lightning earth electrode and a QGEWC earth electrode. weld earth connectors to the top of the rods, in sufficient number to make connection with all incoming cables. Earth Pit: (a) provide a concrete/PVC pit complete with a heavy duty concrete, cast iron or PVC cover with recessed lifting hook to the Engineers written approval, at the head of the earth rod, to protect the rod and allow access to connections for testing. 21.3.2 Testing 1 Testing earthing systems by the earth megger test. 2 The resistance of any one point in the lightning protection earth continuity system to the main earth electrode shall not exceed 10 ohms, unless allowed otherwise by QGEWC, without taking account of any bonding to other services. 3 Install additional earth electrodes in parallel, if these figures are not met. END OF PART QCS 2010 Qatar Project Management (b) 6 Lightning Protection Connections Between Dissimilar Metals: (a) 5 Part 21 Brazed Connections: (a) 4 Section 21 QCS 2010 Section 21 Part 22 Earthing and Bonding Page 1 22. EARTHING AND BONDING .......................................................................... 2 22.1 GENERAL ...................................................................................................... 2 22.1.1 22.1.2 22.1.3 22.1.4 Scope References Quality Assurance Submittals 22.2 PRODUCTS ................................................................................................... 2 22.2.1 Materials 2 INSTALLATION ............................................................................................. 3 22.3.1 Installation 22.3.2 Testing QCS 2010 3 5 Qatar Project Management 22.3 2 2 2 2 QCS 2010 Section 21 Part 22 Earthing and Bonding 22. EARTHING AND BONDING 22.1 GENERAL 22.1.1 Scope 1 This Part specifies the requirements for earthing and bonding. 2 Related Parts and Sections are as follows: 22.1.2 General Provisions for Electrical Installations HV and MV Factory Built Assemblies (FBA’s) Cables and Small Wiring Conduit Trunking Cable Trays References BS 7430 Code of practice for earthing 22.1.3 Quality Assurance 1 Design Criteria: the earthing system shall be in accordance with QGEWC Rules and Regulations. 22.1.4 Submittals 1 Shop Drawing and product data per Part 1. (a) (b) submit full technical details and conductor size calculations of each type of cable or wire proposed submit exact route of each cable or wire proposed. 22.2 PRODUCTS 22.2.1 Materials 1 Generally: (a) 2 products used in the earthing system shall be copper or an approved copper alloy, unless otherwise specified, and specifically manufactured for the purpose. Earth Continuity Conductors: (a) sizes shall be as specified by QGEWC, unless otherwise indicated, but in no case shall size be less than half that of the associated phase conductors (b) insulation shall be of the same material as insulation in associated sub-circuits. 3 Main Earth Loops: (a) 4 25 x 3 mm tinned copper tape, unless otherwise indicated. Rod Electrodes: (a) (b) (c) shall be of the earth rod type earth rod electrodes: 16 mm diameter steel core copper jacketed type, comprising a high strength steel alloy core with a molten welded copper covering to be 3.6 m long, in 1.2 m sections coupled by strong bronze couplers. QCS 2010 Qatar Project Management This Section Part 1 Part 2 Part 6 Part 7 Part 8 Part 9 Page 2 QCS 2010 5 connection of rod electrodes: shall be bolted type. to comprise a bolted copper link fixed on porcelain insulators and complete with studs, nuts and washers to take the earth tape and a bolted lug adequately sized for the final connection of the earth electrode. high copper alloy or silicone bronze. Ferrous hardware is not acceptable. shall be of heavy duty construction shall have a recessed lifting hook shall have a brass plate, engraved “Electrical Earth Below”. 22.3 INSTALLATION 22.3.1 Installation 1 Circuit Wiring (a) Main Earth Loops (a) (b) (c) (d) 3 (b) install and locate in a manner to provide maximum mechanical protection, utilising ceiling corners, suspended ceiling and webs of beams as much as possible. Bolted Connections: (a) (b) 6 fix in every main earth lead to enable the electrode system to be disconnected for testing install in an accessible position, above ground as close as possible to the earth electrode. Exposed Earth Cables (a) 5 fix in mechanical equipment rooms and other areas indicated on the drawings, in convenient locations, allowing two return paths to earth fix copper tape to structure with copper or brass saddles and/or screws. Make tees and straight joints by riveting and seating make branch connections between main loop and major equipment, such as switchboards, switchgears, motor control centres and large motors, with copper tape of same size as main loop tape make other branch connections to equipment with copper conductors of size not less than half that of the relative phase conductor. Removable Earth Links (a) 4 shall have a green/yellow coloured insulated earth continuity cable connecting the earth bus or earth terminal in switchboards, switchgears, motor control centres and panel boards to the motor, equipment, outlet and other device by earthing lugs. All hand rails and other metal works within 2 m of a potentially live metal surface shall be earthed. multiple bolt type where bare copper is bolted in connections contact surfaces shall electroplated. be silver Brazed Connections: (a) where earthing terminal connections are to be brazed to equipment, thoroughly clean QCS 2010 Qatar Project Management Earth Pit Cover (a) (b) (c) 2 Page 3 Bolts, Washers And Nuts In Bolted Connections: (a) 8 Earthing and Bonding Removable Earth Links: (a) 7 Part 22 Earth Connectors: (a) 6 Section 21 QCS 2010 Section 21 Part 22 Earthing and Bonding Page 4 metal prior to brazing and repaint impaired surfaces to prevent corrosion. 7 Connections Between Dissimilar Metals: (a) 8 Equipment Earthing: (a) (b) Fire Fighting Equipment: (a) 10 (b) (b) Connect steel armour to the earthing system. Earth Rod Electrodes: (a) (b) 16 connect the green/yellow coded earth busbar directly to the earth bus-bar in main switchboard with earth copper tape Cable Armour Earthing: (a) 15 connect an earthing conductor from the main distribution earth busbar to an earth connector welded to the cabinet and earthing bushings on the incoming and outgoing feeder conduits. Bus-Duct Feeders Earthing: (a) 14 connect the special earthing lug or busbars inside the cabinet to the main earth copper tape. connect all parts of the switchboards, switchgears and motor control centres other than “live” parts, to the earth bar in the board in an approved manner. Distribution Boards Earthing: (a) 13 connect the motor terminal box to the relative earth loop. The terminal must be mechanically connected to the frame or, where this is not feasible extend the earthing conductor through an insulated bushed opening in the connection box and connect to the frame. Main Switchboards, Switchgears and Motor Control Centres Earthing: (a) 12 earth on a separate ring system. Motors Earthing: (a) 11 connect all non-current carrying metallic parts of the electrical/mechanical installation to the earthing system non-current carrying metallic parts of the electrical installation include: (i) metal conduit, cable armour, raceways, outlet boxes, cabinets, and the like (ii) exposed metal parts of apparatus (iii) enclosures, doors, grills, barriers and the like protecting or shielding electrical equipment from direct access series earthing of one piece of equipment to another is not acceptable. Each item shall be individually connected to earth system extensible rods of the same diameter shall be installed in holes drilled into the ground. If ground conditions permit, rods may be driven into the ground either manually or mechanically. The earth electrode shall be installed at such a depth that it penetrates the summer water table by a minimum of 2 metres. bolt earth connectors to the top of the rods, in sufficient number to make connection with all incoming cables. Earth Pit: QCS 2010 Qatar Project Management (c) 9 protect by: (i) painting with a moisture resistant bituminous paint or compound, or (ii) wrapping with protective tape to exclude moisture. QCS 2010 (a) Section 21 Part 22 Earthing and Bonding Page 5 provide a concrete/PVC pit complete with a heavy duty concrete, cast iron or PVC cover with recessed lifting hook to the Engineers written approval, at the head of the earth rod, to protect the rod and allow access to connections for testing. 22.3.2 Testing 1 Testing earthing systems shall be done by the earth megger test. 2 The resistance of any point in the earth continuity system to the main earth electrode shall not exceed 1 ohm, unless approved otherwise by QGEWC. 3 Install additional earth electrodes if these figures are not met. QCS 2010 Qatar Project Management END OF PART QCS 2010 Section 21 Part 23 Inspection and Testing Page 1 23. INSPECTION AND TESTING ........................................................................ 2 23.1 GENERAL ...................................................................................................... 2 23.1.1 Inspection and Tests at Manufacturer's Place 23.1.2 Inspection and Tests at Site 2 2 ELECTRICAL INSTALLATION TESTING ...................................................... 3 23.2.1 23.2.2 23.2.3 23.2.4 23.2.5 23.2.6 23.2.7 23.2.8 23.2.9 General Verification of Polarity Earth Electrode Resistance Insulation Resistance Ring Circuit Continuity Phase Rotation Continuity of Protective Conductor Earth-fault Loop Impedance Operation Tests 23.3 ELECTRICAL EQUIPMENT TESTING .......................................................... 5 23.3.1 General 23.4 3 4 4 4 5 5 5 5 5 5 COMMISSIONING ......................................................................................... 6 23.4.1 General QCS 2010 6 Qatar Project Management 23.2 QCS 2010 Section 21 Part 23 Inspection and Testing Page 2 INSPECTION AND TESTING 23.1 GENERAL 23.1.1 Inspection and Tests at Manufacturer's Place 1 The Engineer shall be authorised to inspect, examine and test at any reasonable time and in the premises of the manufacturer, the quality of the material used for the equipment to be supplied. These work inspections shall include but not be limited to the following equipment, lighting fixtures, emergency power equipment, switchgears, switchboards, motor control centres, main and sub-main distribution boards. He shall also be authorised to verify the qualifications of the staff employed by the manufacturer. 2 Should part of the equipment be subcontracted to another manufacturer, the Contractor shall ensure that the Engineer is authorised to inspect, examine and test the equipment in the premises of the Sub-Contractor. 3 These inspections, examinations and tests shall not relieve the Contractor, in any case, from the contractual responsibility and commitments. 4 The Contractor shall notify the Engineer in writing at least 15 days beforehand of the date and place at which any equipment shall be available for the tests to be made according to the provisions of the contract. Should the Engineer not have appeared at the place indicated within 7 days following the date indicated by the Contractor, the later shall proceed with the tests and it shall be deemed that they have been witnessed by the Engineer. The Contractor shall send the Engineer duly certified copies of the results of the tests. 5 The Engineer shall notify the Contractor of his intentions to attend the test 24 hours beforehand. 6 Should the Contractor provide for tests to be made in the premises of the Contractor or any Sub-Contractors or suppliers, the Contractor shall afford any assistance, labour, materials, electricity, fuel supplies, equipment and instrument required and which can be reasonably requested for these tests. 23.1.2 Inspection and Tests at Site 1 This specification defines the tests to be made on electrical equipment, distribution systems and installations at site to establish compliance with the specification and to ensure they are entirely suitable for the intended purposes. 2 For all tests a minimum of 15 days notice in writing shall be given by the Contractor to the Engineer to enable the tests to be witnessed, if considered necessary. 3 All electrical tests, unless otherwise specified, shall be made either in a manner prescribed in the relevant: (a) (b) (c) (d) (e) British Standard Specification and Code of Practice IEE Regulation (latest edition) QGEWC regulation Civil Defence Department regulation or where no Standard/Code/Regulation exists, in a manner approved by the Engineer. 4 A pre-closing Inspection shall be carried out on all items of Electrical equipment, cables and conduit to be permanently concealed i.e. underground cables and ducts, conduit in screed or plastered into walls, above ceiling etc. 5 The Contractor shall provide the Engineer with 3 clear working days notice of his intention to cover the works. Failure to comply with this requirement shall result in the re-exposure. QCS 2010 Qatar Project Management 23. QCS 2010 Section 21 Part 23 Inspection and Testing Page 3 Engineer's inspection and re-exposure of the works being carried out shall be at the Contractor's expense. The inspection and tests specified herein do not supersede but are supplementary and complimentary to the tests called for in Project Specifications and clauses for equipment, systems and installation. 7 The Contractor shall supply all necessary instruments, apparatus, consumable stores, connection, skilled and unskilled labours and services with proper, reasonable and safe facilities required for the tests. Any costs which may be involved in the tests shall be included in the tender. The Contractor shall satisfy the Engineer that the instruments and the equipment to be used for any test are adequate as regards accuracy and calibration for the tests to be undertaken. 8 Workmanship shall be checked during work in progress and completed work inspections. Any work not to the satisfaction of the Engineer during such inspection shall be replaced to a standard approved by the Engineer at the Contractor’s expense, and prior to any subsequent inspection. 9 A complete written record shall be made by the Contractor of all inspections and tests. These records shall be made at the time of the tests and shall be countersigned by the Engineer, if present, as a true record. A copy of each record sheet shall be included with the operation and maintenance manual. Inspection or approval of tests, acceptance of test certificate and waiving of tests, by the Engineer, of any equipment, works or installation shall not relieve the Contractor from the obligation to supply the complete equipment and complete work and installations in accordance with the Project Specification and suitable for the purpose intended. 