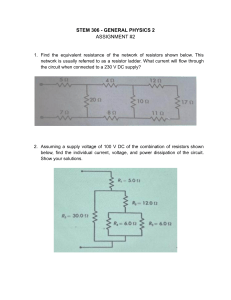
Ohm’s Law Ohm’s Law Measuring Current • Current is measured in unit amps (A) 2A 2A 2A 2A 1A 2A 1A In a series circuit, current is the same at all the points In a parallel circuit, current is shared between all the points What is the current? 3A 3A 4A 1A 4A 1A 4A 1A SERIES CIRCUIT PARALLEL CIRCUIT Measuring Voltage • Voltage – the electrical push that a cell/battery gives to the current • Voltage is also known as Potential Difference • Voltage is measured in unit volts (V) Measuring Voltage 3V 3V 3V 1.5V 1.5V In a series circuit, voltage is shared between all the points 3V In a parallel circuit, voltage is the same at all the points What is the current and voltage? 6V 4A A 4A V 3V V 3V A 4A Current Voltage Series Same Shared Parallel Shared Same What is the current and voltage? 4A 6V A 4A V 6V A 2A V 6V A 2A Measuring Resistance • Resistance – slows down current, adding components to a circuit increases resistance • Resistance is measured in unit ohms (Ω) • More resistance = Less current = Less light In a series circuit, add all resistors to get total Electrical Power What is the current? What is the current? What is the current? How much voltage gives 5 amps of current through a 3 Ω light bulb? I = V/R V = (5A) (3Ω) V = 15V How much current flows in a circuit with a 1.5 volt battery and three 1 ohm resistances (bulbs) in series? I = V/R I = (1.5V) / (3Ω) I = .5A What is the voltage drop across each resistor in the circuit? In a series circuit, voltage is shared between all the points 9V/3 = 3V A light bulb with a resistance of 1.5Ω is connected to a 1.5V battery in the circuit. Calculate the power used by the light bulb? P = IV I = V/R I = (1.5V) ÷ (1.5Ω) I = 1A P = (1A) (1.5V) P = 1.5 W