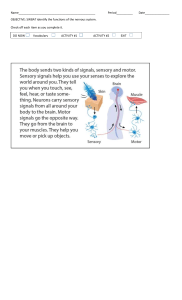
The Nervous System “The right half of the brain controls the left half of the body. This means that only left handed people are in their right mind.” LATERALIZATION OF BRAIN FUNCTION THE LEFT HEMISPHERE SPECIALIZES IN LANGUAGE, MATH, LOGIC OPERATIONS, AND THE PROCESSING OF SERIAL SEQUENCES OF INFORMATION, AND VISUAL AND AUDITORY DETAILS. SPECIALIZES IN DETAILED ACTIVITIES REQUIRED FOR MOTOR CONTROL. THE RIGHT HEMISPHERE SPECIALIZES IN PATTERN RECOGNITION, SPATIAL RELATIONSHIPS, NONVERBAL IDEATION, EMOTIONAL PROCESSING, AND THE PARALLEL PROCESSING OF INFORMATION. Copyright © 2002 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings The Nervous System A physically connected network of cells, tissues and organs that allow us to communicate with and react to the environment and perform life activities. FUNCTIONS OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM 1. Sensing the World vision, hearing, smell, taste, and touch 2. Transmitting Information 3. Processing Information 4. Producing a Response The Structural Components of the NERVOUS SYSTEM Central Nervous System (CNS) Serves as the main processing center for the entire nervous system Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) Made up of all the nerves that carry messages to and from the central nervous system and other parts of the body The Structural Components of the NERVOUS SYSTEM Central Nervous System (CNS) A. Brain 1. Hindbrain Cerebellum Brain Stem and Pons Medulla Oblongata 2. Midbrain 3. Forebrain Cerebrum Thalamus Hypothalamus B. Spinal Cord ( Information Superhighway) • Smaller part of the brain, towards the back • Muscle coordination is developed here as well as the memory of physical skills. • Helps maintain posture, muscle control, and balance (voluntary movements) The Cerebellum If the cerebellum is injured, your movements become jerky. When you see an amazing athlete perform, you are watching a well-trained cerebellum at work. Attaches to the spinal cord Made up of the medulla oblongata, pons and midbrain. Medulla oblongata controls involuntary activities such as heart rate and breathing Pons and midbrain act as pathways connecting various part of the brain with each other. Sometimes called the reptilian brain, because it resembles the entire brain of a reptile. Connects the two halves of the cerebellum. The bulging center part of the brain stem Mostly composed of fiber tracts Pons Medulla Oblongata Composed of nerve tracts to and from the brain May be regarded as an extension of the spinal cord Almost all of the cranial nerves arise from this region Pons and Medulla Oblongata Contains control centers for many subconscious and unconscious functions like: • Heartbeat and breathing • Arteriole constriction • Reflexes (swallowing, hiccupping, coughing, sneezing, vomiting) • Receives signals/information from the Pons and Medulla Oblongata and forwarded it to the Forebrain • Reflex centers for vision and hearing Receives signals/information from the different parts of the body and forwarded it to the proper regions of the cerebrum. • Located below the thalamus and maintains the normal level of different body conditions. • Control sensation of feelings of hunger and taste, body temperature, blood pressure, hormonal secretion of the pituitary gland. Large front part of the brain Wrinkled with countless folds and grooves and covered with an outer layer of gray matter called the cerebral cortex. Divided into 4 lobes Receives and integrates sensory signals/information forwarded by the Thalamus Interprets and allows the body to experience the sensation of taste, touch, smell, seeing, and hearing Responsible for thinking, reasoning, and imagination Controls emotion and memory Regions of the cerebrum are specialized for different functions The cerebrum is divided into frontal, temporal, occipital, and parietal lobes. Extends from the medulla oblongata to the region of T12 Enlargements occur in the cervical and lumbar regions Reflex Arc “ what happens when you step on a nail”? Reflexes are automatic The Stimulus (nail ) is received by the sensory neurons in the foot This info travels to the spine, where the interneuron is triggered The interneuron transmits signal to brain (through the spinal cord)and carries message back and stimulates the motor neuron, to move the foot The Structural Components of the NERVOUS SYSTEM Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) A. Somatic PNS motor neurons carry signals from the brain and spinal cord to voluntary muscles (conscious control) The Structural Components of the NERVOUS SYSTEM Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) B. Autonomic PNS motor neurons carry signals from the brain and spinal cord to involuntary muscles (without conscious control) 1. Sympathetic NS (actions in emergencies “Fight or flight response”) 2. Parasympathetic NS ( works when the body is relaxed ) Spinal Nerves Figure 7.22a Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings Slide 7.64 Olfactory Optic Oculomotor Trochlear Trigeminal Abducens Facial Vestibulocochlear Glossopharyngeal Vagus Hypoglossal Accessory On Old Olympus Towering Tops A Fat Voracious German Viewed A Hop 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. Olfactory- smell Optic- vision Oculomotor- 4 of the 6 extrinsic eye muscles Trochlear- extrinsic eye muscles Trigeminal- sensory fibers to the face and motor fibers to the chewing muscles Abducens- controls eye muscles that turn the eye laterally Facial- facial expression Vestibulocochlear- hearing and balance Glosopharyngeal- tongue and pharynx Vagus- parasympathetic control of heart, lungs & abdominal organs Accessory- accessory part of vagus nerve, neck & throat muscles Hypoglossal- moves muscles under tongue Classification of Nerve Cells Afferent (sensory) nerves – carry impulses toward the CNS Efferent (motor) nerves – carry impulses away from the CNS Mixed nerves – both sensory and motor fibers Check this video Cool Nervous System Facts: As a fetus in the womb, neurons develop at the rate of 250,000 per minute. We have about 100 billion nerve cells in our brain by adulthood (over 600 miles worth) – yet we typically use around 4% at any given time Neurons are our largest cells Messages transmit at speeds up of to 180 MPH REMEDIATION ACTIVITIES Quarter 3 Module 2: Menstrual and Ovarian Cycle 1. 2. What’s More pp. 8-9 Post- test pp. 18-19 Deadline of Submission: March 8, 2023 Performance Task #2 Deadline : March 11, 2023 at 5PM Performance Task #2 THANK YOU!