10 Certificates of tests shall contain or have attached to them, the following information:(a) (b) (c) (d) (e) (f) (g) (h) (i) the job name and number as designated by the Engineer the name, address and contract or order number of the Contractor a description of the item, component, equipment, system or installation tested including any fabrication, block or production number date and time of test environmental conditions including weather, if relevant the testing party (if other than the Contractor) and signature of the Engineer the properties to be tested and the source of the parameters for such properties, i.e. British Standard, Codes of Practice, QGEWC Regulation, Specifications, etc the results of the tests and any divergence from the specification, production drawings or statutory requirements the detail of any works to be completed but which is outside the scope of this test. The Engineer shall have discretion to waive inspection/testing for either any part or of the complete installation. 23.2 ELECTRICAL INSTALLATION TESTING 23.2.1 General 1 On completion of the entire electrical installation work or any separate or distinct part thereof, notify the Engineer, in writing, that the complete part of the electrical work is ready for inspection and testing. Before doing so, perform initial trial tests. Test, correct, adjust, balance, regulate, etc., the section concerned as necessary until required conditions are obtained. 2 The results and readings obtained for tests shall be equal or better than the requirements of the IEE and the QGEWC Regulations and these shall be recorded on Forms similar to the ones described in the IEE Regulations. The tests shall be carried out in a manner as described in these regulations. QCS 2010 Qatar Project Management 6 QCS 2010 Section 21 Part 23 Inspection and Testing Page 4 The Contractor shall supply all instruments and tools required for carrying out the tests. 4 In case the tests specified below are satisfactory and no errors or faults appear in the installation, submit the necessary test forms, duly filled out, to QGEWC to repeat, if necessary, the tests in the presence of QGEWC inspectors. 5 Upon Completion of testing, the Contractor shall follow-up and make all necessary arrangements with the QGEWC and Q-TEL for the purpose of providing permanent electricity supply and telephone services to the new facilities. Also provide all facilities and attendance to QGEWC for any other tests to be carried out before energising the installation. 6 The testing of the installations shall comprise of the following but not limited to:- 23.2.2 Verification of Polarity 1 Verification of polarity shall be made to ensure that all fuses and single pole control devices are connected only on the live phase conductor. The neutral must not be connected through any of these devices. 2 The centre contact of Edison type screw lamp holder shall be connected to the phase conductor, the outer threaded metal part shall be connected to the neutral conductor. 3 Wiring to plugs and socket outlets should be such that that they are connected with phase conductor on the right pole when viewed from the front. 4 A suitable type of testing device shall be used to confirm the above. 23.2.3 Earth Electrode Resistance 1 Upon installation of earth electrode, test shall be carried out to ensure that the installation of electrode has reduced the earth fault impedance effectively to the required value. 2 Resistance to earth of all earthing rods, each earth termination network, continuity of conductors and all bends and joints shall be tested by means of a Wenner test. The electrode resistance shall not exceed 8 ohms requirement or as specified in the QGEWC regulation. 23.2.4 Insulation Resistance 1 Insulation resistance test shall be carried out before a completed installation is permanently connected to the supply. Large installations may be divided into groups. A DC voltage not less than twice the normal supply voltage (RMS value of AC system voltage) shall be applied for the measurement of the insulation resistance. For low voltage installations, where apparatus voltage rating does not exceed 55 V, shall be tested applying 500 V DC only. 2 When measured with all fuse links in place, all switches (including, if possible, the main switch) closed, the insulation resistance for whole installation shall not be less than 1 meg ohm. 3 When measured between one phase conductor and other conductors connected together to earth, in turn for all phases, the insulation resistance shall be not less than 1 mega ohm. 4 Wherever possible, so that all parts of the wiring may be tested, all lamps shall be removed, all current using apparatus disconnected, all local switches shall be closed; where removal of lamps or disconnection of current using apparatus is not practicable, respective control switches shall be opened. QCS 2010 Qatar Project Management 3 QCS 2010 Section 21 Part 23 Inspection and Testing Page 5 5 Where apparatus is disconnected for the tests, the insulation between the enclosure or frameworks and all the live parts (phase) of the apparatus shall be measured separately and shall comply with the requirements as per BS for the corresponding apparatus, where such standard is not available, the insulation resistance shall not be less than 0.5 meg ohm. 23.2.5 Ring Circuit Continuity A test shall be carried out to verify the continuity of all conductors (including the earth continuity conductor) of every ring circuit and all readings shall be tabulated. 23.2.6 Phase Rotation The complete installation shall be tested to ensure that all distribution boards are connected to give correct phase rotation for the corresponding apparatus as required. Continuity of Protective Conductor 1 A test shall be carried out to verify that all protective conductors are connected correctly and are electrically sound, before power supply is connected to an installation. 2 When the protective conductor is a core in multi-core cable or a separate protective conductor, a DC ohmmeter may be used to measure the resistance. Where steel conduits or other metallic structure is used as protective conductor, the test shall be carried out by current injection at a voltage not exceeding 50 V AC or DC and current about 1.5 times the normal circuit current but not exceeding 25 Amps. When using DC source, it must be ensured that inductors are not connected in the test path. 3 A portable hand generator is preferable to use for this test so that the disconnected phase conductor can be connected to the consumer earth terminal and tests can be made between phase conductor and the protective conductor at each outlet point. 23.2.8 Earth-fault Loop Impedance Each completed installation shall be tested for effectiveness of the earthing by means of an earth fault loop impedance test. The test shall be carried out by using earth loop impedance test instrument 23.2.9 Operation Tests 1 This clause applies to relays, Interlocks and any other protective and control device, viz., residual current devices, to ensure correct functioning. 2 Suitable test pro forma shall be prepared, as per the recommendation of the manufacturer for protective relay tests and submit to the Engineer for approval. Logic diagram for control and interlocks shall be prepared, based on the requirement for functional tests, and shall be submitted to the Engineer for approval. Tests shall be carried out according to the approved form and all results shall be tabulated. 3 The RCDs shall be tested by external supply to check for instantaneous operation. The testing device shall be single phase double wound continuously variable type transformer (variac) with maximum output voltage 50 V and loading resistors to control current. While rated current applied, the device shall operate instantaneously or within a time delay as per manufacturer data sheet. The test current to be applied shall be as per manufacturer recommendation. 23.3 ELECTRICAL EQUIPMENT TESTING 23.3.1 General 1 The Contractor shall fully test and commission the whole of electrical installation in accordance with QGEWC and IEE regulations, as per requirements of the Project Documentation and as outlined in this section. QCS 2010 Qatar Project Management 23.2.7 QCS 2010 2 Part 23 Inspection and Testing Page 6 The following equipment will be inspected and tested on site after installation. Any omission or defects, or faults raised by the Engineer are to be remedied or corrected by the Contractor and re-testing made at the direction of the Engineer at the Contractor’s expense: (a) (b) (c) (d) (e) (f) (g) (h) (i) (j) 415V switchgear mains cable motors starters and control gear control and starter panels small wiring etc. elevator, walkway system radio and TV interference fire alarm and detection system public address system Following functional tests shall be carried out to ensure proper functioning of the plant and all apparatus. (a) (b) (c) (d) all protective circuits, interlocks, control and alarm shall be tested for correct operation all lighting circuits shall be energised and checked to ensure that they are operational all motors, plants and electrical equipment connected with mechanical services shall be checked to ensure that they run freely in the correct direction/rotation and in correct sequence fire alarm system, elevator system and building management system (if applicable) shall be tested for correct operation. 4 The testing requirements and procedures for the various items of electrical equipment is specified in the other relevant specification parts for electrical works and relevant standards. 23.4 COMMISSIONING 23.4.1 General 1 This specification deals with the Contractor’s work involved in commissioning to energise the electrical distribution systems, installations and plants after inspections and tests to ensure safety and proper operation; and the evaluation of performance by means of further inspection and tests to ensure the works operate in conformity with the design specification. 2 Commissioning works shall be carried out by the Contractor using trained, experienced commissioning engineers. The commissioning engineer shall perform switching operations and also must be in charge for the opening and closing of circuits, interlocks and safety devices. 3 The Contractor in conjunction with the Engineer shall prepare a commissioning schedule. This shall show a time scale and the extent of power or other services requirements for setting the plant to work. The following information shall be made available to the Engineer: (a) (b) (c) (d) 4 Specification of work Test certificates from works test at manufacturers Test results from site progress tests. Notes from pre-commissioning meetings. The method statement shall be submitted to the Engineer and get it approved at least 1 month before the commencement of commissioning tests. QCS 2010 Qatar Project Management 3 Section 21 QCS 2010 5 Section 21 Part 23 Inspection and Testing Page 7 After commissioning, the plant shall operate for the guarantee period as per the requirements of the Project Documentation, from the date of practical completion certificate issue in accordance with normal requirements without defect of any kind. Any defect which appears shall be remedied forthwith by the Contractor without any cost to the contract and reliability run shall start after re-commissioning. The guarantee period shall be calculated from the latest date of such re-commissioning. END OF PART Qatar Project Management QCS 2010 QCS 2010 Section 21 Part 24 Documentation Format Page 1 24. DOCUMENTATION FORMAT ....................................................................... 2 24.1 GENERAL ...................................................................................................... 2 QCS 2010 2 2 2 2 2 2 3 3 3 3 4 5 Qatar Project Management 24.1.1 Scope 24.1.2 General Requirements 24.1.3 Document format 24.1.4 Time Scale 24.1.5 Approval 24.1.6 Record Drawings 24.1.7 As-Built Drawings 24.1.8 Scales 24.1.9 Scale Bar 24.1.10 Presentation of Drawings 24.1.11 Manuals 24.1.12 Instrumentation Documentation QCS 2010 Section 21 Part 24 Documentation Format Page 2 24. DOCUMENTATION FORMAT 24.1 GENERAL 24.1.1 Scope 1 This Part specifies the general requirements and standards required for the compilation of paper and electronic documents. 2 Related Parts and Sections are as follows: 24.1.2 General Requirements 1 Documents will be presented both electronically and on paper. Documents from an electronic source shall, when printed, conform to the requirements for documents presented on paper. The number of hardcopy manuals shall be determined by the contract documentation. 2 The final approved documentation shall be reproducible in the following sizes. These sizes are defined to ensure that the provided documentation can be easily read and understood. (a) (b) (c) A4 size paper for manuals A3 size for system diagrams A1 size for instrument location and plant drawings 24.1.3 Document format 1 Drawings shall be compiled in AutoCAD DWG or Microstation DGN file format or similar approved with Engineer. Word processed documentation should be presented in Adobe Acrobat PDF format or similar approved with Engineer. Scanned copies of the „as built’ drawings showing all of the required approval signatures and official stamps shall be provided in TIFF format. The files should be presented on optical disc containing a readme.txt file containing an index of the disk. 24.1.4 Time Scale 1 The time scale for delivery of manuals shall be as stated in the contract documentation, with the final versions of the manuals being available before hand over. 24.1.5 Approval 1 During the construction phase of the project, the drawing and manuals status shall be monitored and discussed. These discussions form part of the project meetings / site meetings and are part of the approval process. All documents shall be approved prior to hand over. 24.1.6 Record Drawings 1 This specification defines the production of drawings so they are provided in a consistent way that shall make the drawings easy to use. This section refers to record drawings that relate to the as built product. Documents from an electronic source shall, when printed, conform to the requirements for documents presented on paper. QCS 2010 Qatar Project Management Section 1 Part 7 Section 1 Part 21 Section 21 Part 1 Section 21 Part 23 QCS 2010 Section 21 Part 24 Documentation Format Page 3 As-Built Drawings 1 Drawings produced by suppliers/Vendors shall be of appropriate size as below. Documents from an electronic source shall, when printed, conform to the requirements for documents presented on paper. 2 Drawing information shall be handed over in 'As Constructed’ form and marked-up accordingly in the information panel. 