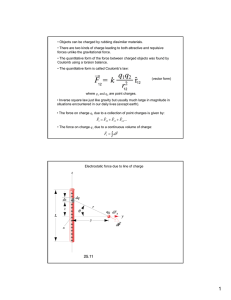
Coulomb's law * An experimental law of physics * Formulated by French physicist Charles-Augustin de Coulomb. * Quantifies the amount of force between two stationary, electrically charged particles. *Gravitational and electric forces decrease with the square of the distance between the objects * The magnitude and sign of electric force are determined by electric charge. *Charge determines how electromagnetism influences the motion of charged objects. *Electrostatic force of attraction or repulsion is directly proportional or inversely proportional. Properties of Electric force for charges at rest. *Like charges repel each other; unlike charges attract. *Two negative charges repel one another * Positive charge attracts a negative charge. *The attraction or repulsion acts along the line between two charges. *The size of the force varies inversely as the square of the distance between the two charges. *If the distance between the two charges is doubled, the attraction or repulsion becomes weaker. *The size of the force is proportional to the value of each charge. Coulomb’s Law Formula *Q1 and Q2 are the electrical charges of two objects. *d is the distance between the center of the objects. *The charged objects are placed in a medium of permittivity εoεr *This formula allows us to calculate the electrostatic force that two charges exert on each other. Coulomb’s First Law * like-charged objects (bodies or particles) repel each other * unlike charged objects (bodies or particles) attract each other. Coulomb’s Second Law *the force of attraction or repulsion between two electrically charged objects is directly proportional to the magnitude of their charge * inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them. Limitations of Coulomb’s Law *Coulomb’s law is valid, if the average number of solvent molecules between the two interesting charge particles should be large. *Coulomb’s law is valid, if the point charges are at rest. *It is difficult to apply the Coulomb’s law when the charges are in arbitrary shape.