24.1.8 Scales 1 As few scales as possible shall be used and each scale used shall be recorded in the title panel. The scale shall be large enough to permit easy and clear interpretation of the information and ensure clarity of prints of all sizes reproduced. The recommended scales are listed in Table 24.1. Table 24.1 Scale Recommendations Category Enlargement Scale Full Size Reduction Scale Recommended ratios of scale 50:1 20:1 5:1 2:1 1:2 1:20 1:200 1:2000 1:5 1:50 1:500 1:5000 10:1 1:1 1:10 1:100 1:1000 1:10000 24.1.9 Scale Bar 1 The original scale shall be indicated by means of a relevant numbered scale bar. A warning against scaling the drawing shall be given. 24.1.10 Presentation of Drawings 1 Title panel and information panel shall contain the following information:(a) (b) (c) (d) (e) (f) (g) (h) (i) (j) (k) (l) (m) (n) (o) (p) client contractor supervisory consultant designer/manufacturer project title name of site/s name and type of installation/s drawing title/description sheet number in the series drawing status identity of persons carrying out the draughting and checking date of drawing drawing scale/s drawing no. with provision for revision suffix (Year/Contract/Number/ /Revision) contents of information panel The nature and date of each revision and the identification of the person approving it shall be recorded in the information panel, starting next to the title panel. General notes shall commence at the opposite end of the information panel 2 All text and drawings shall be in black unless otherwise stated. 3 Amendment of Drawings QCS 2010 Qatar Project Management 24.1.7 QCS 2010 (a) (b) 4 Section 21 Part 24 Documentation Format Page 4 After receipt by the Client of (draft) 'As Constructed' drawings, the Contractor shall notify the Client of any changes by re-issuing a complete draft, with further revision suffix to title and information panel. Each section shall clearly indicate the status of the information in the form of amendment notes. Electrical Schematics (a) (b) Electrical schematics shall be complete with cross references for all contact elements of all components used. The legend for naming and symbols used shall be clearly displayed on the drawing. 24.1.11 Manuals A contents page shall be provided for each Volume listing the contents of that particular Volume. It shall be entitled “Contents of Volume No XXX”. Where there are two or more volumes to a manual then there shall be a complete index to the set of volumes with each Volume. 2 The manual(s) shall be formed containing operational information in the first part of the manual and maintenance information in the latter part. 3 The manual shall be split into the following sections: (a) (b) (c) (d) (e) (f) Section 1.0 - Introduction (i) The introduction shall describe the purpose of the operating manual. This shall include how to start up and shut down the installation and/or process and/or plant as appropriate and maintain it at its optimum performance. The following details shall be included in the body of the manual. Section 2.0 - Technical Description (i) process descriptions (ii) plant description (iii) schedule of equipment commencing with a complete data sheet specific to the equipment used detailing Make, Type or Model No.. Rating, Order No., Quantity used etc. Section 3.0 - Safety (i) safety precautions (ii) hazardous area zoning (iii) confined spaces (iv) emergency procedures (v) site security description (vi) warning labels, etc Section 4.0 - Operating Information (i) plant settings (ii) operating procedure (iii) start up/shut down/power failure (iv) routine check procedure (v) replacement of consumable items Section 5.0 - Control Philosophy Functional Design Specification (FDS) to include the following as minimum:(i) description of mechanical plant (ii) description of electrical plant (iii) description of instrumentation, control and field devices (iv) process & instrumentation diagrams (P&ID's) (v) plant start up sequence for both manual and automatic mode (vi) plant shut down sequence for both manual and automatic mode (vii) power fail and restart sequences (viii) normal process sequences Section 6.0 - Maintenance Instructions including:(i) safety precautions (ii) routine maintenance schedules QCS 2010 Qatar Project Management 1 QCS 2010 (g) (h) Section 21 Part 24 Documentation Format Page 5 24.1.12 Instrumentation Documentation 1 The instrumentation documentation shall be according to the following specification. (a) (b) (c) For the instrumentation the contractor shall supply the following information: (i) instrument loop diagrams (ii) manufactures literature (iii) certificate of calibration (iv) certificate of conformity RTU Documentation For the RTU system, the contractor shall supply the following information: (i) RTU I/O schedules (ii) GA and wiring diagram (iii) isagraph program (disk) (iv) RTU configuration (disk) (v) RTU user manual (vi) RTU programming software user manual (vii) licensed and latest version of the programming software original with all end user license agreements. PLC Documentation For the PLC system, the contractor shall supply the following information:(i) system architecture drawing (ii) rack layouts (iii) PLC I/O schedules (printed sheet + Excel format disc) (iv) PLC memory map (v) PLC hardware listing (vi) annotated PLC ladder logic (printed sheet + disc) (viii) PLC user manual (ix) PLC programming software user manual (x) licensed and latest version of the PLC programming software original with all end user license agreements. QCS 2010 Qatar Project Management (iii) spare parts listing and agreed spares list (iv) lubrication (v) plant strip down/assembly (vi) fault finding instructions Section 7.0 - Suppliers (i) Supplier’s/Vendor’s names, contact person and his title, addresses and telephone numbers, email etc. Section 8.0 - Drawings and Records (i) plant drawings (ii) electrical diagrams (iii) cable schedules (iv) valve schedules (v) instrument loop diagram (vi) vendor manuals (original manuals only-photocopies shall not be acceptable) (vii) vendor test certificates (viii) instrumentation loop test certificates (ix) plant description forms (x) hazardous area zoning drawings (xi) a general description of each plant and how it operates, shall be included at the beginning of each of the M&E sections. The description shall explain the function of the equipment. It shall be sufficiently detailed to enable the reader to understand how the works operates before using the operating instructions. (xii) a complete set of data sheets providing specific details of the equipment used with Order No., Serial No., and specific technical details etc. If a comprehensive spare parts list is not attached to the individual equipment catalogue section, the same shall be compiled by the Contractor and attached to this section. (xiii) a complete list of all components used for Order No., Motor Control Centres detailing Make, Model No., Rating, Quantity used etc. QCS 2010 (d) (e) Section 21 Part 24 Documentation Format Page 6 END OF PART QCS 2010 Qatar Project Management HMI Documentation For the Man Machine Interfaces, the contractor shall supply the following information: (i) system architecture drawing (ii) graphic copy and description of all mimics (iii) description of all trends (iv) alarm handling and schedules (v) operator control functions (vi) HMI database listing with disc, if applicable SCADA Documentation For the SCADA system, the contractor shall supply the following information: (i) system architecture drawing (ii) software user manuals (iii) SCADA database listing and discs (iv) alarm handling and schedules (v) description of all trends (vi) graphic copy and description of all mimics (vii) database point allocation table (disk (viii) application software source code (ix) SCADA latest version of the programming software and IO Drivers with all end user license agreements. QCS 2010 Section 21 Part 25 Electrical Identification Page 1 25. ELECTRICAL IDENTIFICATIONS ................................................................. 2 25.1 GENERAL ...................................................................................................... 2 25.1.1 25.1.2 25.1.3 25.1.3 25.1.4 25.1.5 General Nameplates and Labels Wire and Cable Markers Interconnecting Cabling Identification “ICA” Under ground Warning Tape Installation 2 2 3 3 3 3 Qatar Project Management QCS 2010 QCS 2010 Section 21 Part 25 Electrical Identification Page 2 ELECTRICAL IDENTIFICATIONS 25.1 GENERAL 25.1.1 General 1 Provide identification on all equipment e.g. control panels, FBA, controllers, raceways, boxes and conductors, devices etc in accordance with BS 61346, BS 61666, BS 61175 and BS 60445 standards or latest edition of other applicable standards to the approval of engineer. 2 All labels shall be permanent, and be machine generated. NO HANDWRITTEN OR NONPERMANENT LABELS SHALL BE ALLOWED. 3 Prior to making any label or nameplate for the purpose of identification submit a detailed schedule indicating nameplate size, lettering size, color, material and actual nameplate information for Engineer's review and approval. 4 All external labels, nameplates, operational and warning signs shall be provided in Arabic and English. 5 Material used in making the engraved labels shall be of highest quality suitable for the environmental and climatic conditions as specified in the relevant section. 6 Critical devices such as disconnect switches; service feeders and branch circuit protective feeders shall be legibly labeled to indicate its purpose and point of origin. The legibility distance shall not be less than 2.0 meters. 7 Identification nameplates shall be provided in addition to the manufacturer's equipment nameplates as required by NEMA, BS, IEC or UL. 8 Warning signs and instruction labels wherever needed shall be provided in accordance with local regulations of QGEWC, Civil defence etc. 9 Contractor shall clearly show locations and fixing arrangements of nameplates and labels on layout drawings. 25.1.2 Nameplates and Labels 1 Nameplates: (i) Provide equipment identification labels for all electrical equipment including, but not limited to Switchgear, control panels, switchboards, transfer switches, disconnect switches, transformers, generators, power factor capacitors, fixed equipment, motor starters, FBA etc. (ii) Provided sub classification label for all emergency power system, junction boxes and pull boxes. (iii) External labels: Clear Perspex, back engraved in black letters on white background, in Arabic and English with chamfered edges fixed with stainless steel screws with nuts and flat and lock washers. (iv) Internal labels: Multi-layered plastic to an approved design engraved in Arabic and English, and fixed with stainless steel screws. Alternatively special purpose made DIN rail may be used for fixing labels as approved by the engineer. (v) Adhesive labels shall not be permitted. (vi) Internal components labels shall have circuit designations correlated with the drawings. (vii) Labels shall not be attached to trunking covers or other readily removable items. (viii) Electrical equipment enclosures, vaults, doors and fences shall be provided with "DANGER KEEP OUT" warning sign, showing proper voltage. (ix) Disconnect switches and emergency devices shall have "CAUTION" warning signs as directed by the engineer. QCS 2010 Qatar Project Management 25. QCS 2010 Section 21 Part 25 Electrical Identification Page 3 Locations: (i) Provide Title Label for electrical distribution and all other control equipment, panels etc. (ii) Provide Function Label for door mounted component. (iii) Every internal component - Identification Label. (iv) Provide Identification Label for Protective device - (e.g. fuse/mcb type, rating). (v) Provide Title Label for Communication equipments. (vi) Compartments with doors and covers not electrically interlocked to an isolator, external label - “DANGER, LIVE TERMINALS” with flash and voltage in red letters on white background in Arabic and English. (vii) Provide Function description Label for group of terminal blocks. 3 Letter Size is to be approved with Engineer. 25.1.3 Wire and Cable Markers 1 Description: Interlocking ferrules of white insulating material engraved in black. Letters and symbols to IEC 446 shall be used for control wiring and Flameproof Cable tags for appropriate cable group. 2 Locations: (i) Conductor at pull boxes outlet, junction boxes and each load connection. (ii) Cable laid in trenches, duct, raceways etc. 3 Legend: (i) Power and Lighting Circuits: Branch circuit or feeder number indicated on drawings. (ii) Control Circuits: Control wire number indicated on schematic and interconnection diagrams on drawings. 25.1.3 Interconnecting Cabling Identification “ICA” 1 Each horizontal cable from instruments, transmitter, controller etc. termination blocks or patch panel if any to an outlet box shall be labelled at both ends. 2 Tags shall be consecutively numbered so that no two (2) cables have the same identification number. 3 In addition the cable tag shall indicate the reference of location where the associated outlet is located and the device is installed. 25.1.4 Under ground Warning Tape 1 Description: 100 mm wide plastic tape, detectable type, coloured yellow with suitable warning legend describing buried electrical lines e.g. 0.6/1KV, 11KV etc. 25.1.5 Installation 1 Degrease and clean surfaces to receive nameplates and labels. 2 Install nameplate and label parallel to equipment lines. 3 Secure nameplate to equipment front as specified. 4 Secure nameplate to inside surface of door on panelboard that is recessed in finished locations. 5 Identify underground conduits using underground warning tape. Install one tape per trench at 150 mm below finished grade. END OF PART QCS 2010 Qatar Project Management 2 QCS 2010 Section 21 Part 26 Electromagnetic Compatibility Page 1 26. ELECTROMAGNETIC COMPATIBILITY ....................................................... 2 26.1 REGULATIONS ............................................................................................. 2 26.1.1 26.1.3 26.1.4 26.1.5 26.1.6 26.1.7 General The CE Marking EMC Directive and Standards EU Product Directives Harmonized European Standards CE Marking Vs ISO 9000 26.2 Recommendations for reducing interference ................................................. 4 2 2 2 3 3 3 Qatar Project Management QCS 2010 QCS 2010 Section 21 Part 26 Electromagnetic Compatibility Page 2 26. ELECTROMAGNETIC COMPATIBILITY REGULATIONS 26.1.1 General 1 Ensuring electrical components, equipment and systems supplied are safe and does not interfere with the normal operation of other equipment is the basis for Electromagnetic Compatibility regulation. 2 Low Voltage Directive 73/23/EEC; shall apply to electrical equipment designed for use at a rated voltage of 50 to 1000 V for alternating current and 75 to 1500 V for direct current. Rated voltage shall refer to the input or output voltage of the equipment and not voltages which are generated internally. 3 The electrotechnical product shall also meet the requirements of other applicable directives in addition to the Low Voltage Directives. The compliance of individual components with the requirements of appropriate European Norms (EN) does not imply compliance of the end product. End product testing ensures that interconnections as well as manufactured CE marked components are performing to what is formally stated in their declaration of conformity. 26.1.2 EMC: Electromagnetic Compatibility 1 EMC is the ability of different items of electrical equipment to work together without suffering the effects of interference. All equipment shall operate without interfering with broadcast and communications signals and be immune to normal levels of such signals. 2 EMC implies that equipment shall not generate unacceptable levels of interference, which affect the performance of other products designed to operate in the same environment. Also, equipment shall have sufficient immunity to electrical interference, such that the equipment continues to operate in an acceptable manner. 3 The contractor shall submit a certificate issued by the manufacturer that the electrical equipment's supplied against the contract under execution complies with the requirements of the EMC Directive. 26.1.3 The CE Marking 1 All electrical products shall have CE Marking as an EU recognised certification mark that confirms the product has been tested and complies with the European Union Electromagnetic Compatibility Directive and other relevant directives, standards or norms. 26.1.4 EMC Directive and Standards 1 The electrotechnical products shall be designed and constructed that do not cause excessive electromagnetic interference and are not duly affected by electromagnetic interference. Electrical products shall carry a CE mark and manufacturers 'Declaration of Conformity'. 2 There are four generic standards: (a) (b) (c) (d) EN 50081-1 1992 EMC - Generic emission standard - Part 1. Residential commercial and light industry. EN 50081-2 1993 EMC - Generic emission standard - Part 2. Industrial environment. EN 50082-1 1997 EMC - Generic immunity standard - Part 1. Residential commercial and light industry. EN 61000-6-2 1999 EMC - Part 6-2: Generic standards - Immunity for Industrial Environments. QCS 2010 Qatar Project Management 26.1 QCS 2010 Section 21 Part 26 Electromagnetic Compatibility Page 3 26.1.5 EU Product Directives 1 The EU product directives deal with large families of products or horizontal risks such as those addressed in the Electromagnetic Compatibility Directive. The manufacturer and exporter are responsible for ensuring the product meets the requirements for all applicable directives. 2 The following directives (with the reference between brackets) have been adopted: low voltage (73/23/EEC) simple pressure vessels (87/404/EEC) safety of toys (87/378/EEC) construction products (89/106/EEC) electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) (89/336/EEC) machine safety (89/392/EEC) personal protection equipment (89/686/EEC) new hot-water boilers (92/42/EEC) gas appliances (90/396/EEC) explosives for civil uses (93/15/EEC) recreational craft (94/25/EC) non-automatic weighing machines (90/384/EEC) active implantable medical devices (90/385/EEC) equipment for explosive atmospheres (94/9/EEC) telecommunications terminal equipment (91/263/EEC) 3 Most of the above-mentioned directives are amended by Directive 93/68/EEC, "Rules for the Affixing and Use of the CE Conformity Marking." 26.1.6 Harmonized European Standards 1 EU product directives are limited to essential safety, health or other performance requirements in the general public interest. The technical details of how to meet these requirements are to be certified by the three regional European standards organisations, CEN, CENELEC, ETSI, and government appointed product certification bodies. 2 Products that meet the essential technical standards developed by CEN, CENELEC and ETSI are presumed to conform to the requirements of EU directives 3 For many products, however, a manufacturer can choose not to comply with CEN, CENELEC, ETSI standards, but must then demonstrate that the product meets the essential safety and performance requirements of the directives. 26.1.7 CE Marking Vs ISO 9000 1 Manufacturer having a quality management certificate that demonstrates an efficient organisational confirming low failure rate shall not be acceptable as a substitute to CE marking. 2 The quality system makes no reference to the quality of the product. The quality certificate is only a recommendation for customers that their order will be processed correctly and on time. 3 The CE marking indicates that the product complies with the essential requirements relating to safety, health, environment and consumer protection of the user. 4 Some directives explicitly make use of a quality management system (ISO 9000) as part of the conformity assessment. If a manufacturer wishes to provide the customer with assurance about the functional quality of the product, the manufacturer can then obtain a voluntary QCS 2010 Qatar Project Management (a) (b) (c) (d) (e) (f) (g) (h) (i) (j) (k) (l) (m) (n) (o) QCS 2010 Section 21 Part 26 Electromagnetic Compatibility Page 4 quality inspection mark that guarantees the products conform to safety and functional requirements over the long term. 26.2 Recommendations for reducing interference 1 The contractor shall exercise the manufacturer's recommendation for reducing interference. Following is basic guidelines for ready reference that helps reduce radiated interference by screening of the equipment and cables. The conducted interference can be reduced by filtering of the mains supply. (a) (b) END OF PART QCS 2010 Qatar Project Management (c) (d) (e) (f) (g) keep all cables as short as possible separate power cables and signal cables from each other and from different equipment shield the mains cable to the welding equipment if any apply earthing and equipotential bonding to the welding installation connect the equipment to a separate mains supply spur or using a different phase physically separate welding equipment from other equipment weld at times, which cause minimum disruption. QCS 2010 Section 21 Part 27 Battery and Battery Charger Page 1 27.1 GENERAL ...................................................................................................... 2 27.1.1 27.1.2 27.1.3 27.1.4 Scope Description References Submissions 27.2 PRODUCTS ................................................................................................... 2 27.2.1 General 27.2.2 Batteries 27.2.3 Battery Chargers QUALITY CONTROL AND TEST PROCEDURES ........................................ 4 27.3.1 General 27.4 2 3 3 4 ENVIRONMENT ............................................................................................ 5 27.4.1 General QCS 2010 5 Qatar Project Management 27.3 2 2 2 2 QCS 2010 Section 21 Part 27 Battery and Battery Charger 27. BATTERY AND BATTERY CHARGER 27.1 GENERAL 27.1.1 Scope 1 This Part specifies the requirements for battery and battery charger. 2 Related Parts and Sections are as follows: This Section Cables and small wiring Conduits Trunking Cable Trays Accessories and General Power 27.1.2 Description 1 A single battery and battery charger shall be provided for each FBA of motor control centre, control desk or control panel. 27.1.3 References 1 The following Standards are referred to in this Part: EIC 157 Low Voltage Switchgear and Control gear EIC 158 Low Voltage Control gear 27.1.4 Submissions 1 Submissions shall be in accordance with Part 1 of this Section and Part 7 of Section 1. 2 Shop Drawings submission shall include dimensional drawings of the battery and battery charger, including sections and elevations, showing the following: (a) (b) (c) (d) 3 sizes and positions of components positions and method of fixing cable and boxes location of terminal boards other pertinent data. Submission of project data shall be as follows: (a) (b) full specifications of the enclosure and the components of the equipment with relevant sheets of manufacturer’s catalogues confirmation that the equipment complies with the relevant specifications. 27.2 PRODUCTS 27.2.1 General 1 The batteries and chargers shall be used as back-up power source for uninterruptible and bumpless operation of controls, instrumentation, alarm and monitoring equipment, but not for switchgear tripping/closing or other special function batteries. 2 Where alternate a.c. supplies are available, provide for taking the supply to the battery charger from either source (e.g. from either side of the bus-section switch) with facilities for automatic changeover from one source to the other in the event of failure of the supply system. QCS 2010 Qatar Project Management Part 6 Part 7 Part 8 Part 9 Part 10 Page 2 QCS 2010 Section 21 Part 27 Battery and Battery Charger Page 3 The battery and charger unit shall be housed in the common control section of the MCC provided that the battery is of the sealed type and shall not release any corrosive media. If the battery is not sealed it shall be mounted in a separate compartment. 4 A separate sheet steel floor standing cubicle having adequate ventilation and separate compartments for the batteries (lower compartment) and chargers (upper compartment) with associated control and protection devices and accessories may be used as a stand-alone unit for large capacities where it is difficult to accommodate within a dedicated section of the MCC and in case of all other applications wherever specified. 5 When used as a stand-alone unit, the access to the batteries shall be via lockable, hinged doors, and to the chargers via removable covers. 6 Batteries and charger units shall be suitable for the intended service under the prevailing climate and environments conditions and Tropical use. 7 Unless specified elsewhere the, the battery charger shall confirm to the specification herein. 8 Form 4 panels when equipped with battery and charger shall be provided with fully segregated/shrouded arrangement for the batteries within the cubicle, ensuring proper ventilation. Alternatively batteries may be located in a separate enclosure installed within the close proximity of the control panel. 27.2.2 Batteries 1 Nickel Cadmium sealed batteries shall be used confirming to BS EN 60623. 2 The batteries shall be maintenance free long life Nickel Cadmium sealed type with a nominal output of 24 volts, and shall be of adequate capacity to maintain full operation of the relevant load equipment’s’ plus an additional 20 per cent, for a period of 8 hours during mains failure, assuming a normal charge condition at the start of the mains failure. 3 All batteries shall be protected from mechanical damage and any accidental electric shorting. All batteries shall be supplied in banks sized for easy handling, and all interconnections shall be included. Batteries shall not be housed above charger units or any other equipment and shall be so ventilated that gases do not permeate into adjacent equipment. 27.2.3 Battery Chargers 1 Battery Chargers shall confirm to BS EN 60146-1. 2 Battery chargers complete with associated controls shall be provided and mounted on its own chassis and housed in one of the section of the FBA, stand-alone panel or in a separate enclosure as applicable. (a) The front panel for each charger unit shall include:1 No. “ON/OFF” Mains switch 1 No. Lamp to indicate “A.C. Supply On” (white) 1 No. Charger Ammeter 1 No. Lamp to indicate “Boost Charge” (Red) 1 No. Lamp to indicate “Float Charge” (White) 1 No. Lamp to indicate “Charger Failed” (Amber) 1 No. Lamp test push button (b) Each charger unit shall also be provided with:1 No. “Float/Boost” selector switch, mounted internally 1 No. Set of a.c. supply fuses 1 No. volt-free contact for charger failed alarm 1 No. volt-free contact for low d.c. output voltage alarm QCS 2010 Qatar Project Management 3 QCS 2010 Section 21 Part 27 Battery and Battery Charger Page 4 1 No. volt free contact for loss of d.c. output voltage alarm 3 The chargers shall protect the batteries from deep discharge and over charging. 4 Volt free contacts shall operate in fail-safe mode and be wired to terminal block. 5 The Charger unit shall also be equipped with the following:1 No. DC output voltmeter, scaled to indicate regions of “Low”, “Normal” and “High” output voltages, by the use of different colored sectors. 1 No. D.C. output switch 1 No. D.C. output Ammeter The charger unit shall also be provided with one set of full capacity rated output d.c. terminals and fuses. 7 In the event of failure of the charger, the batteries shall ensure operation of controls, instrumentation, alarm and monitoring equipment for at least 6 hours. A separate relay contact shall be provided to indicate “Critical Alarm Condition – Charger Fail". 8 The chargers shall be of the constant potential type, and shall be designed to regulate the charger output voltage to within +/- 1 percent. 9 A suitable means shall be provided to the approval of Engineer to protect the batteries from deep discharge. 10 The D.C. terminal voltage shall be regulated such that under “Float” or “Boost” charge condition the DC voltage does not rise to more than 10 percent above the nominal. 11 The charger unit shall also be provided with both short circuit and reverse polarity functions. 12 The charger when selected to “Float” shall be capable of restoring the battery to 75 percent capacity within 7 - 8 hours. 13 Under “Boost” condition the charger shall be capable of restoring a fully discharged battery to 75 percent capacity within 4 - 5 hours. 14 Fix inside the cubicle a wiring diagram indicating and identifying all outgoing terminals, components and fuses, and also a warning label in Arabic and English giving maintenance and safety instructions. 27.3 QUALITY CONTROL AND TEST PROCEDURES 27.3.1 General 1 The manufacturer shall provide proof of a stringent Quality Control Program or Inspection Test Plan (ITP). In particular the main equipment manufacturing stages sanctioned by appropriate tests such as: incoming components inspection, discrete sub-assembly tests and complete functional checks on the final product. Equipment shall undergo on-load burn-in leaving the factory. Final inspection and calibration operations shall be documented in a report drawn up by the supplier’s Quality Inspection department and/or qualified Third Party Agency (TPA). 2 Complete charge and discharge tests on each battery and combined battery and charger shall be conducted and results recorded so as to permit verification of the ampere-hour capacity of the battery. During these tests five reference cells shall be selected at random and the voltage curves thereof shall be checked when the battery is discharged over three and ten hour periods. The automatic control feature of the charger shall be demonstrated over the specified load range. QCS 2010 Qatar Project Management 6 QCS 2010 Section 21 Part 27 Battery and Battery Charger Page 5 The integrated functional test shall be conducted at manufacturer’s works to ensure satisfactorily functioning of the equipment. 4 The Assembly shall not leave the manufacturer’s works until the works test sheets have been duly approved and stamped by the Engineer and written permission is obtained for their dispatch to site. 27.4 ENVIRONMENT 27.4.1 General 1 Environmental conditions shall be in accordance with Section 1 Part 1 unless specified herein. 2 Minimum ambient temperature shall be 0C. 3 Maximum relative humidity shall be 95%. END OF PART QCS 2010 Qatar Project Management 3 QCS 2010 Section 21 Part 28 Small Enclosures Page 1 28. SMALL ENCLOSURES ................................................................................. 2 28.1 GENERAL ...................................................................................................... 2 28.1.1 28.1.2 28.1.3 28.1.4 Scope Description References Submissions 28.2 PRODUCTS ................................................................................................... 2 28.2.1 28.2.2 28.2.3 28.2.4 28.2.5 28.2.6 General Hinged Cover Enclosures for use Indoors Cabinets and Junction Boxes for use Indoors Terminal Blocks Weatherproof Cabinets for use Outdoors Small outdoor Enclosures for Pushbutton Stations, Local Isolators, Local Starter or Control Gear etc. 6 QUALITY CONTROL AND TEST PROCEDURES ........................................ 6 28.4.1 General 28.5 5 INSTALLATION ............................................................................................. 6 28.3.1 General 28.4 2 3 3 4 4 6 Environment ................................................................................................... 6 28.5.1 General QCS 2010 6 Qatar Project Management 28.3 2 2 2 2 QCS 2010 Section 21 Part 28 Small Enclosures 28. SMALL ENCLOSURES 28.1 GENERAL 28.1.1 Scope 1 This Part specifies the requirements for small enclosures. 2 Related Parts and Sections are as follows: This Section Cables and small wiring Conduits Trunking Cable Trays Accessories and General Power 28.1.2 Description 1 The use of small enclosures, cabinets and junction boxes shall be limited to enclosing terminal blocks and low voltage (not exceeding 415 Volts) electrical field devices e.g. transmitters, sensors, switches, sockets, local starters and control stations, etc. excluding main motor control and switchgear. 28.1.3 References 1 The following Standards are referred to in this Part: BS 6220 Junction Boxes BS 7671, Requirements for Electrical Installations IEE, UK., BS EN 60947-4-1 NEMA 250 NEMA ICS 4 NFPA 70 - National Electrical Code, U.S.A or other approved equivalent standards as applicable. 28.1.4 Submissions 1 Submissions shall be in accordance with Part 1 of this Section and Part 7 of Section 1. 2 Shop Drawings submission shall include dimensional drawings of the battery and battery charger, including sections and elevations, showing the following: (a) (b) (c) (d) 3 sizes and positions of components positions and method of fixing cable and boxes location of terminal boards other pertinent data. Submission of project data shall be as follows: (a) (b) full specifications of the enclosure and the components of the equipment with relevant sheets of manufacturer’s catalogues confirmation that the equipment complies with the relevant specifications. 28.2 PRODUCTS 28.2.1 General 1 The specification shall be in accordance with latest edition of local and International regulations e.g QGEWC. QCS 2010 Qatar Project Management Part 6 Part 7 Part 8 Part 9 Part 10 Page 2 QCS 2010 Section 21 Part 28 Small Enclosures Page 3 The product selected and proposed shall include manufacturer's Instructions that Indicate application conditions and limitations of use stipulated by Product testing agency specified under Regulatory Requirements. 3 The contractor shall select the product only from manufacturer’s specializing in manufacturing products specified in this Part with minimum five years documented experience of the products being satisfactorily in use in a similar service and climatic conditions. 4 The contractor shall ensure proper co-ordination with related civil and other project associated activities prior to the selection of the equipment. 5 The Contractor shall clearly show locations and fixing arrangements on the drawings. 6 IP ratings are based on short laboratory tests and are not an indication of an enclosure’s suitability for use outdoors or in a harsh environment. All such enclosures need considerable interpretation for each installation. 7 Any enclosure installed in the wet well of a pumping station or in any area where the change of flooding exists shall be rated for IP68 classification. 8 Any enclosure installed the wet well of a pumping station shall be rated for Zone 2 hazardous area classification. 28.2.2 Hinged Cover Enclosures for use Indoors 1 Construction: Galvanized steel with minimum sheet steel thickness of 2 mm with panel fronts of thickness 2.0 mm minimum. 2 Covers: Lift-off hinge held closed by lockable T type handles. Doors shall close on to neoprene or soft rubber sealing strips held in place mechanically. 3 Provide interior metal panel for mounting terminal blocks and electrical components; finish with white enamel. 4 Enclosure Finish: Green to BS 4800, shade 14E53. 5 Enclosure Protection: Dust and vermin proof. Environmental protection to IP 54 or as applicable depending on the application. 28.2.3 Cabinets and Junction Boxes for use Indoors 1 Boxes: Galvanized steel with minimum sheet steel thickness of 2 mm with panel fronts of thickness 2.0 mm minimum. 2 Box Size: To suit equipment requirements. 3 Provide interior metal panels for mounting terminal blocks and electrical components; finish with white enamel. 4 Fronts: Lift-off hinge held closed by lockable T type handles. Doors shall close on to neoprene or soft rubber sealing strips held in place mechanically. 5 Junction boxes enclosing small quantity of terminals with bolted cover shall however be permitted to be used as per the approval of the engineer. 6 Glandplates shall be provided to suit cable, conduit and circuiting arrangements. 7 Provide metal barriers to form separate compartments wiring of different systems and voltages. QCS 2010 Qatar Project Management 2 QCS 2010 Section 21 Part 28 Small Enclosures Page 4 Provide accessory feet, pedestal or pillar for free-standing equipment. 9 Enclosure Finish: Green to BS 4800, shade 14E53. 10 Enclosure Protection: Dust and vermin proof. Environmental protection to IP 54 or as applicable depending on the application. 28.2.4 Terminal Blocks 1 Terminal Blocks: IEC 947-7-1 or BS EN 60947-7-1: Terminal blocks for copper conductors. 2 Power Terminals: Unit construction type with closed back and tubular pressure screw connectors, rated 600 volts. 3 Signal and Control Terminals: Modular construction type, suitable for channel mounting, with tubular pressure screw connectors, rated 600 volts. 4 Provide earth bus terminal block, with each connector bonded to the enclosure. 5 Special terminals e.g. disconnect type, diode type, bridging type, fuse type etc. according to the applications requirements or as directed by the Engineer shall be provided. 6 All terminal assemblies shall be provided with dividers as necessary and end plates. Where included in the manufacturers’ inventory, locking wire shall be installed on every terminal assembly. 28.2.5 Weatherproof Cabinets for use Outdoors 1 Weatherproof cabinets shall be provided for all electrical, control, instrumentation, distribution, etc. equipment which is to be used externally. 2 Outdoor equipment shall be weatherproof and designed to prevent the collection of water at any point. Metal to metal joints will not be permitted and all external bolts or screws shall be provided with blind tapped holes where a through hole would permit the ingress of moisture. The insides of outdoor cubicles shall be coated with an approved anti-condensation finish. 3 Confirmation must be provided from the manufacturer of any equipment intended for use outdoor that the equipment is suitable for use outdoors in the local climatic conditions, in situations where minor accidental damage, e.g. chipping, is likely to occur. 4 All kiosks and cubicles shall be fitted with door operated internal lights and shall be ventilated. 5 All instrumentation and control cubicles, kiosks etc. designed for use outside shall be manufactured having walls of double skinned, resin bonded fibreglass, with a totally encapsulated infill of rigid weather and "boil" proof plywood to DD ENV 12038 between the two skins. 6 The roof section shall have a totally encapsulated infill of end grain balsa instead of plywood. The end grain balsa shall have a minimum thickness of 18mm. 7 They shall be fully wind, dust and water tight and suitable for the prevailing climatic conditions and be of robust vandal proof construction. 8 The cabinets shall have a single door or two or more hinged non-overlapping doors fitted with a double locking bar, with a waterproof lever handle and cylindrical lock. Doors shall have an all round channel recessed gasket of non-fatigue, oil and age resistant material. Hinges shall be strong, smooth action and non-corrodable which allow the door to be easily removed. Doors shall be fitted with a suitable fixing bar to hold in the open position. 9 Box section steel shall be encapsulated into door edges and door frames. QCS 2010 Qatar Project Management 8 QCS 2010 Section 21 Part 28 Small Enclosures Page 5 All door catches and locks shall latch onto steel reinforced surfaces. The door sill shall be protected by a non-corroding alloy material. 11 Door mounted meters and transparent windows shall be of wired glass, which shall be protected from harmful direct sunshine by orientation or other approved means. 12 The cabinet shall be stiffened and/or reinforced when required for additional rigidity. 13 The cabinet shall have an easily removable rear mounting plate on moulded spacers. 14 All internal equipment shall be mounted on supports built into the fiberglass structure. Fixing bolts through the skin will not be accepted. 15 If required by the internal components, encapsulated thermal insulation shall be included. 16 The laminate material shall have flame retardant characteristics in compliance with BS 476 Part 7 Class 2, and shall retain "stability, integrity and insulation" for 30 min. when tested in accordance with BS 476 Part 8. An indicative fire test report shall be provided with the tender. 17 Colour impregnated gel coats backed by coloured resin shall be used to ensure maintenance free and "colour fast" finishes. 18 The cabinet shall be light grey in colour. The finish shall be colour fast and maintenance free. 19 The cabinet shall be constructed to provide environmental protection to IP 55. 20 The cabinet shall have a suitable shade canopy. 21 Ventilation via louvres with efficient sand traps and vermin screens will be permitted. 22 The cabinet shall be floor mounted suitable for bolting down to a concrete base. 23 The locking arrangement shall be suitable for the Master Lock & Key System used by the Employer. 28.2.6 Small outdoor Enclosures for Pushbutton Stations, Local Isolators, Local Starter or Control Gear etc. 1 All push button stations for use outdoors shall be of cast alloy, galvanised iron or stainless steel, heavy duty construction, specifically made for outdoor use and certified by the manufacturer as weatherproof. 2 Stop push buttons shall be of the auto-latch turn-to-release type. Push buttons shall not be prone to U.V. degradation. 3 Clearly visible legend plates to indicate the motor controlled shall be fitted at each push button or control station. 4 Isolator enclosures shall be of similar construction, lockable in the off position and fitted with auxiliary contacts for alarm purposes. 5 A robust factory manufactured and galvanised steel or stainless steel floor standing support shall be supplied and fixed for mounting the enclosure at a convenient height. These shall be pipe mounted with cabling running up inside the pipe, to protect the cables from mechanical damage and sun or fabricated from substantial angle iron and channel. Enclosures shall not be attached to handrailing. Under no circumstances shall enclosures be mounted on channel type supports of the unistrut type. Unistrut will not be accepted as any part of a welded support. 6 Where enclosures are installed in direct sunlight sunshades of an approved design shall be provided. QCS 2010 Qatar Project Management 10 QCS 2010 Section 21 Part 28 Small Enclosures Page 6 Hinged doors shall have a rain trap all round the opening and enclosures shall be fitted with a separate weather protection canopy. 8 Under no circumstances will painted sheet steel enclosures or enclosures with knock-outs for conduit or glandplates be acceptable for use outdoors unless they are mounted inside a heavy duty GRP enclosure and weather canopy. 28.3 INSTALLATION 28.3.1 General 1 Install in accordance with NECA "Standard of Installation" and other standards as directed by the Engineer. 2 Remove dirt and debris from enclosure 3 Install enclosures and boxes plumb. Anchor securely to wall and structural supports at each corner under the provisions of Section "supporting Devices". 28.4 QUALITY CONTROL AND TEST PROCEDURES 28.4.1 General 1 The manufacturer shall provide proof of a stringent Quality Control (QC) plan or Inspection Test Plan (ITP). In particular the main equipment manufacturing stages sanctioned by appropriate tests such as: incoming components inspection, discrete sub-assembly tests and complete functional checks on the final product. Final inspection and calibration operations shall be documented in a report drawn up by the supplier’s Quality Inspection department. 2 The integrated functional test shall be conducted at manufacturer’s works to ensure satisfactorily functioning of the equipment. 3 The Assembly shall not leave the manufacturer’s works until the works test sheets have been duly approved and stamped by the Engineer and written permission is obtained for their dispatch to site. 28.5 Environment 28.5.1 General 1 Environmental conditions shall be in accordance with Section 1 Part 1 unless specified herein. 2 Minimum ambient temperature shall be 0C. 3 Maximum relative humidity shall be 95%. END OF PART QCS 2010 Qatar Project Management 7 QCS 2010 Section 21 Part 29 Underfloor Ducts Page 1 29. UNDERFLOOR DUCTS ................................................................................ 2 29.1 GENERAL ...................................................................................................... 2 29.1.1 29.1.2 29.1.3 29.1.4 Scope Description References Submissions 29.2 PRODUCTS ................................................................................................... 2 29.2.1 29.2.2 29.2.3 29.2.4 General Underfloor Ducts Trench Ducts Service Fittings 29.3 INSTALLATION ............................................................................................. 4 29.4 4 QUALITY CONTROL AND TEST PROCEDURES ........................................ 6 29.4.1 General 29.5 2 3 4 4 6 ENVIRONMENT ............................................................................................ 6 29.5.1 General QCS 2010 6 Qatar Project Management 29.3.1 General 2 2 2 2 QCS 2010 Section 21 Part 29 Underfloor Ducts 29. UNDERFLOOR DUCTS 29.1 GENERAL 29.1.1 Scope 1 This Part specifies the requirements for underfloor ducts. 2 Related Parts and Sections are as follows: This Section Cables and small wiring Conduits Trunking Cable Trays Accessories and General Power 29.1.2 Description 1 Underfloor ducts shall be provided as specified and shown on the drawings. 29.1.3 References 1 The following Standards are referred to in this Part: BS 7671 ------ Requirement for electrical installations. IEE wiring regulations. Sixteenth Edition 29.1.4 Submissions 1 Submissions shall be in accordance with Part 1 of this Section and Part 7 of Section 1. 2 Shop Drawings submission shall include dimensional drawings, including sections and elevations, showing the following: (a) (b) (c) 3 sizes and positions of components positions and method of fixing cable and boxes other pertinent data. Submission of project data shall be as follows: (a) (b) full specifications of the enclosure and the components of the equipment with relevant sheets of manufacturer’s catalogues confirmation that the equipment complies with the relevant specifications. 29.2 PRODUCTS 29.2.1 General 1 Underfloor ducts shall confirm to requirements as specified in BS 7671, NFPA 70 - National Electrical Code, U.S.A or other equivalent standard as applicable. 2 Underfloor duct specification shall be in accordance with QGEWC regulations and IEE latest edition as applicable. 3 The product selected and proposed shall include manufacturer's instructions that indicate application conditions and limitations of use stipulated by the product testing agency specified under Regulatory Requirements. QCS 2010 Qatar Project Management Part 6 Part 7 Part 8 Part 9 Part 10 Page 2 QCS 2010 Section 21 Part 29 Underfloor Ducts Page 3 The contractor shall select the product only from a manufacturer specializing in manufacturing products specified in this Part with minimum five years documented experience of the products being satisfactorily in use in a similar service and climatic conditions. 5 The contractor shall ensure proper co-ordination with related civil activities prior to the selection of the equipment. 6 The contractor shall clearly show locations of ducts, service fittings, junction boxes, and branch circuiting arrangements on the drawings 29.2.2 Underfloor Ducts 1 Sheet metal raceway shall be designed to be embedded in concrete slab. (a) (b) concealed underfloor duct - Type of underfloor duct, which has concrete topping over cover, which shall have inserts for installation of service fittings. flush duct - Type of underfloor duct, which has cover, installed flush with concrete slab. Cover shall have openings for installation of service fittings 2 Steel duct shall be provided with a corrosion-resistant finish. 3 The ducting shall be Underfloor or Flush as specified 4 Configuration of the ducting shall be one or two level systems as specified using ducts in parallel runs as shown on Drawings. 5 Services shall include, 240 volt power - standard size, telephone - extra width size, computer data - extra width size, 415 volt power - standard or extra width size as specified. 6 Underfloor ducting shall be selected from the standard range of the manufacturer. The nominal size shall be 38 x 76 mm or as specified. 7 Underfloor ducting where required for larger width application shall be 38 x 152 mm or as specified. 8 Fabricate distribution lengths with standard height preset inserts on 610 mm centers or provide precut 32 mm diameter holes on 610 mm centers as specified. Close with flat metal screw plugs. 9 Rectangular or round cover and trim single level junction boxes or as specified with adjustable height shall be used. Provide internal barriers, conduit and duct entrances, and extension rings as required. 10 Rectangular or round cover and trim Two Level Junction Boxes or as specified with adjustable height shall be used. Provide separate enclosures for each service to allow feeder ducts to cross under distribution ducts. Provide conduit and duct entrances and extension rings as required. 11 Junction Box Cover Plate shall conform to one of the following as specified: (a) (b) (c) tile trim plate flush with finished floor. smooth cover plate flush with concrete floor carpet trim holders of proper depth. 12 Supports shall be adjustable type and to be adjusted before concrete topping placement. 13 Service Fittings shall be provided in conjunction with wiring devices. 14 Duct Markers shall be corrosion resistant marker screws, with escutcheon. QCS 2010 Qatar Project Management 4 QCS 2010 Section 21 Part 29 Underfloor Ducts Page 4 Manufacturer's standard range of fittings and accessories shall be used as much as is practically as possible. 29.2.3 Trench Ducts 1 Underfloor raceway where specified shall be provided with a removable cover flush with the concrete slab. 2 Steel trench duct shall be provided with corrosion resistant finish. The duct shall be of closed or open bottom type as specified 3 The duct sizes shall be as specified or indicated on the Drawings. 4 Provide adjustable compartment dividers. 5 Supports shall be adjustable type and to be adjusted before and after concrete topping placement. 6 Coverplates shall conform to one of the following as specified: (a) (b) (c) 6.4 mm thick steel removable Coverplates with gasket joints smooth cover plate flush with concrete floor recessed coverplate with tile trim. 7 Manufacturer's standard range of fittings and accessories shall be used as much as is practically as possible. 29.2.4 Service Fittings 1 Pedestal Convenience Receptacle shall have satin aluminum housing with stainless steel device plate in one duplex, two duplex or back to back configurations or as specified. 2 Flush Cover Convenience Receptacle shall be of aluminum or brass in duplex with flap or threaded opening or as specified. 3 Pedestal Communication Outlet shall have satin aluminum housing with stainless steel device plate having One bushed opening 25 mm inside diameter or as specified. 4 Flush Cover Communication Outlet shall be of aluminum or brass with stainless steel device plate having 54 x 25-mm combination threaded opening or as specified. 5 Pedestal Communication Fitting shall have satin aluminum housing with stainless steel device plate having one duplex convenience receptacle with one bushed opening, 25 mm inside diameter or as specified. 6 Flush Cover Communication Fitting shall be of aluminum or brass with stainless steel device plate having 54 x 25-mm combination threaded opening or as specified. 29.3 INSTALLATION 29.3.1 General 1 Install Products in accordance with the manufacturer's instructions. 2 Locate duct in structural slab or concrete topping as specified. 3 Provide expansion fittings with suitable bonding jumper where duct crosses building expansion joints. QCS 2010 Qatar Project Management 15 QCS 2010 Section 21 Part 29 Underfloor Ducts Page 5 Terminate ducts for power service in bottom of panelboard or wireway as specified using suitable fittings. Terminate in junction box for extension of conduit to panel board where specified. . 5 Terminate ducts for telephone service 50 mm above floor in telephone closet or in bottom of telephone cabinet using suitable fittings as specified. 6 Terminate ducts for data services in bottom of data services cabinet using suitable fittings. 7 Level cover plates flush with finished concrete floor. 8 Place rectangular plates square with wall lines. 9 Securely hold junction boxes and ducts in place during installation to avoid floating or other movement. 10 Close unused duct or conduit entrances to junction boxes. Seal duct terminations at junction boxes. 11 Earth and bond duct under provisions of Part "Earthing and Bonding". 12 Install underfloor duct with tops of preset inserts as specified or indicated on the Drawings below finished floor line. Locate ducts on centers as specified or as indicated on Drawings. 13 Install flush duct flush with finished floor. 14 Place schedule on the inside of coverplate of each junction box indicating distance to first insert in each direction, measured from the center of the box. Use self-adhesive labels for schedule. 15 Use blank duct in permanent corridors, passages, lobbies, for connecting parallel ducts less than 1.8 m apart, for feeder duct from cabinet or panelboard to first junction box, and where indicated. 16 Join duct lengths using combination support couplers where practical. Provide additional supports at intervals of not over 1.5 m, within 750 mm each side of junction boxes, and as close as practical to elbows, bends, and terminations. 17 Install insert within 30 mm of edge of junction box. Align inserts on same centers for all services. 18 Do not extend inserts into special floor finishes, such as terrazzo, marble, or wood. 19 Install a duct marker in each insert adjacent to junction box, at end of each duct run, on both sides of permanent partitions, and on both sides of change of direction of duct. Install markers flush with finished floor material. In carpeted areas, install marker screws level with carpet backing. 20 Install surface service fittings after installation of floor finishes. Cut floors as necessary, following duct manufacturer's recommendations. Replace damaged floor construction and finish. 21 Install trench duct trims flush with coverplates. Maintain covering of factory-applied tape for protection. 22 Terminate ducts for X-ray circuits at wall; interface with wall duct provided under Part "Surface Raceway Trunking". 23 Clean ducts and fittings of debris and dust before installing wire and cable. QCS 2010 Qatar Project Management 4 QCS 2010 Section 21 Part 29 Underfloor Ducts Page 6 Pull wire and cable from outlet insert toward junction boxes. 25 Install branch circuit conductors continuous between junction box and farthest fitting. Do not cut conductor to make connections to receptacle devices. 26 Clean finished surfaces before and after the installation in accordance with manufacturer's instructions. 29.4 QUALITY CONTROL AND TEST PROCEDURES 29.4.1 General 1 The manufacturer shall provide proof of a stringent Quality Control (QC) Plan or Inspection Test Plan (ITP). In particular the main equipment manufacturing stages sanctioned by appropriate tests such as: incoming components inspection, discrete sub-assembly tests and complete functional checks on the final product. Final inspection and calibration operations shall be documented in a report drawn up by the supplier’s Quality Inspection department. 2 The Assembly shall not leave the manufacturer’s works until the works test sheets have been duly approved and stamped by the Engineer and written permission is obtained for their dispatch to site. 29.5 ENVIRONMENT 29.5.1 General 1 Environmental conditions shall be in accordance with Section 1 Part 1 unless specified herein. 2 Minimum ambient temperature shall be 0C. 3 Maximum relative humidity shall be 95%. END OF PART QCS 2010 Qatar Project Management 24 QCS 2010 Section 21 Part 30 Duct bank and Manholes Page 1 30. DUCT BANK AND MANHOLES..................................................................... 2 30.1 GENERAL ...................................................................................................... 2 30.1.1 Scope 30.1.2 Description 30.1.3 Submissions 2 2 2 PRODUCTS ................................................................................................... 2 30.2.1 30.2.2 30.2.3 30.2.4 30.2.5 30.2.6 30.2.7 30.2.8 General Rigid Steel Conduit Plastic Conduit Plastic Duct Reinforced Resin Conduit Pre-Cast Concrete Manholes Accessories Cast in Place Manhole Accessories 30.3 INSTALLATION ............................................................................................. 4 30.3.1 Duct Bank Installation 30.3.2 Pre-Cast Manhole Installation 30.3.3 Cast in Place Manhole Installation 30.4 4 5 6 QUALITY CONTROL AND TEST PROCEDURES ........................................ 7 30.4.1 General 30.5 2 3 3 3 3 3 4 4 7 ENVIRONMENT ............................................................................................ 7 30.5.1 General QCS 2010 7 Qatar Project Management 30.2 QCS 2010 Section 21 Part 30 Duct bank and Manholes 30. DUCT BANK AND MANHOLES 30.1 GENERAL 30.1.1 Scope 1 This Part specifies the requirements for duct bank and manholes. 2 Related Parts and Sections are as follows: This Section Cables and small wiring Conduits Trunking Cable Trays Accessories and General Power 30.1.2 Description 1 Duct bank and manholes shall be provided as specified and shown on the drawings. 30.1.3 Submissions 1 Submissions shall be in accordance with Part 1 of this Section and Part 7 of Section 1. 2 Shop Drawings submission shall include dimensional drawings of the duct bank and manholes, including sections and elevations, showing the following: (a) (b) (c) (d) 3 sizes and positions of manholes duct routing location of entry to buildings other pertinent data. Submission of the project data shall be as follows: (a) (b) full specifications of the enclosure and the components of the equipment with relevant sheets of manufacturer’s catalogues confirmation that the equipment complies with the relevant specifications. 30.2 PRODUCTS 30.2.1 General 1 Duct Banks and manholes shall confirm to requirements as specified in relevant standard as applicable. 2 The specification shall be in accordance with latest edition of local and International regulations e.g. QGEWC, NEMA, ASTM, IEE etc. 3 The product selected and proposed shall include manufacturer's instructions that indicate application conditions and limitations of use stipulated by the product testing agency specified under Regulatory Requirements. 4 The contractor shall select the product only from the manufacturer specializing in manufacturing products specified in this Part with minimum five years documented experience of the products being satisfactorily in use in a similar service and climatic conditions. 5 The contractor shall ensure proper co-ordination with related civil and other project associated activities prior to the selection of the equipment. QCS 2010 Qatar Project Management Part 6 Part 7 Part 8 Part 9 Part 10 Page 2 QCS 2010 Section 21 Part 30 Duct bank and Manholes Page 3 The contractor shall clearly show locations and arrangements of fittings on the drawings. 7 To ensure that field measurements are as indicated. 8 Provide detail routing and termination locations of duct bank prior to excavation. for rough in. 9 Provide locations of manholes prior to excavating for installation. 30.2.2 Rigid Steel Conduit 1 Rigid Steel Conduit: ANSI C80.1 or other approved standard. 2 Fittings: NEMA FB 1 or other approved standard, steel. 30.2.3 Plastic Conduit 1 Rigid Plastic Conduit: NEMA TC 2, Schedule 40 or 80 PVC or as specified, with fittings and conduit bodies to NEMA TC 3 or other approved standard. 2 Rigid Plastic Underground Conduit: UL 651A, Type A PVC; UL 651A, Type EB PVC; Highdensity polyethylene, Schedule 40 or Fibreglass-reinforced epoxy as specified or indicated. 30.2.4 Plastic Duct 1 Plastic Utilities Duct: approved standard. 2 Plastic Utility Duct Fittings: NEMA TC 9 or other approved standard. 3 Plastic Communications Duct and Fittings: NEMA TC 10, Type EB or DB as specified or other approved standard. 30.2.5 Reinforced Resin Conduit 1 Conduit and Fittings: standard. 2 Joining Method: specified. 30.2.6 Pre-Cast Concrete Manholes 1 Pre-cast concrete manholes shall be as specified as follows: (a) (b) (c) (d) (e) (f) (g) (h) (i) (j) (k) NEMA TC 6; PVC or ABS Type EB or DB as specified or other NEMA TC 14, Type SW or HW as specified or other approved Tapered bell and spigot joints, threaded joints or saw-cut system as Description: Precast manhole designed in accordance with ASTM C858, comprising modular, interlocking sections complete with accessories or as specified. Loading: ASTM C857, Class A-16, A-12, A-8 or A-0.3 as specified. Shape: Square or rectangular with truncated corners or as indicated. Nominal Inside Dimensions: Specified or indicated mm x mm. Corner Panel Dimensions: Specified mm wide. Inside Depth: Specified mm. Wall Thickness: Specified mm. Base Section: Include 75 or specified mm deep x 350 or specified mm round sump with cast sleeve, and two 25 mm ground rod openings where specified Top Section: Include 1000 mm diameter or other approved size and shape grooved opening for frame and cover. Riser Casting: 150 or 300 mm as specified or indicated, with manhole step cast into frame. Frames and Covers: ASTM A48; Class 30B gray cast iron, 686 or 762 mm size as specified or other approved standard and size, machine finished with flat bearing QCS 2010 Qatar Project Management 6 QCS 2010 (l) (m) (n) (o) (p) (q) (s) (t) (u) (v) Part 30 Duct bank and Manholes Page 4 surfaces. Provide cover marked ELECTRIC, TELEPHONE or as directed by the Engineer to indicate utility. Duct Entry Provisions: Single duct knockouts, window knockouts or windows with plastic duct terminators and diaphragms as specified. Duct Entry Locations: As specified or indicated. Duct Entry Size: 100 or 150 mm as specified. Cable Pulling Irons: Use galvanised rod and hardware. Locate opposite each duct entry. Provide watertight seal. Cable Rack Inserts: Minimum load rating 365 kg or as specified. Locate at specified or indicated distance on centre. Cable Rack Mounting Channel: 38 x 19 mm or approved size steel channel, 1.2 m or specified length. Provide cable rack arm mounting slots 38 mm or at standard centres. Cable Racks: Steel channel, 38 x 19 x 350 mm or other approved size, with fastener to match mounting channel. Cable Supports: Porcelain, Maple or other approved type clamps and saddles. Manhole Steps: Polypropylene plastic manhole step with 13 mm steel reinforcement, Cast steps at 300 mm on centre vertically or as specified or indicated or Ladder: Aluminium rung, approved length, with top hook to engage manhole step in riser casting. Provide one ladder for each manhole. Sump Covers: ASTM A48; Class 30B gray cast iron or other approved standard. Source Quality Control: Inspect manholes in accordance with ASTM C1037 or other approved standard. 30.2.7 Accessories 1 Underground Warning Tape: 100 mm wide plastic tape, detectable type, coloured yellow with suitable warning legend describing buried electrical lines. 30.2.8 Cast in Place Manhole Accessories 1 Frames and Covers: ASTM A48; Class 30B gray cast iron, 686 or 762 mm size as specified or other approved standard and size, machine finished with flat bearing surfaces. Provide cover marked ELECTRIC, TELEPHONE or as directed by the Engineer to indicate utility. 2 Cable Pulling Irons: Use galvanised rod and hardware. 3 Cable Rack Inserts: Minimum load rating of 365 kg or as approved. 4 Cable Rack Mounting Channel: 38 x 19 mm or approved size steel channel, 1.2 m or specified length. Provide cable rack arm mounting slots 38 mm or at standard centres. 5 Cable Racks: Steel channel, 38 x 19 x 350 mm or other approved size, with fastener to match mounting channel. 6 Cable Supports: Porcelain, Maple or other approved type clamps and saddles. 7 Manhole Steps: Polypropylene plastic manhole step with 13 mm steel reinforcement, Cast steps at 300 mm on centre vertically or as specified or indicated or Ladder: Aluminium rung, approved length, with top hook to engage manhole step in riser casting. Provide one ladder for each manhole. 8 Sump Covers: ASTM A48; Class 30B gray cast iron or other approved standard. 30.3 INSTALLATION 30.3.1 Duct Bank Installation 1 Install duct to locate top of ductbank at depths as indicated on drawings or install duct to locate top of ductbank minimum specified or indicated mm below finished grade. QCS 2010 Qatar Project Management (r) Section 21 QCS 2010 Section 21 Part 30 Duct bank and Manholes Page 5 Install duct with minimum slope of 100 mm per 25.4 m (0.33 percent) or as specified or indicated. Slope duct away from building entrances. 3 Cut duct square using saw or pipe cutter; de-burr cut ends. 4 Insert duct to shoulder of fittings; fasten securely. 5 Join non-metallic duct using adhesive as recommended by manufacturer. 6 Wipe non-metallic duct dry and clean before joining. Apply full even coat of adhesive to entire area inserted in fitting. Allow joint to cure for 20 minutes, minimum. 7 Install no more than equivalent of two 90-degree bends between pull points. 8 Provide suitable fittings to accommodate expansion and deflection where required. 9 Terminate duct at manhole entries using end bell. 10 Stagger duct joints vertically in concrete encasement 150 mm minimum. 11 Use suitable separators and chairs installed not greater than 1200 mm on centres. 12 Band ducts together before backfilling or placing concrete. 13 Securely anchor duct to prevent movement during concrete placement. 14 Place concrete under provisions of relevant section. Use mineral pigment to colour concrete where specified. 15 Provide minimum 75-mm or other specified concrete cover at bottom, top, and sides of ductbank. 16 Provide specified or indicated steel reinforcing bars in top of bank under paved areas. 17 Connect to existing concrete encasement using dowels. 18 Connect to manhole wall using dowels. 19 Provide suitable pull string in each empty duct except sleeves and nipples. 20 Swab duct. Use suitable caps to protect installed duct against entrance of dirt and moisture. 21 Backfill trenches under provisions of relevant section. 22 Interface installation of underground warning tape with backfilling specified in relevant section. Install tape 150 mm below finished surface. 30.3.2 Pre-Cast Manhole Installation 1 Excavate for manhole installation under the provisions of relevant section. 2 Install and seal precast sections in accordance with ASTM C891 or other approved standard. 3 Install manholes plumb. 4 Use precast neck and shaft sections to bring manhole cover to finished elevation. 5 Attach cable racks to inserts after manhole installation is complete. QCS 2010 Qatar Project Management 2 QCS 2010 Section 21 Part 30 Duct bank and Manholes Page 6 Where specified or indicated, install drains in manholes and connect to site drainage system or provide DN100 pipe terminating in 1/4 cu m crushed gravel bed under provisions of relevant section. 7 Damp proof exterior surfaces, joints, and interruptions of manholes after concrete has cured 28 days, under provisions of relevant section. 8 Backfill manhole excavation under the provisions of relevant section. 30.3.3 Cast in Place Manhole Installation 1 Excavate for manhole installation under the provisions of relevant section. 2 Formwork: Form inside and outside manhole surfaces in accordance with provisions of relevant section. 3 Reinforcing: Install reinforcing under the provisions of relevant section. 4 Concrete: Provide air-entrained, 2000 psi (20 mPa) compressive strength at 28 days under the provisions of relevant section or as specified. 5 Shape: As specified or indicated. 6 Nominal Dimensions: As specified or indicated. 7 Inside Depth: As specified or indicated. 8 Wall Thickness: As specified or indicated. 9 Base: Include 350 mm drain opening and two 25 mm ground rod openings where specified. Slope to drain at 6.35 mm per m (2 percent). 10 Top: Include 1000-mm diameter or other approved size and shape opening; cast 13-mm rod in opening to accept ladder hook. 11 Duct Entry: Cast ducts openings in walls as indicated. 12 Cable Pulling Irons: Locate opposite each duct entry. 13 Cable Rack Inserts: Locate at specified mm on centre. 14 Construct brick collar with 760-mm or approved size clear opening to bring cover to proper elevation. 15 Manhole Steps: Cast steps at 300 or specified mm on centre vertically or install ladder in each manhole. 16 Attach cable racks to inserts after manhole construction is complete. 17 Install drains in manholes and connect to site drainage system or provide 100 mm pipe terminating in 0.25 cu m crushed gravel bed under provisions of relevant section where specified or indicated. 18 Dampproof exterior surfaces, joints, and interruptions of manholes after concrete has cured 28 days, under provisions of relevant section. 19 Backfill manhole excavation under the provisions of relevant section. QCS 2010 Qatar Project Management 6 QCS 2010 Section 21 Part 30 Duct bank and Manholes Page 7 QUALITY CONTROL AND TEST PROCEDURES 30.4.1 General 1 The manufacturer shall provide proof of a stringent Quality Control (QC) Plan or Inspection Test Plan (ITP). In particular the main equipment manufacturing stages sanctioned by appropriate tests such as: incoming components inspection, discrete sub-assembly tests and complete functional checks on the final product. Final inspection and calibration operations shall be documented in a report drawn up by the supplier’s Quality Inspection department. 2 The Assembly shall not leave the manufacturer’s works until the works test sheets have been duly approved and stamped by the Engineer and written permission is obtained for their dispatch to site. 30.5 ENVIRONMENT 30.5.1 General 1 Environmental conditions shall be in accordance with Section 1 Part 1 unless specified herein. 2 Minimum ambient temperature shall be 0C. 3 Maximum relative humidity shall be 95%. END OF PART QCS 2010 Qatar Project Management 30.4 QCS 2010 Section 21 Part 31 Power Distribution Transformers Page 1 31. POWER DISTRIBUTION TRANSFORMERS ................................................ 2 31.1 GENERAL ...................................................................................................... 2 31.1.1 31.1.2 31.1.3 31.1.4 Scope Description References Submissions 31.2 PRODUCTS ................................................................................................... 3 31.2.1 General 3 INSTALLATION ............................................................................................. 3 31.3.1 General 3 31.4 QUALITY CONTROL AND TEST PROCEDURES ........................................ 3 31.5 Environment ................................................................................................... 3 31.5.1 General QCS 2010 3 Qatar Project Management 31.3 2 2 2 2 QCS 2010 Section 21 Part 31 Power Distribution Transformers POWER DISTRIBUTION TRANSFORMERS 31.1 GENERAL 31.1.1 Scope 1 This Part specifies the requirements for Power Distribution Transformers. 31.1.2 Description 1 Power Distribution Transformers shall be provided as specified. 31.1.3 References Power Distribution Transformers shall be provided in accordance with QGEWC latest specifications and the International Standards referred to to here below: BS EN ISO 1461:2009 ------- Hot Dip Galvanized Coatings on Iron and Steel Articles. BS 381C 1980 ------------------ Specification for Colours for Identification, Coding, and Special Purposes. BS 3692 -------------------------- ISO Metric Precision Hexagonal Bolts, Screws and Nuts. BS 4190 -------------------------- ISO Metric Black Hexagonal Bolts, Screws and Nuts. BS 7079, BS EN ISO 8501, BS EN ISO 8503------Surface Finish of Blast Cleaned Steel for Painting. BS 2562 1979 ----------------- Specification for Cable Boxes for Transformers and Reactors. BS EN ISO 12944, BS EN ISO 14713------Code of Practice for Protective coating for Iron and Steel Structures against Corrosion BS 6435 1984 ------------------ Specifications for Unfilled Enclosures for the Dry Termination of HV Cables for Transformers and Reactors. BS Code of Practice 1010. ESI Standard 98-1. BS IEC 60076, BS IEC 60078----Power Transformers IEC 296/BS 148 ---------------- Insulating Oil for Transformers and Switchgear. IEC 529/BS 5420 -------------- Specification for Degrees of protection Provided by Enclosures. BS EN 60076. IEC 60076 --- Method of Measurement of Transformer and Reactor Sound Levels. IEC 726 -------------------------- Cast risen transformers 31.1.4 Submissions 1 Tender information and drawings shall be submitted to QGEWC through the supervising consultant. Submissions shall be in accordance with the requirements of the latest QGEWC specifications. QCS 2010 Qatar Project Management 31. Page 2 QCS 2010 Section 21 Part 31 Power Distribution Transformers Page 3 PRODUCTS 31.2.1 General 1 The contractor shall supply, install, test and commission Power Distribution Transformers as specified. 2 The transformers shall be ONAN outdoor, mineral oil filled, in compliance with QGEWC latest standards. 3 The contractor shall be responsible for obtaining the latest version of QGEWC specification for Power Distribution Transformers and shall be responsible for obtaining QGEWC approval. 4 The product selected and proposed shall include manufacturer's instructions that indicate application conditions and limitations of use stipulated by the product testing agency specified under Regulatory Requirements. 5 The contractor shall provide full technical details of the proposed transformers together with a copy of all relevant standards for review and comment by the Engineer, prior to submission to QGEWC for approval. 31.3 INSTALLATION 31.3.1 General 1 Install Products in accordance with the manufacturer's instructions. 2 A contractor who is currently approved by QGEWC must carry out installation. The written approval of QGEWC for the contractor to carry out the work must be forwarded to the Engineer, and be acknowledged by him, before any installation work commences. 3 Earth and bond duct under provisions of Part "Earthing and Bonding". 31.4 QUALITY CONTROL AND TEST PROCEDURES 31.4.1 General 1 The manufacturer shall provide proof of a stringent Quality Control (QC) Plan or Inspection Test Plan (ITP). In particular the main equipment manufacturing stages sanctioned by appropriate tests such as: incoming components inspection, discrete sub-assembly tests and complete functional checks on the final product. Final inspection and calibration operations shall be documented in a report drawn up by the supplier’s Quality Inspection department. 2 The Assembly shall not leave the manufacturer’s works until the works test sheets have been duly approved and stamped by the Engineer and written permission is obtained for their dispatch to site. 31.5 Environment 31.5.1 General 1 Environmental conditions shall be as specified in Section 1 Part 1 and/or QGEWC specifications as applicable. END OF PART QCS 2010 Qatar Project Management 31.2 QCS 2010 Section 21 Part 32 11 kV Switchgear Page 1 32. 11 KV SWITCHGEAR .................................................................................... 2 32.1 GENERAL ...................................................................................................... 2 32.1.1 32.1.2 32.1.3 32.1.4 Scope Description References Submissions 32.2 PRODUCTS ................................................................................................... 2 32.2.1 General INSTALLATION ............................................................................................. 2 32.3.1 General 32.4 2 QUALITY CONTROL AND TEST PROCEDURES ........................................ 3 32.4.1 General 32.5 2 3 ENVIRONMENT ............................................................................................ 3 32.5.1 General QCS 2010 3 Qatar Project Management 32.3 2 2 2 2 QCS 2010 Section 21 Part 32 11 kV Switchgear Page 2 11 KV SWITCHGEAR 32.1 GENERAL 32.1.1 Scope 1 This Part specifies the requirements for 11 kV Switchgear. 32.1.2 Description 1 11 kV Switchgear shall be provided as specified. 32.1.3 References 1 11 kV Switchgear shall be provided in accordance with QGEWC latest specifications and the International Standards referred to therein. 32.1.4 Submissions 1 Tender information and drawings shall be submitted to QGEWC through the supervising consultant. Submissions shall be in accordance with the requirements of the latest QGEWC specifications. 32.2 PRODUCTS 32.2.1 General 1 The contractor shall supply, install, test and commission 11 kV Switchgear as specified. 2 The 11 kV Switchgear complete with metering and instrumentation, special tools, accessories, test equipment, etc, shall be in compliance with QGEWC latest standards. 3 The contractor shall be responsible for obtaining the latest version of QGEWC specification for 11 kV Switchgear and shall be responsible for obtaining QGEWC approval. 4 The product selected and proposed shall include manufacturer's instructions that indicate application conditions and limitations of use stipulated by the product testing agency specified under Regulatory Requirements. 5 The contractor shall provide full technical details of the proposed 11 kV Switchgear together with a copy of all relevant standards for review and comment by the Engineer, prior to submission to QGEWC for approval. 32.3 INSTALLATION 32.3.1 General 1 Install Products in accordance with the manufacturer's instructions. 2 A contractor who is currently approved by QGEWC must carry out installation. The written approval of QGEWC for the contractor to carry out the work must be forwarded to the Engineer, and be acknowledged by him, before any installation work commences. 3 Earth and bond duct under provisions of Part "Earthing and Bonding". QCS 2010 Qatar Project Management 32. QCS 2010 Section 21 Part 32 11 kV Switchgear Page 3 QUALITY CONTROL AND TEST PROCEDURES 32.4.1 General 1 The manufacturer shall provide proof of a stringent Quality Control (QC) Plan or Inspection Test Plan (ITP). In particular the main equipment manufacturing stages sanctioned by appropriate tests such as: incoming components inspection, discrete sub-assembly tests and complete functional checks on the final product. Final inspection and calibration operations shall be documented in a report drawn up by the supplier’s Quality Inspection department. 2 The Assembly shall not leave the manufacturer’s works until the works test sheets have been duly approved and stamped by the Engineer and written permission is obtained for their dispatch to site. 32.5 ENVIRONMENT 32.5.1 General 1 Environmental conditions shall be as specified in Section 1 Part 1 and/or QGEWC specifications as applicable. END OF PART QCS 2010 Qatar Project Management 32.4 QCS 2010 Section 21 Part 33 Actuators Page 1 33. ACTUATORS ................................................................................................. 2 33.1 GENERAL ...................................................................................................... 2 33.1.1 Scope 33.1.2 Description 33.1.3 Submissions 33.2 PRODUCTS ................................................................................................... 2 33.2.1 Electric Actuators 33.2.2 Pneumatic QUALITY CONTROL AND TEST PROCEDURES ........................................ 4 33.3.1 General 33.4 2 4 4 ENVIRONMENT ............................................................................................ 5 33.4.1 General QCS 2010 5 Qatar Project Management 33.3 2 2 2 QCS 2010 Section 21 Part 33 Actuators Page 2 ACTUATORS 33.1 GENERAL 33.1.1 Scope 1 This Part specifies the requirements for valve/penstock actuators. 33.1.2 Description 1 Electric or penstock actuators shall be provided for valves and penstocks where specified. 33.1.3 Submissions 1 Submissions shall be in accordance with Part 1 of this Section and Part 7 of Section 1. 2 Shop Drawings submission shall include dimensional drawings of the actuator, including sections and elevations, showing the following: (a) (b) (c) (d) (e) 3 sizes and positions of components positions and method of fixing cable and boxes location of terminal boards wiring diagrams other pertinent data. Project data submission shall contain the following: (a) (b) (c) full specifications of the enclosure and the components of the equipment with relevant sheets of manufacturer’s catalogues confirmation that the equipment complies with the relevant specifications. the torque-speed requirement calculations / data sheet done for this selection. 33.2 PRODUCTS 33.2.1 Electric Actuators 1 Where specified valves or penstocks shall be provided with electric motorised actuators. 2 As far as possible, the actuators shall be the standard product of a well known specialist manufacturer such as Rotork or Auma, which shall be approved by the Engineer. 3 Valve actuators shall be directly mounted onto and supported by the valves/penstocks which they control unless the valve/penstock is underground where the actuator shall be mounted at coping level. They shall be suitable for remote Automatic control and shall also incorporate means for local manual operation using a handwheel or lever. Actuators shall have integral starters and control equipment, unless the actuator motor is of a size that necessitates a panel mounted starter, in which case it will be specified in the particular specification. 4 The output shaft shall be hollow to accept a rising stem and incorporate thrust bearings of the ball or roller type. 5 The design shall permit the gear case to be opened for inspection or disassembled without releasing the stem thrust or taking the valve out of service. 6 Valves stems and threads shall be provided with grease lubrication, rising spindle valves being protected with a totally enclosed grease packed cover tube. 7 The actuator shall be fitted with a drive bushing which is easily detachable for machining to suit the valve stem or gearbox input shaft. Bushing shall be fitted in the base of the actuator to QCS 2010 Qatar Project Management 33. QCS 2010 Section 21 Part 33 Actuators Page 3 enable standard length valve stems to be used. 8 Only two categories of sealing are permitted: (a) (b) UK BASEEFA certified for EExdIIBT4 CENELEC Norm EN50018, BS5501 for defined hazardous locations; or Watertight, dust-tight complying with the requirements of BS 5490 IP67 or better. Actuators shall be suitable for pedestal mounting and interchangeable without removal of the associated valve, penstock, pedestal, etc. 10 Sealing of static joints shall be by 'O' ring on moving components to prevent leakage of lubricant from the machine. 11 The actuator shall provide Double Sealing between the terminal compartment and the internal electrical elements of the actuator, fully protecting the motor and all other internal electrical elements of the actuator from ingress of moisture and dust when terminal cover is removed on site for cabling. 12 For control purposes limit switches shall be fitted to the actuator at both the closed and open positions of the valve. Limit switches shall also be fitted for signalling purposes. All these shall be fitted internally. Limit switches contacts shall be volt-free. The switch contact rating shall be 5 amps, 250 volts AC, 30 volts DC. Valve position shall be clearly marked externally on the actuator. 13 The actuators shall be sized so that they develop sufficient torque to reliably seat/unseat the valve or penstock off its seat, and to provide adequate torque throughout its operating range. The torque output must be at least 20% more than is required under maximum operating conditions (i.e. maximum differential head). The drive shall incorporate a lost motion hammer blow feature. 14 Adequate overload protection shall be provided to prevent actuator motor damage in the event of seizure. This shall either be in the form of torque switches, or over-temperature thermostats. The torque switch shall latch out on operation, and to be reset by driving in the opposite directions. A mechanical latch shall be provided to prevent the open torque switch tripping while the initial unsealing hammer blow is applied. 15 The setting of the torque and limit switches shall be able to be carried out without the need to remove any electrical compartment covers. 16 Adjustable mechanical limit stops shall be provided for open and closed positions of actuators. 17 Actuators supplies shall be 110 volts Single Phase or less for quarter-turn and 415V three phase for multi-turn. Motors shall have Class F insulation, with a time raring of 15 minutes or three times the open/close stroking time whichever is the longer. Motors shall be capable of operating at the sun radiation temperature and certification shall be provided to this effect. Nevertheless, sun/weather canopies shall be provided for all externally installed actuators. These shall give complete shading from the sun during the hottest part of the day and should not restrict maintenance or operational access. 18 Certain valve actuators will require fail safe operation in the event of an electricity mains failure. The Contractor may achieve this either by using fail-safe actuators, or by providing standby power supplies for the affected actuators. There should be no tendency for any actuator to "creep" either open or closed, both in normal operation or under mains failure conditions. 19 Anti-condensation heaters for use on 110 volt a.c. shall be provided for all actuator motors. 20 The actuator motor gearbox shall be of the totally enclosed oil bath lubricated type suitable for operation at any angle and provided with appropriate filling and drain plugs. QCS 2010 Qatar Project Management 9 QCS 2010 Section 21 Part 33 Actuators Page 4 A hand wheel shall be provided for manual operation of the valve. This hand wheel shall not operate during powered actuator movement by reason of a positive means of disconnection from the motor driven mechanism. The wheel shall be maintained in its engaged position once this is selected until powered movement takes place when it shall automatically disconnect and "free wheel". The hand wheel gearing shall be selected to allow valve operation without undue effort i.e. not exceeding 25 kg. 22 It shall be possible to secure hand or powered operation by means of padlocking in the selected mode. 23 Where necessary to present the actuator hand wheel at a convenient operating height, flange mounted pillars shall be provided which fully enclose the necessary valve stem extension spindles. Supplementary support of the extension spindle within its pillar shall be provided for long shafts. 24 The open/close direction of rotation shall be clearly indicated on the hand wheel. 25 A visual position indicator shall be provided within the actuator complete with a pointer showing open/closed and in travel positions, and a sealed potentiometer to transmit continuous remote position. Where specified in the particular specification, this indicator shall be illuminated. 26 Electrical and mechanical disconnection of the motor should be possible without draining the lubricant from the actuator gear-case. 27 The colour code for actuator push button shall be: (a) (b) (c) (d) (e) “Start” actuation “Stop” actuation “Re-set” actuation “Test” actuation “Emergency Stop” Green Red Black White Red (mushroom style, latching on depressing, release on turning). 33.2.2 Pneumatic 1 Where specified valves/penstocks shall be provided with pneumatic actuators. 2 Air actuators shall only be used where specified in the particular specification and shall be of the double acting type and be field interchangeable without the necessity of removal of the valve or penstock. 3 Where a pneumatic actuator is used for modulating control it shall be fitted with integral feedback. 33.3 QUALITY CONTROL AND TEST PROCEDURES 33.3.1 General 1 The manufacturer shall provide proof of a stringent Quality Control (QC) Plan or Inspection Test Plan (ITP). In particular the main equipment manufacturing stages sanctioned by appropriate tests such as: incoming components inspection, discrete sub-assembly tests and complete functional checks on the final product. Equipment shall undergo on-load burn-in leaving the factory. Final inspection and calibration operations shall be documented in a report drawn up by the supplier’s Quality Inspection department. 2 Combined operational lists shall be carried out at the valve/penstock manufacturers works and list certificates provided confirming limit switch and torque settings. 3 The integrated functional test shall be conducted at manufacturer’s works to ensure satisfactorily functioning of the equipment. QCS 2010 Qatar Project Management 21 QCS 2010 Section 21 Part 33 Actuators Page 5 The Assembly shall not leave the manufacturer’s works until the works test sheets have been duly approved and stamped by the Engineer and written permission is obtained for their dispatch to site. 33.4 ENVIRONMENT 33.4.1 General 1 Environmental conditions shall be in accordance with Section 1 Part 1 unless specified herein. 2 Minimum ambient temperature shall be assumed as 0C. 3 Sun radiation temperature shall be assumed as 70C. 4 Maximum relative humidity shall be assumed as 95%. END OF PART QCS 2010 Qatar Project Management 4